Introduction
It is common practice for the human resources department of an organization to fill up vacant positions as and when vacancies arise. But hiring is only part of a long process so that the position may be filled up by someone capable of handling the job requirements. The process involves calling for applications, setting up a proper job description, screening the application, calling the screened applicants for interview, conducting the interview and making the final selection of the right candidates.
Finally, a call letter is sent to the candidate to see whether he or she is ready to accept the post. If so, the person is appointed and then begins another process required to make him/her ready for the job. “A job is a collection of tasks and responsibilities that an employee is responsible to conduct. A task is typically defined as a unit of work, that is, a set of activities needed to produce some result.” (McNamara, 2008).
A very important component of the interview process is the job specification, which is a statement containing the minimum requirement of educational qualification, experience and aptitude of the candidate. The job description contains the details of the job and focuses on the duties and responsibilities of that particular job.
Once the candidate is appointed the next step is to train him or her to be able to handle the specific job functions, familiarize with company policies and procedures and enlighten that person about compensation policies and packages. The training can be an on-the-job or off-the-job exercise. That means within the premises or outside, away from the plant or company. Employees who develop to meet or exceed the job requirements stand a chance to be promoted to a higher position with higher status and higher monetary benefits. This motivates the employees in the organization to perform better.
Retaining the employees is also important for an organization as the most significant problem that organizations face is a scarcity of skilled labor. For retaining to be effective, the employees should be satisfied with their job. The employers are satisfied if they find the right candidate who responds well to the training given by the company. The employee will be satisfied if he finds the compensation and the job itself attractive. Other factors related to job satisfaction are the organizational environment, the formal and informal structure and groups within the organization. As to the job itself, it should be clearly indicated as to what the responsibilities, tasks and level of authority the position carries.
For example, if the job specifies certain responsibilities and duties without indicating the corresponding authority, dissatisfaction with the job will be the result. The same situation will occur if the job description is not clearly given. For this purpose, organizations undertake the practice of conducting job evaluations. A job description is the backbone of job evaluation. The main aim of job evaluation is to see that the employee has understood his duties and responsibilities and to know whether his performance is equivalent to the expected level. If any shortfall performance in is found, it needs to be corrected and controlled.
The research question in this instance will be the importance of defining clear objectives/roles when creating a new position within an organization and arguing the need for a sound, well-constructed job description. The background of this paper will be the post of Health Information Coordinator at the Fond du Lac Indian Reservation. This thesis focuses on the importance of job descriptions. There are many important points discussed in this study about the relevance of the topic. The factors discussed in the literature review will be analyzed with the above-mentioned post in the organization at the end.
Literature review
In an organization, the starting point of any activity is to determine the main objective of the organization. This objective is the base for all the plans and programs prepared. Many subsystems are formed which integrate their work for the achievement of a common organizational goals. One subsystem is the human resources management function which deals with the function of staffing.
Staffing is the process of acquiring, developing and retaining people so that the right type of employees is available for the right positions and at right time in the organization. Human resource planning is the starting point of the staffing function. Forecasting labor needs for the future as well as the present is an important role of the HR department. It is done for all the subsystems or departments with the help of the concerned subsystem head. Each and every job in all departments is analyzed separately.
A job analysis is a process of collecting the relevant facts of a job to know the contents and characteristics needed of a person to perform the job. “A position description provides a clear understanding of the functions and responsibilities of the job, the skills required to perform those functions and the role of the position within the work unit and the organization as a whole.” (Guidelines for writing position descriptions, 2008). A job description provides the written description of the job title, tasks, duties and responsibilities in the job.
The importance of job description is:
- The job description clarifies the role of the job and explains what is expected from the incumbent while performing the job.
- It forms a basis for the performance evaluation of the supervisor.
- It is a formal communication of the work plan and feedback so that the weakness of the incumbent can be identified required training provided to set off the shortcomings.
- It is the framework to decide the required qualities of the candidate while hiring a new person.
- It provides the scope of the job to the candidates to decide whether the job is the right choice for them.
- Database containing written job descriptions will provide guidelines to the managers to take decisions related to the job.
- It forms the backbone for an effective system of job evaluation in the organization.

Organizational behavior
Organizations consist of people and hence are considered to be dynamic systems in nature. Therefore, each organization will have its own culture and style of functioning both of which are part of the organizational behavior. It is up to the employees to adjust or adapt themselves to the organizational behavior. “Organizational behavior is the study and application of knowledge about how people, individuals, and groups act in organizations.” (Organizational behavior: Introduction, 2008). An organization is a system, that interacts with people, groups, the organization itself and the external social system. All these factors will ultimately contribute to shaping its organizational behavior.
