Intangible assets are not physical in nature. Intangible assets cannot be touched or felt by any physical means, but they add value to their owners’ businesses. Corporations are known to have a lot of wealth in intangible assets hence enabling them to supplement their revenue-generating activities. Examples of intangible assets are intellectual property, goodwill, brand recognition, etc.
Intangible assets valuation is done in scenarios where businesses want to merge or are in the process of acquisition. This is the time when managers want to know the actual value of their businesses to get a fair deal from their partners (Mellen and Evans 2010, p. 67). A case study on TUI travel PLC can show some of the asset valuation dynamics. TUI Travel PLC wanted to carry out brand valuation to address issues related to funding and management of its pension schemes. This means that the company was concerned about getting its real brand value so that it can use it as a bargaining tool to approach other companies for a possible merger. Companies need to know their total asset values before mergers so that they can plan on how to share capital when merging.
In fact, during mergers, some companies are required to pay their partners some amount to equalize their stake. Therefore, each company must present its case showing values of both tangible and intangible assets. For instance, on the 31st may 2011 merger, TUI expected one of its TUI UK to pay a given amount for using its brands. Money paid by this company was channeled towards its pension scheme which was the main aim of seeking a merger.
Partners of TUI in the merger are expected to enjoy collaterals provided to them by the Thomson and First choice brands. All revenues accumulating from business carried out by Thompson and First choice brands have to be deposited in the group’s account, but TUI will still enjoy the main role of brand control and management (Anson and Drews 2007, p. 87). In fact, TUI wanted to use its intangible assets to manage its pension liability. This is evident where revenue generated by companies using Thomson and First Choice brands was channeled to the management of pension schemes. There are various methods used by companies in valuation of intangible assets, and these include income valuation, market valuation and cost valuation.
The income valuation approach is commonly used to get the value of intangible assets. This is ideal because getting the real value of intangible assets gets tricky since they are attached to the business and some are inseparable. In this approach, economic income capitalization is used as the basis for valuation. This means that income forecast is done with the current income as the basis for predicting future income. This means that the current income brought to the TUI travel PLC Company by the asset in the subject is used to estimate its future value. The future economic income for TUI travel PLC’s Thomson and First Choice brands is derived from the expected use of the intangible asset. For instance, it is assumed that the intangible asset has to be used by TUI travel PLC for a given period of time, and future income is calculated (Mellen and Evans 2010, p. 67). In addition, income that might be generated by the same asset if rented to other companies is not ignored as it might help guide on the derivation of the future economic income. Economic income in this approach may be defined in various ways some of which are net income before tax, net income after tax and net operating income. For instance, TUI travel PLC should be ready to provide information regarding their financial statements to enable estimates based on their incomes. In addition, there are various ways of accomplishing the income capitalizing procedure and this company should decide on the most appropriate procedure based on their profitability.
When carrying out the valuation of intangible assets of an organization using the income valuation approach, discount rates are enhanced by various factors, which include risks in the environment. TUI Travel PLC should try and make use of all information regarding their business environments. This means that the company should be able to bring challenges they face to the economic environment. For instance, market risks should not be ignored because businesses are prone to such risks. In fact, risks in the business market may end up affecting the expected future income of intangible assets. For example, competition may be tough hence leading to depreciation on brand value or goodwill of an organization. TUI Travel PLC should identify possible threats from their competitors and use them in determining discount rates. Therefore, when forecasting the future economic income, such aspects must be considered. Valuation may be done either in direct capitalization or yield capitalization of income. In direct capitalization, intangible assets are expected to have income that changes at a constant rate. This means that the rate of change is assumed to be constant over a period of time. This change may be resulting in an increase or a decrease in the amount of income generated over the said period of time. In fact, this is the reason why there should be an allowance for a positive or a negative change in income in the valuation results. Depending on financial performance from TUI travel PLC’s financial statements managers should be able to choose the best capitalization method to use. On the other hand, yield capitalization is applied when there are expectations that the intangible asset may generate uneven incomes in a given period of time.
There is the cost approach that can be used in valuation of intangible assets. This method can be ideal in of valuation of assets which may be in the form of services such as the architectural drawings in computer software. This approach also may guide the valuation of assets that are intangible on the principle of substitution. TUI travel PLC should ensure that they have all information regarding their assets to guide in the determination of these costs. This means that the investor would be expected to pay a value that is not more than the amount that would be required to replace the asset to TUI travel PLC. In fact, some intangible assets can be replaced with other assets that can replace their subject with a substitute of functionality. This is to say that there can be another asset that can be used to serve the same purpose with the intangible asset in subject hence substituting it. This approach is profoundly concerned with the cost involved in developing the asset in subject.
