Executive summary
The Walt Disney Company has a well-recognized brand that is synonymous with entertainment. However, the company is also a major producer of information that also runs the various networks that carry its entertainment content. It has a presence in traditional media, including cable television networks. Also, it has a digital presence using its networks and various on-demand content arrangements. This report reviews the strategy of the business and looks at its background and growth prospects. The report analyzes the vision and strategic choices that the company faces in the short-term and the long-term. The report reveals that innovativeness is an all-round component that will drive the competitiveness of the company forward. The report provides some of the strengths that Walt Disney enjoys, which has been instrumental in sustaining a positive financial performance highlighted briefly in the report.
Disney
Company background
The company covers the global market, and it has its headquarters in California, United States. It operates in America, Europe, and Asia. The company’s business is in five segments, which are Media Networks, Disney Interactive, Disney Consumer Products, Walt Disney Studios, and Parks and Resorts. They all play a role in developing the business to realize its objectives. The largest segment of the business is its Media Networks, which are also the most developed. However, the original entity that created the other segments was the Walt Disney Studio, which formed the core business of the company before acquisitions and expansion. This segment was responsible for the development of the Disney brand to its current brand reputation globally.
Stock price in 52 weeks high or low
Currently, Walt Disney trades at about 109.95 dollars and its 52-week high value is 113 dollars. Meanwhile, its 52-week low value is 78 dollars. This implies that the company stock price is operating within the high bracket of its overall performance history.
CEO of the company and how long he is in place
The current CEO of the company is Robert “Bob” Iger. Iger took over the company in 2005 after serving as its Chief Operating Officer. The board of the company chose to replace its leadership with a person who understood the company’s tradition and history; hence the choice of Iger. The CEO has almost completed a decade as the leader and has successfully led the company to expand and increase its share price. Iger’s leadership style allows managers to act independently. The CEO prefers to work collaboratively. Through Iger’s leadership and management style, employees at different levels at Walt Disney had a sense of purpose that drives their organizational commitment behavior (Dokle 5-6).
Main products and services of Walt Disney
Walt Disney covers diverse products and services under mass media. The company runs media networks, parks and resorts, studio entertainment, Disney consumer products business, and Disney interactive business, which are offered collectively as a retail business and, in some specific instances, as business-to-business services. Its media networks include broadcast, radio, digital business, which operate under the Disney or ABC television brands. The company also operates the business using the ESPN Inc. entity. Parks and resorts offer global travel destinations for families, corporate teams, and individuals looking for a recreational destination with an affordable fun package. The company runs a studio entertainment business to sustain its other business, where it develops and sells content for traditional and digital media channels. It then offers merchandise with specific Disney themes that complement its existing businesses and provide it with avenues for penetrating new markets.
Duration of the business
The company has existed since 1923 when its founder Walt started the Disney Brothers Studio. The business went on to expand due to increased numbers of customers and acquisitions of other businesses along with the business interest of the founding entity. For example, the company purchased ABC Television Network because a majority of its shows were already showing on the network. It made business sense at the time to own both the content and the channel for delivering the content to consumers. This move allowed the company to be the direct recipient of advertising and subscription income for its networks. It also increased the influence of the business when negotiating for the rates offered by cable television network companies and digital television channel distributors across the world. The move also gave Disney enough power to package its content for different markets about its business expansion strategy.
Its parks and resort business launched in 1995 to provide a physical attraction related to the themes embodied in the Disney content sold to consumers around the world. This segment of the business continually improves its scope and capacity to allow it to handle millions of guests every year. It competes with traditional holiday and travel destinations around the world. The Disney online division started in 1995. In the same year, the Disney Channel expanded beyond North America to be delivered to European customers. The company opened its California Adventure park in 2001 to improve the offerings of the Disneyland Resort in the area. It also opened the Tokyo DisneySea in Japan under the same business model. Other developments included the acquisition of more channels and the introduction of additional shows under the Disney family. The development of online commerce allowed the company to deliver its popular shows as on-demand content on popular platforms, such as Apple’s iTunes service. The company launched its official Disney fan club in 2009 to take advantage of increased opportunities for customer relationship management. In the same year, it acquired Marvel Entertainment to increase its scope of entertainment content offerings. Disney Junior was launched in the United States in 2012 to offer 24-hour entertainment as a standalone network for TV (The Walt Disney Company para. 4-8).
