Introduction
The notions of work and career are considered integral elements of life and personal growth in terms of modern society. There is an idea that these two concepts are closely intertwined with individual identity and, thus, personal development through work and career might help determine one’s sense of life purpose. According to McDonald & Hite (2016), work and career can be perceived as “means to fulfill one’s potential” (p. 5). As such, the strong career commitment and overall contentment with the job guarantee stable psychological health and facilitate one’s sense of worth and purpose. With that being said, by pursuing career development, one may benefit from the significant impact it has on the way people consider themselves and their attitude toward life.
Furthermore, the concept of meaning and professional development are indicated through the employees’ establishment of career goals. Following the ideas of McDonald & Hite (2016), careers can be examined from two different perspectives, such as “subjective and objective” (p. 7). The subjective view refers to the individual’s sense of self-value and the significance of the pursued goals in life. The objective perspective, in turn, implies the emphasis on the key indicators of success, including pay and promotions. The relevance of the subjective aspect increased due to the changing career environment. Considering the crucial concepts of learning culture and learning organization, only the team of leading managers creates a climate conducive to the learning and development of the staff (Paine, 2019). However, such a strategy involves understanding the right kind of training for the employees that will increase performance, promote individual motivation, and reveal employees’ potential.
Career Development in terms of Changed Career Landscape
The concept of career development varies, as it is directly dependent on the discipline to which it relates. Some people consider the issue of professional development as specifically individual concern that is based on personal interests, as well as abilities and goals. Others view this issue from the organizational productivity perspective, which mainly implies the focus on the needs of the organization and the ways an employee can address them. The core principle of development indicates growth, ongoing achievements, and implementation of skills in daily practice within a work environment. Therefore, the key components of successful and productive career development are personal career planning and the company’s support and opportunities. The collaborative process of these elements, which emphasizes both an individual and the organization’s performance, contributes to the overall business success.
In general, career development is defined as the ongoing process of planning and directed approach toward individual work and purpose in life. However, the current career landscape becomes more unsettled, inconsistent, and challenging within the rapid changes in modern society. Such a transformation of the work climate is caused by several critical factors, including “economic turmoil, technological advances, a more diverse workforce, governmental policies, and societal influences” (McDonald & Hite, 2016, p. 10). The changing lifestyle in a busy life circle also defines the culture of work and career development accordingly. It may be said that a career became integral to everyday life and can be analyzed through personal career identity, which gives meaning to the past and the present, and, for that reason, provides direction to one’s future.
Defining the Relationship between Training and Career Development
Leaders who guide the overall process within a company are responsible for empowering and supporting the employees through continuing career development. As described by Noe & Kodwani (2016), training can be defined as a “planned effort by a company” aimed at promoting employees at learning the job-related competencies, as well as knowledge, skills, and behaviors (p. 7). The main goal of the training is to master the professional qualities of the working team that can be applied to daily operations at work. Therefore, properly designed training that is adjusted to the needs and values the company pursues is a key to the company’s successful performance and leading position in the market. A similar concept associated with training is developed, however, it is considered to be more focused on future achievements and growth.
Apart from training, the concept of development covers formal education, job experiences, work relations, as well as evaluation of personality, skills, and capacities that prepare oneself for future job positions. Bocciardi, Caputo, Fregonese, Langher & Sartori (2017) state that career development and adaptability are “a learnable construct,” which can be enhanced through training with long-lasting effects (p. 68). The ongoing support of employees through their career development contributes to adequate employee engagement, meaning that each worker is fully involved in the working process and is strongly committed to the job. Hence, it contributes to the company’s performance and success. The training of employees creates educational opportunities, such as training programs, but also implies the external courses offered outside the company, self-education, and learning through job rotation. It is a continuing process of performance enhancement, which is instantly measurable as compared to one-time training sessions. For this reason, executives, managers, and trainees must be fully aware of the major benefits of training. Its critical interest implies achieving strategic business objectives and assisting the company in obtaining a competitive advantage.
Competency Models
The current international business environment is becoming highly competitive, which makes it difficult for the organization to define the opportunities the employees can introduce to lead the company towards successful performance. The necessary competencies might vary according to the organizational culture and business strategies, as well as the core objectives the company pursues. Professional competency relates to capabilities that allow employees to be competent throughout work performance by achieving outcomes or completing tasks. This implies knowledge, skills, attitudes, values, or personal characteristics. A competency model identifies the capabilities needed for different types of jobs, as well as individual employee factors underlying each competency.
