Project Abstract
The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between training and career development and employee performance. Studies associate on-the-job training with the acquisition of practical knowledge and skills essential in that profession or position. On-the-job training is not only essential for improved performance, but it is also useful for employees pursuing a specific career path.
The Career Development Center (CDC) offers training to the Emirati workforce to equip them with skills to perform common tasks in diverse sectors. In this study, two thousand online questionnaires will be sent to a purposive sample of CDC graduates (experimental) and non-CDC trainees (control) working in various industries within the UAE’s public and private sectors. A multivariate analysis (correlation) will be done based on the data collected from experimental and control groups after reliability and validity analysis. The study’s results will indicate if on-the-job training has a positive effect on employee performance in the UAE-based firms. Thus, the findings will have implications for local human resource development and skill growth.
Research Background
Globalization has occasioned wide-ranging internal changes to improve the competitive position of firms. One such change relates to human resource development to produce competent staff to drive organizational growth. An organization’s workforce constitutes a crucial asset for achieving its long-term goals and objectives. Therefore, firms need to support staff training and development to enable employees to acquire specialist skills and enhance their organizational commitment.
In recent years, organizations have moved to enhance their human resource management (HRM) function as a way of achieving global competitiveness. The core HRM functions entail training and development and performance appraisal. In training and development, the HRM unit identifies the training needs, implements a training plan, which may cover job rotations, conferences, and workshops, and evaluates the outcomes (Wright & Geroy, 2001). Performance appraisals in contemporary organizations may entail self-appraisal, customer appraisal, and peer appraisal to support further training and development.
Previous studies have established a link between employee training and development and performance. Purcell, Kinnie, Hutchinson, Rayton, and Swart (2003) found a link between staff training and employee performance improvement. The researchers found that training enhances staff skills and competencies to perform better in their current roles. Therefore, training programs enhance the employees’ current performance and prepare them for specialist or supervisory roles in the firm.
The UAE government initiated the Emiritization program in 2008 to increase the population of its nationals working in UAE-based firms and address skill deficits. As Donn and Al (2010) write, the small size of the UAE population coupled with the limited local technological capability has been a hindrance to the Emiritization initiative. As a result, the Recruitment Advisory Committee (RAC) was established to improve the proportion of locals, especially in the oil and gas sector, through training. Another initiative called the Career Development Center (CDC) sought to hire and train locals for deployment in various multinational companies. From these initiatives, it is clear that training and development are gaining interest as a strategy for improving the productivity of the local workforce.
Research Problems
Worker Training
Studies show that worker training and development improve employee skills, which translates into improved performance and overall productivity (Wilkins, 2001). Although training is known to equip workers with work-related expertise that improves their efficiency and output in their current positions, it is not clear whether the performance could be measured based on the amount of training received.
Training is preceded by an employee performance evaluation, which helps identify training or development needs and career paths of each individual. The effectiveness of a training program is reflected by an improvement in performance outcomes attributed to the skills gained. Therefore, employee performance could be measured through training and career development.
Training and Career Development
Performance appraisals help identify the staff career needs while on-the-job training supports employee engagement and talent management. Employees have varying career needs and skill requirements to perform optimally in their roles. Worker training programs must be designed to suit diverse career needs through certification, promotions, on-the-career training, redeployment, and better remuneration of employees completing the training modules (Wilkins, 2001).
The intrinsic and extrinsic engagement motivates employees and rewards high performers in their roles. Public and private institutions must develop an internal career progression strategy that allows employees to assume supervisory roles and positions based on the training modules completed and measured performance or output.
On-the-job Training in the UAE
Developing a qualified national staff has been the key focus of the UAE government’s efforts to increase the proportion of locals in both the private and public sectors. The Learning and Development Policy aims to find ways of developing the worker’s abilities and technical skills through exposure and training (Al-Nuseirat & Biygautane, 2014). The government has also sought to support employee training through job rotation to enable the local workforce to acquire high-level training, which would increase its performance. Besides, the training may increase motivation and job satisfaction of employees in all grades, translating into improved staff morale and performance.
Research Gaps
Training and development translate into improved employee performance. The two factors are important for bridging the performance gap between the present and expected productivity levels. Since training programs equip employees with advanced skill sets and competencies, training and development could be used to measure performance. The outcomes of tailor-made training for various staff cadres could indicate their performance, which may be measured through staff appraisals. An analysis of the relationship between the CDC training received by the UAE nationals and performance would help reinforce the role of staff training in improving workplace efficiency. Trained workers must exhibit efficiency in their roles and creativity to support improved organizational productivity.
