Introduction
Marketing in itself is a simple concept that only requires the marketer to understand and meet the customer’s needs and desires. However, achieving this simple concept involves complex ideas with interdependent factors. This is because such factors are developed against the backdrop of several changes that define the nature of the market (Ford, 2002). Further complication emerges from the fact that managers often encounter incomplete information due to unavailability of enough data, and constantly changing market situations. Often, the changes emerge from the dynamic customer demand and competitors’ behavior to fit into this whole concept (Drummond & Ensor, 2001; Kotler, 2002). This is what finally leads marketers to resort to strategic marketing as the final marketing component that defines the company’s success (Drummond & Ensor, 2001). In other words, properly aligned strategic marketing plan followed by effective implementation should lead to overall marketing goal for any firm.
Ford Motor Company has been one of America’s leading automotive producers for many years. In its efforts to extend the hallmark of American brand image, represented by “made in the U.S.A” slogan, Ford was the first ever company to make hybrid sports utility vehicle for the exclusive market niche (Mitchell, 2002, p. 99). Considering its popular model of ‘Ford Escape’, the SUV product sold highly in the international market and redefined Ford’s market strategy all over the globe. It offered the company a lease of life as it repositioned itself as a more competitive automotive maker. Due to this development, the company has made several efforts to ensure they expand into new areas such those that use alternative fuel in order to appeal more to the global market and ensure sustainable production. This kind of strategy can only be successful if new methods of marketing are adopted for the global market. This paper critically analyzes Ford Motor Company and its products sales in the global market. An analysis of strategic marketing has been critically looked at in order to chat the way forward for Ford Motor Company.
Ford Motor Company Products
Ford Motor Company is one of the American leading car and truck makers with it’s headquarter at Michigan. The company participates in the designing, development, manufacturing, and providing car services all over the world. The company operates in two fronts: the automotive category and offering of financial services. However, its main area of operation is in automotive services, where it sells vehicles under brand name Ford. In addition, other popular brand names that the company uses to sell its products are Volvo, Mercury, and Lincoln. This branch of business helps the company market its products of cars, trucks and vehicle parts all over the world. It has an expansive market share in the global market with over 100 locations. In its efforts to carter for wide range of global customers and enhance the strength of its market niche overtime, Ford has developed several models of vehicles (Mitchell, 2002). Its first hybrid product is the Ford Escape that targets the general public. It’s an electric gas product. In this strategy, it focuses mainly on fleet service production. The other line of production is its Ford Focus which belongs to the fuel cell product category.
Global Marketing Mix
Ford Motor Company has global distribution of its products in over 200 markets. The company has about 3000 staff members. Its long term strategy has been to concentrate its core business as well as enhance its affiliation with other brands. Currently, Ford’s range of products totals 52, with 8 different brands (Mitchell, 2002). At the international level, Ford’s operations are found in several global regions that include European, North America, South and Central America, Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Middle East. Other the 52 models of vehicles the company produces and sells in the United States, its branches in European regions, Asia, and Africa sell about 47 types. In its approach to carter for each market segment, the manufacturing of vehicles is designed and manufactured according to the uniqueness of each market as per the demands. That is. The features of each vehicle type designed for each region exclusively defines the market demand of that region, after thorough market research. The features do change in terms of name and design as per the regional market demand dictates.
Strategic Marketing: A Balanced Scorecard Approach
Marketing philosophy relies on the process in which organizations obtain the necessary approach to acquire their needs and wants by singling out value of the customer, strive to provide it, communicate and deliver it at the right time and place (ReVelle & Frigon, 1994; McCarthy, 1994). In this dimension, it is possible to state that the primary concept in marketing is the need to identify and concentrate on the customer values. To do this, it is important to focus on the product, exchange process, communication and relationships between the company and its partners as well as that of customers (Hambrick & Fredrickson, 2001, p.49). Marketing basically involves a strategic approach to the achievement of organizational long term strategic goals. This also helps the organizations gain competitive advantage in the market share. The specific organization therefore is able to make use of its resources according to the changing environment in order to go with the customer demand and needs, and at the same time continue to satisfy the needs and expectations of the stakeholders (Vithala & Joel, 1998; Sutton & Klein, 2003).
However, as the business environment changes and is continuously defined by different strategies, it is critical to set appropriate measures to meet the success in business development. Instead of solely relying on the financial measures, a particular strategy is needed to give an overall view of the business. This is why Kaplan and Norton (1992), cited in Drummond & Ensor (2001, p.8) developed a ‘balanced scorecard’ approach, which entails financial as well as non-financial measures to find the overall business status. In this approach, a business scorecard depends on the following fours sets of measures:
- Financial measures; involve analysis of how the investors and stakeholders perceives the organization issues,
- Customer focus; what kind of perspectives have the company build in the eyes of its customers,
- The internal events; this involve analysis of the organizational internal resources and activities that help them achieve customer satisfaction and identification of areas that the company will cuts its competitive advantages,
- Innovative and learning initiatives; in order to cut survival tactics and develop prosperity in the business initiatives, organizations will need to develop improvement mechanism (Drummond & Ensor, 2001).
