Executive summary
This study attempts to review the impact of geographic dispersion and technological development in the organisation environment. It has been found that many companies adopt virtual network structure because they may not have all the required knowledge or skills within their organizational boundaries and thus the need to somehow connect with the outside source at either organizational or individual level. One way of making connections with the external source to have the knowledge and skills is by adopting virtual network structure. This study explains how companies are using this concept, whether to integrate companies’ operations with those of the enterprises to create a better product or service. This study also explains that structure affects the performance of organizations, so successful companies seem to adopt structures that favour less formalization, more decentralization and coordination of differentiated units in order to attain maximum productivity or to achieve organizational goal. So it is better to choose virtual network structure because in the present scenario it is more suitable. It also explains the benefits and limitations of using virtual network structure in an organization.
Introduction
Organizations are operating in a complex and unstable business environment. With global pressure, de-regulation and intensive competition arising from the innovative application of information technology to all aspects of business environment, they are increasingly finding the need to be agile, adaptable, creative and innovative to cope up with these uncertainties. In this new environment, old and traditional strategies are no longer applied. The fact is that even if they are applied, there won’t be any improvement in the organization, so managers find it difficult to operate. In a dynamic nature of business environment managers require to take a proactive approach to change. Change is inevitable in the business world and the survival of the business organizations depends on adaptability. This has made it imperative for the managers to undertake comprehensive change-related programs in an organization structure. Before modifying the organization structure it requires a great deal of planning before implementation because it may often meet with resistance from people within the organization as well as organizations themselves. The management has to take steps to overcome such resistance in order to implement the change to be successful in the organization structure. One of the emerging changes in the present scenario is the implementation of virtual network structure in an organization. This model has led organization to create an alliance with groups and individuals from different organizations who possess high competencies in various skills to build a product or service in a short span of time. “The adhocracy characterizes organizations that are temporary by design, approximating Burns and Stalker’s organic form of organization. It is a form highly suited for the performance of complex and uncertain tasks in turbulent environments. It usually involves project teams that come together to perform a task and disappear when the task is over, with members regrouping in other teams devoted to other projects. Sometimes, this kind of enterprise is called a “virtual” or “network” organization, especially when teams and team members are spread geographically, using electronic technology and occasional face-to-face meetings to integrate their activities“(Morgan 1998, p.51) or in other words different or independent firms that join or come together, often temporarily, to produce a service or a product or to accomplish a specific goal. “The virtual network organization is more permeable than the traditional organization structure. The virtual organization may not have a central office or an organizational chart.” (Virtual organizations 2007).
The following are some of the important characteristics of virtual network organization:
- Different organizations with varying skills and core competencies form short term partnership to exploit market opportunities and disperse once the mission is accomplished. This ability of multiple firms creates a world class function and process to create untold functions.
- Organizations located in different geographical locations enter into partnership and use information technology for communication, new linkage and other transactions to achieve their goal.
- Companies share critical information with each other as they work together for a common project, this helps to create a mutual trust and cooperation which in turn helps the organization to use innovative management practices.
- As suppliers, customers and even competitors sometimes collaborate with each other; it may be difficult to define the boundaries in a virtual organization.
- As the organizations use new linkage, advanced information technology becomes important which in turn helps in the success of the virtual network organizations.
- As the best companies enter into partnership and contribute the best skills and knowledge in certain spheres, virtual companies can produce superior or best quality products than that of other companies.
Virtual network structure should continuously evaluate the changes or new activities in the business environment. It should also determine which activities constitute the primary or secondary activities in their business. By determining this, primary activities can be performed in-house and the secondary activities can be outsourced. Companies may outsource any number of activities but it should never give up their control or process in which the activities are performed. Otherwise in the long run it may affect the business products or service. Therefore the companies that are adopting virtual network structure business should establish a real time communication with outsource service providers, the company should continuously interact with them and retain their control over the outsourced activities.
