Abstract
Ford Motor Company is one of three leading global automobile manufacturers, the other two being General Motors and Daimler-Chrysler, all three being based in the US. The present automotive sector is facing the effects of the global economic meltdown and this is particularly so in the United States which are faring badly in local as well as global markets. Ford has been showing downward trend in its financial performances the past eight or more years. But, the recent cash crunch due to low credit availability, maturing debts, lower productivity, higher technological and superannuation and medi-care costs, have made it hard for the company to retain its business.
Some important mergers and acquisitions non-withstanding, and in spite of some crisis driven share and stock issues, Ford still is showing annual losses and is hard put to retain its hold on the global automobile market, faced as it is by its close competitors and the challenge from its Asian competitors who can lower production costs due to low cost of labour in countries like Japan and Singapore. This paper traces the financial performances of the company over the recent years, highlights the reasons for the recent stock issues and also gives the management’s perception on the crisis and the direction that it is leading the company in the near future.
Company Background
Ford Motors Company is one of the largest motor companies of the world and one of top three automobile companies which also includes General Motors and Daimler-Chrysler. Henry Ford created the first motor company in the United States way back in 1903, and in the process created a lasting legend. Based at Dearborn, Michigan, Ford presently manufactures automobiles in around 200 markets worldwide through 108 plants located in six continents (2009). The first car manufactured by the company was known as Model A which was followed by Model T. Later, Ford also introduced trucks, tractors, jeeps and even bombers during the world wars.
Industry Overview
The world automobile industry is dominated by a few players. The International Organization of Motor Vehicles Manufacturers (2005) in one report have stated that the world’s automobile industry manufactured as many as sixty-six million vehicles in 2005. Leading companies manufacturing passenger & luxury cars and other vehicles include General Motors, Daimler-Chrysler, Ford Motor Company, all based in the US and other players like Honda, Toyota, etc.
However, the global economic crisis has also affected this manufacturing industry across the world. A KPMG Survey (2008) has indicated that in the near future, margins and profitability would decline, cost savings would be cause for concern, and restructuring through mergers and acquisitions could be the option of choice for the auto companies like Ford, Chrysler and GM.
Technology would stress on product innovation for increasing fuel efficiency, alternative eco-friendly and energy conserving propulsion systems, etc. In recent years, as an indication of perhaps worse days to come, US car makers like Ford have been facing a cash crisis, which has made these companies seek finance options like sale of securities like stocks and bonds. Also, cost of credit has shot up substantially. In an earlier report, KPMG (2008) has already observed that financing had evolved as the greatest need and obstacle for auto manufacturers, and owing to the credit crunch and demise of many banks, funds flows had diminished and affected operations of the large auto companies like Ford and GM in the US market.
Company Products
Ford boasts of various cars and vehicles both for passengers, and utility vehicles like trucks and jeeps. Company brands include Ford Mondeo, Ford Focus, Ford Fusion, Ford Mustang, Ford Ka (Europe), Ford Galaxy, Ford Fiesta, Lincoln MKS, Ford Flex, Mercury Milan, Ford S-MAX, and Ford F-150 (Best selling & North American Truck of year, 2009). In addition, Ford also has acquired brands like Mazda and Volvo. Segment wise, Ford has four categories of cars, namely, Small, Medium, Large and Premium. Trucks are of three types-Compact Pick-up, Bus/Van and Full-size Pick-up. The SUV/CUV is another category boasting of Medium & Heavy vehicles. Aston Martin, Ford, Jaguar, Land Rover, Lincoln, Mazda, Mercury and Volvo are the top selling brands of the company
Competitors of the Company
The closest competitors in the US for Ford seem to be General Motors and Chrysler. All three companies appear to be closely following one another’s technological advances. Thus none of the three lag behind in providing cleaner Diesel & Flex fuels, hybrid cars and trucks, plug-in electric innovations, and increased use of advanced transmission technologies. Safety, less pollution, better fuel efficiency, more comfort, these are just some of the areas where the three companies are vying with one another to garner larger share of the auto market. The Automotive Trade Policy Council in its report in 2008 has observed that quality, reliability, operational efficiency, safety, environmental conservation, and better technological innovation are the major factors behind the new policies of the three main US auto companies.
Financial Information
Ford has been listed on the New York Stock Exchange since the year 1956 onwards, when the company became a publicly held company. The past has seen various marked changes in nature of holding, profile of top executives and financials of the company. The past few years have been particularly critical for the company financial health owing to the fluctuations in global oil prices, increasing cost of credit, failure of leading banks of the world, increasing competition among major auto manufacturers and marked challenges to the US firms from Asian and European challengers.
A cash crunch led the company to source funds from the market by selling stocks and shares in recent years. Ford has from time to time floated various instruments like a convertible bond, car-loan bonds and other asset-backed securities. The securities included both fixed and floating term instruments. The most current issue of asset-backed securities are the fixed-rate car loan bonds sold by the credit arm of the auto major, Ford Credit in Oct 2008 when the company issued $500 million of 8.625 per cent senior notes maturing in 2010
Overview of Balance Sheet Prior to/After Stock/Share Issue
A comparative analysis of key financial ratios and parameters derived from the company balance sheet both before and after the issue of stocks in Oct 2008 throw light on the changes effected by such issue as also the success in sourcing cash. Important ratios considered were EBITDA, Return on Capital Invested, LT Debt/Total Equity and Total Debt/Total Equity
Key Ratios Considered Before / After Issue
As mentioned, a study of the different financial ratios before and after the stock issue throws light on the performance of the company during the recent months. Accordingly five ratios/parameters have been considered and are furnished below.
