Introduction
Management is the process of getting activities completed through other people effectively and efficiently (Agarwal 2008, p.302). These activities involve planning, organizing, leading and controlling, and they are commonly known as the four functions of management and they are described as follows:
Planning is the process taken to decide activities to be undertaken by the firm in the future (Hill and Jones 2009, p.381). The organizing function ensures that available resources at the firm are used to the maximum distributing them strategically all in accordance to the planning function. Leading is the function that gets everyone to play the assigned role in order to meet set goals according to plan and lastly is controlling also looked at as monitoring that checks the progress according to the initial plan, and imposing modification where need be in case of feedback that things are not aligned to plan (Mullins 2010, p.34).
Organization management is therefore the process forming a relationship between the people and resources in order to reach specific objectives and company goals (Agarwal 2008, p.303). Organization management has five principles that are based on the process, span of control, unity of command, homogeneous assignment, delegation of authority and flexibility.
Organization management is a five step procedure, the first step involves determining of the tasks involved, here nature of the job, qualifications required for the job and time frame required for task completion is considered (Mullins 2010, p.35). The second step is to subdividing major tasks into individual activities, the various available tasks will be portioned as standalone projects that can be performed separately in various departments (Triplet 2007, p.3).
The third step takes assigning specific activities to individuals; the organization at this point has to recognize the abilities of each person before assigning the available tasks. The tasks are matched to the individual and are given to the most capable person to accomplish the tasks effectively. The fourth step in the process is to provide the available resources to assist the individuals to complete the tasks assigned successfully (Moyles 2006, p.176). The organization provides the resources depending on the nature of the task assigned and complexity involved. The last procedure involves designing an organizational structure to determine the plan that will combine the various assigned tasks to one once they are completed and how the various structures of the organization can work together Picot et al 2008, p.12).
Managers in an organization ought to understand the importance of organization and management, the process by which people, various tasks, technology are combined and coordinated so as to effectively achieve organizational objectives (Triplet 2007, p.4). Bob and Lloyd need to realize that connecting the people, tasks and resources in the fast-food business process is necessary. Bob and Lloyd will have to attain optimum use of the organization resources to accomplish all activities and implement their ideas on the fast food business (Triplet 2007, p.5). Organization and management should be centered around setting policies and missions of the fast food business, and deciding on its structures (McNichol et al 2007, p.13).
Analysis issue
The decision by Bob and Lloyd to start a fast food company in Cambridge is going to be a good investment if the two consider carefully organization and management of the fast food business. How they set the structure, build their work team, carry out leadership and in addition address organization culture, will determine their success rate in the fast food industry in Cambridge. Bob and Lloyd need to consider the following four elements in detail to make strategic decisions for their new investment (Chen 2004, p.5).
Organization design and structure
An organization structure is a system of interrelated jobs, job groups and finally authority (Burstein 1991, p.327). An organization structure identifies how the individuals in an organization are grouped to departments and departments grouped to form an organization. It includes the design of systems to ensure effective communication, integration and coordination of efforts across departments. An organization structure is usually represented by an organizational chart designating formal relationships including number of levels in the hierarchy and span of control of managers and supervisor (Schriber and Gutek 2010, p.642). Bob and Lloyd will have to select an organization structure that will reflect the span of control (Alder and Jelinek 2006, p.74). The fast food organization structure should define each person’s role and responsibility.
The purpose of having an organization structure is to provide a common reference that in general shows the overall relationship between top managers, middle management and low level management (Murphy and Willmot 2010, p.268). The type of organization structures drawn traditionally always placed the CEO on top and everyone else arranged in layers depending on departments but today there many modern organization structures that create decentralization and flexibility. Although there is no standard organization structure, Bob and Lloyd should adopt a structure that increases horizontal coordination and communication, to encourage adoption of change (Burstein 1991, p.327). A horizontal organization structure will decentralize decision making in the fast food company. Chart one below is a modern organization structure of an organization with three management levels. (Burstein 1991, p.327).
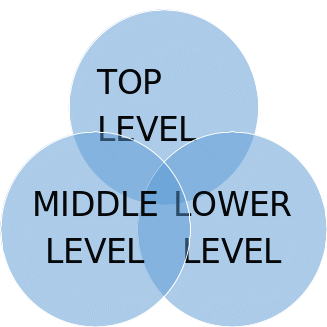
There are four elements that assist a company to design its organization structure, one is job specification, and this involves defining the departments and what they are responsible for (Barry 2000, p.33). Two is departmentalization, where the jobs are grouped and responsibilities distributed in line to company objectives. The third element is span of control, where the management considers the tasks at hand and number of units and hence the two are merged favorably (Chen 2004, p.6). The last element includes delegation of authority, which introduces managers in charge of units and the right to make decisions on behalf of the company is obtained by the head of each unit. Bob and Lloyd should delegate authority to the fast food company managers so they can make decisions easily. Managers in each unit department should make decisions on behalf of the company.