Public/private status
Disney operates like a public company by allowing people to become its shareholders. The company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange.
Financial outlook
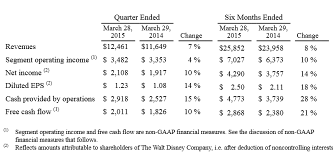
In the second quarter of 2015, the company reported a marginal increase in revenue compared to a similar period in 2014. It had 12,461,000 dollars as the reported revenue figure for 2015, which is higher than the 11,649,000 reported in 2014 for the first quarter. The diluted earnings per share were 1.23 for 2015 against 1.08 for 2014. The company attributes the decrease of its earnings per share from its earlier target to a turbulent operation environment in Venezuela. The company had a contract dispute that led to foreign exchange valuation losses.
A breakdown of earnings in the five business segments of the company for the first quarter of 2015 in comparison to the first quarter in 2014 reveals the following results: Overall, the media networks segment witnessed an increase in revenue of 13 percent while the segment operating income decreased by two percent. Parks and resorts’ revenues increased by 6 percent, while the operating income for the segment increased by 24 percent. In the studio entertainment segment, revenues decreased by 6 percent and the operating segment income lowered by 10 percent. Revenues increased by 10 percent in the consumer products segment, while the segment operating income increased by 32 percent. Finally, revenues lowered to 12 percent in the interactive segment, while the segment operating income increased by 12 million dollars (Walt Disney 2-4).
Strategic analysis
Analysis of the mission and vision
Disney aims to be the leader in its industry. It uses its portfolio and brands to achieve the objective. The employees of the company face the goal of protecting the company’s brand throughout its operations around the world. An analysis of Disney’s mission statement reveals that there is limited mention of customers, technology, philosophy and concern for the public image. Nevertheless, a deeper analysis reveals that the aim of being the top producer and provider of entertainment is an indicator that the company is focusing on its core business, which relates to the fulfillment of customer needs. It is also providing space to embrace technology in its quest to become the best. Moreover, the company has to pursue a strategy of delivering entertainment and must, therefore, have a philosophy, even though it is not explicitly captured in the mission statement. Its vision is to make people happy, which captures the philosophy. In this regard, the recommendation is for the mission statement to include the wordings of the vision and complete the necessary nine components of a good mission statement (Kapferer 59).
An external assessment
General Discussion
The critical success factors for Disney are advertisement, management, market share, global expansion, financial position, product quality, price competition, and revenue. The company has to improve in all the above aspects for it to enjoy sustainable competitive advantages. Currently, it can compare its performance to its closest competitors, which are Time Warner and CBS. They serve most of the market segments also targeted by Disney (Walt Disney 5).
EFE Matrix
Based on the matrix above, the company has a positive score of 2.34, which implies that it has been capable of using its opportunities to address all the concerns facing it as threats. Therefore, it has positive prospects for growth.
Competitive profile matrix
The following table shows the competitive profile matrix of the company.
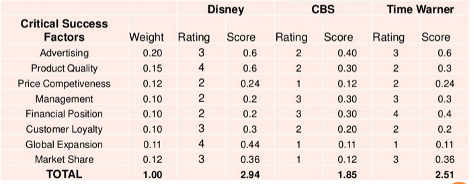
The major competitors of the company include CBS and Time Warner. The table reveals that Disney enjoys a favorable competitive position, but it has to increase its efforts to ensure that the advantages are sustainable.
Internal Assessment
General discussion
Disney has a flat organizational structure, where the CEO and other executives are at the same level. However, each office position has different duties, including the coordination of other office duties by the CEO. The company also differentiates the corporate organization structure and the business organization structure.
Strengths & Weaknesses
IFE matrix
Currently, Disney is pursuing the following marketing strategies to help it achieve its business objectives of having a rapid market growth and strong competitive position. First, the company is developing more products to deliver to current markets. It is looking for more acquisitions to increase its channel distribution advantage and counter competitive pressures in its business areas. It is also diversifying into digital content creation, advertising, and distribution. The company is also embracing vertical and horizontal integration within its corporate structure. The company has continued to release new stories and introduce new characters (Walt Disney 4-6).
