Introduction
Leopard Tools is a German company primarily focusing on the manufacturing of hand tools for both professional and amateur markets. Analyzing the existing strategies of the business group, it has become evident that Leopard Tools is in urgent need of a change of management policies. The current report provides data about the present state of manufacturing and supply chain methods implemented in the company, proposes alternative strategies for the business to be competitive in the industry, and compares the suggested approaches.
Background Data
The first section of the paper is devoted to the assessment of the existing manufacturing policies and marketing strategies within Leopard Tools and addresses the vulnerabilities of the framework implemented in the business group. The primary focus of the manufacturing policy of the company is the quality of the product, and Leopard Tools has been known as a dependable national supplier of hand tools in the traditional market for a hundred years. According to Liu et al. (2017), domestic production might be effective only in the case of high-technology advancements implemented in the framework. However, Leopard Tools has a few severe disadvantages concerning the manufacturing process, such as poor production capability, the deterioration of the tools, lack of a designated process flow, and overall obsolescence of the management policy.
Secondly, the supply chain management system of the company does not meet the modern requirements of the industry. According to Christopher (2016), the fitting framework alongside a proper utilization of logistics might grant a competitive advantage in the market. The following chart demonstrates the current supply chain management system and its flaws:
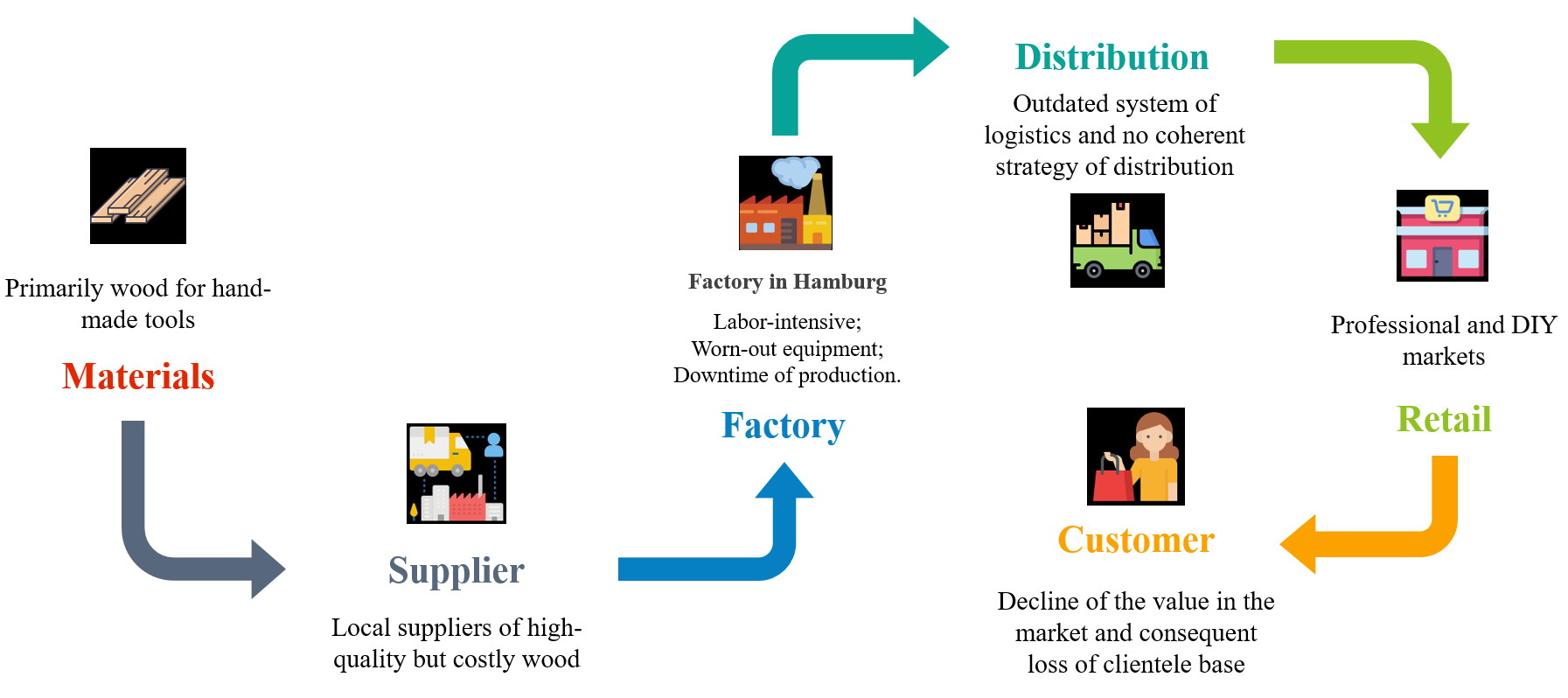
Furthermore, concerning the manufacturing situation of the company, the following issues have been identified:
- An excessive amount of components for manufacturing while most of them are specific to one particular product;
- Lack of comprehensive design maps and drawings for production modeling;
- The variety of products is redundant and leads to the unprofitable distribution of the items;
- The batch volumes are modest and reduce the production capability.
