Multiple cause diagrams on factors that lead to organizational effectiveness
Multiple cause diagrams are used to investigate the main causes of a given issue. In this case, the factors that affect organizational effectiveness were evaluated and a multiple cause diagram developed. This is shown in figure 1 below.
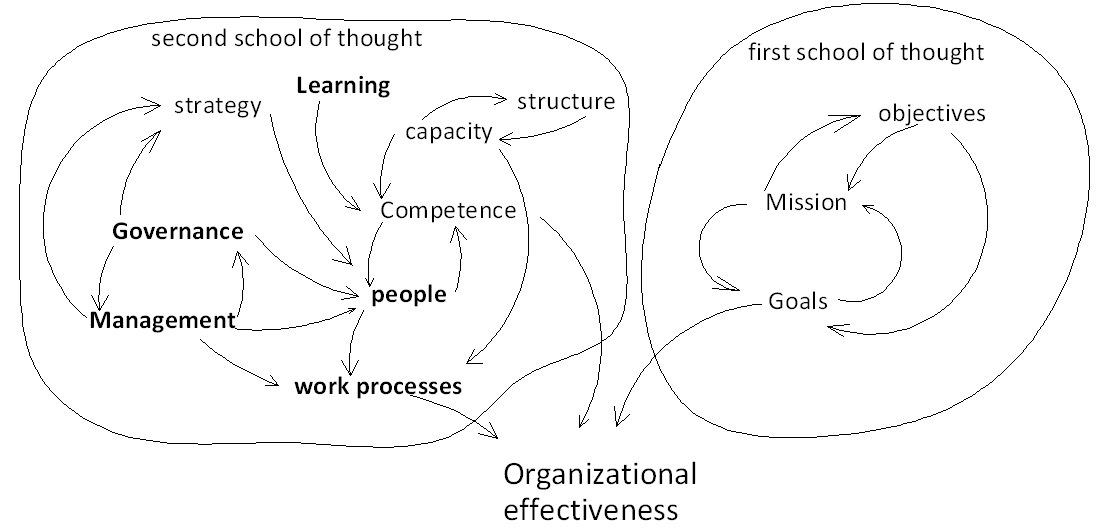
From the diagram, the first school of thought emphasizes that goals achieved by an organization are the main determinants of organizational effectiveness. These goals are influenced by the mission, strategies, and objectives set by the company. This results in a causal relationship between these factors.
The second school of thought argues that competences, people, strategies, processes, and capacity influence organizational effectiveness. Within these factors, the management, governance, people, and work subsystems exist. According to Andreadis (9), all the four subsystems are interrelated and a single system cannot effectively determine the organizational effectiveness. These systems are interrelated as shown in figure 1 above.
Closed-loop control model for the management subsystem
The closed-loop control model for the management subsystem was developed. This is shown in figure 2 below
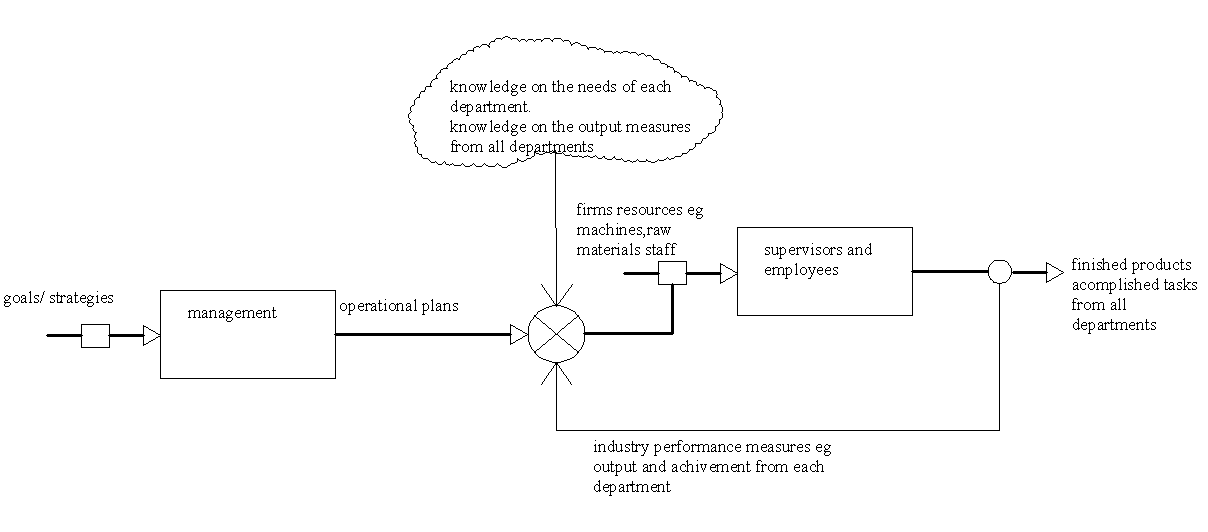
The management subsystem closed-loop control model indicates the main functions performed by the management staff, the outputs, and the people required to perform different tasks. From the diagram, the main inputs to the management system are the goals, objectives, and strategies developed by the top leaders of the organization. The management interprets these goals, strategies, and objectives to effectively implement them. They study them in light of the company’s employees, equipment, raw materials, and other resources. The management then develops operational plans for all the departments. These plans dictate the functions of each department and the resources that have been allocated to them to accomplish the assigned tasks.
To allocate these resources, the management must understand the requirements of each department within the firm. The departments on the other hand are comprised of the supervisors, employees, and equipment. In these departments, work processes and employees are combined to generate the desired end product. The management then evaluates each of the department outputs based on set criteria. The evaluation process determines whether the departments are functioning as intended. For example, the sales department must meet its targets while the production department must produce a set number of products within a specified period. If the departments don’t meet their targets, the management may consider adding more resources or they can analyze the system to detect possible causes of failure.