As such, competency models might be beneficial for training and career development in several ways. Competency models help to determine behaviors that contribute to efficient job performance. They also serve as a determining factor concerning the necessary skills for addressing the current and future needs of the company. Such models might help determine what skills are required at different career points. In addition, competency models establish a framework for continuing education and feedback to prepare employees for existing and future roles. They are also useful in designing a work plan regarding employees developing and determining the candidates for managerial positions.
Needs Assessment
The process of needs assessment is a primary step one should consider before conducting the employee training, which helps to define whether the training is needed. It is the first step in the instructional design process that includes organizational analysis, person analysis, and task analysis. The organizational analysis examines the context of training and determines the training’s relevance based on the company’s business strategy, resources for learning, and the general support for training practices. A person analysis helps to detect who needs the training considering three main aspects. These include investigating the nature of performance deficiencies, which might result from the lack of knowledge and skills, as well as motivational and work-design issues. Two other factors involve identifying the employee who requires new learning activities and analyzing his or her preparedness for the training. The final task analysis is focused on the most crucial tasks and knowledge, as well as skills and behaviors, which serve as the main emphasis throughout the training.
As a rule, the needs assessment process is performed by the trainers; however, now it also engages managers, trainers, and employees within an assessment process. This process is based on four critical methods, such as observation, questionnaires, reading technical manuals and records, and interviewing subject matter experts. Needs assessment is a fundamental approach that helps managers or other company’s clients to determine whether there is a need for training or another gap improvement, including decreased motivation, changing perspectives, or upgrading workflow. Some of the problem-solving solutions within a business practice do not require training activities. Thus, by conducting the needs assessment, one can identify the appropriateness of training and conclude whether it is the right solution for a company and its employees.
Types of Training
The variety of training types is directly dependent on the enterprise’s relatedness to the specific area of expertise and services, as well as the ultimate goal of training. There are two basic types of work education, such as high leverage training and continuous learning. Thus, the high leverage training relates to business goals and objectives; it applies a process to provide effective training and implements a comparative analysis of other companies’ learning programs. This type of practice facilitates a proper working environment that encourages continuous learning. The second type, continuous learning, covers a broader spectrum of work-related aspects and requires employees to be fully acknowledged of the entire work system. This includes the relationships among the jobs, the work units, and the company itself.
As such, the trainees are expected to improve their skills and knowledge and apply them in practice, as well as share the obtained new information with their colleagues. It is important to note that managers take the leading and active role in ensuring that employees implement the training during work and secure the mutual sharing of knowledge and skills between them. In terms of the constant changes in the business climate, training also addresses the need for ongoing changes and modifications. Hence, such practices are currently becoming more performance-focused, which means that it is used to advance the results of employee performance and leads to improved business outcomes.
Designing an Effective Training
The process of designing successful training refers to the systematic approach of developing the training programs. The common assumptions concerning the training design imply that its effectiveness relies upon achieved instructional or training goals, as well as objectives. In addition, it is important to identify the measurable learning objectives before the start of the training process. Another crucial aspect of training design is the assessment that is fundamental for planning and choosing a training approach, monitoring the training program, and suggesting changes to the training design process. With that said, Noe & Kodwani (2016) identified seven critical steps that promote the efficiency of this process, including:
- “conducting a needs assessment
- ensuring employees’ readiness for training
- creating a learning environment
- ensuring transfer of training
- developing an evaluation plan
- selecting training method
- monitoring and evaluating the program” (p. 115).
To be more specific, the first step is based on the assessment, which is essential for determining the particular relevance of the training. Such assessment includes organizational analysis, person analysis, and task analysis. The second step is responsible for providing employees’ readiness, which involves attitudes, motivation, and core competencies required for mastering the training content. The third step emphasizes the need for creating a proper learning environment with the characteristics essential for the training to emerge. This strategy is based on the learning outcomes, meaningful information, practice and feedback, a community of learning, modeling, and program administration. The fourth step guarantees that employees can convey the obtained knowledge and skills throughout the training into their work responsibilities. This step implies competence in self-management, peer and manager relationships, and the significance of the organization’s support.
The fifth step of effective training design relates to the evaluation plan that covers learning outcomes, evaluation design, and plan cost-benefit analysis. It is crucial to determine the training outcomes that can be influenced and develop an evaluation plan to identify the influence of training on these outcomes. The cost-benefit analysis helps to identify the financial benefits caused by training. The sixth step indicates the selection between the traditional and e-learning training methods, which is based on the learning targets and learning environment. Finally, the last step concern the program evaluation and monitoring, meaning that some previous steps might be modified to improve the program and, thus, achieve successful learning and meet the learning objectives. Altogether, the particular type and amount of training for the employees are primarily indicated by the business strategy that the company pursues.
