Operations management is concerned with effective utilization of human, financial, energy and any other type of resources. It is the process by which businesses manage input and efficiently convert it to expected output. The output must be impressive to the investors and must meet the customers’ expectations. The process must be close enough to the senior management to ensure it is well facilitated and supported.
Exxonmobil produces more than 3% and 2% of the world’s oil and energy respectively. Its subsidiary is Nigeria has operations ranging from crude oil extraction, to fuel production and transportation, to other operations related to ensuring oil reach the intended markets. Competition is a significant challenge for the business as more investors come aboard. The challenge creates the need for continuous quality improvement.
This paper analyzes operations management tools and techniques that will allow Exxonmobil Nigeria achieve its quality improvement objectives. Process design and mapping is discussed as a tool to achieve quality improvement in design, delivery will include capacity and inventory management and development will address quality management. Already implemented quality improvement techniques in the company have also been discussed.
Introduction
Nigel et al. (2009), defines operations management as “an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing and redesigning business operations in the production of goods and/or services”. Operations management is concerned with effective utilization of human, financial, energy and any other type of resources. It is the process by which businesses manage input and efficiently convert it to expected output. The output must be impressive to the investors and must meet the customers’ expectations. The process must be close enough to the senior management to ensure it is well facilitated and supported.
“The best avenues for driving a business’ performance gains is managing the implementation of its processes” (Winser and Keah, 2008). Identifying the key processes in a business is the first and most fundamental step for any company planning to execute their operations management strategy. Operations management is only productive if the results will be aligned with the company’s strategic objectives. It also becomes efficient when a business ca identify and work on its major processes. Key business processes are easily identifiable by their level of impact on the success of a company. They are those processes whose success or failure has serious implications on a company’s goals and revenues. For a business to be successful, their implementation and management has to be given priority and has to be right. They should also be specific to an organization’s unique policies, goals and approach (Wells, 2000)
Operations management in Exxonmobil
Background of the study
“Exxon Mobil Nigeria is a subsidiary of Exxon Mobil Corporation, an American global oil and gas company” (Exxonmobil, 2011). The company produces more than 3% and 2% of the world’s oil and energy respectively. The company’s business includes crude oil extraction, fuel production, transportation and other operations related to ensuring oil reach the intended markets. Its upstream operations are categorized into exploration, development, production, gas and power marketing, research and other ventures in the energy industry. Operations management in the business is applicable in all the departments and operations. Key processes included in operations management include exploration, research and development, procurement, transportation, just to mention a few. This paper will address quality improvement through design, delivery and development.
Operations management strategic role in an organization
Operations management plays a significant role in any business, especially the manufacturing industry. Exxonmobil uses operations management to ensure efficiency and effectiveness are achieved in its key processes. Through its activities and investments, the business ensures that investors get value for their money and profits are maximized.
By utilizing operation management and its tools, the company is able to reduce the cost of production, minimize waste and ensure everyone manages their roles responsibly. “One way through which business benefit from operations management is by using minimum resources to achieve maximum output” (Tomar, 2009). Exxonmobil has adopted several operations management tools such as delegation ,budgeting and feedback to maximize output.
Operations management also plays a crucial role when an organization is adopting a new idea, providing support for it and finally implementing it into a product. For Exxonmobil, the energy industry is constantly changing and there are demands for new innovations and ideas every day. By using operations management such as Total Production Management and its pillars, the organization is able to adopt an idea and perfect it as they incorporate it into the business.
Another significant role played by operations management is organization, training and retaining human resources. Operations management allows a business have a well planned and organized strategy to access the best talent in the market and utilize it by ensuring maximum productivity. Exxonmobil Nigeria is a big company and being in a country where population is high, managing the number of interested employees can be a challenge. It is through operations management that the company is able to control and coordinate labor related programs.
Quality improvement in Exxonmobil using operations management
Process design and mapping
As explained by Exxonmobil (2011), “the oil industry handles hazardous fluids and gases through a variety of processes”. As a result is paramount that process design takes into consideration safety, environmental threats and operation integrity. Factors that the process must confirm are whether the appropriate raw materials are being supplied to the system and whether there is respect for quality. Accessibility, energy utilization and technology play an important role during process design.
“Management control and coordination functions cannot be forgone in big processing companies” (Nigel et al., 2009). Exxonmobil relies heavily on technology and design to stay ahead of the competition. “A poorly designed process fails as market needs and expectations are not met” (Tomar, 2009). Any business that cannot link their design and delivery is bound to be disappointed in the market. By realizing this, many business today invest heavily in ensuring that they deliver quality through well enabled process designs.
Design takes into consideration many factors, the most important being cost. The role of operations management in process design is ensuring that appropriate plants are implemented and their manufacturability is possible. It addresses research and development, understanding market needs, creating the designs, evaluating and testing them, prototyping and finally the implementation.
