Abstract
IKEA is one of the best furniture retailers in the world. The company not only manages to ensure efficient processes, but also strives to create modern furniture at a cost effective and to create sustainable competitive advantage through better shopping options for the customers. The purpose of this study is to understand the operations management processes of IKEA. The research question focused on the key processes of the company’s operations management along the supply chain cycle. The research questions also sought to determine if there are any gaps in the process and how these gaps can be utilized through improved processes. Further, the research questions guided the writer on the type of analysis to be conducted as well as the need to review previous empirical data, resulting in information that was used in the discussion part of this research. The research methodology primarily utilizes a qualitative data approach where most of the information utilized was through literature review and analysis of pre-existing information on the company processes.
The findings of the study indicate that the IKEA is a global company with good market distribution all over the world. The study also found that the processes of the organization are aligned to meet the needs of the customer while ensuring that they are not only affordable but of high quality. Moreover, the study established that the operational process of the company does not allow for bulky items and materials storage. Thus, items are made in a way that allows for efficient and flat packing, with the customers being the final assembly point. Further, all the processes of the company emanate from the central point in Sweden, after which global suppliers aid in the manufacturing process. However, the distribution of the final products to local stores all over the world relies on demand forecasts that can either be accurate or not, being that the company insists on minimal storage. However, owing to the minimal number of store attendants, the customers complain of inefficiency at the stores and frustration in locating the key items/ furniture.
Introduction
Operations management is a process through which a company organizes its main activities that aid in the production of final goods and services. In effect, operations management revolves around the organizations of raw materials and work processes that have been identified for the production process. The operations process of IKEA Furniture converts inputs into outputs, through an effective operations management strategy. Notably, the IKEA Company was established about 60 years and headquartered in Sweden. The key idea that governed furniture production was, so long as their furniture price was effective and of high quality, then their customers would travel from out of town to come and buy their products and be able to self-assemble them (“Business: The Secret” par. 2). The mission of the company was formulated by its founder Ingvar Kanprad, which states that the company’s mandate is to offer a wide variety of functional furniture at a quality and price that is attainable by majority populations. In effect, the principles of the company are driven towards facilitating an attainment of the company’s mission regarding providing both economic and quality products (IKEA Retailing Worldwide 8).
Notably, the organization’s primary principle is concerned with the production of a wide range of functional products by enforcing high-quality standards. Essentially, the operations management process of IKEA revolves under key fundamental tenets. These are: to ensure that the company design products that can be efficiently and flatly packed to create site stores of the right size in various locations, as well as, to design a proper store layout that allows for the smooth and efficient flow of materials and goods (IKEA Retailing Worldwide 2). Other core tenets of the company’s operations are, to ensure that the storage area is clean, to ensure that finished products are replenished quickly, and to offer high service quality (Harrison 67). These processes are made possible through constant monitoring and improvement of operational performance from time to time as well as ensuring that all functional jobs contribute to business success
Topic Statement
The research seeks to offer an analysis of the operations management process of IKEA furniture. In effect, this study seeks to cover the main areas of the businesses’ supply chain from the manufacturing process to the distribution stage. Thus, the writer will offer an introduction to the company mission and strategy and how it relates to its operation management strategy. Later, the writer will defend the methodology method that they will apply throughout the research stating why and how it is most applicable to the case. The results of the case through previous literature and empirical data review will be presented, with the writer stating the key operations management issues. This will later be analyzed under discussions. Owing to the global nature of the company’s supply chain, the writer will offer a recommendation for the distribution practices of the company. Overall, this research is important in explaining how to manage supply chain systems for global companies.
Methodology
In this chapter, the writer will justify the methodological choices that they have chosen for the research paper. The elements of this research paper are exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory. Essentially, the writer has utilized these three areas of research as the study primarily seeks to analyze and describe how IKEA manages its operations management, and how it can improve these processes. The purpose of this thesis is to explore the various issues in IKEA’s operations management process, a novel area of research. In effect, the writer aims to gain a greater understanding of the research topic. Further, the study is descriptive in nature as empirical data is collected and used so as to establish the patterns for research. The purpose of this research is explanatory in nature as the writer explains the results they have attained through drawing a conclusion and discussing the finding of the key research questions.
