Introduction
Platt (2002) defines Enterprise Architecture (EA) as a conceptual tool that assists organizations with the understanding of their structure and the way they work’. It is becoming a common tool for large organizations willing to embrace technology. This tool encompasses all the technical aspects into a single software.
In the words of Macaulay (2004), enterprise architecture is normally structured by considering a business or the processes of the business as a series of components (or services) with inter-relationships, without having to consider ‘the detailed design within the individual components’. Enterprise Architecture normally takes the form of a ‘comprehensive set of cohesive models that are fully coordinated to complement each other. Further, these models will take account of all of the enterprise’s needs. The EA needs to be aligned with the enterprise’s short-term and long-term goals. It must be synchronized with the organizational culture as well as the processes and systems used in the organization.
According to Platt (2002), ‘it provides a map of the enterprise and is a route planner for business and technology change.’ Though enterprise architectural tools can provide greater coordination and cohesion to an organization, there are challenges to the application of Enterprise Architecture including ‘architecture planning, governance, taxonomies, and ontologies’ (Platt, M., 2002).
For this paper, I will study the application of Enterprise Architecture in a particular enterprise. The study of a live business model should give me more insight and an architectural understanding of the system. Also, this paper will provide an understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of the system for a fully functional enterprise. This study seeks to provide an organizational optimization mechanism for Epinions.com through the implementation of the IDEF0 model. This research focuses on the analysis of service provision processes, which is in growth alongside the enterprise business entities’ (EBE) structure. Recommendations are provided as to how the scope of activities must be enhanced and optimized to realize the company’s mission.
Business Model: Epinions
The Model
The current situation
When Epinions first opened, its main object was to generate positive reviews for popular customer products. This policy led them to hire domain experts who had an essential understanding of the Internet. “Category Managers” (CMs) were hired to manage the service provision structure. During the era of fast growth, they realized that “Category Managers” (CMs) were spending the bulk of their time in conveying information to their groups and the websites were using external data sources only.
Lately, the CMs’ job revolves around technical and non-technical everyday jobs. Now the CMs are accountable for non-domain exact tasks such as the structure of the website from data chosen by more domain-savvy CMs. Today, as Epinions’ website matures, reviews for the majority crop are available. The corporation has also begun to consider expansion and to re-analyze the work procedure for CMs.
Strategic Objectives of the Company
Founded in May 1999, Epinions is an online trade guide that offers consumer reviews on over 150,000 crops and services. Epinions also presents links to the Web’s best expert reviews and the shopping capital. The company’s focus is to help people make better trade decisions. Epinions provides advice, ratings, and appraisals by employing the information provided by customers who have used the crop and services. Epinions’ major services can be classified into four areas:
- Web of Trust: The research is based on the fact that Epinions has urbanized a technology that helps customers make a decision. Relevant opinions and manufactured goods recommendations are provided to consumers and the customer goodwill depends upon the network of trust.
- The Right Incentives: Epinions’ clientele is ambitious. Epinions provides a possibility for registered members to earn Eroyalties and Epinions prize currency by providing the most popular and adequate reviews for the customers.
- Real Advice from Real People: Customers share their knowledge with the specialists at Epinions. Epinions does not edit these reviews provided by customers. Clients share their reviews, both positive and negative.
- Transparency: Using an automatic peer review tool, users can easily ignore certain members’ recommendations if they have poor experience with the members’ reviews.
Business Concept
Mission
Epinions is moving towards a dangerous growth phase. At present, the association is structured so that each manufactured goods canal is handled by one “Category Manager” (CM). As Epinions expands, the current managerial structure will not be able to hold up. The success of Epinions depends on managerial reforms for the team of CMs. Moreover, growth creates possibilities of more customer-tailored and profit-oriented approaches to the provision of the services, which are now mainly connected with the provision of peer reviews. Hence a process model for changing services provision mechanism must be created. Epinions also wants to expand its product portfolio without any rise in staff costs. Therefore, the key task is to redefine the roles of CMs (Epinions.com).
Vision
Epinions aspires to be one of the giants in the trade evaluation service providers. It aims to expand its operations and to take advantage of the growth in this market. It plans to widen the scope of its services to providing the custom needs of different clients. Furthermore, it wants to expand its network of information by including more expert reviews on its website and relying less on customer feedback and recommendations.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Alternatives
Strategic Projects/Programme
‘Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a normal software package,’ that can be used for any organization. It ought to be tailored to the exact requirements of the individual enterprise. This procedure of software individualization is called modification. ERP-software is application software and the application modules of ERP integrate all the functions and the data produced and needed by these functions. ERP system is based on a common database that stores master and transactional data. ERP-software offer business solutions that support the core procedures of trade and of administration. Its pragmatic nature allows it to provide quality data and system, making ERP unique in its functioning.
