Introduction
Porter (2011) states that operations management is a function in organizations that is concerned with the management of resources needed in the production and delivery of goods and services. Since all organizations, whether large or small, private or public, profit oriented or non-profit making, produce goods and services, it is necessary to manage its operations. Operations management involves various activities that are involved in the production of goods and services within an organization. It is concerned with the transformation of inputs into outputs with respect to the policies of an organization.
The content of this report will explain different concepts of operations management. It will also evaluate the utility and relevance of one of the operations management topics to the contemporary business environment. The topic chosen will be forecasting.
Historical development
Over the years, many organizations have realized the role that operations management plays in promoting development within its constraints and the country’s economy. This concept was first discovered by Adams Smith in the eighteenth century. In his view, he suggested that work should be broken down into various tasks, and that each employee should specialize in the task that they are best skilled.
In the twentieth century, F. W. Taylor applied Smith’s theories to develop his theory of scientific management. Between the year 1930 and 1950, people used the term production management in place of operations management. Most organizations were involved in the production of goods. During this period, organizations invested in enhancing economy in the production process by closely studying the employees to ensure that their efforts boosted productivity in the organization (Sahaf, 2009). By 1970, most organizations had come up management practices that focused on service delivery and not just the production of goods and services.
This led to the introduction of the new term “Operations management.” Service organizations had become prominent by then. Another change that was experienced during this period was great concentration on production and its management involving both goods and services (Kumar and Suresh, 2009).
Operations management concepts
Joseph (2004) defines operations management as a procedure that involves the addition of value to the resources that are input into the system to produce the output that is prescribed in the organizations’ policies. It is the role of the operations manager to harmonize all the required inputs such as supplies, capital and workforce, schedule of activities involved in the transformation process, and provide control over the entire system to ensure high quality outputs that are cost effective are achieved (Torben & Winther, 2010). As the author observes, definition of the concept has four major elements namely:
Resources
They are in various forms such as human force, materials and capital. Human force refers to the labor provided by employees. Material resources are the physical entities for instance machines and supplies. Capital may be in form of loans, bonds or stock.
Systems
This is the combination of various elements in the production process to achieve the set objectives. Since operations are just one of the functions in an organization, it is a sub-system of the organization’s bigger system. It enhances the relationship between the various components in the system including input, transformation process, output feedback, and the environment. The sub-system ensures that, besides pursuing its set goals of producing high quality goods in a cost effective manner, the organization’s overall goals is also met. This means that it should work together with other sub-systems within the organization.
Value addition
Value addition means making the inputs to have more value than outputs. This is done through the transformation process. In today’s business environment, transformation is enhanced through the use of technology. The effectiveness of the process determines the productivity of the organization. Productivity is the rate of output per hour as compared to the cost of inputs. Input will be considered to have had value addition if the ratio between output per hour and cost of input is higher than one. Operations managers should concentrate on maximizing the ratio and enhancing the efficiency of the transformation process.
The main purpose of operations management is to provide quality services to customers that meet their needs and make the most out of the available resources. Operations management is geared towards ensuring that the customer needs are satisfactorily met within the set time limits and at an affordable price. Utilization of resources means, getting the best outcome from the used resources by reducing their waste or under-utilization. While conducting the activities of operations management, the two objectives should be put into consideration. Operations mangers should strike a balance between the two objectives because if one is enhanced it leads to the depreciation of the other. The balance between the two is influenced by market trends, market rivalry and organization’s strength and weaknesses.
According to Stevenson (2007) operations management involves a number of interrelated activities across the organization. These activities range from making predictions, capability planning, scheduling, quality assurance, employees encouragement and training, inventory management among others. To illustrate these activities let us take an example of an airline company in the modern days:
First, prediction activities would involve such elements weather conditions, demand for the flights with the company and the growth of the company in within a given period of time. As Charry (1995) states that, prediction helps an organization to plan well and be able to prepare daily schedules. In this case the airline company will be able to make a schedule for its daily flights putting into consideration the weather conditions at different times.
