Introduction
In any business operations globally, certain factors have to be considered in ensuring smooth operations of the business venture. In addition to using and implementing the latest management methods as well as working at the leading edge of technology, as the business grows and expands to spread within or outside the country, there has to be movement of materials, finished goods and other factors among the various networked subsidiaries of the business. Transporting the finished products to the market would also need proper and systematic planning as well as strategic decisions that would result into reduced costs. The term logistic management therefore gains much meaning in such a case.
Gourdin (2006, 2) explained logistic management to be the systematic management of various involved in moving goods and services from their point of production to the consumers, at the right price and conditions. According to the definition, logistics has been portrayed to have a broader meaning than just the context of movement or transportation of goods and services. Therefore, as Gourding further explained, the issues of logistics have to move beyond the transport factors to consider other important factors such as the timing, quantity, location costs, as well as the supporting services. This therefore as Gouding further explained expounds the definition of logistics from an aspect in transportation to be the process of meeting the consumer’s needs through provision of the benefits (goods and services) to the right consumers, in the right quantity and condition.
Factors that come out in the above definition include; the provision of the right benefits to the right consumers, at the right time, condition, as per the description of the consumer. The place aspects has also been brought out since customers require that the goods be at a specific location at the specific time as explained above, and at a price that the buyer would be willing to pay for the goods. Therefore as United Nations (2010, 10) explained, the quality of trade logistics has the largest bearing in the performance of any company internationally and locally. Poor logistic factors would lead to a poor market for the company’s benefits and this would erode its claim in the market domination. As above explanation portrays, the logistic management aspect covers not only the transportation of the products, but would cover the entire production process up to the provision of the finished products to the customers. Logistic management might be summarized as the flow chart below portrays.
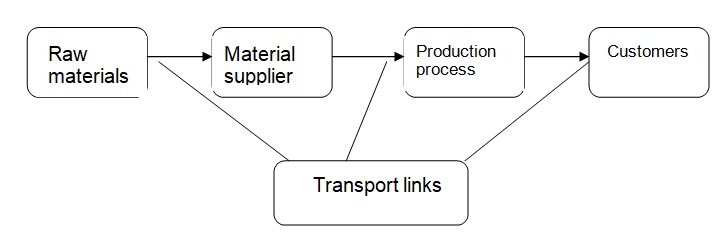
The cost aspects in the process might be considered to be the most important considerations in the process. As the above definition indicates, the customer has to receive the benefits at the right time, condition, and at the price that the customer would be willing to pay in return in the exchange process. The process having involved many aspects and processes therefore would be a likelihood of the prices to increasing due to the increased handling activities in the process. The logistic management would therefore to a large extent be concerned with minimizing costs in the distribution process, an aspect that dictates to a large extent the profitability of the company in the whole logistic process. As would be explained later Momani (2010, 275) stressed on the factors that might amount to hindrances in obtaining a smooth logistics flow in the production process. These are the natural and man made disasters, human errors and technologies. These factors have a direct effect on the cost reduction process in logistic management as would be discussed later.
Logistics v. supply chain management
In most cases, many people have not been able to differentiate between logistics and supply chain management. There is a blurred line between the two business operations, and inmost cases, there is an overlap between the functions of logistics and supply chain management. As earlier explained, logistics has been defined as the systematic management of the process that involve production and delivery of the benefits of production to the final consumer at the right price, and condition. Kouvelis and Nierderhoff (2007,4) offered a description in the supply chain management that would enable the deduction of the real meaning of supply chain management. According to Kouvelis and Nierderhoff, supply chain management would amount to the overall coordination, planning and management in all activities that would be involved in procurement and sourcing, conversion and all other logistic activities.