This means that all costs involved in ensuring that the intangible asset acquires the said value are used in the valuation. For instance, a lot of costs may be incurred for a brand to be leading in the market. There are two main cost approaches that are used in the valuation of these assets and they are replacement cost and reproduction cost. Reproduction costs help in identifying the amount of cost that may be required to produce another asset of the same nature as the intangible asset in subject. Replacement cost helps in determining the costs that can be used to develop an asset with similar utility value. These costs should be determined as of the value on the valuation date, as opposed to historical expenditures. Since costs and expenditures are prone to changes due to market dynamics, the best market prices to consider are those at the valuation date. For instance, TUI travel PLC should consider factors expenditures that are relevant in their current environment at the time of valuation. They should ignore all expenditures they might have used in developing intangible assets.
Economic environments should not be ignored since they influence changes in costs in a great way. This means that valuation that follows cost approach should be able to consider all micro and macro-environmental factors that might have a direct influence on changes in costs. These should include internal factors that thrill in TUI travel PLC those that might have an influence on intangible assets. These include management policies and strategies aimed at improving their operations (Anson and Drews 2007, p. 87). This means that only costs that are necessary for relation to the environment on the valuation date should be considered for the valuation process. This shows that this valuation can be varied only if the expenditures used are up to date in the environment. The reason behind this argument is that only current costs given by TUI travel PLC should be used for the calculations. This is essential as real and current values will be shown from these calculations. In addition, in this approach one does not have to use all costs involved during the development of the intangible asset. Instead, only costs that are necessary to reproduce the asset or produce another asset with equal utility value have to be considered in the valuation process.
Finally, there is the market approach where transactions are analyzed to show how they compare with one another (Mellen and Evans 2010, p. 67). This may involve arrangements made when licensing and these can help one to understand the loyalty rates of TUI travel PLC. In fact, most intangible assets can be evaluated using this approach because the market determines their values. For instance, goodwill in any company is measured directly from the market. TUI travel PLC used this approach to carry out a valuation on its collateral assets which included goodwill and brand equity. TUI travel PLC has the leading Brands in the UK market, and this made it possible for them to acquire strong brand equity. These brands are Thomson and First Choice. In fact, the market approach aided this company to a logical value of its intangible assets since they carried out research in the market and got the real value on the ground (Anson and Drews 2007, p. 87). TUI travel PLC used information from its sales and transactions in evaluating its intangible assets. There was ease in comparability since the company relied on other players in the industry to find out the value of their intangible assets which are dependent on the market.
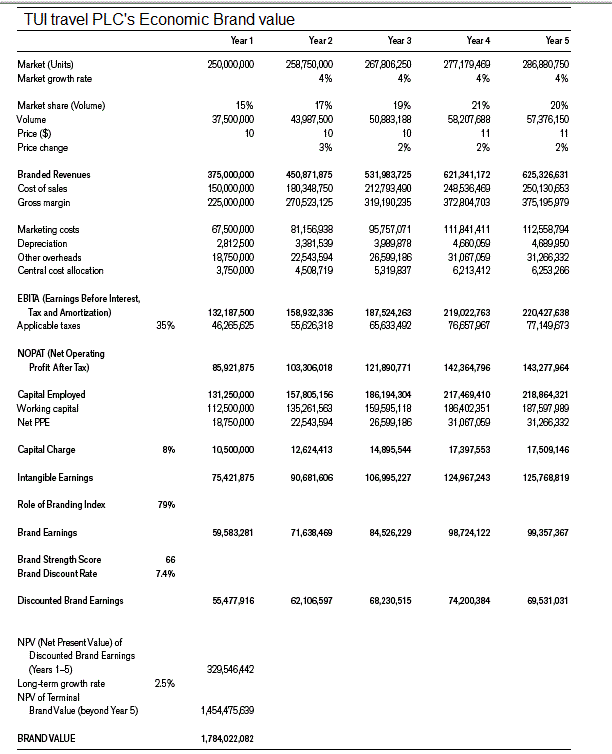
The table below shows how TUI travel PLC’s brand economic value is calculated.
References
Anson, W. & Drews, D. C. 2007. The Intangible Assets Handbook: Maximizing Value from Intangible Assets. American Bar Association, New York.
Mellen, C. M. & Evans. F. C. 2010. Valuation for M&A: Building Value in Private Companies. John Wiley & Sons, New York.