It is through these indicators that organizations area able to develop performance criteria. This enables them to perform objective based evaluation. Drummond & Ensor (2001, p.8) observe that a winning strategy should be in a position to address the above specified areas and provide appropriate initiatives for future applications.
Has Ford Motor Company managed to adopt complete strategic marketing initiatives according to the criteria stated above? In order to clearly understand the position of Ford Motor Company, it is important to elaborate the importance of its strength and weaknesses in terms of its ability to penetrate the global market rather than the United States market only.
SWOT Analysis
Strength
Considering its status in the auto industry in the global market, Ford Company has been identified to have several strengths that help it establish its position in this highly competitive industry. The Ford brand has a lot of recognition and respect all over the world. Its big capital base gives them huge economy of scale more than many other competitors in the industry, hence their ability to handle the production and administrative issues with ease. The company also has three major subsidiaries that reinforce its strength in the global market due to ability to diversify its production range. In other words, the company has a very deeply rooted product line that has made it reach all market segments. They also use in-house suppliers, a strategy that enables them to reduce the costs of inventory, subsequently allowing them to save and venture in other areas of product life cycle. However, the company’s large size may also present one of its main weaknesses. This is because there is a possibility of bureaucratic development in the company management, hence creating a difficult scenario when there is need for change (Grant, 1991). Furthermore, its large size means that sometimes it’s not possible to effect timely changes as may be required time after time.
As stated earlier, Ford has very strong and successful brand recognition. This is because the company is being marketed through recognized brand names in the global market of Ford, Mazda, Jaguar, Volvo, Land Rover, among many other brands. Through these brands, the company is known for its innovative approach to design and production, hence ability to supply consumers with fuel efficient vehicles. The company has based its belief that its integrated strategy in the global market will enable them survive in the continuously dynamic market. Moreover, the company has distinctively established itself as an environmentally conscious institution, considering its clean production and recyclable products. This can be noted when it became the first ever company to install ISO 14001 throughout its global facilities (Schmidt & Wright, 2006, p.129).
Ford Company is also known to be successful in its new initiatives to manufacture new products in the US markets. Currently, it has the best-selling truck brands, sports utility vehicles, and vans. Over the last ten years, the company has been striving to launch new products such as Ford Focus, Mondeo, among many others in Europe that have proved very successful. In other regional markets, the company has successfully introduced new products in addition to the old models.
Financially, Ford has established itself as a very strong networks of finances as well as marketing networks. Its huge financial might helps the company manage its brand expansion strategies and increases its services to its customers. Ford holds over 30%interest in the Japanese Mazda Motor Company, allowing it to have easy access to larger Asian market (Schmidt & Wright, 2006, p.131). Through these initiatives, Ford has managed to develop strong customer loyalty throughout its wide range of market segments.
Weaknesses
Despite its massive financial might and wide range of products, Ford has not managed to exhaustively penetrate European market. For example, the company has not done well with its Scorpio model, which was designed for the low market end. Its inability to make vehicles popular with the vibrant mini and medium sized MPV market makes it a weaker partner in the global market (Schmidt & Wright, 2006, p.131). This is in comparison to Toyota Company that has managed to thrive in this market segment. The company also lacks much presence in the Asian market. Its only significant presence in the larger and prosperous Asian market is through its partial ownership of Mazda brand. In the highly populous India, the company brand has significantly registered failure. Its decision to retreat in its initial plan to enter Korean market through Daewoo Motor Company in the early 2000s did not help much in its international strategies.
Opportunities
In the recent past, several changes have occurred in the global market, particularly in the Asian region. In this market, China represent one of the biggest destination for foreign investors as it is slowly growing into one of the most vibrant markets following their admission into the World Trade Organization (WTO). In the previous years, there have been limited opportunities for foreign investors due to countries stringent trade barrier. There was also “thirty percent cap on any foreign ownership of any Chinese operation” (Schmidt & Wright, 2006, p.132). With their entry into the WTO, China is attracting more foreign companies to venture much into their markets. Currently, the government of China embraces direct negotiations between local car-makers and foreign companies. The former highly bureaucratic nation has changed tact and has now streamlined itself for proper business deals to move faster than ever before.
Ford has an opportunity in this market as it has both the financial and technological ability to penetrate the market in its global initiatives. The extensive use of technology and innovations allow the company to develop extensive brands of vehicles, hence ability to achieve this initiative. There is also an opportunity in the e-commerce and internet that Ford can use to increase its strategic market share.
Threats
Ford faces some threats in its global market initiatives. The increasingly informed consumers are making it difficult for the company to penetrate several available market segments. The global market’s demand for high quality products at cheaper cost has changed the way automakers approach its market segments. The company’s competitors such as GM and Honda are very strong in terms of their brand names and market share. This is despite its large financial capability.