The research has also taken up a qualitative approach of analysis. This research is qualitative owing to nature in it can draw a conclusion and develop finding from non-quantifiable information such as the key processes. It also gives a possibility of attaining more information and investigating some variables to gain an understanding of the chosen area of study. Overall, this study is qualitative as the researcher seeks to establish in-depth knowledge on the operations management processes of the IKEA Company. Through these findings, the research hopes to draw possible conclusions that could be applied in other research.
The research strategy has taken up the form of a case study focusing on a company with the key questions of the study being how and why. According to (Hill and Jones 1), a case study involves the analysis of an entity depending on the chosen variables, with the primary aim of improving knowledge on the particular subject and not a generalization of ideas. This is in agreement with the aim of this research as it seeks to gather in-depth knowledge of the operations process of the IKEA furniture and offer recommendations on how these processes can be improved.
Results
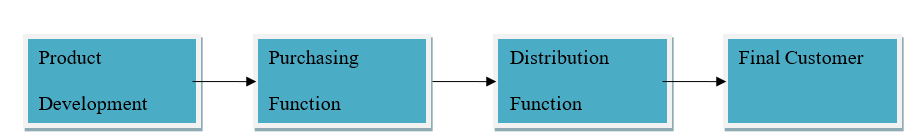
The supply chain of the company is categories by four stages. These are product development, purchasing, distribution and the sales to the final customers. Notably, the supply chain of the company begins with product development, which is done at the business’s headquarters (Hultman, Hertz, Johnsen, and Johnsen 4). After design development, the designs are then relayed to the suppliers in various locations all over the world to take care of the manufacturing function.
Purchasing is the second function. The purchasing role of the company uses some vendors all over the world being that the enterprise does not have a manufacturing facility. These suppliers are in charge of manufacturing the various designs transmitted to them are delivering to the company’s locations (Williams 201). The finished products are then distributed to the various company store locations over the world, depending on the forecasted quantities.
Notably, the company has a total of about 27 distribution facilities in 16 nations worldwide (Hultman, Hertz, Johnsen, and Johnsen 4). After, the products are then delivered to about 186 stores located all over the world, as the company works hard to simplify and rationalize its distribution process (Williams 201). In fact, the company calculates an exact number of products that are required to satisfy the demand of a particular market in a given country before they can send stocks. This way, the company can eliminate wastage and high production costs as well as warehousing expenses. The key functions of the company’s distributions process are
First is a global distribution network that facilitates and furnishes the furniture needs of the IKEA Company. Second is a large product volume. The IKEA Company is a high volume retailer. The total value of items that the business buys is more than 1,800 suppliers in 50 countries. It also operates 42 trading offices so that they can effectively manage their relationships with the vendors (Williams 201).
Third, the company operates minimal costs. One strategy that the company is using to minimize costs is the application of a do it yourself packaging initiative. In effect, most of the furniture is produced as portable pieces, making the customer the final assembler. Essentially, the company seeks to minimize space in both the stores and in the warehouse. In the stores, the products are made available to the customers, who are also the last link to the company’s supply chain.
Discussion
IKEA’s operational strategy involves a set of actions and decisions that dictate the objectives, the role and activities of the organization in support of the organizations’ business strategy. The operations strategies of the business relay and are dependent on the mission statement of the company that seeks to ensure high-quality products at an affordable price. Notably, the company’s business idea is based on the premise of simplicity. Thus, the company uses sophisticated designs in making the simplest pieces of furniture.
Thus, the elements of the company’s model revolve around attractive furniture, reasonably priced furniture at reasonable quality, and limited varieties that can be self-assembled as well as efficient designs for young families (IKEA Retailing Worldwide 2). In effect, the company seeks to maintain that they do not carry out expensive advertisements and that the catalog offers self-service (Williams 201). Consequently, these elements all contribute to the production of cheap priced furniture as they seek to collaborate with one another. Further, the company’s emphasis on certain quality standards implies that they only focus on a small number of suppliers for the supply of key products. Also, these key suppliers are minimal in number meaning that they can be monitored by the company adequately. The flat packaging idea ensures that the company can save storage space when keeping the furniture in stock.