The factors that contribute to employee development relate to on-the-job training and performance appraisal. On-the-job training entails job rotation where employees assume new roles for a specific period in the organization. Coaching and mentoring foster development, especially for recruits (McCourt & Derek, 2003). A suitable mentor could be a supervisor or a senior manager. Other training approaches that could contribute to employee development include orientation to familiarize employees with their roles and role-playing (McCourt & Derek, 2003). Performance appraisals can identify individual training needs and career preferences, hence a useful tool for employee development and engagement.
Objectives
Training and career development upgrade the skills and competencies of the personnel, equips staff with advanced capabilities, enhances productivity and efficiency, and motivates employees, contributing to improved organizational performance. As established in the above section, the skills, competencies, and capabilities acquired through training contribute to improved efficiency and performance. Therefore, the objectives of this study include:
- Examining how training and development contribute to the improvement of skills and competences of staff in the UAE.
- Identifying the specific staff competencies that CDC graduates acquire upon completing the training programs.
- Evaluating the effect of training and development on individual employee performance levels using performance appraisals.
- Exploring the impact of on-job training on staff skills, competencies, and knowledge.
The criteria for evaluating the success of the project objectives include the use of performance appraisals and assessment of knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) of the participants. The study objectives will help explore the key aspects of training and development that affect employee performance. Therefore, the findings will encourage UAE companies to initiate training and development programs that raise the knowledge level of employees as a way of boosting performance and productivity.
Research Impact/ Benefit
Developing a Competitive Workforce
The purpose of this study is to find out the effect of training and development on staff performance in UAE companies. Identifying training options with optimal performance outcomes will potentially enable the UAE government to develop a competitive workforce based on international standards. Also, job grading and role assignment will be evaluated based on the prerequisites for each position, be it technical or supervisory.
As such, the government will be able to meet the demand for quality human resources in the private and public sectors in line with the Emiritization program. It will encourage an emphasis on quality in training and development as well as in career progression in the UAE firms that currently employ a disproportionate number of expatriates due to the local skill deficit.
Private Sector vs. Public Sector
The private sector in the UAE attracts a large number of expatriates and locals. Al-Nuseirat and Biygautane (2014) write that the private sector attracts more employees than the public sector because it offers “career development and learning opportunities” (p. 7). Therefore, career development is an outcome of the training received by employees. Trained workers possess new and unique skills that improve the global competitiveness of an economy.
The UAE ranks among the top 30 countries in the Middle East with the highest global competitive index (GCI). Countries leverage national skills and human resources to compete in various economic spheres. The study will determine the correlation between training and individual or institutional efficiency and competitiveness. Improving efficiency in public service would require workforce training tailored to institutional or national needs.
Workplace Characteristics
Training and development form part of the employee engagement strategy to motivate employees and enhance performance. The study will help develop a profile of workplace environments and management approaches that foster or impede training and career progression. Developing a national culture that promotes training and development as a means of raising performance is important. Also, utilizing performance metrics that reflect local situations and diversity considerations could help in skills enhancement across all ages, genders, and sectors.
Literature Review
Training and Development
Training and development constitute a core HRM function. Gordon (2004) considers training to be a “systematic modification of behavior” achieved through learning programs in which employees acquire advanced skills (p. 31). Employee development encompasses diverse activities aimed at improving efficiency in a particular role (McNamara, 2008). Therefore, training and development are considered to have short-term and long-term benefits for the firm.
Cole (2002) outlines these benefits like improved morale, reduced cost of production, lower turnover, and quality staff for the organization. Training and development may entail on-the-job programs, such as transfers, or off-the-job methods, such as conferences (Cole, 2002). Additionally, some firms have in-house programs for formal employee training in specialized skills.
Training and development have a close relationship with employee performance. In the UAE, researchers observed that training advances the scale of innovation, mental capacity, and rate of adjustment to new technologies in workplaces. Al-Nuseirat and Biygautane (2014) compound the observation when they assert that employee training and development minimized the high levels of inefficiencies, which were common in the absence of training.
When employees go through well-structured training programs, their confidence, and approach to various issues change positively. The implication of the positive change is an improved mental capacity, which refers to the ability to reason and come up with new ideas that foster product quality and amplify consumer satisfaction. The importance of training and development in the UAE is a concept that researchers cannot underestimate in the quest to assess the factors that improve product quality and enhance the application of modern technologies.
Employee Performance
Employee performance encompasses the outcomes or behavior change resulting from training activities (Armstrong, 2005). The need to establish or determine whether training increases productivity among employees has risen over the recent past. Several governments and organizations have engaged in research to ascertain the authenticity of the concept. In actual sense, employee training is a very important tool that is useful in promoting the productivity of individuals living in a particular country. Notably, the absence of skilled employees in a host country compels some organizations to hire experts from foreign countries.