Virtual Network Structure As A Good Structure
The primary benefit of a virtual organization is that it can unite highly qualified people without location restrictions from different organizations. “Other reasons that an organization would want to consider being virtual rather than traditional are the ability to leverage skills throughout the organization, provide customers with the “best and brightest”, balance work/home relationship, save organization overhead costs.” (Talal Yassin 2009).
Organisation adopts virtual structure for many reasons. These are :
- Sharing infrastructure, research and development, risk and costs: single company may not be able to afford.
- Linking complementary core competencies to serve customers: when different companies contribute their skills and expertise
- Reducing cash and time
- Gaining access to markets and sharing markets or it brings loyalty among customers.
- Reducing the need for co-location of workers and promoting work.
- Encouraging sales-at-a-distance while reducing the breadth and depth of retail channels.
“Migrating from selling products to selling solutions, which allows a clear and unambiguous perception of value, since the same product may have different value to different customers at the same time”
“Some of the well-known examples of virtual organizations include Amazon.com – the electronic bookstore, NIKE – the sport company, Dell computers and many others.” (The virtual organization).
The diagram below shows that the alliances are virtual, because products and services are not produced in a single corporation whose purpose is longevity. Rather, these new virtual organizations consist of a hybrid of groups and individuals from different companies that might include customers, competitors, and suppliers who have a focused purpose of bringing a high-quality product or service to market as rapidly as possible. These alliances may be temporary with short concept-to-delivery cycles. These alliances are suitable for many companies when they may not be able to produce high quality products or service. Alliances are so important for the successful implementation of virtual network structure.
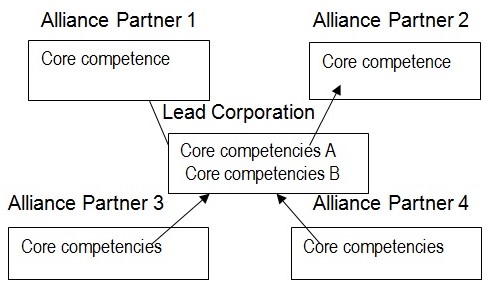
The Virtual Corporation – A network of organizations working independently to bring a product to market. (Virtual organizations 2007).
It is a good structure in case of club computer Inc:
The members of club computer inc, which is a membership based online retailer of computer hardware and software products, were offered free shopping and discounts on over 100,000 products from over 300 manufacturers such as Compaq and Microsoft. They were also provided with shopping discounts at 25 leading websites and catalogues through another member benefit. Club computer inc. was equipped with the features of virtual organization. It considered internet as a powerful tool for the progress of the organization. It doesn’t have warehouses of its own, which means drastic cuts in inventory cost and storage cost. The club computer finds it expensive to set up, manage and to maintain the warehouses, so they decided to join hands and to form partnership with Merisel inc. and Ingram Micro Inc. Merisel and Ingram were the world’s largest wholesale distributors of computer products. Accounts were set up in a way that it allowed club computer to access the distributor’s ordering system over the web and it also allowed them to place orders that are directly shipped from the distributors with the logo of Club Computer slapped on every box. Another impressive feature of Club Computer Inc is that every activity of the company is taken care by their four-person staffs, which includes the chief financial officer, the chief technology officer, the CEO and his wife. Thus they were able to work efficiently; they also see that labour cost and administration cost are kept to minimum. Another important feature of this virtual organization is that it also had to outsource many of its business components. Club Computer Inc. also joined hands with Just4Biz.com which is the developer of I-Marketing model. Through the partnership with Just4Biz.com, the company was able to launch its second website. Thus they were able to offer access to 25,000 office products and furniture at high discount prices to its members. (The virtual organization).
