About the business
Ocean Commercial Holdings is based in North America. The gap in the provision of a wide range pasteurized dairy products and the passion to venture into dairy farming created the need to form a dairy company in the area hence the formation of Ocean Commercial Holding. The primary line of business of the company is the production and sale of daily products such as ice cream, frozen desserts, milk packing, yoghurt, and chilled dairy products among others. Products of the company are sold both in the domestic and international market.
Chart of accounts
In the chart of accounts, codes are assigned to various categories of accounts. For instance, codes starting with ‘1’ are assigned to assets, ‘2’ to liability accounts and capital, ‘4’ to operating revenue accounts, and so on until all classes of the general ledger accounts are coded. The tables below show the chart of accounts of the entity.
Asset accounts
Liability accounts
Accounts for owner’s equity
Operating revenue accounts
Operating expenses account
Non operating losses, gains, revenue, and expenses
Classification of accounts into various groups and allocating codes improves on the audit trail. Besides, it promotes analysis of the financial statements provided. For large corporations, the items on the chart of accounts can be further classified into various sub accounts thus yielding more than seven digit code.
Form of business ownership
The business will be managed by a partnership involving three owners who will be the directors of the business. A partnership is easier to set up than a company. It requires a minimal formal requirement and low cost. Partnership business increases borrowing capacity than a sole proprietorship. Raising more capatial is easier with a partnership business than sole proprietorship. Further, partnership increases knowledge bank for the business (Scarborough, 2012).
General staffing plan
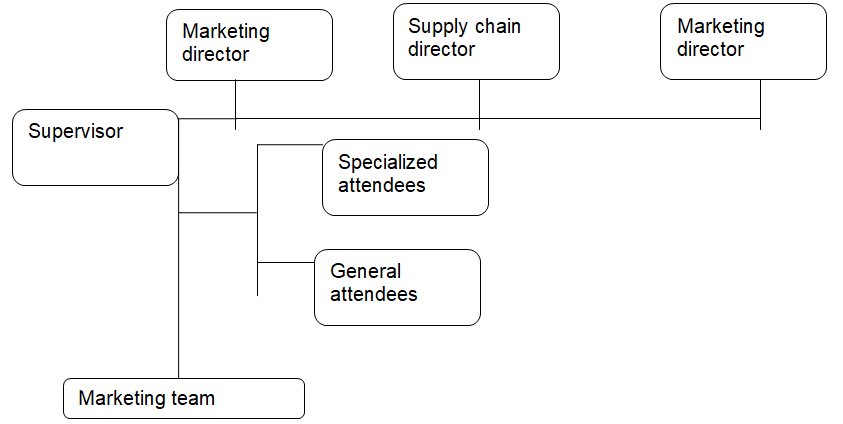
Rationale for the plan
The directors are the owners of the Ocean Commercial Holdings. The supervisor will be entrusted with the duty of offering technocratic skills and be the link between the employees and the business owners. The specialized attendee will be responsible for creating dairy products. General attendee/marketing executive is the person who will directly interact with the customers. The success of the business will entirely depend on their attitude towards the business and customers.
Accounting principle
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is a collection of standards that are developed and maintained by the Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB). On the other hand, the International Accounting Standards Board develops and publishes the International Financial Reporting Standards. The IFRS is principles-based while the US GAAP is rule-based. Considering the nature of the business, GAAP will be used to prepare the financial statements.
Convergence between IFRS an GAAP
The boards have been working together to come up with a common standard on the areas where they have differences. Some of the areas are revenue recognition and leases.Under revenue recognition, “the project aims at coming up with a single and principle-based standards for revenue recognition” (Financial Accounting Standards Board 1).
Under leases, the project seeks to improve clearness and comparability among companies. Once the two standards are merged, the company will have to change the reporting of the nature and timing of revenues. Also, the company will change the reporting the uncertain income to be in line with the joint standard (Financial Accounting Standards Board 1).
Pro-forma financial statements
Assumptions
Financial forecasts are imperative when preparing a business plan for a new product. Since the forecasts are based on future outcomes that can’t be established with certainty, there are several assumptions that have to put forward to render the forecasts valid. The cost assumptions are based the general cost such as production costs, administrative costs and operation costs (Shapiro, 2005). It shall be assumed that costs are categorized as fixed and variable cost.
The variable costs for the new product will be assumed to be increasing at a constant rate. Also, it will also be assumed that there is no change in input price (Shapiro, 2005). It will be assumed that all revenues are perfectly variable with the physical volume of production. In addition, sale price of the new product will be assumed to be constant, thus giving a constant flow of revenue throughout the year. Further, the volume of sales and the volume of production will be assumed to be equal. There will be no improvement in technology and efficiency. Thus, units will be produced as budgeted (Shapiro, 2005).
Balance sheet
The above balance sheet shows total assets, liabilities and capital base of the new business. total assets stand at $772,644 and equity at $392,644 at the end of the first year.
Income statement
The net profit after tax is $238,644. This yields a net profit margin of 18.72% while the gross profit margin is 59.06%.
Internal controls
The first internal controls that can be implemented to safeguard the assets is physical control over the tangible assets. This will be a preventive control. The second control is asset counts. It is an example of a detective control.
Implementation of controls
Implementing physical control will entail keeping assets under key and lock, in fireproof files and safes. This will apply on physical assets. The challenge that will arise is the inability of all staff members to freely access. They will have to go through the control of obtaining keys for the storage room. The resistance can be minimized by educating the staff members on how to access the assets. Assets count will be implemented in the company by coming up with a plan of conducting a count during the year. The frequency of the count will depend on the risk level. In this control, resistance can be minimized by engaging staff members during the counts.
Regulatory frameworks
Legal factors are critical for the establishment and operations of the firm. The legal requirement supports the establishment and growth of businesses. As such, Ocean Commercial Holdings will comply with the legal requirements in order to operate effectively. Some of the regulations that the company will comply with are employment regulation,health and safety, and waste disposal and recycling among others.
Besides, the company will have to comply with the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act especially with regard to external auditors, disclosures and corporate responsibility (Weygandt, Kimmel, & Kieso, 2012).
References
Financial Accounting Standards Board. (2013). International Convergence of Accounting Standards – Overview. Web.
Scarborough, M. N. (2012). Effective Small Business Management: An Entrepreneurial Approach. NY, New York: Pearson Education.
Shapiro, A. (2005). Capital Budgeting and Investment Analysis. New Delhi, India: Pearson Education India.
Weygandt, J., Kimmel, P., & Kieso, D. (2012). Financial accounting. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