Analyzing the background of the company, it is evident that Leopard Tools needs to change its manufacturing strategies to be competitive in the market.
Alternative Strategies
The current report offers two major alternative strategies and several recommendations on the improvement of the overall performance of the company. Both frameworks revolve around the concept of supply chains; therefore, it is vital to elaborate on it first. According to Slack and Brandon-Jones (2018), supply chain management covers all the stages of production and service, and it has six primary objectives: quality, speed, dependability, flexibility, cost, and sustainability. The first alternative strategy concerns the shift from the present supply chain management to the global one. The current trends show a continual increase in the globalization of the market and the business groups have to adapt to survive the competition (Tien, Anh, & Thuc, 2019). Therefore, according to the first alternative policy, Leopard Tools should adopt the global supply chain management system and look for opportunities on the international level.
The second strategy takes the ideals and principles of Leopard Tools into account and revolves around a sustainable supply chain management system. According to Koberg and Longoni (2018), the sustainability component of the framework is represented by accounting for environmental and social principles within the company. To meet the contemporary requirements of the market, the business group should be competent in the three foundations of sustainability: economic, environmental, and multi-stakeholder chains (Barbosa-Povoa, Silva, & Carvalho, 2017). As a result, customers might take a greater interest in the production of the business group (Bastas & Liyanage, 2018). Therefore, Leopard Tools might significantly improve its position in the market by following the rules of sustainability and attracting new customers.
No matter which of the mentioned above frameworks the company adopts, there are several adjustments that need to be made for Leopard Tools to be competitive in the market again. First of all, the business group needs to implement better inventory and quality management. The former covers the amount and cost of the equipment, the available physical space for production, returns of the defective goods, and other matters concerning the tools and materials (Singh & Verma, 2018). The findings also show that quality management and developed infrastructure highly affect the business performance of the company (Patyal & Koilakuntla, 2017). Overall, the executives of Leopard Tools need to conduct a thorough examination of all the stages of the manufacturing process, analyze the results, and act correspondingly.
Comparison of the Frameworks
Comparing the existing policy with the global supply chain management approach, the two primary differences emerge – cost and quality. The alternative framework evidently excels at the financial parameter due to effective logistics; however, global supply chain management comes with the associated risks. In the present circumstances, it is impossible to ignore the potential dangers of isolation due to unexpected circumstances. For instance, Guan et al. (2020), provide the following chart of the pandemic consequences:
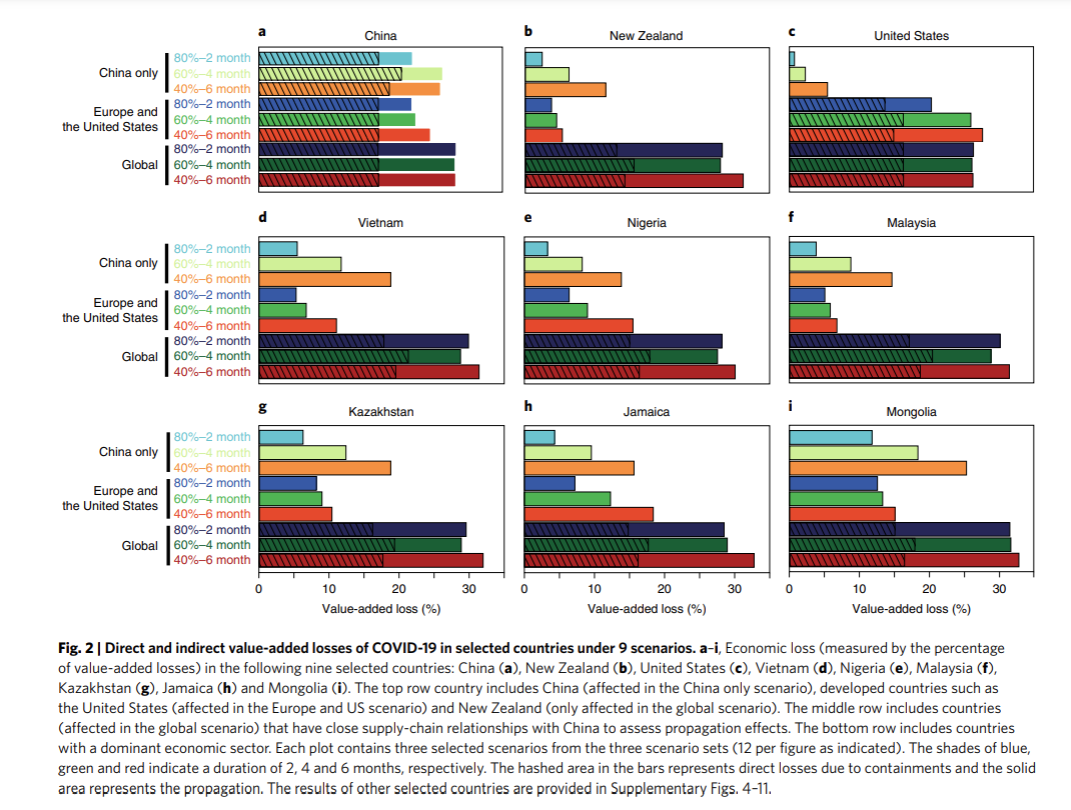
It is evident that the global supply chain management would fall short compared to domestic manufacturing strategies during such periods. Furthermore, this framework is generally associated with demand-side risks that might deteriorate the performance of the company (Kwak, Seo & Mason, 2018). Overall, compared to the current policy of Leopard Tools, the global approach has several advantages, but it is crucial to assess the risks as well.