Teams and team working
For any management to turn around the organization, the management has to encourage the team approach. It has been consistently said by management gurus that a team outperforms individual and set enthusiasm, focus and overcome big challenges. (Mullins 2010, p.46)
A team is a small group of people, who have complementary skills and are committed to a common purpose, which they all feel accountable to (Katzenbach and Smith 1993, p.68). To form a superior team for the hamburger fast food company, Bob and Lloyd have to make sure they follow the five principles of a team.
The team for one has to be small, two to twenty five is a favorable number for a team, and this is because it is easy to work with a small number of people (Hill and Jones 2009, p.385). The second principle is that the members of the team should possess complimentary skill (Leitner 2004, p.35). The third principle dictates that members should share a common goal in purpose and goal, this means the team’s goal must match across and also their mission (Hill and Jones 2009, p.384). The fourth principle states that the team must develop a common working approach were the team pays attention to administration and work aspects, and each member of the team should mark their role in the team’s work (Picot et al 2008, p.84). The last principle states that all the members should be accountable to themselves and to others, to ensure commitment and trust from other members (Katzenbach and Smith 1993, p.68). Chart two below represents a paradigm shift of a team system also called a team structure (Picot et al 2008, p.84).
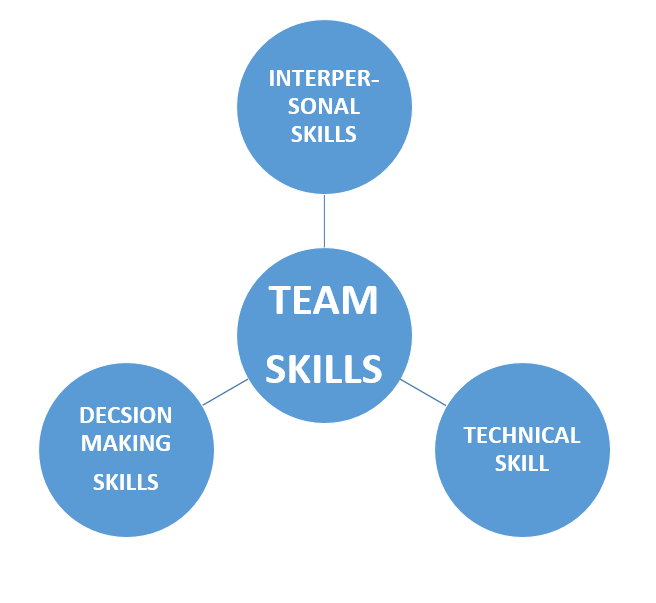
For strategic team building Bob and Lloyd should carry out their staffing and staff selection wisely, to have a motivated, vibrant workforce. The fast food industry requires qualified, fast and efficient workers and anything short to this could lead to the business downfall (McNichol et al 2007, p.2007). Staffing translates to human resource planning; here the company should consider how many employees are needed, with what backgrounds, their qualifications and the cost of hiring each one of them for objective implementation. Another factor to consider is how to obtain the desired workforce, important components to consider for recruitment such as education, experience, human relations, communication skills and motivation (Northouse 2009, p.165).
The management when taking up staff selection, they should device a system used for elimination to choose the best candidates. Having a list of criteria and a score sheet for each individual, ensure that the organization has a successful hiring rate (Baligh 2006, p.126). The organization should define each interview, create a plan, and interact with the interviewee during the interview and finally establishing a conclusion of the interview. Bob and Lloyd should conduct a face to face interview, so as to establish good interpersonal skills that each employee carries (Chen 2004, p.7).
Motivation in any organization is an important aspect; if the workers are not motivated then they are bound to decrease their production levels (Sekhar 2010, p.16). An example of motivating factors include, increase of working conditions, interpersonal relationships, pay, job security, company policies, supervising and administration (Sekhar 2010, p.17). Bob and Lloyd should motivate the fast food employees through providing good working conditions in the business and also giving them bonuses.
Leadership and management approach
A leader can be defined as a person who leads a group of people and organization or a country (Leitner 2004, p.87). Other people follow a leader’s guidelines and steer heads projects, to the followers a leadership model according to Mitchell, Margaret and Casey, John professors of leadership management university of Illinois (2007) stresses on collective strategy that involves all members entertain elements like, improving the overall performance, specifically focusing on strategy and, creating an environment of change (p.53).