Strategic Training
Any kind of training activity should be mainly focused on promoting the company’s business strategy and its achievement. A business strategy is commonly perceived as a plan that integrates the “goal, policies, and actions of the organization” (Noe & Kodwani, 2016, p. 145). It assists in directing the company’s practices to reach targeted goals and improve general work performance. Continuous education within a business environment plays a crucial role in addressing the business challenges and providing a competitive advantage, although the purpose of training in organizations is changing. Training should include an emphasis on learning, creating, and sharing knowledge to enhance the employees’ productivity and respond to the business requirements and challenges. The business strategy is closely connected to the company’s management of physical capital (plants, technology, and equipment), financial capital (assets and cash reserves), and human capital (employees).
Apart from the company’s business strategies and objectives, the role of training is also constantly evolving. Well-designed learning involves job experiences and interrelations between the work colleagues. Training and company advancement facilitate the emergence of the improved workforce that can deal with the change, meet the increasing demands of the telecommunications industry, and prepare the company’s future leadership. Training practices should primarily aim at assisting the company in achieving its business strategy and, thus, promoting the successful performance and results of the organization. Taking into account the variety of business strategies, they all require different needs for training. For instance, a concentration strategy is targeted at increasing market share, reducing cost, or creating and sustaining a market niche for products and services. The internal growth strategy prioritizes new market and product development, innovation, as well as joint enterprises. External growth strategy implies the process of obtaining vendors and suppliers or acquiring businesses that enable the company’s expansion into new markets. Finally, the divestment strategy focuses on the elimination and divestiture of enterprises.
Emphasis on Knowledge Workers: Career Pyramid
Taking into account that employees always seek more resources that can promote their career development, Satellite designed a Career Pyramid, which defines the positions in terms of dialysis career category. This is based on the job titles from lower-level positions to senior management. Therefore, each of the positions has specific requirements concerning education, competencies, as well as experience. The results of the Career Pyramid’s implementation in the Satellite case demonstrated the overall improvement of employee engagement. Furthermore, 92 percent of the personnel reported long-term career expectations with the company (Noe & Kodwani, 2016). The pyramid also provides the standards for promotion and employee development to progress to each professional level. The Career Pyramid might significantly contribute to the entry-level workers, such as patient care technicians since it demonstrated a clear pattern on feasible career moves and the skills that need to be improved.
Employees should remain determined with personal business and development goals, and express them within a work environment to make sure that they align with the managers’ objectives, as well as the company’s business strategy. As for the company, one needs to be focused on providing financial, time, and content resources, including courses, training, and development opportunities, to boost the employees’ expertise. However, the changing business environment constantly gives new challenges to address and, thus, employees need to adapt to a new philosophy of learning. A learning organization promotes a culture of continuous training and education, which allows the employees to obtain further knowledge and skills, and share it continually among their colleagues. The well-structured and ambitious company fosters continuous learning that complies with the workforce’s personal needs. With that said, the key elements that contribute to the development of a learning organization are social collaboration and social networking technology. As such, training and development can be considered as a primary means to support a company’s business strategy.
Learning Theories
Considering the learning organization as a critical component of employees’ career development, it is crucial to define the issue of learning within a business climate. As described by Noe & Kodwani (2016), learning is a “relatively permanent change in human capabilities,” which is not the outcome of developmental processes (p. 157). Such capabilities are connected with particular learning outcomes, including verbal information, intellectual skills, motor skills, attitudes, and cognitive strategies. Verbal information involves all the crucial aspects of knowledge and specialized knowledge required for one’s job practice. Intellectual skills include concepts and rules that facilitate problem-solving solutions, customer service, and product creation. Concerning motor skills, these are based on the coordination of bodily movements. The set of personal beliefs and feelings that make one behave a certain way represent the attitudes. To be more specific, work-related attitudes include job satisfaction, dedication to the company, and job engagement. Finally, cognitive strategies are in control of the employees’ thinking and learning processes.
Furthermore, several theories correspond to the way people learn, and each of them relates to different aspects of the learning process. These theories include reinforcement theory, social learning theory, goal theories, need theories, expectancy theory, adult learning theory, and information processing theory. The reinforcement theory highlights that past outcome, which provoked certain behavior, motivate people to perform or avoid such behavior. Also, this theory indicates that the trainer has to determine what results in the learner considers as most positive or negative and link them to trainees obtaining knowledge, modifying skills, or changing behaviors. A social learning theory emphasizes that the learning process is based upon observing other people who are perceived as credible and knowledgeable. The goal theories suggest that behavior is a result of the conscious goals and intentions of oneself. A goal orientation process involves the goals established by a trainee in a learning situation.