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems is a leading maker of computer workstations. They concentrate on hardware and software design, where it distinguishes itself from that of competitors and outsource everything else in its value chain. Sun has been considered highly decentralized organization comprised of independently operating companies. Sun has positioned its information systems as a top priority, trying to achieve faster and better communication. With numerous “Sun Teams,” members operate across time, space, and organizations to address critical business issues. Sun managers identify key customer issues and then form teams with the critical skills and knowledge needed to address the issue. This team might include sales people, marketing personnel, finance people, and operations people from various places around the globe; customers and suppliers may become episodic members as necessary. Weekly meetings may take place via conference calls. Critical to the team’s success is the selection of talent from the organization, defining a clear purpose for the team’s efforts, and establishing communication links among the team members. They depend heavily on the skills of employees to innovate and differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Sun has been working on further development of technologies such as EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification technology). Both EDI and RFID will impact information exchange globally and across numerous industries.
Bio region is another successful company which uses virtual network structure.
In 1995, the companies within the German Biotechnology sector were appealed to increase cooperation in order to increase the overall growth in the government targeted industry. Soon after this appeal, many companies in the triangle cities of Braunschweig, Gottingen, and Hannover in north west Germany convened structures for regionally established and centralized organizations in order to promote future development.
The founding members of the BioRegioN started by considering the strengths and weakness of the life science organizations in the region. Though there were large number of companies and researchers in the area, there was very little flow of information among the neighbours, but they had occasional discussions between pairs of companies. The most important objective of the BioRegioN was to promote communication among the regional players and interdisciplinary cooperation. The central task of the BioRegioN was regional business development. The important concept of BioRegioN was that the virtual enterprise enables the network members to access the resources to all the other members. It also allows them to ask help when needed for the completion of the essential projects.” The virtual company is characterized by two main components, both of which are enabled by revolutions in data exchange and telecommunications technology: (1) a stable network relationship between the partners based on long-term cooperation through regular meetings and informal exchanges; and (2) partners working together in formally established project teams or even additional virtual companies, depending on the project and market opportunities.” (Jensen & Haufe 2009).
The virtual companies will provide a unified front to the customers with the flexibility to adjust resource allocation in order to meet the performance requirements. The virtual companies also allow the members to draw the disparate talent pools actually employed by the individual companies.
In order to use the virtual structures effectively, a certain degree of trust has to be established between the partners. It has to build up personal and intellectual foundation for future computer assisted transfers of knowledge. The partners will have to be familiar with each other’s structure, competencies and personalities through personal meetings.
Being a virtual company BioRegioN is also organized in the same way like the normal company. The association’s management is at the head, which is linked together in loose networks to provide maximum flexibility. The member company contributes to the individual functions of the virtual company. These are reflected in the infrastructure of different specialist groups. The scientists who want to convert their research ideas into products can contact experts from business and financial sectors. The most important factor that is required by the company for its survival in the current scenario is its flexibility. It should be able to adapt to the market conditions. It should be able to accommodate individual customer requirements and it should be able to identify market opportunities at an early stage. “The structure of the virtual enterprise consists of loose associations of legally independent companies, institutions, and/or individual persons, who render joint performances on the basis of a common business understanding. The resources provided by the partners are aggregated into a virtual company to become a cooperative performance. In doing so, each individual company concerned brings its core skills into the virtual organization”. (Jensen & Haufe 2009).
More than 170 partners, arranged into 25 central competencies constitutes the structure of BioRegioN. “The success of BioRegioN suggests that the competitive advantages obtained from this structure—identifying biotechnology market opportunities at an early stage and creating advantages for market developments—can be of great value for small and mid-sized companies endeavouring to survive and adapt to increasingly global markets”. (Jensen & Haufe 2009).
Forms of Virtual Network Structure
- Virtual Corporation: Resting sourcing, sub contracting, and outsourcing processes on the electronic infrastructure.
- Virtual alliance: Aligning product or market strategies and corresponding processes across organizations.
- Virtual Team: Organizing work processes around dispersed project members.
