Introduction
Hilton is an international organization that provides hotel and hospitality services to clients across North America and the rest of the world. The company managed to create an independent company from each unit through franchising, hence promoting its independence. Besides franchising, the company has established physical branches across the world using the same name. When establishing branches across the world, the management ensures that each unit follows the rules or regulations set by the headquarters in the US. Hilton invests in major continents in the world including Asia, America, Africa, and Europe. The corporate section of Hilton manages its investments in major airports and resorts. In 2012, Hilton received an honor for being the best employer of the year (Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation 41).
Hilton equally offers memberships to people who seek affiliations with the company; they include Blue and Gold VIP among others. Companies come up with such strategies in order to gain competitive advantage over their competitors. A situational analysis studies the macro-environment and microenvironment factors within the US, as well as factors that promote Hilton’s investments in other parts of the world. Through an effective SWOT analysis, Hilton has managed to reach out to a wide population with specific focus on China’s Hainan Island and North America.
Hilton Worldwide
Hilton Worldwide is an American Company dealing in the provision of hotel and hospitality services. Blackstone Group owns the firm under a private equity agreement owning about 40,000 resorts and 700, 000 hospitality outlets in over 90 countries across the globe. The company also provides outside catering services to clients in over 1,000 branches in America. Hilton Worldwide trades its stocks at the NASDAQ and conducts online businesses, which includes shipping to over 80 countries that seek the company’s services. Hilton has its headquarters in Beverly Hills in the US (The Hilton bedside book 129).
Besides providing luxury facilities, Hilton Hotels host wedding receptions, corporate functions, family gatherings, and extended stays among other activities. Hilton’s domestic marketing strategy seeks to introduce other stores in various markets because it succeeded in doing the same in the US. Franchising is a strategy that the North American firm identified because the demand of the public keeps changing and consumers expect something new daily (Toronto 2000 36). Other expansion plans in both the domestic and stand-alone stores in other parts of the world includes online business transactions that incorporate shipping.
SWOT Analysis for Hilton, Marriott, and Starwood
Besides Marriott International, Hilton is the second largest hotel across the world. Competition is a reality in the world of investment, but it matters how an organization manages changes within the environment. At the international platform, Hilton focuses on pricing and quality service delivery as the greatest elements of the marketing strategy. The following SWOT analysis explains the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that the firms face in the competitive economies.
Strengths
Hilton invests in 91 countries with major franchises within the US. In essence, it has the responsibility of incorporating several cultures; its diversity portfolio enables the company to attract the interest of clients within and outside the US. Among the brands that offer Hilton the requisite diversity, include Embassy Suites Hotels, Conrad Hotels & Resorts, and Hilton Grand Vacations among others. Hilton has an advantage for its brand because many people recognize the hotels. Most people recognize Hilton hotels amongst other competitors including the high profiled Marriott Hotels (Toronto 2000 36).
This attributes to the high number of franchises and brands developed around the world. For over 90 years of operation, the Hilton offers quality services to customers and this contributes towards the good reputation that the company enjoys. On the other hand, Marriott International enjoys publicity owed to the high brand appreciation and consumer ability to remember the company. This has helped it to reduce expenses on marketing because many people identify with the organization. Marriott International embraces high-tech services that improve relationships with clients through communication.
In addition, technological assistance allows Marriott International to provide efficient and effective services encouraging quality customer experience. Technology reduces workload for employees. Coupled with good living and working conditions, the company is able to retain over 145, 000 workers in about 4000 branches across the world (Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation 48). Finally, Marriott attains competitiveness in comparison to Hilton because it offers a variety of services that people of different income levels could attain.
Through technological assistance, Hilton Hotels encourage online booking services to reduce physical movements. In addition, visitors in various Hilton Hotels have access to WIFI services in their rooms and within the vicinities of such hotels. Internet connectivity is a prerequisite for success in the current day and age; successful companies such as the Hilton use the strategy to attract and keep consumers. Technology naturally improves customer experiences within such organizations, and it creates room for quick service delivery and improvement.
When consumers get the best services from an organization, they are likely to remain loyal to the entity. Its loyalty program aims at rewarding consumers and resorts that use its services and products. For example, 6 years ago, 17 million loyal consumers received loyalty awards that made them enjoy services of the hospitality industry, which included grooming, vacations, and meals for an entire year. With such a reward scheme, it would be impossible to lose consumers for no apparent reason.
For Starwood Hotels, they generate much income from public recognition. Adverts on social media are the best business strategy adapted by the company helping it receive a grand reception translating into revenue generation. This helps it manage its brand image and to increase awareness for about 1200 hotels owned by the organization (Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation 42). Starwood equally establishes its branches in Green buildings; this promotes the image of the company.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses refer to the setbacks faced by Hilton Worldwide and its competitors in the industry. The companies can deal with such issues by reducing some of them and maximizing on the company strengths.The marketing strategy of Hilton involves physical expansions, online businesses, and franchises. According to the financial reports of the company, only 15% of the branches are outside the US.