Need theories, in turn, can explain the value that a person gives to particular outcomes. A need is considered a deficiency, which motivates humans to behave in a way to satisfy the gap. This theory implies that trainers should focus on determining the employees’ needs to stimulate the learning desire and, thus, provide the employees with a range of training programs. The expectancy theory states that human behavior is dependent on three factors, such as expectancy, instrumentality, and valence. Adult learning theory implies that adults have a need to be self-directed and need to have a reason concerning why they learn something. Moreover, adults contribute to the learning process by providing job-related experiences. They become involved in a learning experience with a problem-centered approach and are driven to acquire new knowledge by both extrinsic and intrinsic motivators. The final information processing theory is primarily targeted at the internal processes that emerge when training material is learned.
Employees’ training is integral to their development and level of professional expertise that also has a direct impact on the company’s strategic performance. With that said, learning can be viewed as a dynamic cycle based on four stages, including “concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation” (Noe & Kodwani, 2016, p. 162). One of the core features of a learning environment, which is focused on significant employee improvement and development implies that workers should know the reason for learning in the first place. Second of all, employees need to understand the goals of the properly designed training program. They also require meaningful training information that aligns with their current occupation, as well as adequate experiences and tasks, which can be successfully applied in daily practice at work. Hence, the organization has to enable opportunities for employees to practice and share the knowledge obtained during training. Most importantly, the staff mainly learns through observation, experience, and interacting with the colleagues and, for this reason, requires properly coordinated and organized training programs.
Training’s Influence on Employees’ Career Development
When paving a path to a successful career and promotion and professional recognition, one should purposefully focus on demonstrating personal skills and expertise in practice. Employees feel appreciated in a case when a company identifies the efforts that they make and their overall contribution to the company’s position in the market. Employees’ training and career development motivate the staff to stay loyal to the organization and create a coherent workforce. As described by Cloutier, Felusiak, Hill, & Pemberton-Jones (2015), career development directly relates to “increased production, higher wages, fair pay, and benefits” (p. 124). It is commonly considered in terms of a business practice that employees should be frequently exposed to training and ongoing learning to become successful leaders. Hence, the leadership training programs and leadership qualities are also crucial for achieving a prosperous career development.
To begin with, a company should devise a goal plan in order to identify the fundamental future needs. This implies defining the internal candidates who will be engaged in training for leadership positions. A leadership approach in managing the business processes is a necessary step for the company’s success, as well as its professional development. As such, by designing leadership and management rotational programs, the future management might get a broader insight into a company, which enables the employees to understand their influence on the company’s bottom line. Cloutier et al. (2015) emphasize the importance of leadership training and perceive it as the crucial aspect of forming the future generation. It should be mainly based on accurately evaluating personal weaknesses and developing solutions to improve them accordingly. The recent research provides evidence on the critical role of continued support in employee training as it demonstrated its strong impact on employee development. With that said, training and career development are crucial for employee retention strategy.
Formal Employee Training and Development Alternatives
The working personnel generally pursues developing in leadership and advancing professional skills through continuing targeted trade-specific training. Employees are usually required to acquire a different skill set with additional training to be better acknowledged with the challenges employers have to deal with and the decision-making process in the role of the business owners. As a result, improved knowledge and skills lead to promotions and better pay. Cloutier et al. (2015) define several propositions concerning the role of training in employee career development. The first suggestion indicates that training has a positive influence on measures of the organization’s competitiveness. In addition, it has to be incorporated into the company’s business strategies. The final idea implies that integration of training into the business strategies might enhance the contribution of training to the competitiveness of the organization.
Employers should create training and development options for their workers, which are related to the nature of employment and responsibilities. Moreover, the job content and responsibilities that employee performs might contribute to the growth of the employee’s role within the organization, meaning that they influence one’s enhancement of career development (Figure 1). A sense of being an essential and valuable work in the organization is enhanced when employees are provided with a leadership role in projects or have a positive work climate and relations with the boss. Therefore, employees can grow and develop with the aid of “leadership goal sharing, self-management, and more access to important information and scheduled meetings” (Cloutier et al., 2015, p. 124). Based on the regression analysis concerning the survey of training professionals in small, medium, and large firms within three different industries, the training or its lack has a powerful influence on business competitiveness and retention. Training and career development promote a decrease in the economic impact of losing crucial employees and their valuable expertise.