The most worrying trend is the global market reduction in car purchase and the slowing American economy as a result of economic slowdown in the last few years. Considering its global market position, Ford has become very protective of its American market. However, the recently high profile cases where some of its models were recalled through Court order have given a wrong notion of the company products. According to the Court ruling, it was established that Ford had “inappropriately installed ignition modules that were prone to stalling” (Prahalad, & Hamel, 1999). This recall affected models made between 1983 and 1995 and was estimated to have cost Ford a whooping $125 million (Prahalad, & Hamel, 1999).
Conclusion
The first approach that Ford needs to consider is its customers, the existing ones and the targeted ones. It must analyze what market segment is made of what kinds of customers. The best way to approach this strategic marketing framework is to learn a thing or two about the competitors within its targeted market segment around the globe (Peteraf, 1993). Secondly, the company needs to balance the internal corporate responsibilities with the needs of the customers as illustrated in the diagram 1 below. The successful management of these initiatives should enable Ford to develop as well as maintain a strong global market position.
Through this strategy, they would also be able to conform to the changes in demand and supply. For example, skyrocketing gasoline prices have increased more demand on high breed vehicles. This can be successfully achieved through segmentation of the global market that would allow for concentrated focus on each specific market segment Moore, 1993). This would help the company develop more hybrid brands instead of the gasoline fueled vehicles that seem less popular with the American and global markets in general.
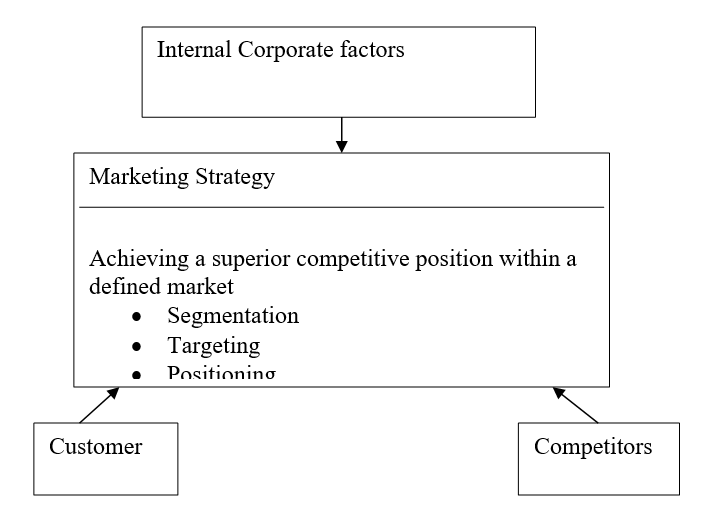
The second strategy is to develop more friendly prices to its sticker prices, considered one of the highest as compared to its global competitors. The pricing strategy is said to be one of the most hindrance to Ford’s variety of products. It is sometimes necessary to lower prices so that it is within the reach of low end consumers (Kline, 1999). By doing this, it would be doing penetrative pricing in order to gain competitive advantage in the market. For example, in Japan, Toyota and Honda have managed to penetrate the market with their low end products of cheaply priced and smaller vehicles (Bradley, 1995). Ford can also develop smaller vehicles, given its massive technological ability and capital base.
Reference List
Bradley, F. (1995), International Marketing Strategy. New York. Prentice Hall.
Drummond, G. & Ensor, J. (2001), Strategic Marketing: Planning and Control. New York. Butterworth- Heinemann.
Ford, D. (2002), Business Marketing Course: Managing in Complex networks. Chichester. John Wiley.
Grant, M. (1991), The resource-based theory of competitive advantage: implications for Strategy formulation’, California Management Review, Spring, 118.
Hambrick, C. & Fredrickson, W. (2001), ‘Are you sure you have a strategy?’, Academy of Management Executive, 15 (4), 48–59.
Kline, N. (1999), Hands-on social Marketing: a step-by-step guide. London Thousand Oaks.
Kotler, P. (2002), Marketing Management: Analysis Planning and Control (8th edn). Englewood Cliffs, NJ. Prentice Hall
McCarthy, J. (1994), Basic Marketing: a managerial approach. Burr Ridge, IL, Sydney. Irwin.
Mitchell, Colin (2002), ‘Selling the brand inside’, Harvard Business Review, 80 (1), 99-105.
Moore, J. (1993), ‘Predators and prey’, Harvard Business Review, 75–86.
Peteraf, M. A. (1993), ‘The cornerstones of competitive advantage: a resource based view’, Strategic Management Journal, 14, 179–91.
Prahalad, C. & Hamel, G. (1999), ‘The core competence of the corporation’, Harvard Business Review, 68, 79–91.
ReVelle, B., &. Frigon, L. (1994), From concept to customer: Management 2000 integrated product development. New York. Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Schmidt. A. & Wright, H. (2006), Financial aspects of marketing. London. Macmillan.
Sutton D. & Klein, T. (2003), Enterprise Marketing Management: The new science of Marketing. Hoboken, N.J. Wiley Publishers.
Vithala, R. & Joel, H. (1998), Analysis for Strategic Marketing. Chicago. Addison Wesley.