Organizational Effectiveness
Organizational effectiveness is a measure of how well a firm meets its goals. Various authors give different definitions of organizational effectiveness. The first school of thought states that organizational effectiveness is defined as a measure of how a firm effectively meets its targets as stipulated in its objectives and goals. The second school of thought on the other hand argues that organizational effectiveness is archived if a firm can use its competencies and capacity to achieve the desired results. Andreadis (6) defines organizational effectiveness as the process through which a firm develops systems, processes as well as culture and utilizes these factors to attain the desired goals. Andreadis’s definition attempts to incorporate elements of the first and second schools of thoughts as well as the 7s model.
From all the definitions, one of the main concepts is that organizational effectiveness measures how effective an organization is towards achieving the results. Thus, organizational effectiveness measures how well a firm transforms inputs into outputs. Some of these outputs include financial performance as well as employee and customer satisfaction. Since most organizations are complex, there is a need to develop carefully formulated strategies to measure the desired results.
One of the evaluation methods is the balanced scorecard method. In this method, the performance of a firm is evaluated based on four parameters, these are financial, customer, internal processes, and learning perspectives. Another evaluation method is the 7s model. In this model, the effectiveness of a firm is measured based on seven key elements. These are; a firm strategy, organization structure, employee skills, staff policies, work process and management systems, style and culture, and finally organizational goals. From these evaluation methods, it is possible to note the main factors that can improve organizational effectiveness.
Factors affecting organizational effectiveness
The ability of a firm to achieve its set goals is influenced by many factors. According to Andreadis (8), most of these factors are interrelated and integrated such that one system cannot operate effectively without the other. These factors are discussed below
Employee engagement
Employees working in any organization influence organizational effectiveness. Employees ensure that the firm’s strategy, missions, and goals are achieved through their input. According to Andreadis (9), employees from the people subsystem. This is one of the four main subsystems affecting organizational effectiveness. Employee level of commitment affects the client’s satisfaction and overall success of a firm. For a firm to achieve organizational effectiveness, the following must be done:
- Encourage teamwork between employees and management.