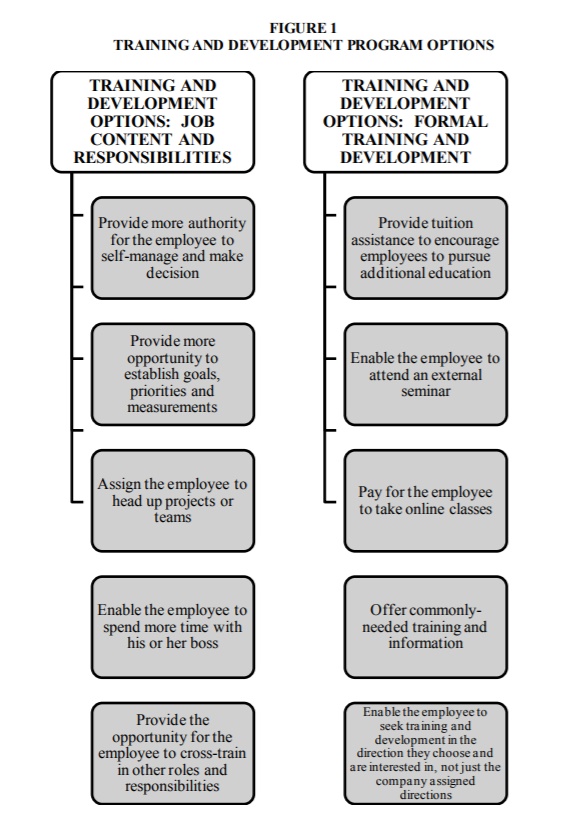
From the individual perspective of each of the company’s employees as a significant part of an organization, companies must focus on productive discussions and adapt the in-depth analysis of data, as well as employee feedback. Such a strategy will promote the employees’ retention and foster their professional development. Business enterprises should necessarily invest in their workforce and perceive them as stakeholders. This implies that companies are obliged to make efforts so they can better understand the employees’ philosophy. The employees, in turn, should try to comprehend the corporate needs of the organization. As a result, such a mutual understanding might benefit both the employee and the employer, and, hence, impact the overall business success. The training approach will not only enhance the employee’s career development, but also motivate the workers to remain loyal, productive, and competitive for achieving the corporate objectives. To sum up, employee training has to be formal, related to work, and accessible as an option to choose for all the employees.
Conclusion
Within a current challenging and competitive business climate, a determined employee is in constant need of reorganizing the professional image or role. As such, ambitious workers can significantly benefit from investigating new career paths, planning their future development, efficiently building work relationships, and maintaining professional commitment. One of the environmental factors that can influence the relevance of occupational competence is employee education, namely training. The following discussion provides evidence that training activities implemented by organizations can result in the immediate gain of highly skilled employees and improved business outcomes. One of the essential linkages implies training’s enhancement of the employee’s career development, which is dependent on the changing career landscape and properly designed training. However, it is particularly important to adapt the needs assessment to identify the relevance of training according to the company’s objectives and business strategy, because training is not always a solution to organizational issues. With that said, companies should focus on providing a sufficient amount of resources to support employees’ career development since improved work performance is closely intertwined with the organization’s overall business success.
The variety of learning programs, continuing education opportunities, and on-the-job training are critical factors that facilitate employees’ career development. Such an emphasis on career enhancement and training’s contribution is caused by the comfortable work climate that prevents oneself from reaching their potentials. Thus, a competitive and challenging business environment can motivate employees to grow and focus on their career development. A company can thereby secure itself with a skilled workforce that promotes its economic success. The goal-setting approach helps the workers to identify personal knowledge gaps based on current competencies and those needed to move up to the next career level. The continuing training of employees helps to alleviate such skill gaps and provide accessible opportunities that give employees more content with the job and overall engagement with the team and their work responsibilities.
References
- Bocciardi, F., Caputo, A., Fregonese, C., Langher, V., & Sartori, R. (2017). Career adaptability as a strategic competence for career development. European Journal of Training and Development, 41(1), 67–82.
- Cloutier, O., Felusiak, L., Hill, C., & Pemberton-Jones, E. J. (2015). The importance of developing strategies for employee retention. Journal of Leadership, Accountability and Ethics, 12(2), 119–129.
- McDonald, K., & Hite, L. (2016). Career development: A human resource development perspective. Routledge.
- Noe, R. A., & Kodwani, A. D. (2016). Employee training and development (7th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
- Paine, N. (2019). Workplace learning: How to build a culture of continuous employee development. Kogan Page Publishers.