Another significant role of operations management in process design is managing inventories during the process, standardization, managing quality and ensuring reliability. “Before and during the implementation of a new process, a business must be able to perform a value analysis on its output, evaluate its utility, esteem value and market value” (Sheldon, 2006). Exxonmobil Nigeria recently announced the launch of two new products that have done tremendously well in the markets. According to the business, like many of its products, the Mobil Pegasus 805 and the DTE 800 Series have had an impressive reception in the market (Exxonmobil, 2011). The company attributes the trend to professional design and implementation of new technologies that guarantee satisfying output.
Process mapping can be achieved by following four basic steps illustrated below:
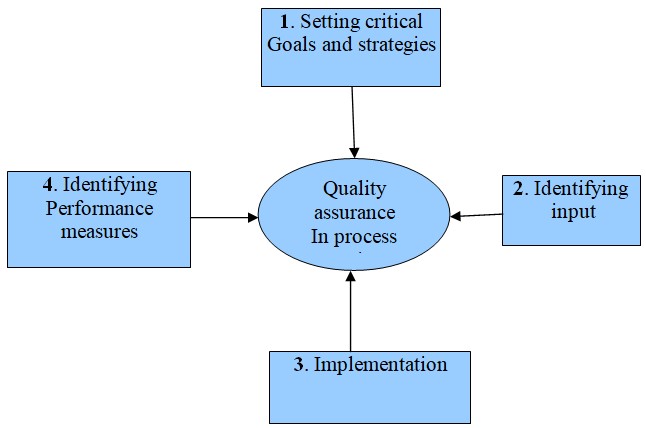
Delivery
Competition is an enormous challenge in Exxonmobil. Staying ahead requires quality and cost delivery measures that allow the business to develop key performance indicators and continuous improvement in quality. This can be done through capacity management, inventory management and lean operations.
Capacity management
“Capacity management is the process used to manage information technology to ensure that it meets current and future business requirements in a cost-effective manner” (Sheldon, 2006). Capacity management involves performance analysis, implementing monitoring measures and tools, capacity planning and understanding the needs of present and future workload of a business and its anticipated growth. Supporting tools for the process include performance engineering and other input management systems.
Performance analysis and tuning act as correctional measures in capacity management. These two processes influence quality in any capacity management process, and many times influence the duration taken to accomplish different tasks and projects. Network performance supports capacity management by breaking data and information into usable components that can be easily transmitted to relevant teams.
Inventory management
“Despite a weakening economy in the recent times, Exxonmobil is among the few companies which have been able to maintain a fast inventory turn over rate” (Winser and Keah, 2008). The company’s wide clientele requires that the business be able to understand everyone’s quality expectations and delivery what is acceptable to everyone. Inventory management therefore play a significant role in managing quality, and is not easy for a company such as Exxonmobil Nigeria. The business manages its inventory by a well established market research and survey system. Having up-to-date information on markets allows the company identify specific market needs.
By having enough market information on consumption levels and consumers’ preferences, the company is able to save on the cost of returning or transferring products from one market to the other when they don’t sell in one region. It also saves it the cost of warehousing products which are experiencing a slow movement in a certain market. Any cost of damaged or stolen inventory is minimized, as well as the cost of time spent on managing the inventory (Keong, 2000). The result is more savings that can be directed towards improving quality.
In quality improvement, inventory management allows the business access and deliver raw materials and other inputs at the right time and amounts. Since Exxonmobil outsources some of its manufacturing operations, its inventory management system has to be inter-linked to the manufacturers and constantly monitor quality. They are also able to advice the manufacturing companies on what consumer expectations and help them implement relevant adjustments.
Markets study is an important part of Exxonmobil’s inventory management. It gives the organization an understanding of consumption trends. For example, people are likely to consume more fuel and energy products during the festive seasons and quality may be easily compromised during bulk product. Understanding these trends makes it easy for the company to adjust its production, purchasing and selling plans, to suit the market activity at a particular period.
Today, technology makes it possible to manage inventory more easily using inventory software. Software companies have been able to come up with a software which gives such companies an integrated inventory management and control. “Exxonmobil’s inventory management technology allows an end-to-end procure-to-pay process that gives the business a competitive advantage” (Exxonmobil, 2011). As a result, the company has an in-depth view of their market activities and consumer expectations.
Lean operations and supply chain solutions at Exxonmobil
“Value chain transformation enables the energy companies keep their production going, provide energy for the markets and save money” (AIT Group, 2011). Exxonmobil Nigeria has been working with the AIT group to help them implement total production management and continuous improvement programs at their drilling and oil manufacturing plants. The project’s main focus is to improve quality. The groups has done this by helping the organization increase productivity, minimize waste and time taken for the cycles.