BCG Matrix
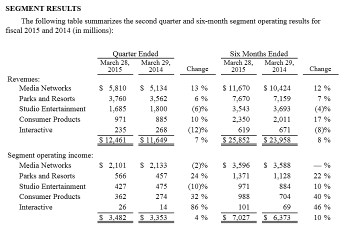
The analysis of the performance of the five main business units of Disney at this stage reveals its most profitable units. The results of the BCG matrix also show potential growth areas. The company can see that none of its business units is raising question marks about its validity as part of the Disney business. On the other hand, there is a tight contest between best performing units in terms of growth and contribution to the business, and sustainable units in terms of consistent revenue increases to deliver overall business growth. The biggest winner, the cash cow, is media networks with high revenue and relative market share. On the other hand, studio entertainment comes last because of reduced revenue and operating income. The matrix follows six-month segmented financial results presented in the appendix section. Although “Interactive” has a substantial increase in operating income, which points to the potential market growth rate as high, it has a drop in revenue. This implies that there are questions to be asked about its efficiency and causes of increased costs of operations.
Table 3: Disney BCG Matrix.
Decision-making
Primary concerns
The main concerns of the business are employees, growth of its portfolio, the profitability of the portfolio, and penetration of new markets (The Walt Disney Company para. 3-7).
SWOT Matrix
Based on the above SWOT matrix, several important details arise concerning the evaluation of the Disney business. The company has a wide range of products and strategic business units that allow it to cover many market segments at the same time. Thus, it can capture diversified sources of revenue and any other opportunity for a business that comes up. The company has a robust asset to power its growth, given the significant audience reach of more than a combined 500 million subscribers. Its brand reputation is also a contributing factor to its success. The business has cultivated the brand for more than 90 years. Also, the previous and current leadership has demonstrated sufficient aptitude in making acquisitions that increase the scope of the business, without becoming a cost burden. This includes the acquisition of Marvel Entertainment in 2009, which has become an important business segment that increases the relevancy of the business in the highly competitive entertainment industry. With diversified businesses as a strategy, Disney can grow in four different directions and enhance its creativity due to the mix of different employee backgrounds and roles together with the matching of content to localized demand (Walt Disney 6).
Key weaknesses for Disney are as follows. It is relying heavily on the business performance of North America. All its networks, parts, and other businesses are most successful in North America. Therefore, the company will be badly exposed financially when the market suffers external shocks. Acquisitions alone will not deliver long-term growth. Therefore, its leadership has to consider other avenues for growth that may not be as lucrative as acquisitions. Also, the size of the company exposes it to various government controls against monopoly practices.
As for opportunities, the company has a rich heritage that it can capitalize on to attract the best talent in its respective industries. It can also sustain its current structure and concentrate on increasing its efficiencies so that it retains its highly profitable business. This will also make it relevant as a strategic partner to local authorities keen on improving their tourism markets and fiscal revenues. Disney can provide special rates for institutions like schools for its various products to increase the reach of its business. A growing trend exists in the paid TV industry through traditional and digital media, especially in emerging economies. The company can increase its presence in these markets and capture the trend with significant investment whose return will be realized in the short-term period. It can also launch into novel markets. With the development of sufficient capacity for movie and television content production capacity, the next frontier for growth in the business will be localized production and internal partnerships with movie and television content. It will be easier for the company to proceed with a strategy of introducing new characters and movies or television shows centered around other locations in the world, given that the Disney characters and Marvel characters have global recognition. This step will improve the recognition of the company as a global entertainment business catering to the needs of consumers beyond its North American stronghold.
The main threats for Disney are as follows: There continues to be intense competition in the general entertainment industry. The increase in global household incomes due to the emerging, strong economies leads to an increase in demand for entertainment. Many companies have discovered this trend and are making inroads into the industry by being innovative and coming up with hybrid business models. It is difficult for a company like Disney to embrace new trends fast because it has very large management and leadership team. In this regard, an increase in competition will always be a threat that the business has to consider in every strategic move. The media, tourism, parks and resorts industries already have several major international players and various local players for every market covered by Disney. The challenge is to exist profitably on the competitive landscape. Also, online platforms reduce the barriers to entry for new companies, which pose a bigger competitive threat to the Disney business empire. Moreover, smaller companies can rival them in specific business segments. Overall, Disney has to consider actions by major competitors and pay attention to the collective action of many small rival companies.
