Problem Statement for of the Study
The Emirates Group is the national carrier of Dubai that has already established as a global giant for aviation, travel, tourism and leisure industries with its successful records of accomplishment of eighteen years with employees strength of 36652 in the Airlines and 13298 employees of Dnata in 2011 (The Emirates Group, 2011, p.53). EDIL (2012, p.1) mentioned that the demography of the UAE evidenced that the country composed with a small population of 8.26 million around 90% of them are foreign workers that prove the fact that the economic performance of the country strongly dependent on the importation of foreign workers. Being a Group of companies owned by the Government of Dubai Emirates, also dependent on the foreign employees rather than the local ethic groups and the company is in practice of human resources collaboration as well as strategic alliances with foreign companies and outsourcing agents to establish a successful array of HRM. This research has aimed to investigate the extents of value addition in the business through the human resources collaboration of the Emirates Group.
Rationale of this Study
There are enough research with the continuous economic and financial success of the Emirates Group, but there is no significant research with the human resources collaboration of the Emirates Group, so it is rational to conduct the research with” Value addition in business’s using joint venture association, in Emirates Group Human Resources collaboration”
Research Questions and Objectives of the Study
The objective of this study is to identify to what extent the Human Resources collaboration assist a company to generate additional value for its business and to do so this research would investigate with the following research questions-
- What are the categories and process of formation of such strategic alliances for human resources collaboration?
- How the conceptual framework of human resources collaboration would coordinate with the prolonged human resource management of a company?
- What are the outcomes of outcomes of such Strategic Alliances?
Literature Review
Conceptual Framework of Human Resources Collaboration
Todeva and Knoke (2005) pointed out that literature of international business has already accredited the positive impact of strategic alliances for human resources collaboration and urged that the cooperation among the global companies would provide superior return on equity, satisfactory performance and improved return on investment rather than merger or acquisition. The strategic human resource executives required an array of well understanding regarding the necessity and influential factors that would lead to organising human resources collaboration through strategic alliance and to what extent the cooperation would prolong where the theory of co-operation assist to identifying the right strategic and economic basis for such joint venture association among the companies.
Iyer (2002) demonstrated that a huge number of companies recognised that they formed strategic alliance for human resources collaboration with the aim to gaining sustainable competitive advantage, additional value creation for customers, along with the operational motives to gain learning outcomes through the cooperative practice and it would increase skills and productivity of the existing HR. Such strategic alliance would provide enhanced strength for the organisation by inter-organisational learning that would change competencies to address the dynamic and interactive aspect of both organisation regarding their process and mechanism of operation with exploration of business wings and expansion of customers service where awareness to selecting partner and commitment to bilateral relationship are the foundation of cooperation.
The World Economic Forum (2012) explored that the Talent mobility is the basic factor that functions as the fuel of global economy in both the public and private sector, it is a process the immediately meet the skills gaps of an organisation moving human resource to the company suffers from lack of skilled HR. To makeup such gaps, there are huge service companies who have ready storage of talents with particular segments of economics, business and industry to respond to the labour market failures by supplying skilled labours in a cost effective way that stimulates a superior equilibrate in context of employees cost, quality and unemployment movements.
Categories and Formation of Strategic Alliances
Hamel (1991) argued that companies in the international business engaged into competition with skill endowments of their human resources where collaboration would provide an enhanced opportunity to formulate joint venture to exchanging the skills of one with another in order to improve the existing position of both companies who join into the alliance. The human resources collaboration through strategic alliance yields well accepting determinants of inter-partner learning, although all partners are equally integrate learning scheme; but the collaboration modifies the virtual bargaining capacity of the partners that bring stability, longevity and success of their collective initiatives formed through different process.
Todeva and Knoke (2005) pointed out that there are several schemes to organising strategic alliances aimed to human resources collaboration of the companies and these are as follows –
- Joint Ventures: – Under this scheme, any number of firms could establish a third organisation with joint ownership to serve particular common purpose interested by the participants;
- Hierarchical Relations: – This type of strategic alliance or joint venture would be formed through acquisition or merger, where a company captures bursting control over all physical and financial resources of another firm and introduce different actions empowered by the ownership mechanism;
- Equity Investments: – The human resources collaboration can also organise through an equity investment holding of one company to another, some other forms of strategic alliances for human resources collaboration are as –
- Cooperatives;
- R&D Consortia;
- Strategic Cooperative Agreements;
- Cartels;
- Franchising;
- Licensing;
- Subcontractor Networks;
- Industry Standards Groups;
- Action Sets;
- Market Relations.