Generally, As Kouvelis and Nierderhoff (2007,4) explained, supply chain management might be taken to be the overall integration of the demand and supply management, that would cover within the specific company as well as across other companies, with whom the company deals with. Supply chain management would be considered as the integrating function whose responsibilities would be to link major business functions and process within and across companies so as to achieve a very effectively performing and cohesive structure the interrelationship. Logistic management is therefore a process that would be considered to be part of the supply chain management. In this article, supply chain management would be taken to cover a broader area that would cover the goods procurement and sourcing, conversion in the production process as well s other logistic management activities that would include marketing sales , information technology as well as manufacturing.
Logistic management in transportation
The hearing aids have been described as to have their place of origin form China, a highly growing economy while the market would be mostly in the North American countries where the market has been defined as being very lucrative, Australia, and North Europe. On the other hand the sales president is situated in Europe. One factor that is evident is that, the network in marketing and making the hearing aids is very extensive and requires a sophisticated management network so as to accomplish a well integrated supply chain management and logistic management. As Manage (2010, 83) explained, strategic management requires that the management staff involved as well as other people who are concerned in the logistic process be of commendable knowledge as well as having the necessary skills that would lead to an effective process.
It requires an effective team that would be able to anticipate risks, delays as well as the market dynamics and carrying out effective strategies that would be inline with the market demands and dynamics. Transportation of the hearing aids would require that, the products be transported to the market at the right time and condition as explained above. As Gourdin (2006, 4) explained, value creation to the customers amounts to the largest competitive advantage that a company would have over its competitors. Companies therefore as Qingjiang (2003, 139) explained, companies in the current global market compete not on technologies but on the effectiveness of chain supply chain management process, which includes logistic management.
One of the factors that have a direct bearing on the logistics in transport mostly in Asian countries, china included is the port logistic problems. As United Nations (2010, 10) many countries in Asia have logistical problems which involve the port congestion and dealy of goods in transportation. The higher volume of goods in export and imports in the ports has in sometimes resulted into delays, which have slowed down the logistics effectiveness in reaching raw materials of the factory as well as getting the finished products to the market as earlier explained. Zsidisin and Wagner (2010), explained that delay of products in the transportation process might amount to a risk in the production process, since it would affect the customer delivery programs, increase costs in transportation as well as warehousing costs. The increase of these costs would lead to an increase in the production cost in general, since the company would be expected to incur the costs incurred due to delay. This might in turn result to an increase in the costs passed to consumers, or the company might absorb the costs leading to reduced profitability. This would call for a better logistic and supply chain management program, which would pout into considerations the delay expected in the transportation process. Wagner and Zsidin (2010) explained that, one aspect of the supply chain management would be to determine how the company in the production of the hearing aids and the subsequent provision to customers would become resilient to the disruptions in the supply chain management.
To reduce the costs above, the transportation program has to be designed in advance enough to necessitate the proper timing in delivery of the hearing aids to the markets as well as receiving the necessary materials in the production process. This would call for the implementation of technologies in material acquisition, production process as well as the transportation of the finished products to the market. Technologies such as JIT would enhance the logistic management to be achieved in the process. In production activities, any organization is aimed at maximizing profits while at the same time minimizing the costs of production.
It therefore follows that, companies operating at the front line edge of the current technologies have to install all measures to ensue that costs have been reduced to the optimum level. This is because, one of the objectives in any company is to grow in size in operations and infrastructure, the necessary tools to ensure the same would be very important in such a case. This was the reason behind the Just In Time production. The JIT strategy ensures that the product is right in the expected place in the line of production. According to Gourdin (2006), JIT is a value adding strategy in the production process where the goods are expected to be at the right places when required. It means that the supplier would deliver in time the raw materials, the production process takes place as planned, and the customer gets the goods on time. At the end, the customer is satisfied and the company has a better competitive advantage in the market which is in accordance with the objectives of the company.
On the other hand as Gourdin (2006) explained, the Statistical Process control is the use of statistical methods to guide operations in the work place. It requires use of graphics to explain the processes or schematic representation of any process in production. By using the SPC, the management is able to guide the workers in all the expected operations thereby increasing the efficiency in production. They are very effective where systematic production process is involved in that, by guiding the employees, there is a lot of time saved in which the employee could have stop producing to inquire on a specific issue. It is therefore a value adding strategy. This when implemented would lead to a better logistic management in the delivery of the hearing aids to the consumers in the Markets as explained.