Secondly, using a collective approach starts to create a good community relationship because everyone is well represented and therefore, the basis of partnerships is formed in the institution and this benefits the community as a whole (p.58). A competent leader will in the most significant way combine all members in a strategic manner to work collectively; the leader should also be intelligent and inspiring (McNichol et al 2007, p.104). In addition, a leader should suggest new strategies that work and that will yield good results in terms of performance and hence this will serve as an inspiration to all the members.
Manpower planning would be the best approach to use in trying to take the company to “imposed- incremental change” (Cooper 2005, p.231).Manpower planning as described by Cooper Crown a professional management guru and consultant in management issues (2005) is the process of forecasting and planning the human resource organization in every institution in order to plan for the future in line with the institution’s objectives and organization (p.232).
The skill proposes to be helpful when the organization has limited resources to spend but its activities must be carried out (Northouse 2009, p.168).Well the best way to improve on the good leadership qualities is to have manpower planning skills that will see the regulation of projects and a structured staffing to carry out the tasks.
A leadership mission means deciding of long terms and short term objectives, and giving priorities to strategies in order to acquire good leadership (Moyles 2006, p.178; Bass and Avolio 1993, p1). A good leader should have a strategy formula that is concerned with effective allocation of resources, making decisions about diversifications and entering into international markets to merge and participate in an organization venture. A leaders’ strategy commits it to the specific vision, mission and goal over an extended period of time through which it is achieved (Northouse 2009, p.169; Moyles 2006, p.179).
The success of implementing the policies relies on the ability of the leadership function to lead everyone else to assist in strategy redesigning (Moyles 2006, p.179) Re-designing improves an organization process, and helps adjust to the external environmental constraints that the leader has no control over (Murphy and William 2010, p. 268). To achieve the implementation of policies, Bob and Lloyd should develop a strategy-support culture in the fast food company, and create an effective and functioning structure (Moyles 2006, p.522). Bob and Lloyd should motivate the managers of each unit and the employees to learn ways in which they can contribute to the implementation process (Normore 2010). Implementation requires personal discipline, commitment and sacrifice. This is because at this stage is considered to be unstable and involves new systems that everyone has to adopt (Picot et al 2008, p.86).
Organization culture
The term organization culture is a set of attributes specific to a particular organization that may be induced from the way an organization fosters and identifies the characteristic of cultures that encourage learning and those that block the learning organization process (Adler and Jelinek 2006, p.74).
Organization culture reinforces the process of learning, organizations today are coming under a lot of pressure to perform, and this forces them to learn, change and adopt and take actions that are ethically acceptable to respond to the expectations of the competitive industry and the multi-shareholders (Schriber and Gutek 2010, p.645).
According to McNichol et al (2007) there are many types of approaches when it comes to organizational learning culture. The three most common types include (p.104):
Supportive organization learning culture: This is learning through support either from team members or from the management of an organization. Concreting organizational learning culture: this is where the learning culture is based on concrete processes and practices such as billing, logistics, and product development (Mullins 2010, p.35). Leadership organizational learning culture: this is an approach that uses leadership to reinforce learning in an organization. This means the leader in the organization; steer heads the learning process by learning the organization limitations, acknowledging these limitations and seeking alternatives to improve on organization performance (Sekhar 2010, p.17).
With the changing times there is the pressure to keep up with the changing patterns in organization learning. In the past people were redundant to make fast decisions but today people are obliged to make the decisions in uncertain situations. A learning organization is seen as an institution where workers succeed in transferring of knowledge (Leitner 2004, p.89).
By trying to cultivate an efficient learning organization, the fast food company will shows its effort is being put to redefine organization culture process. There two ways to improve organizational learning approach, the first is a single looping learning process which involves, making changes in environment without changing the structures (Chen 2004, p.8). The second involves a double loop where new systems are adopted and learning process is redefined and challenged (Murphy and Willmot 2010, p.270). Bob and Lloyd should come up with new ideas that will develop the fast food company and create a competitive advantage in Cambridge. Chen (2004) states if it is single loop would not require much training unlike the double loop (9). The double loop changes the structure and system of operations and will require Bob and Lloyd to train the employees and encourage them to adopt the new systems easily (Chen 2004, p.9).
Conclusion
Organization management is vital to any organization and hence managers should understand its approach. How an organization has a deeper understanding of this approach to run a business will reflect on organization performance. The need to connect the people, tasks and resources in the organization process is necessary. Managers today are also required to attain optimum use of the organization resources to accomplish all activities and implement its ideas. Bob should look at the resources at hand and find ways to maximize these resources to implement the ideas they have for the fast food company.
The type of organizational structure to be applied in the hamburger fast food company is very important this is because the organization chart indicates the structure of control. The design picked out should be decentralized so as to improve organizational flexibility and encourage productivity from its employees. Decentralization often increases the employee’s responsibilities, helping them to build their competencies in various fields. Bob and Lloyd should note that when all parts of the organization work together, then the Hamburger fast food company will survive. When choosing design, the various branches on the organizational structure, should learn to run separate to achieve the common goal of the organization.