The second strategy offers an approach with emphasis on the quality and environmental safety of the product. The focus of this framework is the sustainability of the manufacturing and logistics processes implying the improvement of quality. The current policy aims to create a profound clientele base that appreciates high-quality products and is willing to spend more expenses for them. The risk is, however, that this framework might not pay off due to the increased competition in the market. Furthermore, the sustainability efforts might pose an additional financial burden on the company (Gouda & Saranga, 2018). Ultimately, this approach is associated with more potential risks than the global supply chain framework but follows the primary principles of the business group.
Conclusion
Summing up, the current report describes the present state of Leopard Tools as a business group, offers two alternative strategies mentioning both pros and cons of the approaches, and proposes several general recommendations on the improvement of the framework implemented by the company. Leopard Tools should focus on one of the strategies depending on the general direction the executives want to follow. Nevertheless, it is essential that the company does shift its policy from the existing one since the present course might lead Leopard Tools to bankruptcy.
References
Barbosa-Povoa, A. P., Silva, C., & Carvalho, A. (2017). Opportunities and challenges in the sustainable supply chain: An operations research perspective. European Journal of Operational Research, 268(2), 399-431.
Bastas, A. & Liyanage, K. (2018). Sustainable supply chain quality management: A systematic review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 181, 726-744.
Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics and supply chain management (5th edition). Pearson Education Limited.
Gouda, S. K., & Saranga, H. (2018). Sustainable supply chains for supply chain sustainability: Impact of sustainability efforts on supply chain risk. International Journal of Production Research, 56(17), 5820-5835.
Guan, et al. (2020). Global supply-chain effects of COVID-19 control measures. Nature Human Behaviour, 4, 577-587.
Koberg, E. & Longoni, A. (2018). A systematic review of sustainable supply chain management in global supply chains. Journal of Cleaner Production, 207, 1084-1098.
Kwak, D. –W., Seo, Y. –J. & Mason, R. (2018). Investigating the relationship between supply chain innovation, risk management capabilities and competitive advantage in global supply chains. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 38(1), 2-21.
Liu, F., Ding, Y., Gao, J., & Gong, P. (2017). Effects of cost factors on national manufacturing based on global perspectives. Economies, 5(45), 1-16.
Patyal, V. S. & Koilakuntla, M. (2017). The impact of quality management practices on performance: An empirical study. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 24(2), 511-535.
Singh, D. & Verma, A. (2018). Inventory management in the supply chain. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(2), 3867-3872.
Slack, N. & Brandon-Jones, A. (2018). Operations and process management: Principles and practice for strategic impact (5th edition). Pearson Education Limited.
Tien, N. H., Anh, D. B. H., & Thuc, T. D. (2019). Global supply chain and logistics management. Academic Publications.