Warehousing costs would also be reduced using the above technology. When materials get to the company on time, the process of production would proceed on time and hence there would enough time to transport the goods considering the possible risks, due to delay until delivery is achieved to the consumers in all the markets.
Inbound logistics
Svenson (2002, 112) explained inbound logistics as the systematic process involved in the storage and distribution of incoming materials and goods for use in the company. The processes involved in inbound logistics would include sourcing of the materials through placing orders and expediting the material delivery system, through the suppliers and receiving the materials through transportation. According to the Svensson, inbound logistics are more dependent on the external factors mostly the supplier being the main party that makes the company vulnerable to disturbances in the production process. The supplier when not well selected might result into added costs in the production process.
To reduce the overall costs in the inbound logistics as Svensson (2002, 112) explained, the supplier has to deliver the required contents of materials at the required time and in the required quantity. Gourding (2006, 5) explained that the effectiveness of the supplier to a large extent has bearing on the performance of the company in enhancing its production process as well as meeting the required timelines in the production process. The hearing aids would be required to be made in the factory in Guangzhou China in the right time to avoid delays in getting to the market. The suppliers required to serve the company with these materials should be therefore vetted to ensure high compliance to the company’s program. The entire supply chain management would be to a large extent be influenced by the effectiveness of the supplier. To reduce costs, the company has to accept only the materials that have been inspected to be of high quality and only those ordered by the company. Poor quality materials would lead to poor quality hearing aids with cases of in returns from the customers. This would be an added cost to the company. Quality has therefore to be ensured as Gourdin (2002, 5) explained.
Documentation as would be explained later has been explained to be one of the vital requirements in inbound logistics. Documentations enable the proper control of the production process and proper movement of the materials as well as completed hearing aids to the different markets. It would be required in the general planning process where the costs in the whole process would be calculated for further action in cost reduction initiatives such as comparing the materials to the final products as well as in process control while producing the hearing aids. As Momani (2010, 275), the use of the materials supplied according to the budget constrains, diversifying the sources of the materials as well as keeping of well updated inventories would ensure a smooth and uninterrupted logistic management in the production process. Manage (2010, 83) further explained the importance of maintaining high caliber of suppliers in the process as well as ensuring delivery of high quality materials in reducing the overall costs in the whole logistic management and to a large extent the supply chain management process.
Outbound logistics
Leung and Cheung (2007, 4) explained the requirements that a company has to meet in attaining globalization in business operations. According to Leung and Cheung, companies geared at competition in a global scale would require implementing strategies that would be aimed at reducing costs, while at the same time implementing high levels of technology, which has been described as the best strategy towards cost reduction in the production process. The outbound logistics therefore play a vital role in this function. Svenson (2002,113) explained outbound logistics to be the movement of the producing benefits which would entail; transportation, storage and the distribution process of the hearing aids to the final consumers. The hearing aids being made in China, the outbound logistics require to be systematically implemented to enable timely delivery at the best process possible to the customers. As Leung and Cheung (2007, 4) explained, competition to large extent between the global leaders plays its significant role in the way the products are delivered to customers , as pertaining the final quality, cost and the timing. The figure below summarizes the process that would be expected in the outbound logistic operations.
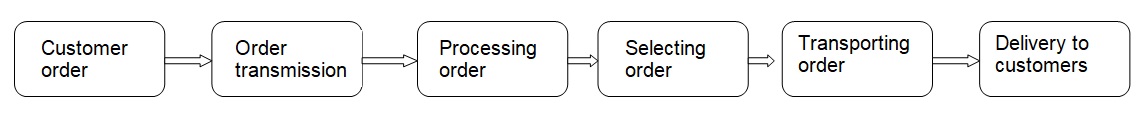
Manage (2010, 84) explained that to large extent, the above processes as involved in outbound logistic would result to timely customer delivery as well as effective management in the process of demand and supply. International logistics as involving outbound logistics might be considered to be more complex and involving than the above flow chart would portray. Wood (2002, 5) explained that international logistic management in the delivery of the hearing aids to the different markets as explained above would be more involving due to the process of shipment. Wood further noted that, there has to be a well drawn balance between the transportation costs, as well as inventory cost. As Busch and Tobin (2010, 8) explained, the high cost involved in international business operations requires complex strategies to reduce the overall cost in the process.
