Organization Overview
Founded in the year 1983, the Costco Wholesale Corporation is one of the leading merchandise warehouses in the US. The headquarters of the corporation is in Issaquah, Washington. In the beginning of the 2016 financial year, Costco had about 700 warehouses spread across the US (493), Spain (2), Japan (25), Taiwan (12), South Korea (12), Australia (8), Canada (90), the UK (27), and Mexico (36). The key executives of the Costco are Jeffrey Bortman (chairman), Craig Jelinek (CEO and president), and James Sinegal and Pradumal Thakker (founders) (Costco Wholesale Corporation, 2016).
Mission Statement, Basic Values, and Philosophy
The mission statement of the Costco Wholesale Corporation is to provide quality products and services to customers. The company’s philosophy is excellence in entrepreneurship with a unity goal for exceeding the expectations of the customers (Costco Wholesale Corporation, 2016).
Geographic Location
The primary market for the Costco Wholesale Corporation is in the US, where the company is currently the second largest within the retail industry. Within the US, the Costco Wholesale Corporation has an active presence in 43 states with the largest location being in Hillsboro, Oregon followed by Salt Lake City in Uttar. The Costco Wholesale Corporation has adopted the merchandise mix strategy to appeal to the local tastes and integrate the local and American products it retails (Costco Wholesale Corporation, 2016).
Current Product Mix
As part of the depth and product life cycle, the Costco Wholesale Corporation has continued to use innovation and expertise capabilities in the development of different products through multiple branding to appeal to a myriad of customers across the globe. For instance, the Costco Wholesale Corporation has opted to deal in different product brands such as hot dog, smoothies, bulgogi bake, and gelato among others to ensure that the local culture is appreciated in developing the product mix (Cheverton, 2004).
Most of the products retailed by Costco are positioned as the first of their kind besides existing in the form of multiple brands. The average price for food items being sold within the Costco Wholesale Corporation’s foot courts across the globe is between $1 to $3 dollars (Costco Wholesale Corporation, 2016). The low prices for high quality food menus have endured customers to Costco since they are able to enjoy good food at a reasonable price (Blythe, 2006). As a result, the corporation has been successfully packaged as a center for satisfaction, fulfilling customer desires, and expansion into new territories.
As part of the strategies meant to increase the visibility of the Costco Wholesale Corporation products, the company has adopted focused differentiation as part of business and product management. For instance, the company has adopted different lines of products since Costco has resounding information about the customer trends across the globe. In addition, the Costco Wholesale Corporation has endeavored to create a permanent bond with the customers through sponsorship events as part of the corporate social responsibility (Cone 2011).
Through these differentiation mixes, the Costco Wholesale Corporation has become one of the most visible and affordable retail store brand in the US and across the globe. For instance, the loyalty cards, shopping coupons, and private membership services have created a cult-like following for the Costco Wholesale Corporation’s products. In the year 2016, the company has been able to open 36 new branches within the US and across the globe.
Nature of Demand
The demand for the Costco Wholesale Corporation’s products has also been on the rise as a result of increased market penetration strategies. For instance, within the targeted retail market, the Costco Wholesale Corporation has been able to increase product intake through offering competitive pricing that appeals to different categories of clients.
Most of the customers of Costco are inspired by the high quality and affordability of the products retailed by the company. Besides, most customers are moved by the convenience and appreciation since the Costco Wholesale Corporation has series of after sales services, large discounts, and many products under-one-roof. Since most of the products retailed by Costco fall in the category of necessities, the level of demand has been predictable and stable (Dagnino & Rocco, 2009).
The main customer segments for the Costco Wholesale Corporation are corporate bodies and individual customers. The corporate bodies function within the business to business retail model while the business to customer segment serves individual customers. Under the individual customer segment, there are three sub-segments consisting of the youthful customers, adult customers, and the home user segment (Farris et al., 2010).
Extent of Demand
The target market is spread across the globe with the highest concentration in the US. The Costco Wholesale Corporation serves approximately 400 million customers in a year within the 700 branches. Within the US, the Costco Wholesale Corporation controls 12.5% of the retail industry. At the global level, the company controls 8.69% of the retail business industry, which is the largest for a single brand.
Based on the sales generated in the 2015 financial year, estimated at 17 billion dollars, the creation of 36 extra branches might increase the sales to 18 billion dollars. The growth trend of the Costco Wholesale Corporation has been on the rise in the last ten years with an average growth rate of 3.25%. The highest growth was recorded in the 2012-2013 financial year at 4.8% with the least growth being in the 2008-2009 financial year at 1.94% (Costco Wholesale Corporation, 2016).