In essence, the United States alone has about 3,060 franchises under the management of Hilton Worldwide (Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation 53). This makes Hilton Worldwide to lose focus from other countries that would probably contribute to increase in the profit margin. Focusing on the domestic market equally affects the performance of other rivals such as the Sheraton and Hyatt. On the other hand, Marriott has an equal distribution between the domestic and international market making it possible to enjoy publicity from both markets. Even though it is the best chain of hotels to visit across the world, Marriott International faces competition from Accor, Starwood, and Taj Hotels. Such companies equally have technological assistance and brand recognition in an environment with a limited number of consumers.
When Hilton invests in another country, it purchases already established buildings. The cost of real estate increases annually because, naturally, the real estate business has the potential to appreciate over a certain period. During franchising and expansion, the company has to adhere to the rates of purchasing buildings, and this affects profits. In 2006, the company had one of the greatest expansion plans and it managed to buy buildings in China leading to massive financial losses. When the value of buildings increases, it affects the purchasing power of the company causing its reduction because it cannot make profits from the hospitality services to cover for the costs.
Through a private equity plan, it would be impossible for Blackstone to have joint ventures until it reviews its ownership plan. This affects the company, especially when losses occur. Joint ownerships support risk sharing, which is an advantage for most business. Since Hilton Worldwide lacks private equity plan, there are high possibilities of experiencing several losses and bearing the burden independently. Recently, the stock exchange rate reduced and this affected stock sales at the Starwood Hotels and Resorts. When this happened, some shareholders withdrew because their businesses were at stake while others reduced the number of shares they owned. Besides, Hilton and Marriott, few people recognize that Starwood exists because of the limitation in franchising within the US.
Opportunities
Opportunities refer to the aspects of the society that provide a chance for improvement. Hilton needs to take advantage of such chances in order to expand physically and in terms of brand positioning. Opportunities are external to the organization even though they promote growth. As such, Hilton Worldwide cannot control opportunities in the existing market. Market and product research are vital for performance in a competitive environment.
By providing unique luxury brands, Hilton Worldwide manages to command the market dominated by major players such as Marriott and Sheraton. Consumers enjoy unique travel experiences, but they would not get this if companies never carried out extensive research to fulfill such demands. As this happens, Hilton has to shift from a product-based to a service-based customer satisfaction plan, as this is the relevance of creating uniqueness. Since there is a demand for uniqueness, the company has to offer such services because technology supports the same. Technology helps in branding, bookings, and offering WIFI services to consumers. Offering such unique services requires technology, and Hilton takes advantage of the global platform to introduce technology in most of its systems. Competitors across the world equally employ such measures even though the level of efficiency and effectiveness of each entity differs.
A promising market offers Marriott an opportunity to grow and remain innovative because the greatest intention is to fulfill the growing consumer demand. All organizations only need capital and willing customers in order to create a niche; this explains Hilton’s success at the Sanya Island in comparison to other 5-star hotels including Starwood. Food is a necessity for human consumption and the demand for good services increase daily. Markets emerge daily and this is an opportunity for growth in India and China. Additionally, technology keeps improving and this would help to improve customer experience.
Initially, people viewed climate change as a threat to overall development of an organization, but organizations such as Hilton used the green business appeal to attract consumers. Most tourists are likely to visit hotels that promote clean and secure environments. This means that green business is important, and Hilton Worldwide took the best initiative by investing in Green buildings (Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation 50).
Since the hotel managed to recycle water, and to provide clean and safe energy to their customers, it lowered the cost of operation and maintenance. As such, the clients have the value for their money when they visit these hotels. Besides, Hilton Hotels also support health care programs enabling the less privileged families to acquire quality health care services at an affordable price. The ability to embrace such cultures positions this company in a competitive climate. Ability to embrace Green technology and business operations would help in creating a sustainable organization. In addition, it would increase brand loyalty for willing consumers. To increase brand recognition within the US, the company can employ most Americans to the over 150, 000 employee base it already commands.
Threats
Threats refer to the negative societal influences that are likely to affect a business. They include social, economic, political, and technological barriers to growth.
Social
Cultural differences in countries of investment make the company spend many resources in establishing diversity. Consumers have different choices and in each culture, the choices differ. Currently, Marriott, Accor, Starwood, and Hyatt Corporation have shifted from product-based to service-based cultures. Social interactions with other hotels in the US and other countries equally influence the public perception towards Hilton Worldwide and its competitors. As such, inability to embrace new cultures and changing social trends threatens the sustainability of businesses including the ones in the tourism and hospitality industry. In over 540 investments across the world, the company has to comply with the rules and regulations of the legal system that the law demands.