Outcomes of Strategic Alliances
Todeva and Knoke (2005) also added that the organisations with different viewpoints and expectation come into strategic alliance for human resource collaboration from their motivation of economic, organisational, strategic, and political needs, but the real fife scenarios most of the time gives both negative and positive both outcomes that may comply with a party, but contrary to each other. Elmuti (2012) conducted a well-organised study with the strategic alliance of collaboration through outsourcing, and identified that such collaboration is very effective for economic prosperity, cost effective human resource management and explored the positive outcomes for service provider and service buyers while the US companies spent over $100 billion for different area of business activities outside the USA.
Research Methodology
Research Design
This chapter will provide methodological framework to organise this dissertation, and there are several ways to formulate research, but this paper will concentrate on both qualitative and quantitative research approach to analyze the topic “value addition in business’s using joint venture association, in Emirates Group Human Resources”; however, the next figure shows more idea of research framework –
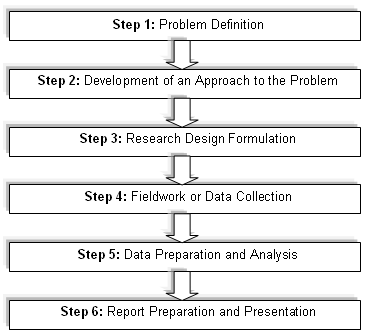
Primary and Secondary data
Malhotra (2009, p.72) stated that secondary data is the processed data and more authentic sources; thus, it would consider annual report of Emirates, several reports on human resource collaboration, proposal of the research and so on. In addition, Malhotra (2009, p.72) further argued that primary data is collected specifically to point out a specific problem and the researcher of this dissertation will prepare a questionnaire to interview to the managers and the employees of Dnata; however, the questionnaire includes –
- Section B: The purpose of this section is to know the view of managers of Dnata about the effectiveness of the Human Resources collaboration
- Section A: This section designed with general question ion about the respondent
Limitations of the Study
- Number of words was the main limitation to cover all issues
- Short-time to plan and conduct such a significant research;
- The managers of Dnata have not time to co-operative in some extent;
- Lack of useful secondary data related with Emirates Group Human Resources collaboration
Discussion
Overall Hr Management System Of This Group
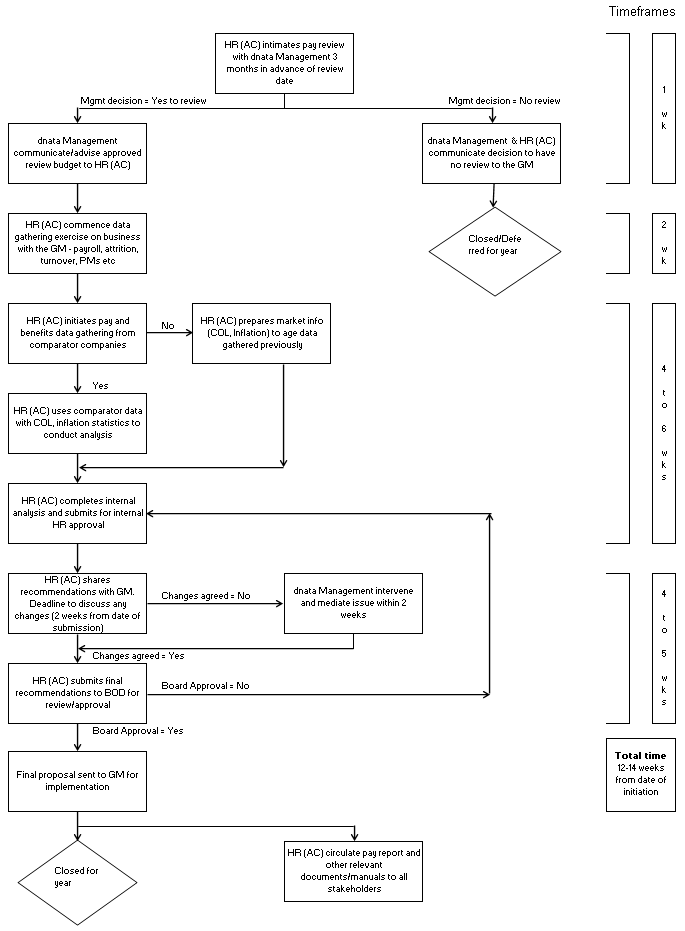
Emirates Group (2012) reported that the employees of this company came from more than 150 countries all over the world and the third parties or collaborators provide their human resource in accordance with joint venture agreement; thus, it gave the opportunity to the employees to think and plan to maximize staff innovation and productivity levels. This Group designed the remuneration policy not only for the Emirates Group’s employees, but also for its associated companies by conducting research in this sector to remain competitive within the specific local market where it operates to attract and retain efficient and dynamic employees; in addition, the HR departments also keeps up-to-date with appropriate legislative requirements and code of conduct. The managers of Dnata said that the overall HR management system of this group is outstanding to motivate employees and serve customers’ need; in addition, Employee Service Centre and The Recruitment Administration unit to provide initial supports; however, the following figure shoes the pay review process in detail –
Explanation About Emirates Group’s High Potential Indicators to Develop the HR
The company has created a high potential framework to develop the HR and generated certain indicators to identify the potentials; the company has investigated and identified seven indicators to help the entire identification process, which has been illustrated in the following diagram –

There should be four personal characteristics, which could indicate the high potential workers; for example, such workers would be self- aware (recognize how to work productively for assuring an optimistic working-relationship and atmosphere), self- motivated (with inner-confidence and endeavour for greater-responsibility), learning agile (keen to learn from circumstances), and problem solver (display the cognitive-thinking and analytical-ability to sensibly appreciate concerns).