- Virtual Office: Resting the organization of work on tele-community
- Web: Resting the delivery structure.
- Store front: A process on web. (Travica 2002)
Benefits of virtual network structure
- Access to specialized knowledge and resources, worldwide.
- Workforce flexibility and speed
- Less investment in fixed assets
- Ability to scale operations, work can be spread across the time zone.
- Significant productivity improvements.
- Cost of savings or overheads (Howard et al 2003).
Challenges faced by virtual organization
There are various problems faced while implementing virtual network structure in an organization because they are very complex and problematic. They even fail; often they succeed. Few of the challenges of the virtual organizations are:
- Strategic planning dilemmas: virtual organization poses new challenges as the virtual structure determines combination of core competencies. Common vision and common goals are essential for cooperative firms because when an organization develops common goals the firms can develop close interdependencies which may make it difficult to determine when one company ends and other company begins.
- Boundary blurring demands: These boundaries should be managed effectively. Coordinating mechanism are the critical or crucial elements for supporting these loose collections of firms.
- Loss of control over some operations: loss of control requires communication, coordination and trust among the various partners as well as to set new managerial skills.
Limitations of virtual network structure
- Lack of control, weak boundaries
- Loss of confidentiality/security
- Employees’ loyalty weakend
- Increased dependence on information technologies
- Dependence on suppliers and their stability
- Difficulties in forming and managing multiple contracts. (Howard etal 2003).
Best practices for the successful implementation of virtual organization:
- Enhance trust among the partners.
- Enhance cooperation and empowerment.
- Provide technical assistance.
- Ensure smooth flow of information among the members.
- See to that every member is trained properly.
- Ensure that the technology is reliable and compatible
- Ensure that the skills and competencies are complementary and not overlapping.
- Ensure that the partners are adaptable to change in the market conditions.
- Contractual agreements should be made clear. (Virtual organizations 2007).
Conclusion
Any organization, when faced with the challenges of a highly dynamic external environment, must employ its design dimension in such a manner as to provide it with adequate agility and dexterity, so that drastic strategic choices may be implemented in a timely and successful fashion. The existence of virtual network structure will create a number of business opportunities. From the above study it indicates that structure affects the performance of organizations, so successful companies seem to adopt structures that favour less formalization, more decentralization and coordination of differentiated units in order to attain maximum productivity or to achieve organizational goal. So it is better to choose virtual network structure. From the above study it is clear that the process of the creation and functioning of virtual network structure in an organization is not simple but functioning is accompanied with various problems which can be successfully solved only with an adequate action of the virtual organization management. Regarding the new swift developments due to new millennium and the current wave in the developing countries it is quite sure that the companies will adopt virtual network structure in their organizations.
Reference
Howard, Nigel etal 2003, Exploring the virtual company strategy through outsourcing in the biotech industry, Mayer Brown Rowe & Maw, Web.
Jensen, Uwe & Haufe, Ursula 2009, Success from a virtual structure: building trust, Bio Entrepreneurs, Web.
Jensen, Uwe & Haufe, Ursula 2009, Success from a virtual structure: transfering the concept, Bio Entrepreneurs, Web.
Morgan, Gareth 1998, Images of organization, Berrett- Koehler Publishers, Web.
Talal Yassin, Alla 2009, challenges and success achieve factor for virtual organization concept: new trend(challenges) of virtual organizations-companies, Ezine Article, Web.
The virtual organization: reasons for the emergence of the virtual organizations, 2009. Web.
The virtual organization, 2009, Web.
Jensen, Uwe & Haufe, Ursula 2009, Success from a virtual structure: a unified front, Bio Entrepreneurs, Web.
Travica, Bob 2002, Virtual organization and electronic commerce, university of Manitoba, Web.
Virtual organizations 2007, Business reference, 2009, Web.
Virtual organizations: the new business 2007, Business reference, Web.
Virtual organizations: background 2007, Business reference, Web.
