Employee engagement has been found to be positively linked to business and organisation success. Employee engagement is a concept used to describe the connection between employees and organisations (Singh et al, 2016). Employee engagement is the force through which employees feel zealous and excited towards their jobs and their organisations. The relationship between employee and employers is considered as transactional, employees get paid for the work they do for the organisations (Roukolainen et al, 2018). Employee engagement takes the transactional relationship to the next level by formulating and implementing strategies to make employees feel passionate about their organisations and have emotional aspect in the transactional relationship. Shuck et al (2017) describes employee engagement as a force through which employees are drawn emotionally towards the organisations for which they work in order to work towards getting positive work outcomes. Employee engagement makes employees go beyond their basic duties and also show creative, innovative and motivating behaviour which becomes the foundation of an efficient working environment. Employee engagement strategies makes the employees less stressed out and depressed even in the stressing times which make them a valuable asset for the company (Anthony-McMann et al, 2017).
Business Excellence is referred to as approaches and strategies which result in excellence in all the business functions and activities as well as performances which determine the overall organisational efficiency and effectiveness (Dubey, 2016). Business excellence is a concept which guides the organisations towards achieving high quality performance in all the areas which affect the final performance of the organisation.
This research aims to study the effect of business excellence on employee engagement in government and semi-government organizations in the UAE. The research aims to conduct empirical research through a survey research to determine whether business excellence strategies and approaches impact on the employee engagement.
Importance of the Research
Employee engagement is significantly important for the public sector because of the inherent demotivating behaviour and workplaces as well as unwillingness of employees to engage in extra activities leading towards improved performance (Singh et al, 2016). The employees in public sector are known for their poor performance, lack of motivation, inability to connect emotionally with the organisation and invest long term in the organisation and its success (Chandani et al, 2016). This makes the concept of employee engagement imperative for public sector since government organisations and departments can improve employee performance and productivity through implementing measures leading to improvement in employee engagement.
Public organisations in UAE are working towards achieving business excellence through adoption of relevant approaches (Lasrado, 2017). Since the employee motivation and performance is highly desirable by public organisations, the study will provide key insights into the effect of business excellence adoption on employee engagement in government and semi-government organisations in UAE. The research will theoretically and practically contribute towards the area and will provide government and semi-government organisations in UAE the information about the link between business excellence and employee engagement. The organisations can benefit from the research for improving their employee engagement and thus overall organisational performance.
Problem Statement
Although UAE Government and semi-government sector provides better compensation and benefits to the employees, the employee turnover rates have been reported to be higher in the public sector in UAE (Jabeen et al, 2018). The employees in the public sector in the country are found to be lacking the motivation to continue with their jobs in the long term which affect their engagement levels (Jabeen et al, 2020). According to Jabeen and Isakovic (2018), public sector in UAE is characterised by specific culture which leads to dissatisfaction amongst employees and leads to higher turnover rates. The government sector in the country is found to be actively implementing business excellence programs which have proven to increase employee engagement from the previous researches and thus reducing employee turnover. The effect of business excellence programs are thus needed to be evaluated on the employee engagement in the public sector in the UAE.
Research aims and objectives
The aim of the research is:
“To study the effect of business excellence on employee engagement in the government and semi-government sector in the UAE.”
The research objectives of the present research are:
- To study the business excellence practices of government and semi-government sector in UAE’
- To explore the links between business excellence and employee engagement in the government and semi-government sector in the UAE;
- To identify if employee engagement can be increased by implementing business excellence programs in the government and semi-government sector in the UAE.
Purpose of the Research
The government and semi-government sector in the UAE are found to be implementing business excellence programs actively. This research studies the impact of business excellence on employee engagement to determine whether business excellence can increase employee engagement and make them more loyal to the organisations thus decreasing the employee turnover.
Research Questions
The research questions the present research aims to answer are:
- What are the major business excellence practices adopted by the government and semi-government sector in the UAE;
- Does the business excellence positively affect the employee engagement in the government and semi-government sector in the UAE;
- What impact (positive or negative) does business excellence have on the employee engagement in the government and semi-government sector in the UAE.