Political
Political factors often interfere with companies in their entry levels. Competition at the macro-environmental level affects relationships between people at Hilton and among rivals within the same industry. Dealing with competition could be difficult especially in a new environment. Competition also reduces the growth rate of the Hilton Hotels in the US and China. Power rivalry, would be the worst thing that could happen to a company.
However, such situation is not evident at Marriott and Hilton Hotels. When power struggles occur, it becomes impossible to delegate or share duties and authority. At the entry level, Marriott International has to deal with harsh political and economic climates in some countries especially in war tone areas. Politics influence economics and this affects exchange rates, which would increase the price of real estates and supplies in the competitive market. As such, the company becomes unproductive and gives room for competitors to succeed. Finally, political instability in most parts of the Arab North affects businesses in the hospitality industry. Politics affect many things especially business.
Economic
Economic instability and recession are threats to growth. The hospitality industry faced major challenges between 2009 and 2011 because of the financial meltdown (Wharton 85). The US economy was the worst affected because it sets exchange rates between countries. Economic recession between 2009 and 2011 affected societal spending on luxury and the hospitality industry. If the same happens, Starwood hotels will lack the potential to maximize its profits and this could equally affect stock exchange prices. Markedly, increasing the interest rates affects business because few people have money to spend in luxurious commodities. Additionally, poor performance in the airline and tourism sector directly affects business at Marriott, Starwood, and other hotels. As such, the company has a professional chief financial officer at the headquarters who studies economic trends across different countries of investment. Finally, government policies that govern taxation rates sometimes become too stringent for investment and this could affect business at Hilton.
Five Forces Model Competition and Competitive Matrix for Marriott, Starwood, and Hilton Hotels
Five Forces Model of Competition
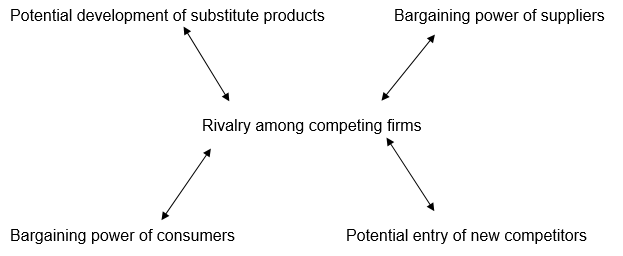
Substitutes
Hilton has the responsibility of learning the development of substitute companies in the environment of investment. In China, 4-star hotels including the Sheraton Hotels provide affordable and efficient services to consumers. They offer WIFI services to customers within the organizational premises. This made Starwood Hotels to introduce its first line of 3-star hotels in the same country (Toronto 2000 36). As such, Starwood needs to understand the weaknesses of the substitutes, and develop alternative strategies of dealing with each substitute. The long-term profitability of Starwood depends on how it manages its substitutes. It can follow the strategies that Marriott International applied to maintain market dominance.
Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers needs to be high in order to provide Hilton Hotels with affordable products and services. This includes power suppliers, technology, and food suppliers. In order to cut the costs of supplies, Hilton Hotels recycle water, and use Green buildings for energy conservation. Supply cost differs depending on the country of investment and the type of franchise in the region. The 9 brand hotels of the company including Conrad have some of the most costly supplies.
On the other hand, Starwood Hotel, on its part, is devising an ‘asset right’ strategy to ensure that it records sales of more than 10 billion from their non-strategic properties. The bargaining power of the Starwood Hotels needs to be high in comparison to the amount offered by suppliers. For instance, before introducing the real estate portfolio, the company consulted affordable suppliers from Africa and the Middle East (Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation 44). Naturally, the supply decisions aim at benefiting the supplier, but the consumer had the ability to bargain and assess the market before making decisions.
Consumers
Consumers form a significant part of Hilton’s progress. Through advertising, quality service provision, and a good marketing strategy, Hilton Hotels attract many consumers across the world. The company’s “hospitable” promotional strategy raised curiosity among consumers who never tried the hotels in 2006 (Kader 70). The company’s slogans, mission statements, and overall strategic plan determine their intentions towards the public. Hilton commands thousands of consumers across the world with over 3,060 franchises within America alone. In 91 countries, the company manages to attract consumers second to Marriott. It has many consumers in comparison to Starwood, Hyatt, and Sheraton among other companies of the same industry. The bargaining power of consumers should be low in order to increase the amount of money acquired by both Marriot and Starwood Hotels. Coupled with a high supplier bargaining power, the company will regain stability in the competitive hospitality industry.