Human Resources Collaboration and Implications of UAE Labour Law
Emirates Group follows the provisions of the UAE labour law in order to select, recruit, or terminate employees of this company along with the function of the employees of Associated Companies. According to the UAE labour law, Emirates Group must have to concentrate on following issues –
- Most importantly, the HR teams must consider the terms of the agreement and labour law in order to ensure other facilities, for instance, give residence permit, no objection certificate, work permit by which foreign employees can get visa;
- Emirates Group has the opportunity to recruit the employees for limited (not exceed four years period) or unlimited period (Article 38); the human resources department can terminate the contract at the end of the period or can renew the agreement as well;
- According to the UAE labour law, the highest approved working hours for an adult worker is eight hours per day (The Emirates Group, 2012);
- Ministry of Law (2012, p.9) stated that the employers can terminate contract for the violation of ten specific reasons including fake documents, end of probationary period, error causing substantial material loss, violation of safety policy, fail to carry out fundamental duties, reveal any secrets, found drunk or under the influence of drug, commit an assault without lawful excuse;
Findings And Results
The main idea of the findings chapter is to scrutinize the results of the actual survey carried out among the general managers of the Emirates Group in Iraq, India, Saudi Arabia, Philippines, Bahrain, and Qatar along with certain top- level employees of the company in order to assess the key area of the research. The survey questionnaire was handed over to 100 respondents working with the company and the data analysis is as follows:
Section A
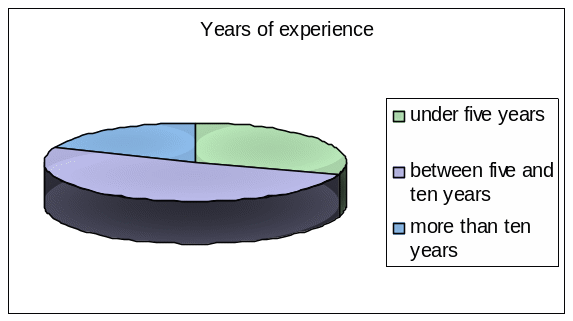
Question 1: – The respondents were asked to mention their years of experience in working with Emirates Group:
Finding out the experience level of the respondents is imperative in the appraisal procedure of the results as it assists to discover the most precise and dependable answers. As the following figure demonstrates, the survey has suggested that there were 30% respondents under five years experience, 51% between five and ten years of experience, and 19% more than ten years of experience:
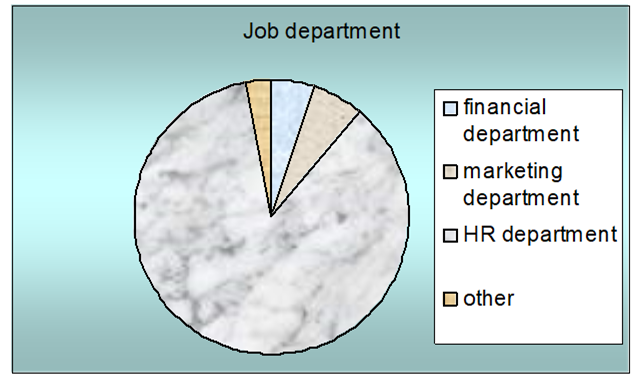
Question 2: – The respondents were asked to select their job department in this company:
According to the conducted survey, 5% respondents were from financial department, 6% was from marketing department, 86% was from HR department, and 3% was from other departments; this data is demonstrated in the following figure:
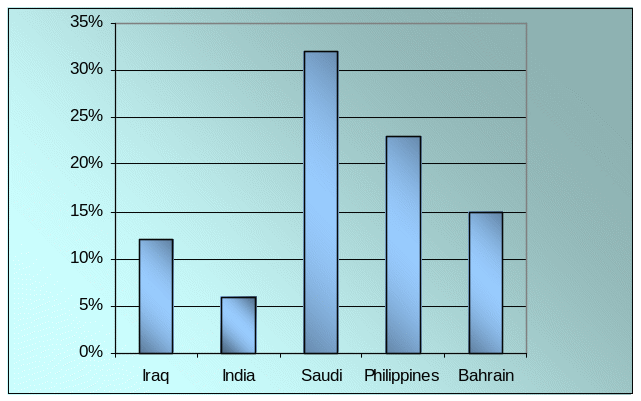
Question 3: – The respondents were asked to select their country:
In order to conduct a proper research in the topic area, it was essential to survey the general managers and certain top- level employees of Dnata Iraq, Dnata India, Dnata Saudi, Dnata Philippines, Dnata Bahrain, and Dnata Qatar. The survey conducted suggests that there were 12% respondents from Iraq, 6% respondents from India, 32% from Saudi, 23% from the Philippines, 15% from Bahrain, and 12% from Qatar; the chart below clearly illustrates this point:
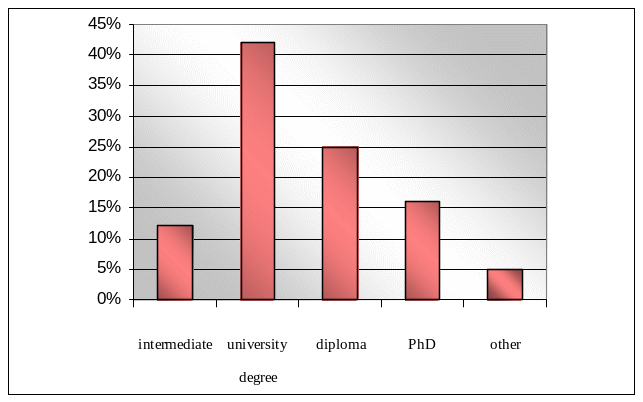
Question 4: – The respondents were asked to select their highest education level:
The survey suggests that there were 12% respondents with intermediate education, 42% respondents with university degree, 25% respondents with a diploma, 16% with PhD, and 5% with other degrees:
Section B
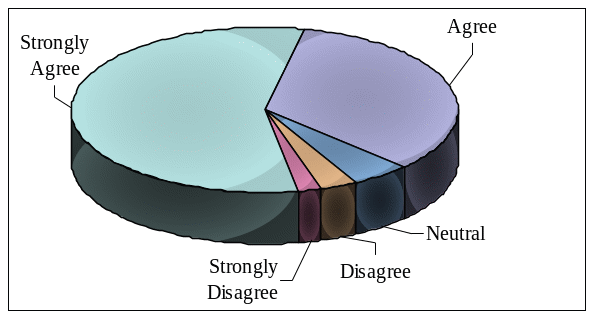
Question 1: – To what extent the respondents agree that Emirates Group Human Resources collaboration plays vital role to enhance the business:
The researcher put this question forward in order to find out whether or to what degree Emirates Group Human Resources collaboration is actually operating to develop the overall performance of organization. It has been found that 56% respondents strongly agreed that the business was enhanced, 34% agreed to this, 5% stayed neutral, whereas 3% disagreed and 2% strongly disagreed to this statement. This is shown in the graph below –
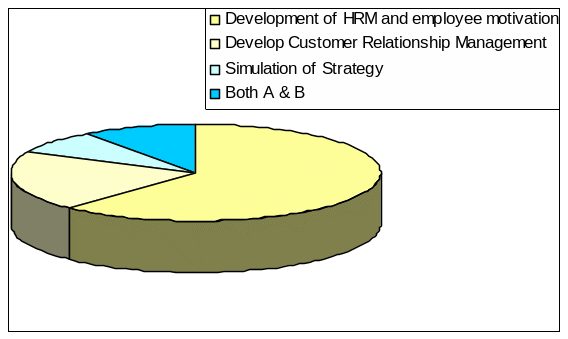
Question 2: – Which one is the most effective way to manage the company to increase profit in the competitive world:
The reason behind asking this question was that the researcher wanted to identify the strategy in which the company emphasises the most in order to increase its profit in the competitive market and to find out whether or to what extent Emirates Group is concerned with the development of HRM and employee motivation. It is seen that 62% respondents emphasized development of HRM and employee motivation, 20% on developing customer relationship management, 8% on simulation of strategy, and 10% on both A & B:
Question 3: – The respondents were asked what could happen for an ineffective HR system:
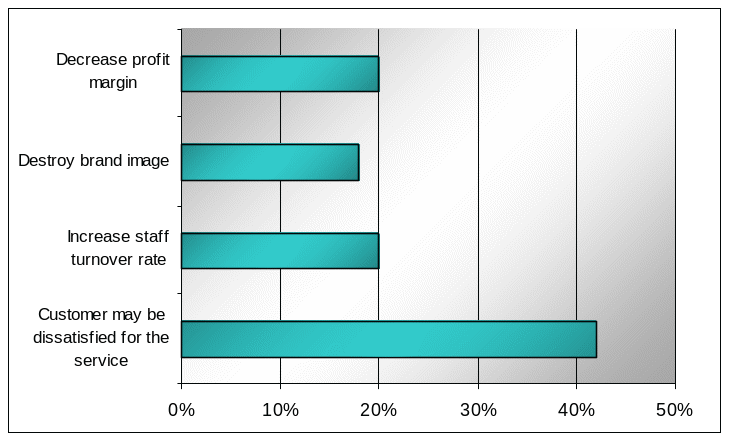