Depending on the level of demand for the company’s flights it will be possible to increase the number of airplanes and trips if the demand is high. Secondly, capability planning would entail proper maintenance of the cash flow in the company through assessing the company’s capacity in terms of available assets. The airline company should be able to determine its capacity to own a specific number of planes. Too many planes whose maintenance is poor will cost a lot to the company.
A company can opt to have a few planes maintain them well and still be able to achieve the optimal profits. Third, scheduling in the company would involve preparing a time table that shows when different pilots and other plane attendants would be allocated their duties. The other activity is quality assurance which comprise of activities geared towards ensuring that the company offers quality services to its clients. The airline company’s focus would be to ensure safety of the passengers, and ensure efficiency and courtesy is observed in the delivery of services. The various departments that would be affected by the issue of quality control would include ticket booking centers, the telephone systems and cargo services department.
The fifth activity is inventory management. In any organization different items are procured to enhance the running of an organization. The airline company would procure items such as foods and beverages for the passengers, safety equipments, reading materials like magazines and beddings. There is a need to keep and manage the inventories of such items. Finally, employees’ encouragement and training entails inspiring the employees in all levels of operation.
The staff at all levels should be trained on how to carry out their roles and be helped to appreciate their different roles. Companies whether service operations or manufacturing operations have a lot in common in as far as operations management is concerned. All involve scheduling of activities, employees’ motivation, equipments maintenance, quality assurance and most importantly the desire to satisfy customer needs.
Operations systems
Operating system within an organization setting helps to transform inputs into outputs as described in the customers’ specifications. The system adds value to the input which could be a physical material or an intangible object. Similarly the output which has more value than the input can be a physical good e.g. in vehicles manufacturing companies or a service e.g. in hospitals and education institutions. Everett and Ronald (1994) define operating system as a component within an organization that helps in the production of goods and services. Ray Wild on the other hand defines it as a combination of various resources to help in the provision of goods and services in an organization.
As defined by Morris (1978), an operating system is a combination of many resources that are aimed at providing goods and services. The author further defines operations management as the activities aimed at designing, planning and controlling the operating system.
Theory and concepts of operations management
When theories and concepts are developed they remain to be of no benefit until that time they are applied in real life situation. This means that it is one thing to come up with a theory and it another thing to put it into practice. Operations management theories and concepts are not an exception. Operations management is all about what one needs to get a deeper understanding of how things work. Concepts and theories have been developed by different authors in order to help the operations managers to manage all the activities involved in the production of goods and services. This is by enhancing production and at the same time reducing wastage of resources (The Restoration Resource, 2009).
In relation to what is mentioned above, ICAB tutorial (2013) observes that, operations management is responsible for the control of the organization’s performance by ensuring proper utilization of resources to meet the customer’s specific needs. This function is to build up the value for inputs used in the production process. Every business organization whether manufacturing-oriented or service-oriented has some operational activities. In the recent years, some major concepts and theories have emerged in the field of operations management. They are considered to have greatly influenced the performance of organizations by helping them to achieve the set goals. The author further describes the concepts and theories below:
Total Quality Management (TQM)
This is an effort that is made by the organization’s management of ensuring that the quality of a product or service is improved at every level of its production. This is ensured through the effective management of the workers and the production process. This means that every activity of the human resource in the entire process is closely monitored to ensure that the final product meets the customer’s standards. This gives an organization competitive advantage over the others. Besides having a high quality products in the end TQM also ensure that every employ fully participates in the process.
Just-in-time
In this concept the organizations procure materials just in time for use in the production. They do not procure so many materials to stock them in their storage but they only procure the materials to use at a particular time. This helps to enhance production efficiency and at the same time it enhances the cost effectiveness of an organization (Badenhorst & Brevis, 2008). This is by reducing storage costs that are associated with storing materials that are due for use in the production process. This concept has been applied mainly in the best manufacturing companies for instance Toyota, Coca Cola and Dell computer.