Rivals
Rivals are central to the five forces because they influence each element of the competitive cycle. Established in 1949, Sheraton is the greatest rival of Hilton in Hainan’s Sanya Island. In addition, the 4-star hotel contributed towards Hilton’s decision to introduce such hotels in the Island and in the US as well. Sheraton has branches in Israel and other countries (Kader 72). Starwood is also Hilton’s competitor that formed joint ventures with Sheraton in order to succeed in the flourishing Asian market. At NASDAQ, Marriott rates as the best hotel and hospitality outlet in the world followed by Hilton Worldwide. In order to deal with competition, Hilton established a new branch in Orland where Marriott initially existed at the World Trade Center. Following the 9/11 attack, the building collapsed causing major losses for the company. Similarly, its strategy is to acquire markets established by Sheraton in the area.
Entrants
Market entrants refer to the new companies seeking to provide competitive services to the same market that Hilton share with substitutes and rivals. In India, and China, Hilton deals with Sheraton and Starwood who equally deal in franchising. In Orland, a similar occurrence leads to high competition levels forcing Hilton to introduce top-notch security, transport, and technology in order to deal with competition. Its forty hotels in the Asian market provide Hilton with knowledge in dealing with entry strategies. Just like Marriot and Hyatt International, Hilton Hotels can use their financial strength come up with new products or employ different production and marketing strategies to enable consumers differentiate their services from the competitors.
Competitive Matrix and Industrial Analysis
The hotel industry has numerous fragments, as no hotel owns more than 20% of the market share; Marriott commands the largest market share with 9%. In 2006, the hotel had a market cap of $16.97 billion, which was the highest in the hotel industry. Hilton Hotels follows in the ranking (The Hilton bedside book 147). The table below represents a competitive profile matrix that indicates avenues for improvements that Hilton can pursue in order remain competitive in the hotel industry. The values used in rating have the following interpretations: major company’s strength = 4, minor strength of the firm = 3, minor weakness = 2 and major company’s weakness = 1.
The weight allocated to each factor shows how significant the parameter can bring success to the respective company. From an industrial analysis perspective, just because Marriot received an overall score of 3.46 does not imply that Hilton is far much below in its operations; it has the capabilities to move up to be at par with Marriott if it addresses the results of the success factors. With Marriot and Hilton having the same financial position, Starwood has to devise strategies of attaining high financial status.
Competitive Profile Matrix
(The Hilton legacy 74).
Industry Analysis: IFE and EFE
The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix and the External Factor Evaluation (EFE) give top factors that Hilton and its competitors can focus on in order to address the weaknesses. Some of the factors for success include superior ratings by employees, hotel diversification, and significant presence in luxury markets; ratings on external factors include customer loyalty, focus on franchising, brand strength, guest programs, and employee dedication.
Grand Strategy Matrix
Rapid Market Growth
Slow Market Growth
Factors on the second and third quadrant represent the weak competitive positions of the firms, while the first and fourth quadrants represent the strong competitive positions in the hotel industry.
Recommendations
Evidently, barriers range from political, social, technological and economic factors. All the barriers work in multiplicity to bring down businesses but somehow, the group develops strategies of curbing the barriers. Hilton should develop mutually beneficial relations with competitors and distributors in order to win consumer goodwill. Additionally, the Hilton franchises should work in unison to refute this by implementing new strategies that incorporate online marketing, brand positioning, logo changing, CSR and philanthropy, quality assurance among multiple other factors. The power of technology and online marketing makes this a reality for the company.
Finally, it is only through research, a thorough SWOT analysis that the company can understand the areas that they need to improve, and those that require good equipment. Through a periodic research program, Hilton Worldwide will learn the prevailing competition and develop strategies of becoming better and attaining monopoly amid rivalry. Companies that invest within the industry have to develop new strategies of doing things in order to match the growing competition (Kader 63). In addition, it should increase the number of substitutes in target markets in order to meet consumer demands. External variables provided by Hilton helps the company in dealing with competitive forces within various environments of investment.
Works cited
Informational hearing on Hilton Hotels Corporation: an inquiry into its employment practices and treatment of the immigrant workforce. Sacramento, CA: Senate Publications & Flags, 2006. Print.
Kader, Magdy G.. Review of management accounting research. Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan, 2011. Print.
The Hilton bedside book; a treasury of entertaining reading. Chicago: Hilton Hotels Corp., 1964. Print.
The Hilton legacy: serving humanity worldwide. Los Angeles, Calif.: Conrad N. Hilton Foundation, 2009. Print.
Toronto 2000, Musical Intersections: 1-5 November 2000, Sheraton Centre and Toronto Hilton Hotels, Toronto, Ontario. Philadelphia: American Musicological Society, 2000. Print.
Wharton, Annabel Jane. Building the Cold War: Hilton International hotels and modern architecture. Chicago: University of Chicago, 2001. Print.