Research Hypotheses
The research aim to test the following hypotheses:
- Employee engagement has a statistically significant influence on the adoption of business excellence practices.
- Demographics (age, education, job role) have a statistically significant influence on employee engagement.
Literature Review
This section provides the review of the previous literature on the area of business excellence and employee engagement with the aim of forming a theoretical underpinning for the present research. The literature review discusses the concept of business excellence and business excellence models and approach before exploring business excellence practices in government and semi-government sector in general, effect of business excellence on employee engagement and business excellence practices in the UAE.
The concept of Business Excellence
The growing competition in the globalised world has led to significant increase in the popularity of business excellence all over the world (Sampaio, et al, 2012). Business excellence, also referred to as organisational excellence and total quality management (TQM), is a set of well-coordinated and well-aligned activities in the organisations aimed at improving the financial and non-financial performance and outcomes of the organisation (Mallur et al, 2012). Business excellence and quality management has been used interchangeably by previous researchers and the definitions of both were found to convey the aspects of achieving total improvement in all areas of the business to achieve higher level of stakeholders’ expectations (Dubey, 2016).
The concept of business excellence has existed since more than 25 years and has been growing to gain attention across the world because of increased competition and globalisation (Carvalho et al, 2018). Business excellence and quality management are found to be linked since excellence is rooted in the management of quality at all levels of the organisation thus leading to achieve total quality. Business excellence helps and guides organisations to be proactive in today’s fast changing environment through adopting innovative and technology based approached with the aim of becoming superior from the competitors and provide higher satisfaction to customers and other stakeholders (Israr, 2018).
Business excellence programs are straightforward approaches and techniques planned and implemented organisation-wide to ensure efficiency and effectiveness at every level ensuring that all functions, departments, processes and procedures are well-aligned to achieve excellence (Samawi et al, 2018). According to Toma and Naruo (2017), the business excellence concept is an umbrella term for all the activities implemented with the aim of improving products, services, production, processes and procedures so that the higher level of customer satisfaction is achieved and the organisations in turn become more profitable. The business excellence and quality management practices fulfill the explicit and implicit expectations of all the stakeholders and thus increasing total value of the business (Dawabsheh et al, 2019). Various business excellence and TQM models have been proposed in the researches guiding the organisations to implement excellence strategies (Thurer et al, 2018). More than 100 excellence models have been documented during the past years providing strong theoretical foundations to organisations interested in adopting business excellence (Samawi et al, 2018).
Business Excellence Models and Approaches
Various business excellence models and approaches have been proposed over the past years which determine the key factors in implementing the business excellence models. Some key business excellent models and tools are EFQM (European Foundation for Quality Management), Japan Quality Model, Australian Business Excellence Framework, Lean Management, Quality Management Systems, Lean Management, Total Quality Management and Malcolm Baldridge. The models, tools and approaches identify the factors which need to be addressed to achieve excellence by organisations and help them achieve higher performance. The key factors identified by the model to achieve business excellence can be summed into, leadership, process management, customer focus, valuing employees, innovation and creativity, corporate social responsibility, ethics and transparency, achieving financial success, knowledge management and delivering value to all the stakeholders (Toma and Marinescu, 2018).
Although each model takes different approach towards achieving excellence, the aims of the models remain considerably similar. The business excellence models guide the organisations to achieve better financial and non-financial performance, help in creating a visionary leadership, identify ways for innovation and creativity, improve customer service, increase productivity and improve employee engagement (Toma and Marinescu, 2018).
Business Excellence practices in the Semi-government and Government sector
The semi-government and government sector have been noted to implement business excellence approaches all over the world (Pimentel and Major, 2016). The semi-government and government sectors have been known for their inefficient traditional practices affecting their performance and the dissatisfaction of the stakeholders. The business excellence and quality management approaches have provided a potential solution to the public sector on improving their performance as well as reducing the costs (Altamony, 2017). The business excellence and quality management particularly gained attention from researchers and practitioners over its potential to completely transform the public organisations through continuous improvement, knowledge sharing, cost reduction, process re-engineering and thus increasing reliability and creditability of the public services (Rodgers et al, 2019).