Kaizen system
Kaizen is a word with Japanese origin which was introduced in by companies in Japan immediately after the Second World War. It is used to mean perpetual improvement. This system comprises of all people in the production department and even those in the higher levels of management. All these people are involved in improvement. Improvements are manifested in the production process through ensuring safety and operational efficiency through the reduction of waste (Lawrence & Klimberg, 2009). It also ensures that the production process meets the highest standards and it also ensures that all the employees from the lowest to the highest level are brought on board.
Theory of constraints
This theory mainly focuses on identification and removal of all limitations or hindrances that affect the efficiency of the production process. This process follows a sequence. This theory is also used by various organizations to make tactical decisions for perpetual improvement in the organization.
Another additional concept as stipulated by The Restoration Resource (2009) is project planning described in the context of controlling floods damage. The author observes that after floods are experienced in an area there is a need to carry out a clean up to restore what has been misplaced and ruined by the floods. Operations management concepts would be of great help in the clean-up activity. It will help to make the process faster, and efficient.
Projects planning concept will ensure that before the clean-up process begins a good plan has been laid showing the schedules to be followed. This ensures that those people involved in the get an understanding of various activities to engage in hence avoiding wastage of time once the program commences. The plan also helps the supervisors to exercise control over the entire process and are able to identify the people who are idle in the operations.
The layout shows the different processes in the clean-up program and how they follow each other chronologically. For instance the area has to be cleared by removing all the rubbles, repairing of roads and other infrastructures such as electricity poles and wires. The outline of the various processes helps to avoid confusion that may arise in performing roles by different members of the clean-up team. The second one is the concept of capability analysis.
The clean-up team has to examine the capability its staff and machine have in dealing with the situation. This helps to make the entire process smooth by removing any hiccups that may arise on the way to affect the process. Once a team learns about ability and potential, the number of people needed in completing a job and the relevant skills are then determined. Finally, there is the concept of location planning. The supervisors involved in the clean-up process should be able to identify flood prone areas and locate their offices there well equipped with the necessary equipments. Aspects that should be considered in setting up the facility are distance to the affected area, travel time among others.
All the above concepts and theories aim at helping an organization to establish its strategy for the future and how to run its operation in the present. As seen each concept has distinct feature that distinguishes it from the others (Turner, 2002). For instance TQM concentrates on all the operational activities while Kaizen focuses on minimizing wastage in the production process.
Production system
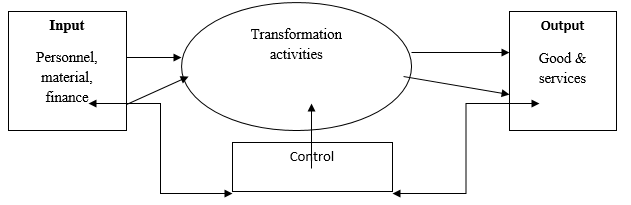
Production is a process that involves the transformation of inputs into high quality outputs as stipulated in the organization’s policies. The process may be by the use of chemicals or mechanical. Basically production adds values to the inputs (Bijak, 2011). Production system on the other hand, refers to entire structure that facilitates the production of goods and services in an organization. The system is made up of various components which work together to enhance the entire process. This means that failure in one of the components will affect the others and eventually the whole system. These components include:
- Inputs: this comprises of elements such as workers, finances, raw materials both tangible and intangible like information.
- Transformation process: this include activities such as designing, planning etc
- Outputs: These are either goods or services
- Control: this is ensured through the use of feedback information. Feedback information about the performance of the system helps to fine tune it.
- Environment: These are factors within (internal) and outside (external) the organization that affect the performance of the system (Kumar and Suresh, 2009).
Production management
As Everett and Ronald (1994) observe, production management is the application of management functions of planning, organizing, coordinating and directing in the production process. It incorporates and controls various resources used in the production system. The main purpose of production management is to produce goods and services that are of the right quality and amount in a cost effective manner. The quality of goods or services is measured with reference to the customer needs’ specifications.
