Introduction
Investment is a part of contemporary economic activities. It serves a number of purposes for investors. One of them is the generation of profits (Abdul-Rahman 2010). Investment can be analysed from an economic perspective. To this end, it involves the acquisition of products for future consumption. The acquisitions are utilised at a later date to generate wealth (Brealey, Myers & Allen 2013). The financial sector is characterised by a wide range of investments. It involves acquisition of monetary assets. The investor hopes that the value of their purchase will increase at a later date (Damodaran, 2015).
In this paper, the author will analyse ComfortDelGro Corporation Ltd. The financial and investment portfolio of the company will be reviewed. To this end, the operational activities of the company, as well as its yield curve, will be assessed. In addition, ComfortDelGro’s market risk and performance will be analysed. The paper will focus on the operations of the firm over the past three years. Finally, the beta of the firm will be computed. Based on the findings, investors will be advised on what to do with the company’s shares.
Operational Activities of ComfortDelGro Corporation
ComfortDelGro Corporation Limited is one of the biggest and well established land transport companies in the world. The organisation operates by analysing the global outlook of the business (International directory of company histories 2014). In addition, ComfortDelGro has a strong global workforce and shareholder base.
ComfortDelGro Corporation Ltd. has a number of operational activities. The businesses include taxi, car rental, automotive engineering services, and insurance booking. Other operational activities of the company entail outdoor advertising, inspection and testing services, bus, leasing, and driving centre (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd (C52.S1) 2010).
The company was established on 29th March, 2003. Since its inception, ComfortDelGro Corporation Ltd. has experienced extensive success. It has grown to become one of the biggest land transport entities in Singapore. According to financial analysts at Yahoo, the organisation has a global fleet of 46,000 vehicles (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd (C52.S1) 2010). The vehicles operate in seven countries in the world. The nations include China, the United Kingdom, Malaysia, Australia, Ireland, and Vietnam.
Between 2012 and 2015, ComfortDelGro Corporation Ltd. has registered positive performance compared to its major competitors in the land transport industry. Its main rival in Singapore is SMRT Corporation Ltd. The two firms operate in the bus, taxi, and rail businesses sector. However, ComfortDelGro has reported a competitive advantage over its rival in the past three years. The advantage is in terms of scale, revenues, and exposure. In 2015 financial year, for example, the revenue registered by the company stood at $4,112,000 (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd (C52.S1) 2010). On its part, SMRT Corporation’s total revenue was $1,236,000. In 2014, 2013, and 2012, ComfortDelGro’s returns were $4,051,000, $3,748,000, and $3,545,000 respectively. On its part, SMRT Corporation registered revenues of $1,178,000 in 2014, $1,119,000 in 2013, and $1,057,000 in 2012 (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd C52 2016).
ComfortDelGro Corporation Ltd.: Beta
Beta is calculated using the formula below:
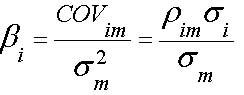
Based on the weekly data of share and market-wide index from 1st June, 2015 to 31st May, 2016, ComfortDelGro Corporation’s beta is estimated to be 0.5163. The beta was calculated by dividing the covariance of the stock return by variance of the market return. The formula below was used:
covariance/variance = 0.0003427/0.0006637 = 0.5163
A beta of 0.5163 is relatively low. As a result, the volatility of the company is lower than that of the market. Based on the beta estimation and calculations, the behaviour of ComfortDelGro’s share with respect to market index shows that the price of the stock has being appreciating throughout the year. The appreciation is influenced by such factors as the revision of train and bus fares by the Public Transport Council (PTC) and strong operational results. The positive growth recorded from 1st June, 2015 to 31st May, 2016 translates to an increase of 1.08%. The figure is based on the close price of $2.74 per share (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd (C52.S1) 2010).
An Analysis and Evaluation of the Company’s Yield Curve
The yield curve is an important concept in Finance (Constantinides 2015). The reason is that it shows the revenue generated from a set of similar stocks. The revenue is reviewed in relation to the maturity of the stock. In addition, the yield curve helps investors and financial experts to compare the gains provided by short, medium, and long-term bonds (Booth, Cleary & Drake 2013).
An evaluation of Singapore’s yield curve shows that the line is sloping upwards. The slope reflects an increase in the length of maturity. The reason is that the spot rate percentage increases throughout from year 2 to the 30th year. As a result, the figure represents a positive growth. What this means is that the investors expect the economy of this country to continue growing. It is also expected that inflation rates will rise. The development will lead to high interest rates. Mankiw (2011) describes the expectations of the various stakeholders when the arc is normal. For example, financiers expect increased gains from the risks taken. It also shows that investors in Singapore anticipate the government to put in place stringent fiscal measures. Such policies will be implemented as a result of increased inflation rates.
Equity Market Risk Premium in Singapore
Market risk premium is equal to the anticipated return on an investment minus the risk-free rate (Geringer et al. 2015). The concept is used in finance to help investors calculate the minimum fee to be received on equities. It is also used to determine risky asset classes as compared to the gains made from peril-free ventures (Robinson et al. 2012).
Between May 20th, 1999 and June 30th, 2016, the market risk premium rate in Singapore has been rising and falling during different times of the year. The rate shot up from 1.93 in May 1999 to 5.71 in June 2016 (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd C52 2016). On its part, the risk free rate reduced from 4.33 in May 1999 to 1.91 in June 2016. The equity risk premium rates were calculated on the basis of long-term averages of stock market returns. Over the past three years (2013 to 2016), the average premium has been 5.32 (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd C52 2016).