The difference between private sector and public sector adoption of excellence approaches the absence of profit factors in the government sector as well as the lack of personal interest which cause the government organisations resist the adoption and implementation of excellence programs (Saraiva, 2019). The sense of urgency and the leadership commitment provide the necessary impetus to the public organisations to adopt the excellence approaches and once adopted, the outcomes provide the basis for the continuation of the excellence programs in the long run (Paraschi et al, 2019). The driving forces thus found for the public sector to implement the excellence approaches are different as compared to the private sector making the excellence adoption a distinctive practice in the government sector.
The government and semi-government organisations find themselves under pressure from increasing expectations of the public and customers to improve their processes and services. The need to respond to fast changing internal (like employee competencies, technological capabilities) and external environment (market pressure, increased competition) cause the government and semi-government organisations to adopt business excellence practices to become agile and high performing organisations (Metaxas et al, 2019). Public organisations all over the world are found to be implementing business excellence practices and achieve performance improvement through synergistic relationships, process re-engineering, waste reduction, self-evaluation, knowledge sharing, change management, efficient management of resources and other similar approaches which result in achieving total excellence in all the areas (Adamek, 2018). The approaches and strategies are not generally applicable to organisations and there is a need to customise the approaches on the basis of the size, context and environment of the organisation. Since the inherent structures and cultures of public organisations are found to be hierarchical and bureaucratic in nature, the implementation of excellence programs in government organisations require major transformations in terms of structure and culture since aspects like open communication, employee involvement, delegation, team work, increased collaboration and better alignment between departments and functions are found to be important pre-requisites of excellence approaches (Samawi et al, 2018).
Impact of Business Excellence on Employee Engagement
As discussed above, the business excellence models and approaches take a holistic view of the organisational performance and aims to address all the factors which impact the organisational success. Since employees are considered to be a key asset for the organisation, implementing business excellence programs involve valuing employees such that to improve their productivity and delivering values to all the stakeholders (Toma and Marinescu, 2018). Business excellence programs have found to improve engagement and reduce turnover rates by creating organisation-wide improvements.
Employee engagement refers to higher degree of passion in employees which make them connect to their organisations better and encourage them use discretionary efforts to perform their duties (Mone et al, 2018). Eldor and Vigoda-Gadot (2017) argue that the topic of employee engagement has received increased attention from researchers and practitioners because of its impact of organisational performance and productivity. Since employees are considered an important asset and high turnover rates are associated with increased direct and indirect costs, it has been found imperative for organisations to engage their employees to reduce turnover as well as make them a valuable asset for the organisation.
Osborne and Hammoud (2017) argue that business excellence and employee engagement have a two way relationship, business excellence improves employee engagement whereas better engaged employees are found to be dedicated to higher quality standards. When organisations implement business excellence programs, there is an organisation-wide sense of achieving excellence and relevant tools and approaches are being implemented including training and development, streamlining the processes, delivering value, top management support and commitment all towards achieving higher financial and non-financial performance. The quality culture makes the employees enthusiastic leading to a positive change in their behaviour. This leads to higher employee engagement (Lasrado and Pereira, 2018). Engaged employees on the other hand go beyond their routine duties to excel in their performance and help organisations achieve excellence through better involvement, productivity and innovation (Domun and Talwar, 2016). A highly engaged workforce do not need constant supervision and is automatically putting efforts in the quest of quality and thus meeting organisational aims of achieving business excellence.
According to Graban (2016), business excellence practices like lean management increase the quality, customer satisfaction as well as employee engagement. Employees are found to connect on a deeper level with the organisations which implement lean practices since employees consider these practices to improve the overall performance. The factors needed to address to achieve business excellence like leader commitment, customer focus, creativity, ethics and transparency and knowledge management cause employees to get involved in the quest of quality because of the overall improvement in the culture. The business excellence models, approaches and tools are found to focus on creating an engaging workforce to achieve the excellence at all levels (Toma and Marinescu, 2018).