Furthermore, the ERP solutions all have a process-oriented view of enterprises. Typical trade procedures are supported across functions so that the user often does not realize in what practical module he or she is actually working. Currently, the complete execution of ERP solutions requires massive documentation. In addition to the usual software documentation, reference models have to be produced to depict the holdup processes, managerial structures and the structure of the data and objects. These models allow easy execution and provide focus where there are conflicting views involved. In addition, hot-links to the ERP documentation and related data is provided to authorized personnel.
Values/Policies/Principles
ERP is useful for companies that operate in more than one country. Therefore, ERP is an effective system for organizations with global strategies. Pre-organized country-specific chart-of-accounts, pre-formatted text types like quotes, release notes or invoices, HR-related rules (e.g. payroll) and currency-related procedures are the ERP tools that help transnationals (Hubbard, 2004). ERP supports recurring trade procedures like procurement, order processing or payments and is not focused on the less unorthodox aspects of business like marketing, product growth or project management (Hubbard, 2004).
The SAP Modules
Material Management (MM)
The R/3 (“R” for “Real-time data processing”) applications are typically categorized in three core areas: capital, human resources, and logistics. The core areas comprise hundreds of processes that address all the needs of contemporary trade applications. There are many modules to handle these areas. Those modules are well integrated and have some sub-modules in a hierarchical structure.
According to SAP R/3, the logistics applications manage all processes involved in the supply chain: from raw material purchases to final customer delivery and billing. These applications contain comprehensive procedures to allow the functioning of flexible manufacturing systems and tools for decision-making support. Furthermore, these applications integrate flawlessly with almost every other R/3 application, from the financial and controlling modules to the human resources processes. The logistics application contains several sub-modules: General logistic (LO), Materials Management (MM), Plant Maintenance (PM), Production Planning (PP), Project system (PS), Quality management (QM), and Sales and Distribution (SD).
The purpose of the Materials Management (MM) module is to offer detailed support for the day-to-day activities linked with material attainment (purchasing) and control (inventory-taking, warehousing, etc.). A brochure published by SAP by the title of Functions in Detail Brochure (1998, 1-2) explained that the Materials Management component includes the following processes.
Consumption-Based Planning (MM-CBP)
Consumption-Based Planning provides procedures that work on the assumption that stock has been consumed and should be replaced by preparing new orders and purchasing new stock. The purchases made depending on the record for usage. The users use this data to generate forecasts. Alternatively, they might use the data to prepare orders based on reorder point principle. Consumption-based Planning also records additional requirements of stock as requisitions and allocates them to the responsible buyers in Purchasing Department. In the process, the system determines the appropriate order quantities, and through that, it ensures that an adequate level of stock is maintained at all times.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
In an MRP system, the quantity of materials required for production is calculated. The main task of MRP is to monitor stock levels. Moreover, the system automatically generates orders for purchasing new stock. Consumption-based MRP is used to generate orders using forecasts or the reorder point principle. It depends on usage data and is therefore integrated with R/3 components like Purchasing, Warehouse Management, and Inventory Management.
Purchasing (MM-PUR)
The purchasing module is designed to mechanize purchasing in an organization. The module has quite a few tasks such as acquiring materials, sorting out the requisitions issued by the material preparation and control system, dealing with requirements arising straight within a user department, and monitoring deliveries and payments to suppliers. R/3 system’s purchasing functions range from generating purchase requisitions and printing purchase orders to preparing long-term purchase agreements.
Purchasing decides whether the user can place orders using existing quotations or if the user must first issue requests for new quotations. The system can, hence, automatically generate purchase orders based on the existing data.
Purchasing also provides information for vendor evaluation, vendor selection, Volume (material or vendor) determination, and order monitoring. Buyers and material planners can obtain information on stock levels, stock availability (at different locations and times), different vendors’ credibility records, possible delivery dates, and open-order quantities. Purchasing module coordinates with other modules in the SAP system to ensure a steady flow of information. The major modules that it communicates with are Controlling (CO), Financial Accounting (FI), and Sales and Distribution (SD).