In answering this question, 42% respondents stated that the customers might be dissatisfied for the service, 20% stated that staff turnover rate could be increased, 18% stated that brand image can be destroyed, and 20% stated that profit margin could decrease. The graph below illustrates that the majority of the respondent believes that customer dissatisfaction may occur. It has argued that HR collaboration system with call centres, for example, may lead to wrong information provided to customers by the call attendants, causing customer grievances.
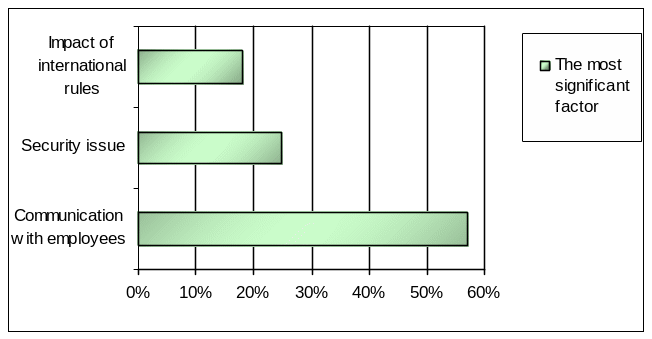
Question 4: – What is the most significant factor to manage expatriates and Emirates Group Human Resources collaboration:
The following figure demonstrates that according to the survey, 57% respondents believe that communication with employees is the most significant factor to manage expatriates and Emirates Group Human Resources collaboration, 25% thinks that security issue is the significant factor, whereas 18% thinks that impact of international rules is the most significant factor.
Recommendation
Emirates Group or Associated Companies will behave with employees in accordance with the terms of the contracts and must assess the significance of the dismissal and give adequate compensation at the time of termination since national regulation has incorporated rights for the staff to take action against the employers for any kind of arbitrary termination or unjustified cause;
Conclusion
This study identified the value addition of the Emirates Group using joint venture association with different companies has extended its human resources collaboration through Dnata Contact Centre that provides call centre outsourcing service, business process outsourcing and technical solutions inbound and outbound calls for flight reservations, ticketing, hotel bookings as well as ground transportation and continued its stable growth.
Reference List
EDIL. 2011. Expatriate Population in UAE Approaches 90%. Web.
Elmuti, D. 2012. The Perceived Impact of Outsourcing on Organizational Performance, Web.
Hamel, G. 1991. Competition for competence and inter-partner learning within international strategic alliances. Web.
Iyer, K. N.S. 2002. Learning in Strategic Alliances: An Evolutionary Perspective. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. 2009. Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. 5th edn, Prentice-Hall, New Delhi.
Ministry of Law. 2012. UAE Labour Law – Federal Law No. (8) Of 1980 Labour Law and Its Amendments. Web.
The Emirates Group. 2011. Annual Report 2010- 2011. Web.
The Emirates Group. 2012. Human Resources of Emirates group. Web.
Todeva, E. & Knoke, D. 2005. Strategic Alliances & Models of Collaboration. Web.
World Economic Forum. 2012. Talent Mobility Good Practices Collaboration at the Core of Driving Economic Growth, Web.
