Introduction
Geographical Location
Haiti lies on Caribbean. It occupies one-third of Hispaniola Island. The Island is located between the Caribbean Sea, the North Atlantic Ocean and West of the Dominican Republic. The country was the first black republic to declare its independence on 1st of January, 1804. France colonized Haiti. The government is an elected type. Haiti occupies a total area of 27,750 square kilometers. Land occupies 27,560 while water occupies 190 square kilometers. Coastline bordering the country stretches up to 1,771 kilometers. The climate of the country is tropical. There are some semiarid areas especially in the east where mountains cut off trade winds. The semiarid areas have rough and mountainous terrain. There are a number of natural resources in Haiti. They include Marble, calcium carbonate, copper, bauxite, and gold, among others.
The major causes of low economic growth in Haiti are poor governance, natural catastrophes, political instability, poor infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
Environment
The country lies in the middle of the hurricane belt. It faces harsh storms especially between the months of June to October every year. It also faces earthquakes, periodic flooding and drought. The country also faces extensive soil erosion which seriously affects plantation. It faces insufficient supplies of water. Finally, there is a lot of deforestation in the country. Remaining forest in the country is being cleared for agriculture.
Population
The country has an approximate population of about 8 million. The age group between 15 to 64 years makes up 53.9% of the whole population. 0 to 14 years are 42.6% of the whole population. The rest, that is, 3.4% comprises of people aged above 65years. The median age of the population is 18 years. As at 2005, the population growth rate was 2.26%. 95% of the population comprises of the black. The remaining 5% comprises of mulatoo and white. Further, 80% of the population attends the Roman Catholic Church. The official languages spoken by the population is French and Creole.
Economic analysis
Overview
Haitians have endured a long post colonial history of poverty, political and oppression, and underdevelopment, a trend that continues to challenge the sustainability of the country’s fragile political stability. The January 12 2010 earthquake worsened the economy. Until this moment, the country has not been able to overcome a legacy of weak governance, economic inequality and social unrest. The country’s unbalanced social structures are the cause of the vicious cycle. The country’s social, political and economic development has been on a slow path since the transition from dictatorship to democracy. Despite the fact the country attained independence in the 17th century and the abundant natural resources, Haiti ranks as one of the poorest countries in the Western Hemisphere. About 80% of the population languishes below the poverty line. This is majorly because of the natural calamities which constantly sweeps the nation and poor governance.
Economic activities
More than 67% of the population depends on agriculture. These are small scale farmers who grow crops such as sugarcane, mangoes, rice, corn, sorghum, wood, and coffee. The country has a few industries such as sugar refining, flour milling, textiles, cement and a few light assemblies for imported machineries. Other than agriculture, the country also relies on production of apparel. Production of apparel is capital intensive. However, it requires low level of skill. The country has been doing well in production and export of apparel. However, it faces stiff competition from countries with well to do machines and with superior technology. The poor state of infrastructure is a key drawback in production of apparel.
Grant, Aids and Loans
Before 2000, the country heavily relied on aids from the US, European Union and other international donors. However, there were a lot of irregularities in use of the aids. Therefore, the international donors stopped funding the nation. This led to an extensive deterioration in the economy from 2001 to 2004. Contraction in the economy was estimated to be 1.2% in 2001, 0.9% in 2002, and 3.5% in 2004. At the beginning of 2003, the amount of aid and loan disbursed that had been suspended amounted to over $500 million. In 2005, the country repaid the debt owing to the World Bank. Thereafter, the country was able to reengage with the Bank and other donors. In addition, after the devastating earthquake that occurred in January 2010, many international donors come in to offer humanitarian aid to the citizens. US also revamped the HOPE Act.
Inflation and GDP
The country suffers from out of control inflation from year to year. This is the major cause for decline in real wages by more than half from 2000 to 2008. However, the 2009 global recession helped arrest the inflation in the country. The country lacks investments. It heavily relies on export which contributes to about 60% on the GDP. Also, it suffers from endless trade deficits. This is because it relies on imports for basic commodities such as oil. Unfortunately, about 92% of their exports go to US. Reliance on trade with one country puts the country. In 2006, the GDP of the country was $5.0 billion. It rose to $6.7 billion in 2007, and in 2008 the GDP was $7.0 billion. The graph below shows trend of GDP for three years.
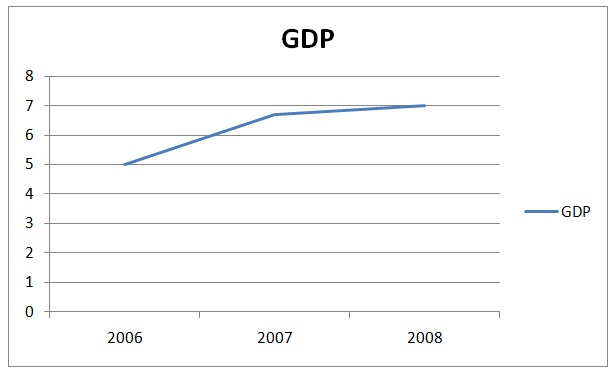
- Horizontal axis represents years
- Vertical axis represents GDP
Unemployment and productivity
In 1991, the Haitians opposed the elected president. They were supported by the United States and other countries. The countries wanted to restore the democratic state. To achieve this, US imposed a trade prohibition with the Haiti. They channeled this ban through Organization of the American States and UN. Estimates of the multiplier effect indicated that there were more than 200,000 jobs lost. The country could neither import nor export to her key trade partners. There are no employment opportunities in the country. More than 80% of the population works in the informal sector. The effect of the trade ban profoundly impacted on economic growth of the country. The employment status has not recovered since then.
The country is considered to be one with the lowest or negative productivity. This is caused dismal investment in the private sector and lack of human source capital. Poor state of education, health care and infrastructure has negatively impacted on the productivity of the country.
Conclusion
Poor governance plays a key role in the devastating state of economy. Negative productivity of the nation cannot spark up economic growth in the country. Environmental factors also contribute negatively to economic growth. These factors still remain key setbacks to development of the nation. The effects of the 2010 earthquake are immeasurable. It brought the economy to its knees. The country had to build from start. Even though it is receiving support from US, UN and other international donors, there is still much to be done. Plenty of work needs to be done on the drivers of economic growth such as infrastructure, education and health care.