Environmental Analysis
Competition Analysis
The retail business industry in the US is dominated by Costco, Wal-Mart (Sam’s), and BJ’s as summarized in the graph below.
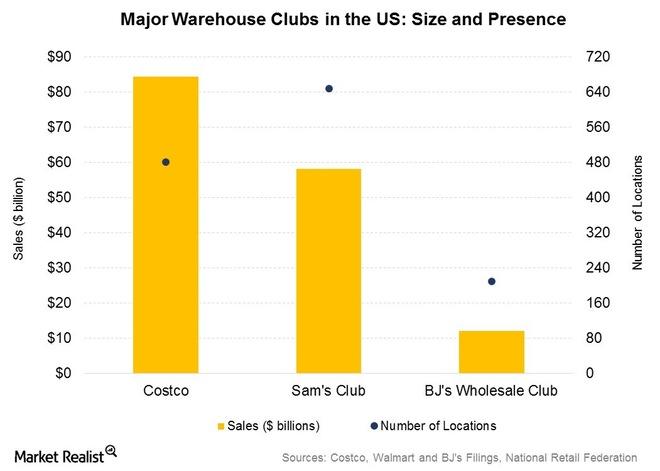
The table below summarizes the competitive forces among the three major players.
(Source: Costco Wholesale Corporation, 2016)
Legal Environment
The Costco Wholesale Corporation is a registered entity that observes the business regulations and remits its taxes to the federal government. The company has a certificate of compliance and has been in the business for more than a decade (Liu, Liao, & Peng, 2005).
Technology Environment
The Costco Wholesale Corporation operates in the dynamic business environment and has invested heavily in the latest technology in supply chain management in order to remain competitive (Roberts, 2005).
Demographic/Socio-economic Environment
The Costco Wholesale Corporation targets customers across the globe and has customized its products to meet the needs and cultures of different categories of customers. The company observes culture and heritage in designing different products targeting different regions (Winchester, 2006).
Costco Wholesale’s SWOT
Strengths
The company has clear product differentiation and strong global brand image. Besides, the company has competitive pricing, which has facilitated its expansion across the globe.
Weaknesses
The high inventory cost in managing more than 700 branches across the globe is threatening the sustainability of the business, especially as compared to other competitors such as Wal-Mart, which relies heavily on vertical integration.
Opportunities
The strong global presence can be translated into further market penetration. Besides, the company should create more products to remain competitive.
Threats
Fierce competition is threatening the sustainability of the business. Besides, the high power of the suppliers within the retail industry has reduced the revenues of Costco. In addition, threat of changed preference might affect the business. This is summarized in appendix 1.
SWOT on Steroids
S/O
Direct-to-consumer market-place (S1, O1)
Expand inventory diversity (O2, O3, S1, and S2)
S/T
Diversification into premium markets (S2, S3, T1, and T2)
Diversification of suppliers (S1, S3, T3)
References
Blythe, J. (2006). Essentials of marketing communications. New York, NY: FT/Prentice Hall.
Cheverton, P. (2004). Key marketing skills: strategies, tools, and techniques for marketing success, Sterling. London, UK: Kogan Page.
Cone, S. (2011). Steal these ideas: Marketing secrets that will make you a star. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons.
Costco Wholesale Corporation. (2016). About us. Web.
Dagnino, G., & Rocco, E. (2009). Competition strategy: theory, experiments and cases. New York, NY: Rutledge.
Farris, P., Bendle, N., Pfeifer, P., & Rebstein, D. (2010). Marketing metrics: The definitive guide to measuring marketing performance. Alabama, AL: FT Press.
Jin, H., Suh, J., & Donavan, T. (2008). Salient Effects of Publicity in Advertised Brand Recall and Recognition: The List-Strength Paradigm. Journal of Advertising, 37(1): 45-57.
Liu, S., Liao, S., & Peng, C. (2005). Applying the technology acceptance model and flow theory to online consumer behavior. Information System Research, 13(2): 205-223.
Roberts, J. (2005). Defensive marketing: How a strong incumbent can protect its position. Harvard Business Review, 83(11): 150-210.
Winchester, M. (2006). Positive and negative brand beliefs and brand defection/uptake. European Journal of Marketing, 42(6), 553-570.