Business Excellence practices in the UAE
The UAE has been very advanced in business excellence practices. The country introduced the business excellence awards for the public and private sector more than two decades ago which confirm that the attention given to quality and excellence is not something new in the country (Lasrado and Uzbeck, 2016). The government has been very supportive in the implementation of quality and business excellence programs and encourages private as well as public sector organisations to adopt excellence and provide best products and services to customers. The excellence programs are implemented in both private and public sector organisations in UAE because of a number of drivers. The fast changing environment, tough competition, stricter laws and increased globalisation have caused the organisations in UAE to implement business excellence programs and approaches to ensure that they are able to improve their performance and productivity.
Various excellence awards are being implemented in UAE at federal level and local level. The awards provide the quality frameworks to be implemented by private and public organisations in UAE and guide them in the adoption of excellence models. The government ensures that the organisations are engaged in excellent customer service and products highest quality products to maintain the overall quality standards high as per the government’s vision.
A government excellence model is implemented by the public organisations in UAE which us evaluated through Mohammed bin Rashid Government Excellence Award (Salah and Salah, 2019). The public organisations are provided with quality framework consisting of three main pillars, vision achievement, innovation and enablers to guide the public organisations in the implementation of excellence. According to AlNuaimi (2019), government organisations in UAE are driven by government policies to ensure the high standards of government initiatives and services with the aim of achieving customer happiness and satisfaction. The federal government organisations implement customer happiness initiative which seeks to achieve highest levels of customer satisfaction through implementing quality management and business excellence practices. Participating in excellence award programs enable the organisations to deploy the award criteria which are based on a comprehensive model to guide the organisations to meet excellence standards. The excellence programs encourage the organisations to implement practices which achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction and thus improving the quality of products and services. The private and public organisations in UAE are guided by the award giving bodies as well as other consultants on the implementation of excellence programs which is the reason of high number of success stories in UAE with regards to business excellence implementation.
Conceptual Framework
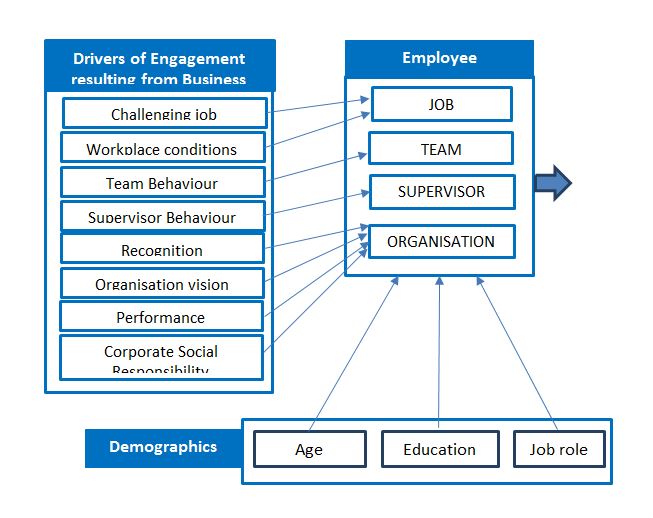
The employee engagement results from various components (Eldor and Vigoda-Gadot, 2017). Since business excellence is a holistic approach aiming for total quality, all the components of employee engagement get affected by the implementation of business excellence programs. The employee engagement components can be grouped into four main categories which get influenced from the business excellence as discussed below:
- Job: A job being challenging and favourable workplace conditions affect the employee engagement positively (Dash and Mohanty, 2019). The business excellence programs ensure that the job tasks become challenging and the workplace conditions are improved to increase motivation, reduce safety risks and create a productive environment.
- Team: Team behaviour affects the employee engagement since it is the immediate group with which the employee works (Gopinath and Saleem, 2019). Business excellence aims to create effective and high performing teams with positive attitudes which influence employee engagement.
- Supervisor: Business excellence creates engaging environment and supervisor behaviour gets directed towards the quest of quality and the employees get facilitated (Meral et al, 2018).
- Organisation: The recognition offered to employees for their work, organisation vision, performance and corporate social responsibility are driven by the business excellence programs which in turn improves employee engagement (Jaeger, 2018).
It is also proposed that demographic factors like age, education and job role affects the employee engagement.
The conceptual framework for the research is developed as follows:
Research Methodology
The research methodology presents the philosophies, approaches, strategies and methods used to gather data and its analysis for a research (Kumar, 2019). Formulating a research methodology is a process through which a research is planned in order to achieve the research objectives. Since a research is done through data, the research methodology essentially explores the options of data collection and analysis and how the process will be conducted to get answers to the research questions.