Inventory Management (MM-IM)
The Inventory Management module helps the user handle transactions that lead to alterations in stock levels. It includes the following steps: management (recording and tracking) of stocks on both quantity and value basis, preparation of stock, entering and documenting all stock movements, counting goods receipts and issues goods issues, and physically counting inventory (stocktaking).
Invoice verification (MM-IV)
The Invoice Verification (IV) wraps up the materials attainment transactions which start using the requisition, continues with goods purchasing and receipt, and end with the receipt of an invoice. The system also allows invoices that are not created through a method of requisitions and automatic orders (for example, services, expenses, and course costs) to be processed. It also allows credit memos to be produced, either as invoice cancellations or discounts.
Information is available from the master record and the original documents are present in the form of purchase orders and goods receipts. According to the Functions in Detail brochures, the users only need to enter the total amount for the items on the purchase order. If the total matches the preplanned values, the system makes all postings and releases, or clears, all invoices for payment. If preset budgets are exceeded, the system blocks payment of the incoming invoice.
Logistics Invoice confirmation is incorporated with other SAP components, in exacting Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO).
Warehouse Management (MM-WM)
The Warehouse Management defines and administers complex warehouse structures. It supports the slow movement of goods and upholds current stock inventories in the organization’s warehouses. The user can divide the structures into different physical or logical units, such as high-rack (or high-bay) and block storage areas. The system allows users to choose to organize and administer them on a random basis or the fixed storage bin principle. However, it uses defined strategies that indicate clearly where the goods should be transferred. For example, it might specify where goods should be placed for storage till they can be moved to their destination or till transport can be arranged.
The Warehouse Management is mostly interfaced with more than one module, for example, the Inventory, the Sales and allocation, the Quality Management, and the manufacturing development systems.
Information Systems
The Logistics Information System supports both day-to-day and long-term decision-making given every variable. It is divided into quite a few sub-modules like the ones associated with acquiring Information Systems, Inventory Controlling, or seller assessment. The Vendor Evaluation sub-module, for instance, built in the Information Systems unit, supports optimization of the purchase transactions.
Formal model (recommendation) of a selected business process (in IDEF0)
This study seeks to provide an organizational optimization mechanism for Epinions.com through the implementation of the IDEF0 model. This research focuses on the analysis of service provision processes, which are revolutionized by the growth of the enterprise business entities’ (EBE) structure and the scope of activities, which have been enhanced and optimized in the view of the company’s mission. This research applies an expert analysis to the Business Model of Epinions to replace the EBE involved. Planned relationships in the middle of participating EBEs are also symbolized. Since all life-cycle relations are shown in the commerce model, these signify which EBE plan is developed for which EBE.
The current service provision structure is managed by CM and must be enhanced given the challenges of the company’s expansion. Moreover, growth creates possibilities of more customer-tailored and profit-oriented approaches to the provision of the services, which are now mainly connected with the supply of peer reviews. Hence, a process model needs to be created which changes the sources of reviews.
Context model of service provision process
The model which is created for service provision optimization works through the creation of plans that map out the process of service realization and its provision to the customer. The current mechanism of service provision is not adequate for the much larger organization that the firm aims to become with increased product categories and increased data that needs to be reviewed.
To meet the new challenges presented by the changing environment and the expected and aspired growth of the organization, the existing number of CM must be increased. New employees must be hired which might increase the costs of the company and reduce its profits. The current model seeks to redefine and realign the functions of CM with the service provision processes to guarantee the employees’ productivity and the company’s efficiency. Moreover, it seeks to provide the groundwork for the provision of new services which would make it more profitable. The main innovations recommended to service the provision model include the following:
- There is a need to reorient the CM’s roles. We consider that this will allow the organization to take advantage of the ever-widening variety of services while preventing the extra headcount. It is further believed that this will encourage them to deal with problems with a cross-functional view, resulting in cost economy and worker efficiency.
- The organization must divide functions processing into some categories between the CM and the registered members who enjoy Eroyalties and other advantages.
- The organization must provide and charge for a new service of professional but tailored analyses of products’ categories recognized by Category Managers (CM).
- There is also a need to steer Category Managers (CMs) towards greater customer communication for specific category groups rather than the structuring of information for existing categories.
In sum, the modeling of new service provision processes will allow the association to absorb the ever-widening variety and scope of aid while limiting extra headcount. Further, the provided plan will make it possible to bring the company back on track and gear it towards cost-efficiency and economy while maintaining the quality of service.
The following diagram (Diagram 1) characterizes basic features of the service provision process, which will become more specific and different in the IDEF0 model.