Most furniture retailers are seeking to create competitive advantage owing to the overcrowded and competitive nature of the furniture industry. In effect, differentiation is a key factor that most of the companies in the furniture industry employ. In the case of IKEA, their sustainable competitive advantage is attained through an additional quality services offered to their customers at the stores. As it is, customers try to identify buyers with an ability to offer high value at minimal costs. Consequently, IKEA has learned of this strategy and implements it. As a means to provide added value and attract more customers, the company offers superior services compared to other competitors in the furniture industry (Harrison 68). One thing that the company representative does when meeting with a potential customer is to carry a catalog, measuring tape, note paper, and pens. This who’s the customer that they are crucial to the business and that the company is always ready for them. Further, being that the business has a minimal number of sales people, customers have the liberty to walk around in the stores and to shop for the products of their choice. Moreover, the company offers care to young toddlers as their parents walk around and shop for their desired furniture items.
One reason that IKEA has some stores located all over the world in its 16 constituents is because the company lacks a manufacturing facility. Lack of a manufacturing facility implies that the company uses subcontracted producers and manufacturer in every part of the world to supply the business’s key supplies. However, the research and development of all the products and furnishings are done are the company’s headquarters in Sweden. As a low cost is a core objective of the company’s operations, the company lets it customers to buy their products, as well as decide on how to assemble them.
Despite having the key operations processes of the company located at the company’s headquarters in Sweden, IKEA still faces some operational issues. First, it is facing customer problems with moist customers complaining of being frustrated while shopping at the stores. Ideally, most of the stores are located far away from the city causing most of the customers to communicate only to get to a crowded store, with poor product availability and long lead times. While the company has come up with some measures to help address these customer complaints and hiring assistants to help their customers at key points, this is still not enough as the number of clients that the store receives is overwhelming to the attendants too. However, operations management principles are applied in most of the stores for processes such as store management and organization to create and efficient store layout and facilitate, for instance, customer location of products. Also, the stylish designs facilitate flat packaging. The store attendants are also exposed to an effective job design so that they can contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of the store.
Recommendations
Overall, the operations management process of IKEA is highly functional. First, the company’s supply chain makes the products of IKEA associable to potential customers. However, the main issue that is affecting the company could be the inventory management process. From the results, it is impertinent that the company forecasts demand so that they do not send excess stocks and to minimize warehouse costs. However, the company could implore the use of the just-in-time inventory management system sets to ensure that they eliminate the problem of inventory management or stock gamble. The just-in-time inventory management technique is a stock keeping method that enables a company to maintain zero stock levels, as well as minimize stock keeping costs. The advantage of this method of inventory control is that eliminates waste in the production process ensures high-quality products and increases the satisfaction of the customers. In fact, this technique is applicable and in line with the mission of the company. Consequently, this strategy can be applied by the company to help with proper stock management, as well as eliminate waste in the supply chain. Further, the company could consider this as a way of increasing output and as a means of production scheduling.
Conclusion
The research has identified that the key operational processes of the company are product development, purchasing, distribution and retailing the final products to their customers. The manufacturing function is not listed as a key operational process to the company being that it is an outsourced function. Essentially, IKEA does not carry out manufacturing activities, so, it has outsourced the function to global suppliers all over the world, who are expected to deliver depending on the product specifications offered. The findings of the study suggest that the company has several store locations all over the world, with key offices to ensure a close relationship with its suppliers.
Despite the functional operational system managed by the company, there are key problems with meeting customer needs, the location of the stores and with inventory management. The customers of the company complain that the layout of the stores is not functional and that the service attendants are not enough. Further, the locations of the stores outside the urban areas mean that the customers have to commute long distance to get the products they need. These issues show that the inventory management processes are not effective. To ensure efficiency, especially during the distribution process, just-in-time inventory management could be implemented. This way, they can be able to avail the right products to the customers when they require them with zero storage costs. This will also help to solve the problem of poor forecasting leading to either under- stocking or over stocking tendencies.
Works Cited
“Business: The Secret of IKEA’s Success: Furniture Shops.” The Economist. 2011.
Harrison, Nicola. “Analysis: How IKEA Changed Furniture Retailing Forever.” Retail Week 2012. Web.
Hill, Charles, and Gareth Jones. Strategic Management Cases: An Integrated Approach. New York: Cengage Learning, 2012. Print.
Hultman, Jens, Susanne Hertz, Rhona Johnsen, and Thomas Johnsen. “Global Sourcing Development at IKEA–a Case Study.” Manuscript, Jönköping International Business School 2009. Web.
IKEA Retailing Worldwide. 2011 Facts & Figures. 2011. Web.
Williams, Chuck. Management. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning. 2008. Print.