Organizational culture can be referred to as the personality of the organization. “Culture is comprised of the assumptions, values, norms and tangible signs of organization members and their behaviors.” (McNamara, What is culture? 2008). In other words, it is the culture followed by all the members within the organization. Each member has his own culture imbibed from the society and environment he belongs to. But beyond that, the organization in which he joins has a culture of its own that he has to follow or at the least adjust to.
Any mismatch of his culture with organizational culture can create problems for the organization as well as the individual himself. The importance of the organizational culture becomes apparent when there is a change in the organizational environment. Organizational change is the alteration of the work environment in an organization. It implies any change in the technology, structural arrangement, job designs and people and this essentially necessitates a new equilibrium. In a competitive environment, organizational change becomes a continuous process. Some changes are minor and are easily absorbed by the organization, but some are major changes that need a lot of effort to be effectively incorporated into the existing system.
Changes can occur because of external factors and internal factors. External factors include technological changes, changes in the marketing condition, social changes as well as political and legal changes. Internal factors are brought about by a change in the managerial position and deficiency in the existing organization, mergers and acquisitions, etc. A major change requires careful planning because it involves a transformation of all aspects of the organization which is closely interrelated, like technology, task, structure and people.
Any planned change needs change agents. Change agents are the persons who initiate change in the organization. The objective of the change agent is to bring desired changes to the organization. The organization can seek the help of external consultants or experts to bring the desired change to the organization. It can also implement changes through internal change agents. They are usually the CEO, departmental heads and other managers who act as a change advisor. The managers are known as change agents because they are the persons who generally implement the change. Managers usually understand organizational and individual behavior and are better equipped to manage and oversee the required change.
Whenever there is a change, resistance to change will exist. To overcome resistance, employees should be educated or provided extensive information and knowledge about the need to change and about the change itself. Participation and involvement of all the employees in the change on a regular basis or for a particular change program is necessary. Gaining employees’ commitment is another step to overcome resistance. This will bring about an agreement between the change agent and those who resist the change to take an active part in the actual mechanics of the change. Leadership also plays an important part in bringing down the resistance to change.
Since a manager cannot always use his formal authority to get support for the change, he sometimes relies on his personal skills, qualities and other characteristic traits to influence people for accepting the change. Motivation is always needed for an employee to increase efficiency in performance. It can be provided through words or through monetary benefits like incentives, rewards, etc.
Leadership
Leadership is the process of influencing and supporting others to work willingly and enthusiastically for achieving a particular goal in an organization and is a continuous process. It can be said that a leader in the molding machine and employees are the molded products. A leader can make his team effective through his own skill and personal ability. Effective leadership can motivate the employees to work willingly and enthusiastically to achieve organizational goals. Different leaders have varied leadership styles depending on their personality and the situation at hand.
The prominent leadership styles are autocratic, bureaucratic, charismatic, democratic/participative, laissez-faire, people-oriented/relations-oriented, servant, task-oriented, transactional and transformational leadership. (Understanding leadership styles: Leader styles, 2008). It is common that many leaders will not just stick to one style, but it will be predominantly dominated by one of the styles mentioned above. Leadership is essential in retaining and motivating staff. A good leader will also see to it that the job descriptions are clearly laid out for employees to understand their roles.
Role and objectives
This is one of the key areas of this paper. It is essential that the employee needs to know what role he will have to play. This should be clearly defined in the job description. Unless this is known, the employee will be confused about his position in the organization. He may leave out some of his responsibilities and may also duplicate someone else’s work. He might also step out of his line of authority. All the above may be done unintentionally. If such a situation continues, the employee will become discouraged and ultimately quit the organization. If roles are not defined across the organization, there will be high labor turnover which may even result in the collapse of the organization.
Job Satisfaction
This is also an important factor that can affect the performance of an employee. “Job satisfaction is in regard to one’s feelings or state-of-mind regarding the nature of their work.” (Job satisfaction, 2008). A lot of factors affect an employee’s level of job satisfaction. The nature of the job itself would be the most important factor in this context. Other factors include pay and other benefits, the leadership, the management style, organizational culture, race and ethnic mindset of the employee, his personal and social upbringing and culture, working conditions and atmosphere, the existence of formal and informal groups, etc.
In this case, where, in the absence of a clear-cut role or objective, one cannot expect job satisfaction. How can this factor be there if the employee is not sure what his job is in the first place? Instead of job satisfaction, there would be confusion and uncertainty. Lack of job satisfaction can also cause poor quality of work, absenteeism and high labor turnover.
Employee turnover and retention
Any organization will require a stable number of employees for its smooth functioning. Usually, there will be industry-level statistics with which the organization can compare. If the turnover is higher than the industry average, there is something wrong with the HRD department in the organization. It is evident that employees are not happy working with the organization. The organization needs to take immediate steps to see that this trend is reversed if it is on par with industry levels the HRD department should be on its guard and should see that it is above or at least remains at par with industry levels. If it is above the industry level, then it indicates that the HRD department and the company as a whole are doing well.