Ratios Considered Quarter ended Sep 2008
Long Term Debt/Total Capital 1.01
Return on Capital Invested (ROCI) –7.4%
EBITDA 7.9%
Total Debt/Total Equity 19.80
The relevant data from the Balance Sheet of the company for the Quarter ended Sep, 2008 and identical data also for year ended Dec 2008 are also furnished below
Quarter ended Sep, 2008
Total Sales: $ 32 billion
Net Cash (Gross Cash -Tot Debt) -$ 7.2 billion
Capital Invested: $ 4.7 billion
Total Debt: $ 26.1 billion
Total Long Term Debts: $ 24,856 million
Initial Sale of Security
Starting from August 2008 till Oct end, Ford issued 88.3 million shares in Ford Common Stock priced at $434 million (total), and used the funds from such sale to buy $493 million in principal amount outstanding of Ford Credit debt security instruments which would mature before 2012 for a total price $434 million.
Target market, Bankers etc
Ford, through its financial arm Ford Motor Credit, has already floated the bond issue which has been managed by Citigroup, Merrill Lynch & Co., Lehman Brothers, BNP Paribas, Morgan Stanley and Royal Bank of Scotland
Trends during Last 18 Months/MDA
Ford lost as many as 18 months back, its investment-grade credit rating and currently is saddled with a $121 billion junk-rated debt. The past years have seen its market shares sliding and its costs increasing (mostly due to health-care and retirement payouts which have increased). S&P therefore cut their credit ratings on Ford and Ford Credit to BB-, while Moody’s Investors Service downgraded Ford to Ba3 & Ford Credit to Ba2.
Credit Rating for the Issue
In August 2008, DBRS lowered the senior secured rating for Ford from B (High) to B. In October 2008, Fitch likewise revised downward their long-term senior unsecured rating from CCC+ to CC and the issuer default rating to from B- to CCC. In October 2008, S&P placed Ford on Credit Watch with negative implications, and Moody’s placed them on review for possible downgrading. A comparison of the different ratings could be seen from the Chart 1 appended below under the Appendix.
Justifying Rating with Recent Financial Performances
Recent financial performances of Ford Motor leave much to be desired, although the general decline in automobile industry worldwide is now well known and directly related to the global economic meltdown. That leading rating agencies like Moody’s and S&P have lowered ratings for Ford is amply justified as can be seen from the deteriorating financial performance of the company over the years, although, its performance in Europe may be the only silver lining (www.advfn.com, 2009)
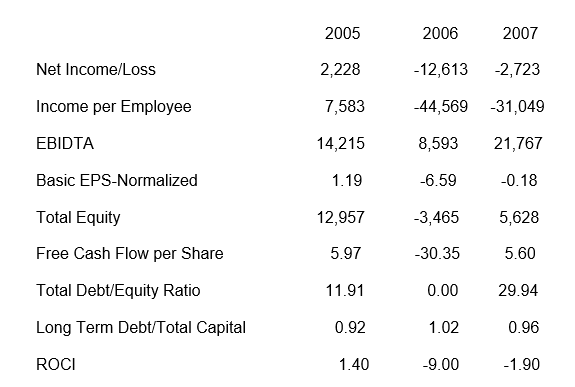
Analyzing the Reasons for the Issue
In the present economic situation, credit has been hard to come by. Many major banks have been liquidated. The automotive sector has seen sluggish growth with depleting number of vehicle sales and decreased revenues/incomes. Furthermore, intense competition from leading players both locally and from Asian competitors like Toyota and Nissan have led to declining profits and even losses to the company in recent years.
Added to this has been the ongoing problem issue of the Ford management with the employee union (UAW). Increased costs by way of more technology oriented outgoes, higher Medicare expenses for its employees and substantial retirement payments have added to the worsening situation at Ford Motor Company. The fast approaching maturity payments due on its earlier stocks and bonds issue had also necessitated the floating of the current issue of bonds and asset-backed instruments
Project Characteristics and Takeaways
The project derives its benefits in the in-depth knowledge of the financials of a company like Ford, the environmental & economic effects on the parent industry, viz automobiles, the nature of the industry and how it impacts on the company, the key issues that challenge the higher management of the company driven by cost cutting and profit retention motives, as also the understanding of the need for improving productivity, developing innovative energy saving methods, ensuring environment friendly technology and vehicular design and emergent management concerns for meeting cash commitments both in the present and the future, both in short term and long term.
An overview of the key financial ratios that are derived from major indicators of financial performance as obtained from the company annual and quarterly financial performance reports is an essential part of the learning process. How the ratios are formed and what they signify as also how to improve them is the core issue for any management in running a company profitably over the years
References
ADVFN PLC, (2009), “Ford Motor”. Web.
ArticlesBase. (2009), “Ford Motor Company: The pride of Michigan”. Web.
KPMG International, (2008), “Momentum: KPMG’s Global Auto Executive Survey:/Industry concerns and expectations 2009-2013”.
KPMG International, (2008), “A rough road: the effects of today’s financial crisis on the global automotive industry/Global automotive trends”.
The Economywatch. (2009), “Ford Motor Company”. Web.
The Ford Motor Company, (2009). Web.
The International organization of Motor Vehicles Manufacturers, “The World’s Automotive Industry”, Published Online, (29/11/2006). Web.
Appendix
Table 1: Credit Ratings As at Quarter ended Sep 2008.
