Introduction
Emaar Properties is one of the leading real estate developers in the Middle East. Since 1997, it has developed and grown rapidly and is already represented in multiple markets. The company is known for its major projects and premier real estate (Rizvi, 2017). While being a stable company, Emaar Properties is still operating in a highly competitive environment and is influenced by many external and internal factors on which its success depends.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
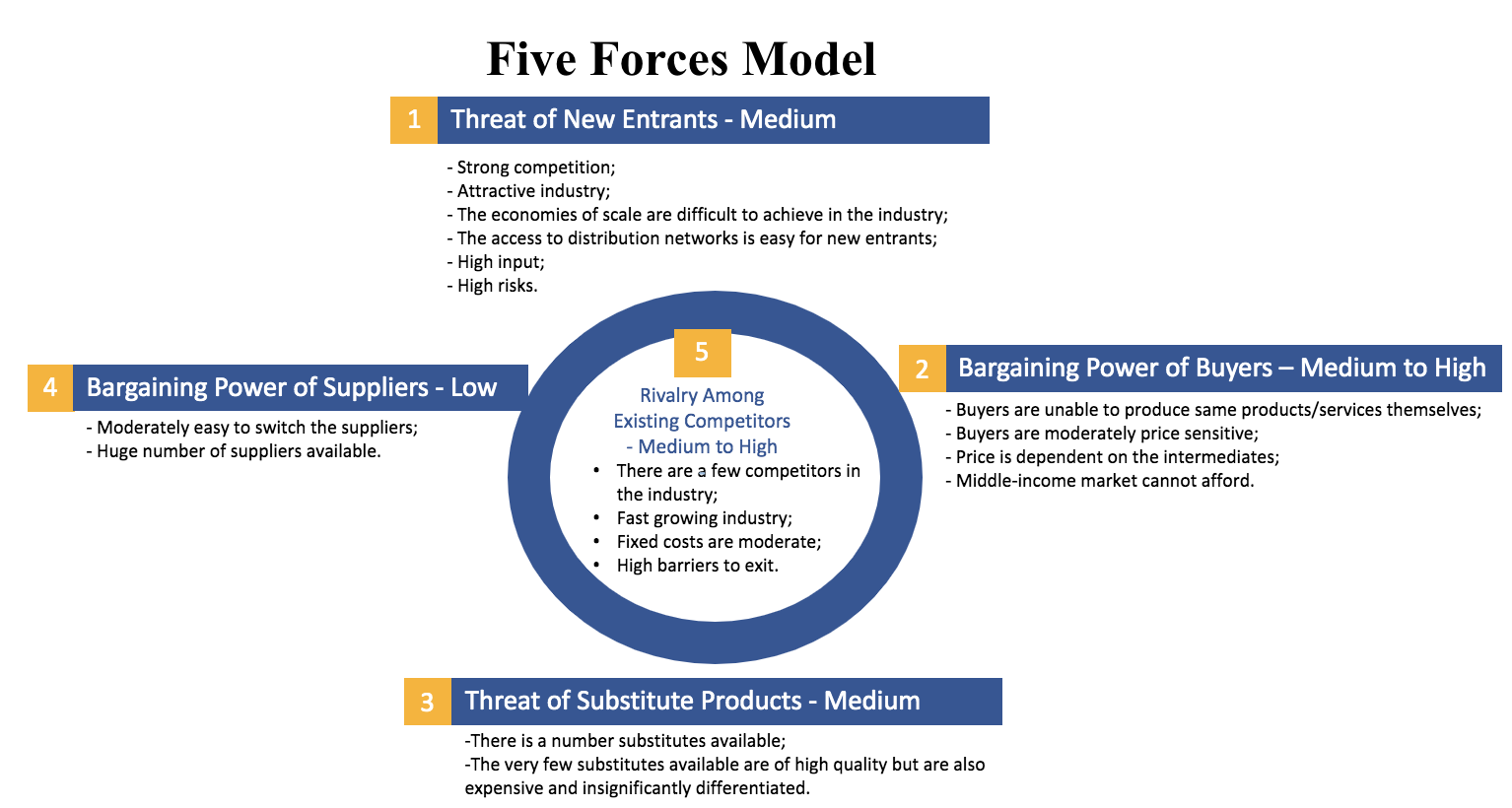
Threat of New Entrants
In accordance with the developed Porter’s Five Forces Model Threat of new entrants was found to be medium. There are a number of strong existing competitors, including DAMAC Properties, Nakheel, and MEERAS in the real estate development industry in which Emaar Property operates (Bodolica et al., 2018). At the same time, the industry is attractive for new entrants as it has a high yield, and the UAE is a fast-developing market.
The country is attractive for investment for opening a business, bank accounts, and for purchasing real estate for further residence or sale. In addition, it is easy to attract the attention of the desired audience through advertising, agents, and direct contacts. However, economies of scale are difficult to achieve in the real estate development industry since the planned implementation of a building often has a limit and boundaries for a certain period of time. Moreover, there are high barriers to entry, including investment requirements and high risks of significant losses in the event of a business failure.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers in the industry is medium to high. In this industry, buyers can greatly influence the price by their preferences. In addition, the price depends on the resellers who receive commissions from sales and can influence the pricing. At the same time, in the case of Emaar Properties, most consumers are in the high-income class and are more focused on quality, which is why they are relatively flexible in terms of price (Xue et al., 2018). However, this limits the target market and can affect sales.