- Develop appropriate human resource policies and practices that create a conducive environment for all employees
- The firm should continually educate employees to improve their skills
- The firm should develop adequate employee motivation and incentive programs that will encourage them to work towards achieving the organizational goals
Management
A firm’s management staff affects its organizational effectiveness. The management translates strategies and objectives of a firm into operational plans that are used to produce the desired outputs. According to Andreadis (9), the management subsystem needs to function with other systems such as the work process and people subsystem to achieve the intended goals. The management also coordinates employees and staff members to ensure the production process is effective. Through appropriate scales and measures, the management determines the performances of the firm. By determining the sales, profits, employees’ performance, and efficiency of the work process, the management can improve organizational effectiveness.
Leadership and governance
Top leaders provide direction and guidelines to the organization. Top management uses external and internal information to develop a firm’s strategies, mission, and vision. The top management also formulates goals and policies which guide an organization towards future success. Leaders determine the current and future viability of an organization and this directly affects its organizational effectiveness. According to Andreadis (8), an effective governance subsystem need to interact with another process in the organizations to ensure that appropriate strategies, goals, and objectives are formulated. The decisions made by the top leaders are influenced by technological advancement, market prospects, internal strengths, and competition from other firms.
Work processes
These are organizational processes that convert inputs into outputs. These processes include employees, machines, and equipment used in the production process. The efficient utilization of workers and equipment results in the production of high quality and reliable products that satisfy the customer. This in turn increases the organizational effectiveness. Organizations should, therefore, optimize the production process, use lean methods, and determine the responsibilities of all staff members (Olmstead 25).
Learning
Learning is one of the ways that the employees can acquire new competencies. According to Andreadis (9), firms that don’t encourage their employees to learn are plagued with inefficiencies and often stagnate. Through learning, employees can gain competencies such as knowledge, skills, and personal attributes. These competencies are used by the employees to improve the capacity and capability of employees. When employees gain these capabilities, they use them to improve governance and management systems which ultimately results in better organizational effectiveness. Highly trained workers also develop unique skills that enable them to innovate new products and processes (DiBella 8). These new processes improve the production process while new products lead to increased customer satisfaction. Thus, educating employees is one of the critical methods of improving organizational effectiveness.
Organizational culture
The organizational culture is a set of shared behavior that employees and staff of a given firm have. Organizations have different cultures and this in turn affects the way work is done. Firms with good organization culture have high organizational effectiveness as they can satisfy their customers and employees. Organizational culture and firms values are interconnected and they determine how effective an organization is. Good organizational culture means that employees are satisfied, highly motivated, and educated. This in turn improves the organizational effectiveness. Organizations with good values and culture maintain high levels of customer satisfaction and this translates to greater organizational effectiveness.
Organizational structure
Organizational structure is one of the key elements of the 7s model for improving organizational effectiveness. Organizational structure details the way communication, duties, and power are distributed within an organization. A good organization structure enables the effective distribution of duties to all the workers and staff within the organization. It shows the roles of different employees and the powers of the top leaders. The organizational structure shows the people who make decisions and their relation to other employees within the organization (Dressler 85). A good organization structure will allow the effective implementation of the company’s objectives, mission, and goals. This is because all tasks, duties, employees issue are well handled.
Strategies
Strategies are specific actions that an organization needs to take to evolve over a given period. To develop effective strategies, the organization’s current state and future expectations are analyzed. These analyses are then used to develop methods of improving the organization to achieve intended goals. An organizational strategy influences its culture, structure, and workflow processes. All activities must be streamlined with organizational strategies. For firms to formulate appropriate strategies, leaders and management staff must have adequate knowledge and education (Dressler 39). This means that employees must be well educated. Also, for strategies to be effectively implemented, all the subsystems within the organization need to be integrated into one whole unit.
Works Cited
Andreadis Nicholas. “Learning and organizational Effectiveness: a system Perspective”. Performance Improvement 48.1(2009):5- 11. Print.
DiBella, Anthony. Learning practices: Assessment and action for organizational improvement. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2007. Print.
Dressler, Soeren. Strategy, Organizational Effectiveness and Performance Management: From Basics to Best Practices. Boca Raton, Fl: Universal Publishers. 2004. Print.
Olmstead, Joseph. Creating the functionally competent organization: An open systems approach. Westport, CT: Quorum Books, 2002.Print.