The first step is identifying the research philosophy. Research philosophy refers to theories and approaches adopted to conduct the research as per the appropriateness (Dougherty et al, 2019). The key philosophies include positivism, interpretivism, realism and pragmatism (Saunders et al, 2015). This research adopts the positivism philosophy which refers to establishing a particular body of knowledge after a thorough analysis and exploration of the relationships between different facts which are already existed in the field (Dudovskiy, 2016). Thus no new knowledge is developed in this approach and the relationship between the existing factors is studied under the positivist philosophy. Since the present research aims to study the effect of business excellence on employee engagement, this approach is considered appropriate.
The next step is identifying the research approach which can be either inductive or deductive. The research approach describes how the research will relate to the theory. If an existing theory is being tested, it is referred to as deductive approach whereas if the data is used to formulate a theory, it is called an inductive approach (Saunders et al, 2015). Since the literature review conducted for the present research has identified a strong effect of business excellence on employee engagement and this effect is being tested on government and semi-government organisations in UAE, the research approach suitable for the present research is deductive approach.
The research method is needed to be selected for the research to identify the data collection and data analysis methods. The research method can either be quantitative or qualitative or a combination of both. Quantitative method is considered suitable for the present research which involves numerical data and its analysis through statistical methods (de Oliveira and Rabechini, 2019). The present research aims to collect data which is numerical in nature and the statistical analysis is done thus making it a scientific method for exploring the effects of business excellence on the employee engagement in government and semi-government organisations in UAE.
The research strategy selected for the present research is survey which is conducted through a data collection instrument i.e. Questionnaire. A Questionnaire is designed consisting of close ended questions to explore the opinions and perceptions of the respondents which are then analysed through the statistical means to determine the relationship between business excellence and employee engagement in government and semi-government organisations in UAE. The questions are multiple choice or Likert scale questions providing a scale to the respondents to provide their answers.
Purposive sample is done for the present research since own judgment is relied upon for choosing the sample of the survey (Etikan et al, 2016). Since the research aims to study the effects of business excellence on employee engagement on semi government and government organisations in UAE, one government and one semi government organisation is selected in UAE and 10 personnel are selected in each organisation in the senior management roles, team leaders, and line managers. This makes the total number of respondents to be 20. The Questionnaire is emailed to the respondents with prior consent and respondents are requested to reply back the filled surveys by return email.
The data collected through the survey is processed and analysed through SPSS which is a statistical analysis tool. The relationship between different variables is analysed and determined through the statistical analysis and the research hypotheses are tested. The data collected through the survey is analysed and discussed to get the answers of the research questions formulated for this research.
The present research considers the ethical aspects of the research by ensuring the consent of the respondents and informing them about the purpose of the research as well as ensuring them about the non-disclosure of their identities and their responses. Moreover, the respondents are informed that the survey results are only used for the academic purposes.
References
Adamek, P. (2018). An investigation of interconnection between business excellence models and corporate sustainability approach. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 7(1), 381-381.
Alnuaimi, H. K. M. (2019). Metrics, indicators and analytics to support government excellence programme:: the case of Dubai Government Website Excellence Model (WEM) (Doctoral dissertation, Aston University).
Altamony, H. (2017). A theoretical perspective view on the relationship between the EFQM excellence model and innovation activities in the public sector in the United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research, 8(2), 902-911.
Anthony‐McMann, P. E., Ellinger, A. D., Astakhova, M., & Halbesleben, J. R. (2017). Exploring different operationalizations of employee engagement and their relationships with workplace stress and burnout. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 28(2), 163-195.
Carvalho, A. M., Sampaio, P., & Rebentisch, E. (2018). Business Excellence Models: supporting the cultural perspective to operationalize excellence sustainability in manufacturing organizations. 3rd North American Industrial Eng. and Operations Management. Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Washington DC, USA, September 27-29, 2018
Chandani, A., Mehta, M., Mall, A., & Khokhar, V. (2016). Employee engagement: A review paper on factors affecting employee engagement. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 9(15), 1-7.