The process is costly and increases the level of unemployment in the host country. In the UAE, companies engaged in oil production and exportation are forced to hire experts from foreign countries in the quest to ensure that their products match consumer demands. The high cost of hiring foreign employees and the need to reduce unemployment in the UAE compelled the state to encourage organization and learning institutions to train indigenous communities on aspects of product delivery. According to Mozael (2015), employee training improves productivity among the indigenous populations globally. Therefore, with the realization that training boosts the productivity of the native or indigenous people, the number of organizations that are currently training their employees is increasing.
It is important to elucidate that effective training of indigenous communities amplifies productivity. Through training, natives acquire new skills and apply them to their respective organizations. With the skills, the indigenous people can perform well and engage in the right procedures that reduce inefficiencies and delivery of low-quality products. Essentially, when individuals acquire the skills and expertise, their self-esteem improves, and hence, they approach their daily requirements with a positive attitude, which is a key ingredient in excellent product delivery.
In the explanation of Donn and Al (2010), the UAE has instituted a policy, which requires companies to recruit and train natives in the course of a production. Concisely, the explanation by Donn and Al (2010) affirm the essence of training in the improvement of productivity among indigenous populations in the UAE.
The Training and Development Outcomes
When organizations train and develop their human resources, issues relating to strikes and consumer dissatisfaction decline. In effect, training enables employees to engage in productive communication, which leads to a peaceful resolution of issues at tender stages. By training employees, organizations can successfully engage in vertical and horizontal communication conveniently.
Remarkably, employees get the chance of airing their views in an informed manner, and in turn, establish a productive working environment. It is fundamental to explain that well-trained employees air their grievances in an organized format and have the ability to think critically and solve problems. In the perspective of Khan (2016), employee training enables employees to think critically and solve problems. The ability to solve problems implies that management only deals with complex issues.
Furthermore, employee training and development lead to successful communication within and outside organizations. In the aftermath of a well-structured training program, employees acquire the skills that help them communicate well amongst themselves and the management. The training empowers the human resources on the essence of following a due process when conveying a message to various departments in and out of the organization. Additionally, employee-training programs instill values such as assertiveness, honesty, and politeness on human resources, and in turn, boost their communication skills (Uden, Heričko & Ting, 2015).
In the UAE, employee training helps in ensuring that employees communicate successfully and cooperate in product delivery. By communicating well and cooperating, human resources develop a culture, which is beneficial in the successful operation of the organizations. Therefore, staff training has a pronounced effect on the expertise and communication of employees in the UAE.
Research Methodology
This section describes the specific elements of the research process of the study, including:
- Conceptual framework (the diagram);
- Hypotheses (if quantitative);
- Data collection methods;
- Questionnaire design (if using survey);
- Research design;
- Type of research
- Population
- Sample size
- Sampling frame
- Sampling technique
Conceptual Framework
This study aims to determine the relationship between training and career development and job performance. Therefore, it will focus on the CDC trainees absorbed by UAE-based firms. The CDC training exposes employees to the technical and managerial skills required in their job grade. This study will focus on three developed concepts, namely, learning, behavior, and creativity of the training/career development. A schematic presentation of the theoretical framework for this study is given below.
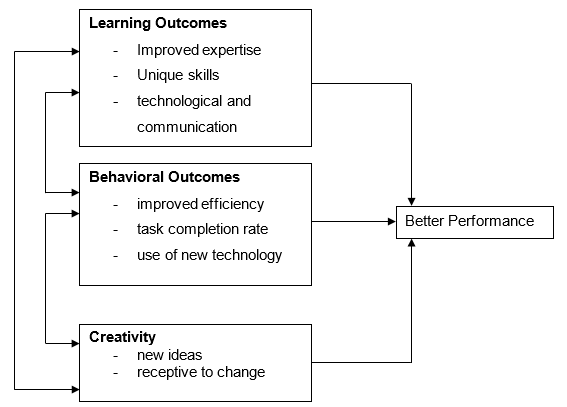
Hypotheses
For this study, the following four hypotheses related to employee training and performance will be tested:
- H1: Employee training and development affects job performance.
- H2: CDC programs influence staff competencies.
- H3: Training and development influences productivity levels in the private and public sectors.
- H4: Job training affects staff expertise and communication skills.
Data Collection Methods
The study will use a pre-tested performance questionnaire and an employee questionnaire to assess the performance of CDC-trained staff (experimental group) and UAE-based workers who have not received any job training.
Questionnaire Design
As stated, two types of questionnaires will be used: a performance questionnaire and an employee questionnaire. The performance questionnaire filled by experienced supervisors will evaluate key performance areas, including learning outcomes, behavioral outcomes, and creativity based on the Likert scale. On the other hand, the employee questionnaire completed by employees will capture the socio-demographic variables of the respondents.