A team can be productive if the employees are exposed to friendly working environment, good interpersonal relationships and assured job security, the employee is bound to attain high levels of job satisfaction and as a result improve organization performance. Bob and Lloyd should encourage the use of employee motivation in the fast food company to ensure comfortable functioning of employees in a company.
A good leader should be able to understand the importance of these relationships in the company because the communication barrier is broken at every level so that member is heard and this leads to reasoning of problem solving because they begin to understand the nature of the problem. And lastly, is the organization culture aspect that should see the management conventionally encourage a culture of learning in an organization. All this process and approaches if well applied will impact positively to organization performance because the management will be intervening at an early stage to curve good company design and approaches. The fast food company will have good performance if Bob and Lloyd monitor and control business activities in all units.
Recommendations
Organization and management is an acknowledged process that should be implemented in the day-to-day running of a business. I would recommend that for the four major elements of management planning, organizing, controlling and monitoring, the fast food company establish a customized system of this elements to suit the new business. There should be a systematic internal flow unique to other fast foods in Cambridge, for instance the process of making the hamburger should undergo through the four elements in a unique version that set apart the Hamburger fast food from other fast foods that sell hamburgers.
Because the fast food company is being set to a competitive market, the ideal design for the business should be more horizontal to eliminate protocols and allow the workers to make decisions. Both Bob and Llyod should give the employees the responsibility to make decisions in certain situations to create fast response to customer’s demands.
Bob and Lloyd to build a good team, they ought to be keen in selecting key team players and look for personnel who fit in a team. To strengthen the team they should organize team-building activities to increase their bond and also increase the level of cooperation. Leadership is very important in any organization and I would advice Bob and Lloyd to choose motivated and knowledgeable leaders. The leaders should also have interpersonal skills and good communication skills to be effective in handling a diverse workforce. Lastly the organization in order to adapt to changing times should establish itself as a learning organization, through training, orientations, attending workshops and researching on how to improve internal levels.
References
Adler, N. J and Jelinek, M. (2006) Is “organization culture” culture bond? Journal of human resource management.25(1). P.73-90. Web.
Agarwal, R. D. (2008) Organization and management. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill. Web.
Baligh, H. H. (2006) Organization structures: theory and designs, analysis and prescription. New York, Springer publisher. Web.
Barry, J. (2000) Organization and management. New Jersey, Business press. Web.
Bass, B. M and Avolio, B. J.(1993) Transformational leadership and organizational culture. Public administration quarterly. 17(1).P.1-4. Web.
Burstein, P. (1991) Policy domains: organization, culture, and policy outcomes. Annual review of sociology. 17(3). P.327. Web.
Chen, L (2004) Examining the effect of organization culture and leadership behaviors on organizational commitment, job satisfaction, and job performance. Journal of American academy of business. 99(3). 5-9. Web.
Cooper, C. L. (2005) Leadership and management in the 21st century: business challenges of the future. London, Oxford university press. P.231-244. Web.
Hill, C and Jones, G. (2009) Strategic management theory: An integrated approach. New York, Cengage Learning.P.381-389. Web.
Katzenbach, J. R and Smith, D. K. (1993) The wisdom of teams. Small business reports. 18(7). P.68. Web.
Leitner, A. (2004) concepts of leadership and management within the manufacturing industry. Norderstedt, Grin verlag. P.34-43. Web.
McNichol, E et al (2007) Leadership and management. London, Nelson Thornes Ltd.p.12-15. Web.
Mitchell, M and Casey, J. (2007) Police leadership and management. Sydney, The federation press. P.44. Web.
Moyles, J.(2006) Effective leadership and management in the early years. Berkshire, open university press. P.522. Web.
Mullins, J. L. (2010) Management and organizational behaviour, (9th Ed.) New York, Prentice Hall. P.45-48. Web.
Murphy, D. J and Willmot, H. (2010) Organization theory and design. New York, Cengage learning. P.106-109. Web.
Northouse, P. G. (2009). Leadership: theory and practice. New York: sage publications. Web.
Picot, A et al. (2008) Information, organization and management. Berlin, Springer-verlag. P.83-87. Web.
Schriber, J. B and Gutek, B. A. (2010) Some time dimension of work: measurement of an underlying aspect of organizational culture. Journal of applied psychology. 72(4).P. 642-650. Web.
Sekhar, G. V. (2010) Business policy and strategic management. New Delhi: I. K international publishing house PVT Ltd. Web.
Triplet, J. (2007) Organization design: A holistic view. New York, Collective Erudition publishing. Web.