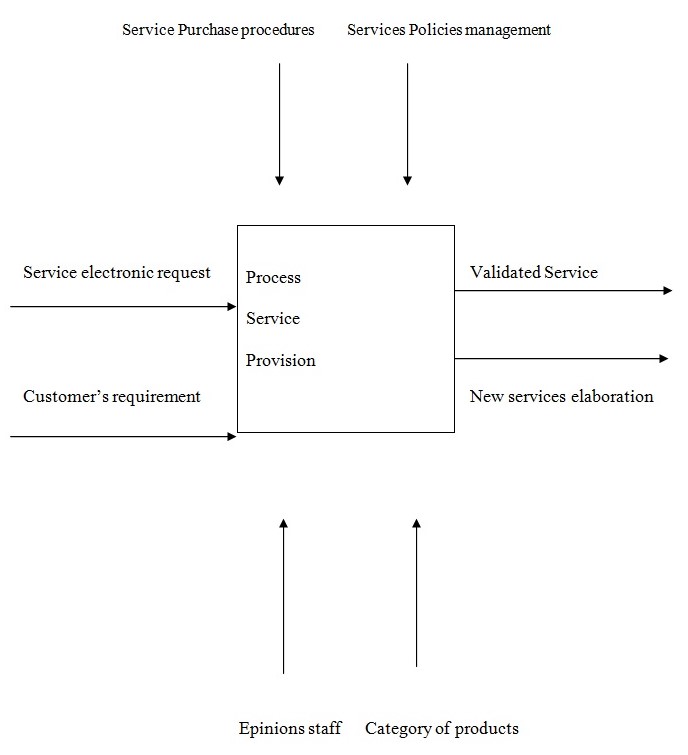
As various services will be provided and ensured by both the CMs, who will take the functions of CC, and by the registered members, the delivery of service would be differentiated during this specialization. The development of products category structures and cooperation with product companies would be realized on the permanent basis of the service provision process as an innovative mechanism of designing new services and possibilities for the customers. The acknowledgment of requests would be provided by the company’s online support as well as the process of communicating requests to CM and registered stakeholders.
Communication with customers on the matters of service delivery would be maintained at every stage of the service provision process to ensure guaranteed quality and complying with responsibilities. Structuring services, updating product data systems, and delivering tailored services for individuals and companies would be realized through specialization. The data system is enabled to process acknowledgments of service requests at the stage of service delivery and using the elaboration of new services as a support tool.
The full model is represented in the diagram below (Diagram 2). A1 stands for the first stage of the process, which presupposes acknowledging requests; A2 explains the process of service delivery and realization. A2 is then subdivided into A21 and A22; the former presents the process of structuring products categories and elaborating them (Category Managers and registered members) and the latter realizing tailored services for customers (Category Managers). Finally, A3 stands for developing new services for the customers.
Mission Implementation
The arrangement of firms at the enterprise level – in the core, general management and control reforms for the organization – used to be comparatively easy to implement in the past. Traditional organizations consisted of patterns of practical units occupied by product expansion, production, and sales. Depending on the degree of trust between the groups, necessary for the individuals to interconnect their work with the actions of others, the administration would create a sequence of connecting instruments to organize their work. Furthermore, there was a fundamental supposition that “big is beautiful” and “more is better”. Recently, it became imperative to add new separations, internalize some external aspects of the business environment, acquire more contributors, and divide the business into more units.
The researchers in the 1990s have observed a noticeable turnaround of that trend. More and more enterprises noticed they had guzzled more new and unconnected activities than they could effectively integrate. It became obvious that companies could try new markets and new technologies by the means of tactical alliances that didn’t necessitate risky, pricey, and energy-sapping attainments. Several firms, like Xerox, Dodge, Google, and later Epinion.com, realized the untapped bloodthirsty forces that could be set free by rethinking the way they arranged their inner operations.
Requirements for mission implementation
As the current mission of Epinions.com is to help consumers in any location, who are both individuals and commercial entities, to use the power of information to find, compare and buy anything. The best way of implementing the objectives of the organization is to study the experience of the companies, and search engines that act, or acted in this sphere of the market. To enhance the activity, managers need to invent a new approach of acting, thus attracting the competitors or investors to either cooperate or invest in the new implementation. The company may need to start the activity in the previously undiscovered segment of the market or capture the related one. This requires devotion and commitment on the part of the organization and the management, as it is the most crucial step in the history of any company.