Statistics in the United States show the average overall employee turnover to be around 23%. The highest turnover is for the hospitality industry which is as high as 56%. (Findings: Retention and management metrics, 2006). Turnover in the government sector is very low as the following chart indicates. The figures are for the year 2006.
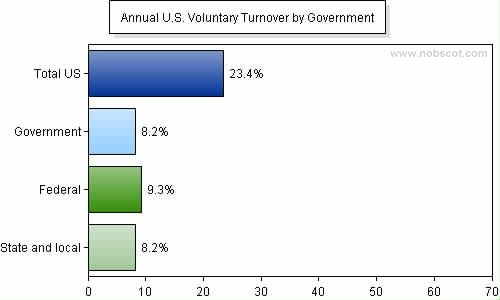
A turnover rate of more than 10% is unusual in government and public sector jobs. This could be because of the security that a government job offers even if compensation levels and other factors may not be on par with the private sector. There is a simple method by which employee turnover and retention can be measured, which is given below.
Employee turnover
- Total number of leavers over period x 100.
- Average total number employed over a period.
Employee retention
- Number of leavers with more than one year’s service x 100.
- Total number of staff in post one year ago.
Both the above formulae are taken from the website mentioned below. High employee turnover will be costly for an organization due to the following reasons. They are the administration of the resignation, recruitment costs, selection costs, training costs, etc. (Costing employee turnover: Employee turnover and retention, 2008).
The reasons why an employee leaves an organization include lack of job satisfaction, better career prospects elsewhere, lack of job advancement in the present organization, lack of clarity in job role, lack of security, etc. The above-mentioned article considers job satisfaction as a key factor in employee retention. A very satisfied employee will remain in the same organization even if he is offered another job with a higher salary and benefits.
Organizational development
Any organization that remains static runs the risk of slowly failing to catch up with the rest of the industry. Organizational development is a process whereby this risk can be eliminated. This requires “expertise, encompassing the ability to conduct overviews, interviews, analyses and any other assessments required to determine the overall structure and function of an organization, including all the inter-dependent parts and how they function together.” (Organizational development: About coaching, 2003).
Such an analysis will help the organization to identify many of the problems and challenges existing within their system. It can also help to understand whether the job descriptions are not adequate. A change agent will be required if changes to be made are extensive. The role of a change agent has been mentioned in earlier sections.
Organizational performance
There is no need to elaborate on the fact that the performance of an organization is critical to its success. In other words, if an organization fails to perform the activities that it has set out to do, it will result in not achieve its goals, targets and vision. There are many factors that will determine the performance of an organization. Almost all the issues mentioned below affect organizational performance in one way or the other.
According to a journal article titled ‘Communities of practice and organizational performance’, organizational performance can be improved by two factors namely community of practice and social capital. “Further, we have used the concept of social capital to highlight the mechanisms by which communities deliver this value.” (Lesser & Storck, 2001).
In this article, the authors argue that social capital can in fact lead to a formation of communities of capital and both are beneficial in improving the performance of organizations. “Communities of practice are groups of people who share a concern or a passion for something they do and learn how to do it better as they interact regularly.” (Wenger, 2004). A community of practice, according to the author is not a club or a committee. It is more of an informal organization where members have a shared vision and the capabilities to find ways in achieving the vision. The word practice in the term indicates that action apart from sharing and acquiring information forms an integral part of their work. In other words, the members are practitioners in their field of expertise.
The author gives a few examples of this community. A group of nurses may regularly get together and share information. With this information, they can try a build up a better practice in serving patients in the hospital. In the automotive sector, engineers may have brainstorming sessions to improve the performance of windshield wipers. These are just a couple of examples out of hundreds of instances where such a community will be useful to enhance performance. In organizations, such communities are valuable in promoting organizational learning and improving organizational performance. The concept of social capital is also quite similar. “Its central thesis can be summed up in two words: relationships matter.” (Field, 2003).
This small definition indicates that social capital is based more on relationships rather than on shared visions. Another difference is that there will be no informal group meetings like in the case of the community of practice. An example given by the author is an instance where an employee is in need of some advice or assistance. He can take the formal organizational course in getting this advice or assistance. But he would prefer to bypass this and find a friend or colleague who can help him. In other words, networking is the way in which social capital is formed. As mentioned earlier, the existence of such groups will go a long way in improving organizational performance. The matter that a proper job description does not exist in a particular case can easily be identified with the help of such groups.
Health Information Coordinator at the Fond du Lac Indian Reservation
The writer of this paper has had experience in working for the Fond du Lac Indian Reservation as a health information coordinator. In fact, it is the first job held by the writer. He has held a variety of posts including military service since then and has been rated highly by his various employers. Even with his limited experience, the fact that the job description was not clear became evident after a period of time.
