A brief description of Apple
Apple Inc. is a US-based company headquartered in California. The company was incorporated in 1977 as Apple Computer, Inc. and later renamed Apple Inc. Apple I was a personal computer kit that the company produced. However, in 2007, the company shifted its attention towards consumer electronics. Some of the consumer electronics produced by the company include online services, computer hardware and computer software (Cummings & Worley, 2009). The core products of the company are computers and Smartphones as well as iTunes, iCloud and App Store services. Today, the company has almost 425 retail points in fourteen countries (Conaway & Laasch, 2014). In addition, the company boasts of more than 75,000 workers, both permanent and temporary.
Mission Statement
The mission statement of Apple Inc. is “To make a great contribution to the world by developing tools for the mind that aim to advance humankind.” (Conaway & Laasch, 2014). This statement means that Apple produces the best products through innovation intending to assist people to advance their experience.
Strategic Goals
- The company aims to be a major online platform for online advertising;
- The company targets to redouble its efforts in Research and Development;
- Apple tries to reach more customers by expanding its distribution networks.
All these strategic goals are very crucial to Apple Company (Cummings & Worley, 2009). Since the company, which specializes in consumer electronics, is faced with intense competition from other companies, such as Samsung and Nokia. However, Apple continues to invest heavily in its R&D to produce user-friendly technologies that will be efficient in terms of use and maintenance.
Social Responsibility
Apple has started entrenching waste management processes in its strategic goals. The company aims to recycle used electronics to make the environment clean. To ensure this goal is achieved, Apple has managed to implement e-recycling centres in many countries across the globe (Conaway & Laasch, 2014). The company is also shifting from nonrenewable energy to renewable. It sets up facilities that can only be powered by green energy, such as solar and geothermal.
Management
The management team and their qualifications
There are about sixteen members of the board of management:
Arthur D. Levinson is the Chairman of the Board (Cummings & Worley, 2009). Before joining Apple, Levinson worked in several private and public companies, all of which specialize in the technological sector. Therefore, he has a wealth of experience on top of being an expert in financial and brand marketing matters.
Timothy D. Cook is the Chief Executive Officer of the company. He is an expert in technological and leadership matters. He has also served in global operations, support and services. This adds a lot of knowledge to the company operations.
Luca Maestri is the Chief Financial Officer of the Company. Before joining Apple, he served in other private companies in the financial sector. Therefore, he is of advantage to the company as he has a lot of experience in financial matters (Conaway & Laasch, 2014). He also has some other qualifications in Economics and Management Science.
Philip W. Schiller is a Senior Vice President in the marketing section. He has served the company in this position since 2002. He has qualifications in marketing.
Eduardo H. Cue is also a Senior Vice President working in the Internet section of the company. He joined Apple Inc. in 1989, but he has been holding the current position only for three years. He specializes in mobile software Engineering.
Craig Federighi is also a Senior Vice President in the Software Engineering section of the company. He qualifies for Software Engineering. He has been with the company since 1996 but assumed his current position in 2004.
Daniel Riccio is a Senior Vice President in the section of Hardware Engineering. He has held his current position for about two years.
Other members of the management team are Ronald D. Suga, Andrea Jun, Robert A. Iger, Albert A. Gore. They are independent directors of the company, and their qualifications range from software engineering to management.
Organizational Structure
Apple’s organizational structure is a closely guarded affair. Even employees have very little idea of how their organization is organized (Cummings & Worley, 2009). What is known has been summarized into the organizational chart shown below:
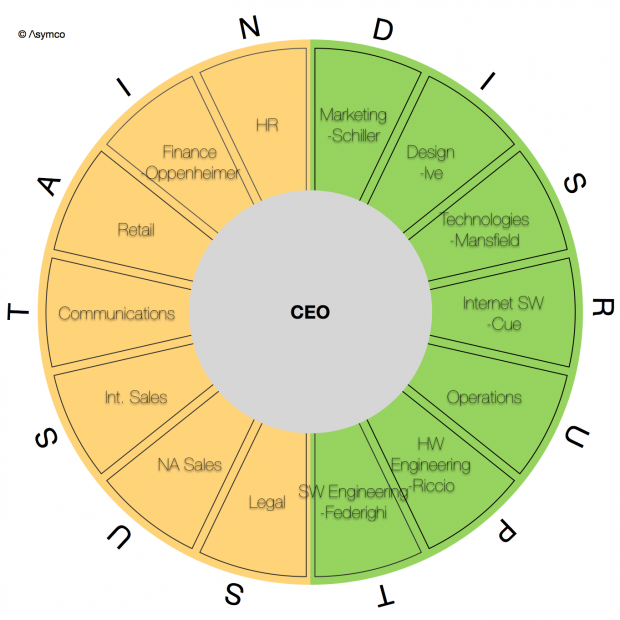
The above is a simplified organizational structure of Apple and is split into “Sustaining” and “Disruptive” functions. The main point was to separate the product creation functions from the administrative and management functions of the entire organization.
Employee Recruitment and selection
Many scholars have discussed how Apple successfully recruits their retail workforce and what they look for during the process (Conaway & Laasch, 2014). Apple does not look for technical mastery or extraordinary intelligence (Cummings & Worley, 2009). Instead, there are seven characteristics that recruitment officials look for during their wide-ranging interview process:
- Demonstration of passion
- Being jovial and friendly
- They do not look at whether or not the candidate knows their products
- Speaking up and showing confidence
- Interacting with the people and asking for assistance
- Showing commitment to the client
- Talking with humility
Looking at these qualities, the company focuses on recruiting and hiring people with great “attitudes” that fit their values and organization.
Employee Training and Development
For Apple Company, employee training and development is intended to help the company horn the skills and talent needed for the success of their business. In other words, Apple considers employee training and development as an important way to its general success. In addition, the company believes that employee training and development has the potential to attract and develop the best minds not just within the company, but also from outside.
A resource library
The company has a comprehensive resource library with collections of information on careers via a range of sources, including magazines, newspapers, audio/videotapes and books (Conaway & Laasch, 2014). A bulletin board is also provided in the library, which presents up-to-date information regarding changes and trends in the industry. In addition, the company organizes Brown bag seminars. These are sessions organized to help workers exchange current information regarding career development and opportunities available in the industry.
Assessment and counselling
The company has a resource centre that offers a variety of interest assessments and skills to workers. This helps them to appreciate how they can approach career choices and career planning (Conaway & Laasch, 2014).
Networking groups
The company also organizes weekly networking groups to help workers grow in their jobs (Cummings & Worley, 2009). Most importantly, it focuses on employees who are interested in knowing one or two things from the company such as a change in career and employee developmental matter.
References
Conaway, R., & Laasch, O. (2014). Principles of Responsible Management: Global Sustainability, Responsibility (5th ed.). New York: Cengage Learning.
Cummings, T., & Worley, C. (2009). Organization development & change (4th ed.). Mason, OH: South-Western/Cengage Learning.