Dash, B., & Mohanty, P. K. (2019). The Effects of Work Environment, Self-evaluation at Workplace and Employee Morale on Employee Engagement. Srusti Management Review, 12(1), 33-39.
Dawabsheh, M., Hussein, A., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2019). The triangular relationship between TQM, organizational excellence and organizational performance: A case of Arab American University Palestine. Management Science Letters, 9(6), 921-932.
de Oliveira, G. F., & Rabechini Jr, R. (2019). Stakeholder management influence on trust in a project: A quantitative study. International Journal of Project Management, 37(1), 131-144.
Domun, R., & Talwar, B. (2016). Evolving a business excellence model based on sustainable human capital resources for Mauritius: a qualitative approach. International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research, 5(10).
Dougherty, M. R., Slevc, L. R., & Grand, J. A. (2019). Making research evaluation more transparent: Aligning research philosophy, institutional values, and reporting. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 14(3), 361-375.
Dudovskiy, J., 2016. The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: A Step-by-Step Assistance, July 2016 edition, eBook Journal of Mixed Methods Research 4(1). pp.6–16
Eldor, L., & Vigoda-Gadot, E. (2017). The nature of employee engagement: Rethinking the employee–organization relationship. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28(3), 526-552.
Etikan, I., Musa, S. A., & Alkassim, R. S. (2016). Comparison of convenience sampling and purposive sampling. American journal of theoretical and applied statistics, 5(1), 1-4.
Gopinath, C., & Saleem, F. (2019). Effect of structuring on team behavior and learning. Journal of Education for Business, 1-8.
Graban, M. (2016). Lean hospitals: improving quality, patient safety, and employee engagement. CRC press.
Israr, N. (2018). BUSINESS EXCELLENCE VIA ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY AND LEAN-AGILE MANUFACTURING. Journal of Marketing, 104. 29(1). 2-24
Jabeen, F., Al Hashmi, M., & Mishra, V. (2020). Should I stay or should I go? The antecedents of turnover intention among police personnel. Safer Communities.19(1). 1-14
Jabeen, F., Friesen, H. L., & Ghoudi, K. (2018). Quality of work life of Emirati women and its influence on job satisfaction and turnover intention. Journal of Organizational Change Management. 27(4). 737-761
Jabeen, F., & Isakovic, A. A. (2018). Examining the impact of organizational culture on trust and career satisfaction in the UAE public sector. Employee Relations.
Jaeger, A. (2018). Achieving business excellence through self-assessment for personal and professional excellence. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 29(13-14), 1612-1632.
Kumar, R. (2019). Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. Sage Publications Limited.
Lasrado, F., & Pereira, V. (2018). Sustaining Business Excellence. In Achieving Sustainable Business Excellence (pp. 231-241). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Lasrado, F., & Uzbeck, C. (2017). The excellence quest: a study of business excellence award-winning organizations in UAE. Benchmarking: An International Journal. 24(3). 716-734
Lasrado, F. (2017). Perceived benefits of national quality awards: A study of UAE’s award winning organizations. Measuring Business Excellence. 24(3). 716-734
Meral, E. L. Ç. İ., Yildiz, B., & KARABAY, M. E. (2018). How burnout affects turnover intention? the conditional effects of subjective vitality and supervisor support. International Journal of Organizational Leadership, 7(1), 47.
Metaxas, I. N., Chatzoglou, P. D., & Koulouriotis, D. E. (2019). Proposing a new modus operandi for sustainable business excellence: the case of Greek hospitality industry. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 30(5-6), 499-524.
Mallur, S., Hiregouder, N. L., & Sequeira, A. H. (2012). The relationship between TQM practices and business excellence in small and medium sized manufacturing enterprises of North Karnataka region. Available at SSRN 2041439.
Mone, E. M., London, M., & Mone, E. M. (2018). Employee engagement through effective performance management: A practical guide for managers. Routledge.
Osborne, S., & Hammoud, M. S. (2017). Effective employee engagement in the workplace. International Journal of Applied Management and Technology, 16(1), 4.
Paraschi, E. P., Georgopoulos, A., & Kaldis, P. (2019). Airport Business Excellence Model: A holistic performance management system. Tourism Management, 72, 352-372.