Threat of Substitute Products – Medium
The threat of Substitute Products was found to be medium. There are few apartment developers of the same class as Emaar Properties, but they do not have a lower price. Moreover, upscale apartments in the UAE have a fairly similar minimalist style with pastel colors. Temporary apartments rented through Airbnb or other similar sites are gaining popularity (Zhang et al., 2017). There are also hotels with long-term stays and the ability to rent an apartment for short and long term. However, in the case of the same quality, the prices in the long run comparison are the same or higher. In addition, a rented apartment cannot be a complete replacement in terms of quality and comfortability.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers was found to be low. The state in the UAE provides land for rent; governmental organizations are flexible and do not create legal complications. There are many construction companies and suppliers of equipment, finishes, and furniture. This reduces the influence of suppliers in terms of quality or price since Emaar Properties have alternatives to choose from.
Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
Rivalry among existing competitors was found to be medium to high. This is based on the fact that with a limited target market, companies are forced to compete with each other. Competition affects quality, price, and special offers are required to attract new customers. In the industry, Emaar Properties is a leading developer, and its profit is several times higher in comparison with the closest competitors. At the same time, the industry is growing rapidly along with the UAE’s infrastructure (Henderson, 2017). The fixed cost risk in the industry is often covered by an attractive yield. The high barriers to exit are due to specific planning requirements, and when the construction of buildings is stopped, the development company suffers heavy losses.
Nature of Industry Competition
At the moment, the structure of competitive relations in the development of real estate in the UAE is an Oligopoly. There are several large companies in the market, and there is no single leader capable of single-handedly influencing pricing. Thus, these few large firms have a large market share, and barriers to enter the market are high.
Changes Analysis
- Political Factors – government supports the development and provides preferential conditions for registration and company management, taking into account the local founder. In addition, there is a stable political situation within the country and preferential terms for investment.
- Economic Factors – stable local currency rate and economic progress within the country positively affect Emaar Properties. Dependence on the global economy and inflation rate as it affects the wealth of the buyers is a negative factor. High dependence on purchasing power is risky with the possibility of a global crisis.
- Sociocultural Factors – changing preferences and demographics, employee culture, and diversity affect the company (Jaiswal, 2019). A low share of the local population in UAE is provided with all the amenities for life on the part of the state and do not oppose the development.
- Technological Factors – transformation of working responsibilities and improvement in technology affects the operations of the company (Majumdar, 2017). UAE is one of the most innovative countries and constantly adopts new technologies and processes.
- Legal Factors – Real Estate Regulatory Authority is organizing all the reporting activity.
- Environmental Factors – sustainability concerns around the construction activity are present, but CSR initiatives by Emaar Properties are a preventive measure to the risk of social or government discontent.
Opportunities and Threats
Opportunities
- Expansion to new markets – currently, Emaar Properties are presented in 36 markets around the world, and the income is concentrated in UAE. Therefore, there is an opportunity to expand to the developing countries and split the main revenue sources.
- Residency visa for investments – the UAE has begun issuing resident visas for investment, and real estate is one of the popular investment types.
- Stable political and economic environment is attractive for investors – the opportunity to use the stable situation in the country as a competitive advantage in advertising.
Threats
- Economic Crisis – global economic downtown may affect the purchasing ability of the target market.
- Force Majeures – such as COVID-19, travel and gathering restrictions have a direct effect on the operations of the company.
- Loan Limitations – direct effect on the purchasing power.
- Competition – new strong competitors may appear on the market and govern quality and prices.
- Fluctuation of Interest Rates – affects the revenue of the company.
- VAT enforcement – currently, only 5% tax is paid for the real estate release in (UAE Zafarullah, 2018).
Conclusion
Emaar Properties has taken a stable position and is one of the market leaders. Porter’s Five Forces Model of the real estate development industry in the United Arab Emirates was used as a representation of the current market competition and profit potential. The company has a strong market position and is well prepared for external influences and threats.
References
Bodolica, V., Spraggon, M., & Shahid, A. (2018). Strategic adaptation to environmental jolts: An analysis of corporate resilience in the property development sector in Dubai. Middle East Journal of Management, 5(1), 1-20. Web.
Henderson, C. (2017). The UAE as a nexus state. Journal of Arabian Studies, 7(1), 83-93. Web.
Jaiswal, P. (2019). The effect of motivation on employee performance: A case study in Emaar Mgf Land Ltd, Gurgaon. International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies, 7(7), 26-36. Web.
Majumdar, S. (2017). Performance analysis of listed companies in the UAE – using DEA Malmquist index approach. American Journal of Operations Research, 7, 133-151. Web.
Rizvi, K. (2017). Dubai, anyplace: Histories of architecture in the contemporary Middle East. A Companion to Islamic Art and Architecture, 1245-1266. Web.
Xue, K., Yang, Q., Li, S., Wei, D. S., Peng, M., Memon, I., & Hong, P. (2018). PPSO: A privacy-preserving service outsourcing scheme for real-time pricing demand response in smart grid. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(2), 2486-2496. Web.
Zafarullah, M. (2018). Impact of VAT on UAE economy. Asian Development Policy Review, 6(1), 41-49. Web.
Zhang, Z., Chen, R. J., Han, L. D., & Yang, L. (2017). Key factors affecting the price of Airbnb listings: A geographically weighted approach. Sustainability, 9(9), 1635. Web.