To execute the elaborate strategies to bring the ideas to life, it is necessary to be fully fuelled with commitment, as it is almost impossible to achieve any goal without powerful motivation. The tactics for capturing the new sector of the market are to get all the necessary information. Thus, an essential step for it would be acquiring new business contacts with people, companies, or services that would be able to provide trustworthy, relevant, and expert information. Another important factor is to not tolerate the leakage of the information so that competitors could not outstrip the business in this maneuver and succeed at the organization’s cost.
As it has been outlined, the main mission (objective) for Epinion.com is communication with the customers and among the customers. Thus, the successful realization of the mission requires high-quality communicational technologies: customers with various Operation Systems and various browsing systems need to be supported, and guaranteed better communication, and sufficient security and confidentiality level. To provide the necessary levels, the company needs to possess the necessary technologies and highly experienced and qualified staff to provide the required equipment and technology.
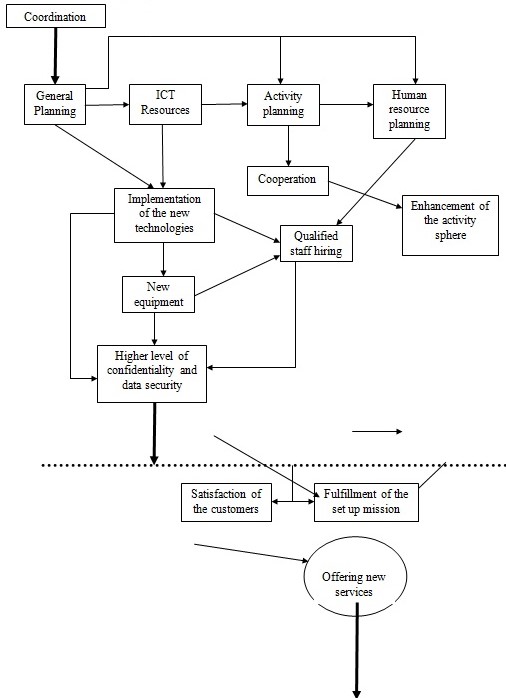
The outline above (GRAI GRID) reveals the necessary steps for reaching the objectives of the mission. Thus, General coordination means the conferences and meetings within the company, to decide the further actions by the company. Coordination usually results in general planning, which is further subdivided into several spheres. These are the ICT resources (responsible for the technologies and equipment), activity planning (planning of the internal and external affairs, such as the restructuring of the company, or the conclusion of the agreements with the other companies, or separate workers).
Human resource planning includes the staff decisions to support future activities. HR administration plays an essential role in the realization of the plans. Thus, the selection of the staff may either increase or decrease the quality level of the services, depending on the proficiency level of the employed workers. The new staff is required for servicing the new equipment and technologies and for managing the newly formed departments. The skill level and the experience of the new staff influence the future work, the quality of the work, and the level to which the activity sphere may be enhanced. As a result, the better equipment and staff experience will result in higher levels of services, i.e., the increased level of data confidentiality and data security, which is the most important factor in the activity of any company of such a profile as Epinion.com.
Thus, we can outline the specific functions of management for the current research. However, to define the functions of management, it would be necessary to understand the meaning of the word “Management” itself. Management is about solving problems, matters or issues through an application of conceptual, technical, and human skills. It is accomplished through four functions of Management: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. The proposed result is that the enterprise’s resources are used in such a way that the organization’s goals and objectives are accomplished. This definition is changed to align a bit more closely with the paper’s aims and to correspond with the claims of the enterprise analysis.
Organizing is divided into organizing and staffing so that the importance of staffing in a small business receives emphasis alongside organizing. In the management literature, directing and leading are used interchangeably. Planning is the continuing process of enhancing the business objective and defining how they will be accomplished. This involves both the broadest meaning of the enterprise: its mission, and the narrowest: a strategy and a tactic for accomplishing an explicit aim. Planning has been included in the GRAI GRID of the Epinion.com activity as the basis for any campaign, which requires thorough control and attentiveness.
Organizing is stating the internal plans of the organization. The emphasis is made upon separation, harmonization, and management of tasks and the flow of information within the organization. It is for this purpose that administrators dispense power to job owners. Organizing is necessary for any undertaken action, as unqualified performance may fail. Epinion.com may be characterized as a company with a high organizational level, as it is considered the leading company in its sphere of marketing activity.
The same may be said about the level of the next management function – Staffing – which means keeping all jobs in the company filled with skilled people. Employing, training, estimating, and balancing are the precise activities involved in this function. In the electronic business, staffing comprises all paid and voluntary jobs held by the managers of the company including the holder/workers.