Pimentel, L., & Major, M. (2016). Key success factors for quality management implementation: evidence from the public sector. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 27(9-10), 997-1012.
Rodgers, B., Antony, J., Edgeman, R., & Cudney, E. A. (2019). Lean Six Sigma in the public sector: yesterday, today and tomorrow. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 1-13.
Ruokolainen, M., Mauno, S., Diehl, M. R., Tolvanen, A., Mäkikangas, A., & Kinnunen, U. (2018). Patterns of psychological contract and their relationships to employee well-being and in-role performance at work: longitudinal evidence from university employees. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(19), 2827-2850.
Salah, S., & Salah, D. (2019). Comparison between the UAE Government Excellence System, Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award and European Foundation for Quality Management model: implications for excellence models. International Journal of Quality and Innovation, 4(3-4), 121-131.
Sampaio, P., Saraiva, P., & Monteiro, A. (2012). A comparison and usage overview of business excellence models. The TQM Journal, 24(2), 181-200.
Samawi, G. A., Abu-Tayeh, B. K., Yosef, F., Madanat, M., & Al-Qatawneh, M. I. (2018). Relation between Total Quality Management Practices and Business Excellence: Evidence from Private Service Firms in Jordan. International Review of Management and Marketing, 8(1), 28-35.
Saraiva, P. (2019). Excellence 4.0 in the public sector: some lessons from the UAE experience. International Journal of Excellence in Government.1(1), 15-17
Saunders, M., Lewis. P. and Thornhill, A. (2015) Research methods for business students. 6th ed. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
Shuck, B., Adelson, J. L., & Reio Jr, T. G. (2017). The employee engagement scale: Initial evidence for construct validity and implications for theory and practice. Human Resource Management, 56(6), 953-977.
Singh, S. K., Burgess, T. F., Heap, J., & Al Mehrzi, N. (2016). Competing through employee engagement: a proposed framework. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management. 63(3). 308-323
Thürer, M., Tomašević, I., Stevenson, M., Fredendall, L. D., & Protzman, C. W. (2018). On the meaning and use of excellence in the operations literature: a systematic review. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 1-28.
Toma, S. G., & Marinescu, P. (2018, May). Business excellence models: a comparison. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence (Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 966-974). Sciendo.
Toma, S. G., & Naruo, S. (2017). Total quality management and business excellence: the best practices at Toyota Motor Corporation. Amfiteatru Economic Journal, 19(45), 566-580.
Survey Questionnaire
Dear Respondent,
I would like to take this opportunity to thank you for your participation in this research.
This Questionnaire attempts to ask the respondents about the impact of business excellence on employee engagement. The research is done for academic purposes, and the findings will not be disclosed to any third party.
If you wish to withdraw from the research, you can quit the survey at any time.
Regards
Section 1. Demographics (Please tick one for each question)
Section 2. Assessment of the Organisation’s Business Excellence Factors
This section is dedicated to the factors that determine a company’s business excellence. It uses the Baldrige model, which consists of seven different elements: leadership, strategic planning, customer and market focus, knowledge management, workforce focus, process management, and business results. For each factor, a set of statements is provided on a 5-point Likert scale. Please read each sentence and select one option for each.
- SD = Strongly Disagree
- D = Disagree
- N = Neutral
- A = Agree
- SA = Strongly Agree
Section 3. Assessment of Business Excellence Factors influencing Employee Engagement
In this section, the factors influencing employee engagement in the workplace are evaluated.
Job-Related Factors
Team Related Factors
Supervisor Related Factors
Organisation Related Factors
Impact of Employee Engagement factors on Organisational Performance
In this section, the impact of factors of employee engagement on organisational performance is evaluated. For each element, a set of statements is provided on a 5 point Likert scale. Please read each sentence and select one option for each.
- SD = Strongly Disagree
- D = Disagree
- N = Neutral
- A = Agree
- SA = Strongly Agree
Section 5 – Feedback
Do you think that the business excellence programs implemented in your organisation (if there are any) positively affect employee engagement?
- Yes
- No
- Don’t know
Please provide feedback about how employee engagement is affected by business excellence programs. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Thank you for your time