According to AIT Group (2011), “value chain transformation overcomes process and technical challenges inherent in complex processes”. The company’s objective is to impact the global energy industry by making a contribution towards energy security and push quality levels to perfection. Exxonmobil Nigeria is among the few companies in the region to fully implement the lean and six sigma improvement process. Other production management tools that the company has implemented for better operations management include kaizen, the 5s and quality management.
Development
Quality management
Sheldon (2006) explains that “quality management addresses four main components; planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality improvement”. It focuses on both the end product and the means by which quality is achieved in it. In the recent past, Exxonmobil has had to deal with quality problems related to environmental performance and spill prevention, especially after the recent BP tragedy.
To address this, the company is required to adopt several principles that can be used to guide it to the highest quality level. These principles include customer focus, appropriate leadership, involving all the stakeholders, strategic management, well-informed decision making, continual improvement and a beneficial relationship with suppliers and distributors.
Exxonmobil has been able to adopt some of these principles by implementing different quality management tools. Among the highly prioritized tools are ISO certification, quality function deployment, total quality management, business process engineering and zero defect programs. The company has integrated these tools with knowledge, expertise and financial investments to ensure results.
At a day and age when markets are demanding new quality standards every day, the company requires tools and techniques that ensure continuous improvement and consistency. To address these challenges, the company needs to implement tools that allow it to anticipate the needs of the market through real-time feedback from the markets.
Among the tools that the business can use include Kansei Engineering, which according to Sheldon (2006), “is an approach that focuses on capturing customer emotional feedback about products to drive improvement”. Another significant technique in quality management is Taguchi methods which will allow Exxonmobil achieve target specifications and a robust quality tradition. Of great importance for the business is implementation of quality standards such as quality management system and quality scorecards to ensure a productive quality exercise.
Conclusion
In the recent past, Exxonmobil has had to deal with quality problems related to environmental performance and spill prevention, especially after the recent BP tragedy. “Quality management addresses four main components; planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality improvement” ( Sheldon, 2006). It focuses on both the end product and the means by which quality is achieved in it.
Operations management offers different industries a well defined structure to address strategic development challenges. To ensure quality improvement and consistency, Exxonmobil can adopt several principles that can be used to guide it to the highest quality level. These principles include customer focus, appropriate leadership, involving all the stakeholders, strategic management, well-informed decision making, continual improvement and a beneficial relationship with suppliers and distributors.
In Exxonmobil, operations management plays a significant role. The company uses operations management to ensure efficiency and effectiveness are achieved in its key processes. Through its activities and investments, the business ensures that investors get value for their money and profits are maximized. By utilizing operation management and its tools, the company is able to reduce the cost of production, minimize waste and ensure everyone manages their roles responsibly. Exxonmobil has adopted several operations management tools such as delegation ,budgeting and feedback to address quality standards.
To achieve continuous improvement, the business needs to focus on capacity management, its lean operations strategies, quality management techniques, inventory management and capacity management. Supporting tools available for the business include quality function deployment, total quality management, business process engineering and zero defect programs, just to mention a few. Integrating them with knowledge, expertise and financial investments will ensure the business continuously invests in its quality and stays ahead of the rest.
Technology is important for effective operations management. “Technology influences management and workforce in organizations by analyzing production, resource impact, routine to non-routine operations, structure impact, industry impact and work impact as well” (Winser and Keah, 2008). It allows the managers together with the work force match the resources available with technology through different approaches. The management is able to run operations more easily by changing techniques and processes to better and modern ones.
Finally operations management would not be complete without putting in place performance measures. These measures should be a continuous process to help an organization establish what is working and what is not at an early stage. They also help an organization identify where to make improvements or put more investment. Performance measurements include scheduling operations and setting targets to ensure implementation of key processes is done on time.
References
AIT Group, 2011. Lean six Sigma at Exxonmobil. Web.
Exxonmobil, 2011. Taking on the world’s toughest energy challenges. Web.
Keong, L., 2000. Capacity Management Best Practice Handbook. New York: Routledge Publishers.
Nigel, S. et al., 2009. Operations & Process management: Principles and practice for strategic impact. New York: Prentice Hall.
Sheldon, D.H., 2006. World class sales & operations planning: A guide to successful implementation and robust execution. Florida: Ross Publications.
Tomar, R., 2009. Commercial operations management: Process and technology to support commercial activities. New Delhi: Global India Publications.
Wells, S., 2000. Choosing The Future: The Power of Strategic Thinking. Boston, Mass: Butterworth-Heineman.
Winser, J. and Keah, T., 2008. Principles of Supply Chain Management: A Balanced Approach. Mason, OH: South-Western Cengage Learning.