Research Design
Type of Research
An exploratory design will be used in this study. The approach will involve a non-random survey of control and experimental groups to assess the outcomes of the CDC training and development based on descriptive data.
Population
The CDC trainees, corporate managers, UAE workers, and expatriates will constitute the target population for this study.
Sampling Size
The sampling size will depend on the respondents required to reach data saturation. A purposive sample size of 80 is considered large enough to achieve data saturation.
Sampling Frame
The sampling frame for this study will consist of UAE nationals and expatriates working in private and public sectors. Two thousand online questionnaires will be sent to CDC-trained employees and professionals working in different sectors in the UAE
Sampling Technique
A purposive sampling approach will be employed to sample CDC-trained staff working in various sectors in the UAE. Simple random sampling will be utilized in sampling the control group from non-CDC trained nationals and expatriates.
Source of Data
The study will use primary data collected from the participants using the distributed questionnaires. The quantitative data measured using the Likert scale will be analyzed to test the aforementioned hypotheses.
Analysis Techniques
Reliability and Validity Analysis
Reliability
The reliability of the developed 7-point scale will be measured for internal consistency using the Cronbach’s alpha coefficients. This measure estimates the interrelations between items by evaluating the concepts. Items that show a high internal consistency, i.e., α≈1, will be retained in the questionnaire.
Validity
Factor analysis can reveal the validity of the items to measure the hypothesized concepts. A factor analysis will be used to determine if the items evaluate the theorized concepts.
Data Processing
The study will use the SPSS software to determine the correlation between the identified variables based on numerical values assigned to the questionnaire responses. Descriptive statistics will also be used to describe the data.
Statistical techniques
A multivariate analysis (one-way ANOVA) will be used to determine test the study’s hypotheses as summarized in Table 1 below.
References
Al-Nuseirat, A. & Biygautane, M. (2014). The Impact of Effective Training on Organizational
Performance in Dubai’s Public Sector. Policy Brief, 1(37), 1-12.
Armstrong, M. (2005). A handbook of personnel Management Practices.London: Kogan Page Limited.
Cole, G. (2002). Personnel and human resource management. London: York Publishers.
Donn, G. & Al, M. (2010). Globalisation and Higher Education in the Arab Gulf States.Oxford: Symposium Books.
Gordon, B. (2004). Are Canadian firms under investing in training? Canadian Business Economics, 1(1), 25–33.
Khan, A. (2016). Impact of Training and Development of Employees on Employee Performance through Job Satisfaction: A Study of Telecom Sector of Pakistan. Business Management and Strategy, 7(2), 29-46.
McCourt, W. & Derek, E. (2003). Global Human Resource Management: Managing People in Developing and Transitional Countries. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
McNamara, C. (2008). Employee Training and Development: Reasons and Benefits. Web.
Mozael, B. (2015). Impact of Training and Development Programs on Employee Performance. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications,5(11), 38-42.
Purcell, J., Kinnie, N., Hutchinson, S., Rayton, B. & Swart, J. (2003). Understanding the People and Performance Link: Unlocking the Black-Box. London: CIPD Research Report.
Uden, L., Heričko, M. &Ting, I. (2015). Knowledge Management in Organizations: 10th International Conference, Kmo 2015, Maribor, Slovenia, August 24-28, 2015, Proceedings.London: Springer.
Wilkins, S. (2001). International briefing 9: Training and development in the United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Training and Development, 5(2), 153-165.
Wright, P. & Geroy, D. (2001). Changing the mindset: the training myth and the need for word-class performance. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 12(4), 586–600.
Questionnaire
Gender:
Age:
Educational background (tick where appropriate)
- Primary
- Secondary
- Diploma
- Degree
- Above degree level
Job Position…
This section specifically focuses on the sections on the training and development of personnel from the UAE companies
- Period of employment with the organization (tick where appropriate)
- 1-15 years
- 16-25 years
- 26-35 years
- Over 36 years
- Have you ever participated in training and development programs? (Yes/No)
- What criteria were used for your selection for training? (tick as appropriate)
- On joining the organization
- Supervisor’s recommendation
- Mandatory for all employees
- Employee request
- Performance appraisal
- Don’t know
- What is the training schedule? (tick as appropriate).
- Quarterly
- Semi-annually
- Annually
- Once in two years
- No particular schedule
- Methods used in the training programs (tick as appropriate).
- Lecture
- Demonstration
- Discussion
- Seminar
- Discussion
- Job rotation
- Did the training impact on your skill? (Yes/No).
- How was the quality of the training received?
- Very poor.
- Poor.
- Average.
- Good.
- Very good.
- Excellent.
- How relevant was the training to your work?
- Not relevant;
- Not sure;
- Effective;
- Very effective.
- Did the training impact on your performance? (Yes/No).
- Do you feel like you need further training? (Yes/No).