The rate is higher than the global equity risk premium. The latter is estimated to be around 3.5% (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd C52 2016). According to Pugel (2015), the beta of the local market in Singapore is 1.2. As a result, the nation’s index increases by 12% when that of the rest of the world rises by 10%. The figures show that Singapore is riskier than the global index. In addition, the country’s average ERP is expected to increase to around 5.5% in the near future. However, the impacts of a rise in long-run ERP will be minimal (Pugel 2015).
The Price of ComfortDelGro Corporation’s Shares
Based on the information above, the price of ComfortDelGro’s share as at 1st June, 2016 was $2.74. The two techniques used for valuing the price of the company’s stock were asset-backing and yield-basis methods.
Asset-Backing Method
Asset backing was one of the preferred techniques. The reason is that it is used to make valuations on the basis of the assets held by a firm. In addition, the method values shares based on the real internal value of the corporation (Koller, Goedhart & Wessels 2015). For proper valuation of shares using the technique, a number of points will be taken into consideration. The facets include goodwill, fixed and fictitious assets, and provision for bad debts. Other points include all the unrecorded and external liabilities (Parum 2001).
The formula for valuing ComfortDelGro Corp’s shares using the asset backing method is as shown below:
Value of each Share = (Net Assets – Preference share capital)/ Total number of equity shares (Ross, Westerfield & Jordan 2013).
Yield Basis Method
The company’s yield is calculated as follows:
Yield = normal profit/capital employed × 100.
Under the yield technique, valuation is made on the basis of profit or dividend (Bernstrom 2014). When using the profit method, the earnings are ascertained based on the previous average income (International directory of company histories 2014). The capitalised value of revenue is then calculated on the basis of normal rate of return. It is then divided by the number of shares to find the value of each stock (Mankiw 2011).
The profit-based formula for valuing shares is as shown below:
Capitalised value of profit = profit 1/Normal rate return × 100.
Value of each equity share = capitalised value of profit/Number of shares
Value of each equity share can also be calculated as follows:
profit/Normal rate of return * number of equity shares × 100 (Villalonga 2014).
Conclusion: The Preferred Method of Valuation and Recommendations on Whether to Buy, Sell, or Hold
The best method of valuation for ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd. is the yield basis technique. The reason is that the approach provides investors with a wide range of strategies to calculate the value of shares over time. In addition, the rate of profit is based on yield (Miller-Nobles, Mattison & Matsumura 2015).
The value of each share of ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd. as of 1st June, 2016 was $2.74 (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd C52 2016). Based on the company’s success and strong market position, the share value is expected to appreciate. As a result, the best option for investors would be to buy and hold their stock (Pratt 2011). Under the strategy, financiers will be focusing on long term holding of the shares and selling them at a profit. However, for the high returns to be received, long-term investors must stick with the outlay throughout market retraction and recession periods (Lacarte 2012).
Over the past five years, ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd. has registered huge profits at the end of each financial year (ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd C52 2016). Investors who buy and hold the company’s shares are likely to benefit from quarterly dividends and stock value appreciation over the investment period. Even in instances when the share prices remain at a constant, financiers are expected to gain profits from the dividends paid.
References
Abdul-Rahman, Y. 2010. The art of Islamic banking and finance: tools and techniques for community-based banking, John Wiley & Sons, North Ryde.
Bernstrom, S. 2014. Valuation: the market approach, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Booth, L, Cleary, S & Drake, P. 2013. Corporate finance, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ.
Brealey, R, Myers, S & Allen, F. 2013. Principles of corporate finance, 11th edn, McGraw-Hill Irwin, New York.
ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd. (C52.SI). 2010. Web.
ComfortDelGro Corp Ltd. C52. 2016. Web.
Constantinides, G 2015, Financial derivatives: futures, forwards, swaps, options, corporate securities, and credit default swaps, World Scientific Publishing Co., New Jersey.
Damodaran, A 2015. Applied corporate finance, 4th edn, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ.
Geringer, M, McNett, J, Minor, M & Ball, D 2015, International business, McGraw-Hill Education, London.
International directory of company histories. 2014, St. James Press, New York.
Koller, T, Goedhart, M & Wessels, D. 2015. Valuation: measuring and managing the value of companies, 6th edn, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ.
Lacarte, J. 2012. Applied corporate finance: what is a company worth?, Free Press, New York.
Mankiw, N. 2011. Principles of economics, 6th edn, South-Western Cengage Learning, Mason, OH.
Miller-Nobles, T, Mattison, B & Matsumura, E. 2015. Horngren’s financial & managerial accounting: the managerial chapters, 5th edn, Pearson, London.
Parum, C. 2001. Corporate finance, McGraw-Hill Education, New York.
Pratt, J. 2011. Financial accounting in an economic context, 8th edn, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., London.
Pugel, T. 2015. International economics, 16th edn, Irwin McGraw-Hill, London.
Robinson, T, Henry, E, Pirie, W & Broihahn, M. 2012. International financial statement analysis, 2nd edn, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ.
Ross, S, Westerfield, R & Jordan, B. 2013. Essentials of corporate finance, 8th edn, McGraw-Hill Education, New York.
Villalonga, B. 2014. Finance and strategy: advances in strategic management, Emerald Group Publishing Ltd., Bingley.

