Introduction
In the contemporary business world, competition has intensified. Organizations are tasked with putting in place strategies to ensure that they stay relevant to the industry of operations. The competition necessitates the need to restructure the operations of business in order to remain profitable. According to Van Dijk (2009), organizations should embrace change in order to remain competitive and relevant.
However, the process of change is not always as planned due to resistance by the employees who require maintaining status quo. Van Dijk (2009) noted that the management of organizational change is crucial in the aligning business operations with the strategic goals. Change is pivotal in any organization. The management of change determines the success or failure of the business. The following paper discusses the change models that can be adopted by Sea Treasures in order to turn around the business operations.
Short-Term Changes
The changing business environment and the advancement in technology present a situation where businesses should expand their capabilities by adopting strategic changes. However, due to complex change dynamics, the change may not be as planned. Kotter and Cohen (2002) noted that for change to be successful, it must be acceptable and in line with the prevailing business environment.
Therefore, in order to overcome the employee resistance and create an online platform t to sell the large inventory, the Burke- Litwin change model will be applicable for the Sea Treasures. The model is based on clear understanding of the business environment and striving to create a synergy that can motivate employees to accept the change.
The model is composed of 12 drivers that are applied to bring swift transformations in organizations (Burke, 1992).The model stipulates that the integration of the 12 factors of change leads to a holistic transformation. Figure 1 is a diagrammatic illustration of the 12 drivers. The factors influence the motivation level of the employees. Motivated employees are more likely to accept the change process and hence improve performance.
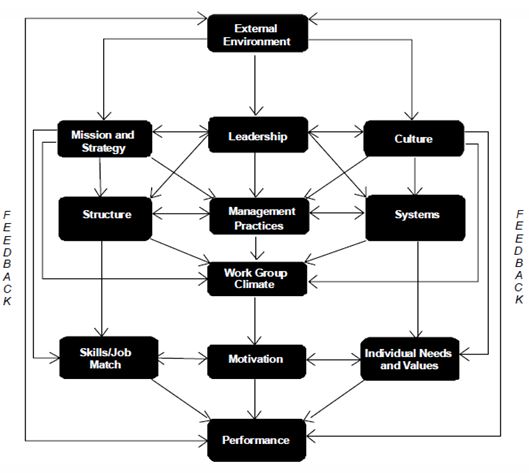
The Burke-Litwin change model enhances performance of a team by establishing a link between the internal factors and the external factors. Therefore, for the change to be successful, the organization is assessed to determine the factors that may be hindering change. Subsequently, the environmental factors are evaluated to determine the opportunities available for the change (Burke, 1992).
In the case of Sea Treasures, the dominant factors that impede the change are the resistance from the employees and slowed uptake of the technology. The external factors include the competition and the advancement in the technology, which the company has been slow in up taking.
Van Dijk (2009) noted that the main factors that impede change in an organization include poor motivation of the employees; thus, the model, addresses the challenges of poor motivation that fosters integrated work platform in which leaders set strategies and motivate employees to work towards realizing the change process.
Long-term Changes
Successful organizational change should incorporate all stakeholders and enhance the sense of ownership and teamwork within the organization. In order to set a long term online platform for selling their products, the Kotter’s eight step change model will be appropriate. The change model is based on making the employees buy into the change (Kotter & Cohen, 2002). The leaders campaign for the change and make it seem urgent.
The acceptance of the change is then flowed by a gradual change process that integrates the change process to the business culture. The processes include the establishment of the sense of urgency. The process makes employees and the line managers understand the need for making the change to take place; therefore, it fine-tunes the minds of the employees to align with the change initiative. The second process is the formulation of the coalition to guide the change process.
Kotter and Cohen (2002) pointed that coalition building entails the inclusion of the key stakeholders that are to be involved in the change process. In addition, for a change to be effective there must be vision and the strategy to guide the change. Organizational change depends on the leadership to provide the vision and inspire the employees to embrace the change (Van Dijk, 2009).
The fifth process entails the communication of the change and the vision to the staff and other key stakeholders. Communication fosters understanding and reemphasizes the need for the change process.
A change that is broad-based starts with achievement of short-term wins, according to Kotter’s 8-stage process, the short-term wins serve as indicators of the progress of the change process. The seventh step entails consolidation of the achievements made in the various areas and producing more change. The final stage is the integration of the change approaches to the culture.
Conclusion
In the modern world, change has become part of our lives. Organizational change has become a common feature in modern day business operations. The selection of appropriate change model increases the acceptance of the change process is critical for the survival of businesses.
Therefore, the adoption of the Burke-Litwin change model will guarantee the Sea Treasures short-term success of the online selling of the inventory. On the other hand, the Kotter’s eight-step change model will integrate the change process to business culture, which will lead to long-term success in the online selling platform.
References
Burke, J. (1992). A Causal Model of Organization Performance and Change. Journal of Management, 18 (3) 523–545.
Kotter, J., & Cohen, S. (2002). The Heart of Change. Boston: Harvard Business School Publishing.
Van Dijk, R. (2009). Navigating organizational change: Change leaders, employee resistance, and work-based identities. Journal of Change Management, 9 (1), 143-163.