In addition to the cost of transportation, the documentation process in the outbound process to the above markets would also be expected to be complex. To strike a balance between inventory cost and transportation costs, it would be required that , large volumes of the hearing aids be shipped at any particular time, and as earlier explained process explained where delivery timely delivery has to be ensured at the right time to customers. Shipping large amounts to North America, Europe and Australia would require effective warehousing facilities that would be required to hold the hearing aids awaiting customer orders from those regions. The bulk transportation would largely reduce the overall transport compared to cost per unit, and the documentation process would be made much simpler and cheaper, instead of processing documentations on small volumes. These factors when observed as Busch and Tobin (2010, 8).
The above process in outbound logistics would require a well structured and technologically viable communication and record handling method by management. This as earlier explained would prevent the problems that result from poor logistic management from many managers. Momani (2010, 275) explained the importance of incorporating technology in the process management in terms of effective communication channels and information feedback, document processing and record keeping. These might be some of the factors that have largely affected many companies in outbound logistics. The hearing aids in the different market regions would require proper and updated records, a method that might be achieved using the Just in Time (JIT) record management methods. These methods are aimed at reducing the costs in record inventory, communication as well ensuring that the entire system in the outbound and inbound logistics involving the hearing aids would be smooth, timely and accurate to avoid unnecessary costs and loss of market to competitors (Heneman, 2002).
Conclusion
Logistic management is a subset of supply chain management involved in ensuring smooth flow of materials to the production process and the delivery of finished products to the markets on time, at the right quality and at a cost that the customers would be willing to pay. It might be considered as the management of production process to consumption. Companies in the current highly competitive arena have been geared at maintaining a better supply chain management which would include the logistic management compared to their competitors, which has been argued as the competing niche in the market today. To ensure as a smooth flow in logistic management, it would be prudent to ensure implementation of an appropriate technology such as JIT, which largely improves the overall objective of logistic management, which is reducing the overall costs in the production process.
References
Busch, M.L. & Tobin, J.L. (2010). A bit is better than a lot: Bilateral investment treaties and Preferential Trade. World Politics. 62(1).
Gourdin, K.N. (2006). Global logistics management: a competitive advantage for the 21st century. MA: Blackwell Publishing.
Heneman, R.L. (2002) Human resource management in virtual organizations.NC: Information Age publishing Inc.
Leung, L., H.& Chung, Y. L., (2007). Building supply chain excellence in emerging economies. NY: Springer Science &Business Media LLC.
Manage, J. (2010). Procurement practices and supply chain performance of SMEs in Kampala. Asian Journal of Business Management. 2(4) 82-88.
Momani, M.N. (2010). Business Continuity planning: are we prepared for future disasters. American Journal of Economics and Business Administration. 2(3), 272-279.
Qingjiang, K. ( 2003). Closer Economic Partnership Agreement between China and Hong Kong. China: An International Journal. 1(1), 133-143.
Svenson, G. (2002). A conceptual framework of vulnerability in firms’ inbound and outbound logistics flows. International Journal of physical Distribution & Logistic Management. 32 (2), 110-134.
United Nations. (2010) Impact if Trade facilitation on Export competitiveness: A regional perspective. Bangkok: United Nations.
Wood, F.D. (2002), International logistics. NY: AMACOM.
Zsidisin, G. A.& Wagner, S. M. ( 2010). Do perceptions become reality? The moderating role of supply chain resiliency on disruption occurrence. Journal of Business logistics 30 (2).