Another threat is the increase in piracy globally due to the high penetration of broadband internet and laxity in law enforcement and legislation. The company has insufficient capacity to deal with the terrorism threat in emerging markets, where high-income households are fewer compared to the developed markets. Cost is the main influence of piracy (Karaganis 10). Besides piracy, an increase in broadband Internet penetration is also fuelling a strong growth in online TV and online movie renting across the developed markets in the world. Many people are opting to rent content online, instead of purchasing DVDs or going to cinemas. Therefore, the business has to establish strategies that allow many people to buy or rent its content with ease in the various platforms that they prefer or face the risk of losing customers. The younger population is used to content-on-demand, which is a business model that also threatens Disney. Many independent TV networks can gain entry into the market and serve customers with high-quality content to rival Disney.
SWOT conversion matrix
Table 2: SWOT Conversion matrix (Source: Author)..
The SWOT conversion matrix above presents several strategies that are open to Disney. The company is free to pursue any of them, and each has several strong and weak points. The current strategy of the company’s leadership is to follow a combination of ST and SO strategies. This involves market development and increases in management competencies. Also, the increase in management competencies leads to an increase in product development that drives the growth of the company. In a way, all strategies are related. However, as outlined above, the major strategies followed are market development and better management of costs and development of the business.
Evaluation of alternative generated long-term objectives and corporate strategies
The company has three long-term targets that support its overall business strategy. The first goal is to have zero net greenhouse gas emissions, which implies that the company does not want to continue being a polluter of the environment. This is in recognition of the fact that consumers around the world are becoming conscious of the products they consume and their impact on the environment. The company has set the year 2020 to achieve its environmental strategy. It hopes to have reduced its emission by half of the overall figures that it recorded in 2012. This is a substantial objective because it forces the company to be innovative and seek control of its supply chain and distribution chain. It also calls for Disney to consider growth opportunities that reduce its overall impact on the environment (Hill, Jones, and Schilling 108).
A second longer-term objective of the company is to have zero waste, which matches the overall objective of innovativeness. The other long-term objective is to conserve water resources. These objectives are only environmental and ensure that the company can keep up with consumer expectations or regulatory requirements about sustainability. In retrospect, the above SWOT analysis presents new prospects for the company, with the recommendation being a combination of ST and SO strategies. The company has a strong internal position, where it has high liquidity, average working capital, and a good position to return on investment, cash flow, and earnings per share. In terms of competitive advantage, the company is not enjoying a good position in market share, product quality, customer loyalty, and diversification. It must improve the uniqueness of products to ensure that it regains its competitive advantages. Meanwhile, the external position of the company is also threatening and Disney has to focus inwards to sustain current progress in growth and address emerging threats from the environment and competition (Hill, Jones and Schilling 108-111).
Strategic recommendations
Long term overview
The company has to keep being innovative in its business approaches and product development. Fostering the culture of innovation will not come easily. The company has to ensure that its operating environment, organizational tradition, and human resource can deliver innovative solutions and embrace a problem-solving attitude at all levels of the organization. Being responsive is the best way to sustain a long-term strategy. This implies that the company must be open to the option of merging or selling some of its segments if that comes up as a future solution.
Specific long-term objectives and corporate strategies
Create a bottom-up strategic business unit development structure
The company should be able to build from the bottom up with its strategic business units, instead of only having the top management decide on what avenues the company is going to expand. With strategic business units growing independently, the company will be able to capture significant investment opportunities and market growth opportunities that might enhance the company’s portfolio. Therefore, concentrating on product development under strategic business units will fall within the innovative strategy, which should build well to the long-term growth strategy. It will be possible to maintain a vibrant culture with the independent development of business within units. One important long-term strategy is to ensure that the culture of the company remains vibrant, even without the current leadership. Equipping business units to embrace overall creativity within the development framework of the company and respond to localized threats is the best way to come up with a vibrant culture that lasts for long.