This was the reason for leaving the post. This report is mainly intended for the Reservation Business Committee so that they may incorporate relevant points into their policies. It is also very useful for organizations where high labor turnover is a problem. This turnover need not be related to poor job description alone and is useful in dealing with other factors also. An analysis with reference to the main factors mentioned above will be done now.
The writer has seen that this post has an unusually high turnover ratio. Three coordinators have come and gone over the past five years. The Health Informatics Coordinator could serve as a wealth of information for the agency if the management hierarchy, position objectives, and organizational objectives for the position were clearly defined. This paper has given ample importance to a proper job description.
It will clearly require the candidate to focus on what exactly he has to do. It should be in such a way as to get the maximum benefit from him to the organization and the community he serves. Only a clear description will enable higher-ups to evaluate his performance. Any shortcomings can be pointed out and corrected only if this is done. The knowledge and information provided by the coordinator will help in making policy decisions at the reservation.
This type of job is not suited to everyone. A sense of service and the need to help others is necessary here. A detailed job description will also help to eliminate the wrong candidate from applying to the post in the first place. A review of the job description will be enough for a candidate to decide whether a particular job is suitable for him or not. With regard to organizational culture, reservations are occupied by a community with a very different culture. Close contact with them is essential here. The organization’s culture itself will be affected by this difference. An applicant for a particular post should be able to understand and work within this culture. Providing proper job descriptions will involve an organizational change to a certain extent.
The description may result in other employees being affected as well. It may happen that they may find some of the responsibilities and rights being taken off. They may also get additional responsibilities. Proper management of the change is necessary here. Leadership within the organization is also an important factor in bringing down employee turnover. The coordinator holds a very important and useful post for the parties concerned. Proper leadership will definitely help in exploiting the usefulness. The role and objectives would already have been addressed if a correct job description is created. All necessary information will already exist in the job description. Job satisfaction is incumbent on many factors including the type and nature of the job.
A service-minded person will immediately be willing to try out the post. Others may not even apply thereby eliminating wrong candidates. A wrong candidate may find himself being dissatisfied after a period of time had been accepted the post (without understanding its nature). Ambiguity regarding role and duties will also lead to job dissatisfaction. All these factors, if rectified, will definitely bring down the labor turnover and increase retention. Three replacements in five years indicate a higher than average turnover (when compared with the industry average). Organizational development will definitely be useful for any employee who is willing to accept change. A system of community practice could be developed within the organization.
It can include employees, managers and representatives of the Indians in the reservation. It can also include service-minded people from the society (outside of the reservation) and other political and social leaders. Social capital is bound to exist already. It is the job of the organization to identify them and put them to good use. This will also help in identifying shortfalls and defects in the organization.
Counter argument
A good employee and proper leadership will eliminate the need or overcome the defects of the poor job descriptions. The employee with the help of the management and co-workers can effectively work out his job requirements. In fact, in some cases, this is more beneficial because employees can multi-task in case of a vacancy or when a worker is absent. Work within the organization will not suffer due to these problems.
Conclusion
A comprehensive report on the drawbacks of the poor or improper job description has been given here. Only in rare instances, the lack of a proper job description will result in a problem-free situation. This can be proved in the case of the reservation job presented in the case study. Many other factors relevant to this issue have also been included. In addition, certain factors that may help in building a strong and efficient organization have also been included.
This will help in eliminating the above-mentioned problem. It will also bring down the turnover rates for all the posts in the organization including that of the coordinator. It is hoped that this report has been able to put ample emphasis on the importance of a proper job description and also in improving the productivity and performance of organizations. This report will be useful in addressing the above matter for both private and public sector organizations.
References
McNamara, Carter. (2008). Employee job descriptions. Free Management Library. Web.
Guidelines for writing position descriptions. (2008). RMIT University. Web.
You need job descriptions for the following reasons: Why job descriptions. (2003). Absolute HR Solutions. Web.
Organizational behavior: Introduction. (2008). Baclubindia: Interactive Platform for Management Professionals. Web.
McNamara, Carter. (2008). What is culture? Organizational culture. Free Management Library. Web.
Understanding leadership styles: Leader styles. (2008). Mind Tools. Web.
Job satisfaction. (2008). Free Management Library. Web.
Findings: Retention and management metrics. (2006). Nobscot Corporation. Web.
Annual U.S voluntary turnover by government. Nobscot. Web.
Costing employee turnover: Employee turnover and retention. (2008). CIPD. Web.
Organizational development: About coaching. (2003). InterLink. Web.
Lesser, E. L., and Storck, J. (2001). Conclusion: Knowledge management. IBM Systems Journal. 40(4). Web.
Wenger, Etienne. (2004). What are communities of practice? communities of practice: A brief introduction. Communities of Practice. Web.
Field, John. (2003). Introduction: What is social capital and why does it matter?. Social Capital. Routledge. P.1. Web.