Directing is having the authority over staff’s behavior through inspiration, contact, group dynamics, control, and obedience. The aim of directing is to channel the activities of all the employees to achieve the company’s objectives while concurrently helping them achieve their aspirations from the job. As for the directing in Epinion.com, it can be said that directing has played the greatest role in the development of the company; indefinite measure it involves the previous functions, and in the full measure it defines the following. Controlling is a four-step procedure of stating presentation averages based on the company’s aims, gauging and reporting the current situation, evaluating the two, and taking counteractive or defensive action as required.
The Decision System
The decision system for Epinion.com may be as it is shown in the chart. The decisions are taken according to the plans and objectives of the company. It is important to note that the required decisions can be taken not only at the stage of coordination, or general planning, but at any stage. If the situation goes out of control – the performance levels have deviated from regular levels or the situation on the market has changed and the performance flow needs to be urgently amended – important decisions have to be made.
But the question is: are the workers going to use the decision system for every small alternative? It’s impractical and would be very unprofitable. You can use it to make larger deliberate and managerial conclusions. Even then, it is more of a supporting tool to a manager, who takes the results of the decision system as one of many pieces of data and makes a conclusion from there.
Even if it was possible to solve the problem and have a proper decision system procedure to estimate all the subtle cues a person gets throughout the choice-making course, it would be still necessary to figure out a way to explain cues into data tips and decide what each cue means. But it is quite unnecessary to perform it explicitly because the decision system needs to know the prompts and know what they signify. It also needs to be able to pick up on new cues that enlarge as background shifts.
The Requirement Specifications
The management and control system requires thorough investigation and elimination of the likelihood of the faults as much as possible. To attain the goals to the fullest, it is essential to appoint talented and experienced managers to create the plan. As the management and control systems need to be included in the plan, these requirements are similar to both. Plan and the management/control system need to be:
- Complete: Must be clearly defined and must not include circumstances that will not be taken into account or needless;
- Consistent: There should be no conflict between individual obligation statements that define the performance of necessary capabilities;
- Correct: It must be exactly and precisely recognize the individual states and restrictions of all situations that the desired ability will stumble upon and it must also define the potential’s proper reply to those circumstances;
- Modifiable: For obligations requirements to be modifiable (adaptable), associated concerns should be grouped jointly and unconnected concerns must be divided;
- Testable: For a plan to be testable it must be affirmed in such as way that pass/fail or quantitative estimation criteria can be gained from the condition itself and/or oriented information;
- Unambiguous: A scheme that specifies a plan, or control system is unambiguous if it can only be realized one way;
- Verifiable: To be verifiable control system and its specifications must be consistent.
Conclusion
It is recognized that adult content is the ideal market segment for Epinions to enter. This market opportunity can have far-reaching effects for the corporation as it has been profitable for the incumbent group of actors and allows Epinions to gain a technical advantage. As present categories get bigger and new categories are added, Epinions will be grateful to adapt the job plan of its Category Manager. Moreover, the scalability answer that we suggest would be to rethink CM roles. CM adopting the role of CC would be very against his conventional role.
This change of roles will allow Epinions to benefit from the new expanding market without having to increase its labor force. The recommendations will also make the approach more cross-functional and will allow Epinions to benefit from increased productivity and reduced costs. CMs will also have more time to direct their employee’s behaviors and make them more profit-oriented. These reforms may also result in external expansion, endorsement within Epinions, and improved network for communication and information transfers across groups that will make Epinions’ in a home in order base more healthy (Hax & Majluf, 1996).
In conclusion, it is necessary to emphasize that automated management and control systems are the most essential success tools in any organization. The systems used by Epinion.com enterprise will result in great success for the company. If the recommendations are implemented, Epinions.com will not only expand its market share but also it’s quality of service and will become one of the most successful actors and one of the leading companies on the market of web communication.
References
About Epinions, 2007. Web.
Hax, A. C. & Majluf, N. S. 1996, The Strategy Concept and Process: A Pragmatic Approach (2nd Ed.), Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Hubbard, G. 2004, Strategic Management (2nd Ed.), Prentice Hall, Sydney.
Macaulay, A 2004, ‘Enterprise Architecture Design and the Integrated Architecture Framework’, The Architect Journal, 1, 2007. Web.
Platt, M 2002, Enterprise Architecture: Microsoft Architecture Overview, MSDN Architecture Centre, 2007. Web.
SAPR/3 (2007), Wikipedia. Web.