Develop an acquisition plan for new business and competencies
The company should continue with its acquisition strategy. This strategy has played well in the quest for Disney to remain innovative. For example, the acquisition of Marvel Entertainment was bringing new business opportunities to the company. It also increased the level of creativity in the overall business as new employees, concepts, and business strategies were acquired. Such moves enable Disney to sustain its build-up of strengths so that it can take advantage of any opportunity that arises and ensure that threats are not very significant to dethrone the company from its global leadership position in the entertainment industry.
Short-term overview
A short-term overview of the company includes the management of the transition from dependence on North American business performance. As Disney moves to other developed countries in Asia and Europe, it must transform those businesses into sources of income. The company must aim for a 30 to 40 percent growth for the next five years. The company has been growing over the last decade, and it should continue to embrace challenges and opportunities to sustain growth. Its project coordination teams must ensure that independent business units can cut costs and increase revenues.
Specific short-term objectives/annual objectives
The best way to sustain short-term growth is to maintain centralized leadership for projects, especially business development unit management and acquisition. Although independent units will be doing the implementation, the top leadership should sustain the operations to prevent drift from the company position.
Develop centralized coordination
Centralized coordination will also allow better utilization of internal resources at the company. Another relevant objective is to ensure that business units and independent subsidiaries compete against each other. Promoting competition is the best way to sustain its growth momentum and ensure that units are innovative in their respective operations.
Elevate strategic business units to embrace own strategic plans
The other objective would be to allow the single business units that have projects with the highest value and revenue generation potential to receive the highest funding from the company. Change management practices will be crucial for the company’s realization of its objectives while doing this. The changes introduced at the local or global level can affect the company negatively, given the many business areas to focus on. It is important to keep the employees motivated to take up change and contribute creatively to the company’s growth. Disney must enhance its corporate innovative culture by including internal and external trainers and expanding the program throughout the organization.
Strategic concerns
The main concerns of the business include the environment, talent sustainability, business ethics when dealing with piracy, and the safety of workers and operations. These concerns will be addressed independently, based on their risk profile and collectively within the overall business strategy and objectives highlighted in this report. The company has to rely on leadership and management training to ensure that the execution of its overall corporate strategy goes as planned, which will lead to a minimization of most of the strategic concerns highlighted here.
Evaluation tools
The strategic business units can become its evaluation centers, given that Disney already realizes on four key areas of operation to grow its business. Also, the company will require a net benefit analysis of its investments from the onset of its short-term and long-term strategic plans. The company will look at the return on investment as an indicator of its performance. It will also look at its share price to determine investor sentiments about its business performance. Moreover, the profit and loss account of the company, prepared annually will provide a financial evaluation of the performance of the added investment or acquisitions by Disney. Also, the use of the overall balance sheet of the company will indicate the growth in assets of the business and reveal opportunities for using its assets to fund growth and provide security for future financial support. Lastly, with a triple bottom line approach, the company will be able to determine its contribution to shareholders, stakeholders, and consumers as it grows its business. Besides, it should also look at its objectives and goals before the start of the strategic development period and determine whether it has achieved them at the end of the period.
Control mechanisms
The top leadership will provide overall management and supervisory resources for the business. Meanwhile, each business unit will operate on specified budget allocation. Therefore, funding for businesses will determine the scope of operations that they can engage in. Also, human resource management departments in respective departments will be tasked with employee conduct during the program delivery period. Managers and supervisors at all levels of the organization must play their supervisory roles. It means that there will be top-down communication of goals and objectives, as well as strategies. In return, there will be bottom-up communication and reporting of progress to ensure that there is accountability. The company will provide support based on delivery of objectives in phased business development initiatives, rather than deliver funding based on total project estimates.
Works Cited
Dokle, Eda. “Walt Disney: CEO and Supervisory Board.” 2012. Web.
Hill, Charles, Gareth Jones, and Melissa Schilling. Strategic Management Theory: An Integrated Approach. 11th. Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning, 2014. Print.
Kapferer, Jean-Noël. The New Strategic Brand Management: Advanced Insights And Strategic Thinking. London: Kogan Page, 2012. Print.
Karaganis, Joe. Media Piracy In Emerging Economies. New York: Social Science Research Council, 2011. Web.
The Walt Disney Company. “Disney History.” 2015. Web.
Walt Disney. “The Walt Disney Company Reports Second Quater and Six Months Earnings for Fiscal 2015”. Web.
Appendices