Concerning the quantity or amount, the production should not exceed demand neither should it be short of demand. Products or services should be produced within the period set. Failure to produce within the set time affects the efficiency of the production department. Organizations should focus on producing goods and services within the set period of time with the lowest cost possible.
Forecasting and its relevance in the contemporary business organizations
Chary (1995) describes forecasting as a basis upon which planning in an organization is established. It involves examining the current and past information regarding the organization with an intention of predicting the future. The better an organization is in a position to predict its future the better it will be placed to deal with the future. According to Boone & Kurtz (2011), Different methods are used to do forecasting for instance time series, causal and opinion based methods. In the causal method the concentration is on predicting the factors that have affected demand for goods and services.
The time series method has its bearing on time while the opinion-based method goes beyond the quantitative feature. The author further observes that forecasting is a very important aspect in making various decisions in production and operations management. First it helps in making yearly plans. These strategies help in guiding the activities of an organization for the entire period of one year. Secondly it helps in preparing weekly and daily schedules for the production of goods and services.
Schedules as seen earlier in our discussion helps employees to know the duties allocated to them at specific times. This helps in preparing them psychologically for the tasks and gives them an opportunity to equip themselves for the task. Third, it helps in the procurement of raw materials and finally it helps to allocate duties to the employees.
Tangient LLC (2013) observes that forecasting assist the managers to come up with plans for the organizations and reduces the risks that might face them in the future by dealing with uncertain events. For example, for managers to ensure a balance between supply and demand they should be able to estimate the kind of space to accommodate the supply for every demand. The level of accuracy and expected demand are related to forecasting and are its main components.
According to the author there are three methods of forecasting. Each method can either be qualitative or quantitative. The first method is judgmental which depends on biased inputs from different sources. Time-series forecast is the second one and it examines patterns that have been repeated recently (Kreitner, 1983). Forecasting based on quality is biased while forecasting based on the quantity is objective. As Chary (2009) further reveals, different organizations will use different forecasting techniques at a go.
This means that no one particular technique works best in every situation. Forecasting is important in today’s business organizations since it is the basis of preparing daily schedules and long-term plans. Depending on the accuracy of the forecast, an organization is able to determine the amount of resources to input, the level of output, and the allocation of time to various tasks in the production process.
David (1995) defines the term forecast as an objective estimation of the future with reference to the patterns that have been established from the organization’s past performance. In the context of operations management demand forecasting is defined as a process in business organizations that helps in approximating the amount of materials used as inputs so as to facilitate their purchase prior to the transformation or value addition process.
Hyndman (2009) observes that forecasting is a process that involves statistics. It basically helps in making sound decisions on scheduling of the production process and human resource management. It also gives direction to an organization in making long-term plans. As Brown (1959) observes forecasting means predicting about the future of an organization by using historical information that could have an influence on its future. Most organizations have confused forecasting with planning. However, it is important to note that forecast does not have the same meaning as forecasting. Rather, forecasting acts as the basis upon which planning in an organization is carried out. Accurate focusing would result to proper planning.
Conclusion
As revealed in the discussion above, it is clear that operations management plays a great role in business organizations in the present society. An effective operation will help to cut down the costs associated with the production of goods and services, increase customer satisfaction by providing goods and services that meet their standards and be able to provide a good foundation for the future of the organization (Slack, Johnston, and Chambers 2007).
This is through forecasting. Forecasting should be part and parcel every management activity. This will help in making informed decision in various departments within the organization. Organizations in the modern society need to make short-term, medium-term and long term forecasts before arriving at any decision. Short term forecasts help in preparing daily and weekly schedules on personnel duties and the production process. Medium-term forecasts on the other hand, help in determining the resources required within an organization, e.g. raw materials, workforce and equipments. Finally, long-term forecasts are used in making strategic plans. They related to issues such as the analysis of market trends and environmental factors.
Reference List
Badenhorst, H & Brevis T 2008, Business Management: A Contemporary Approach, London, Juta and Company Ltd.
Bijak, J 2011, Forecasting International Migration in Europe: A Bayesian View, Springer, New York.
Boone, L & Kurtz, D 2011, Contemporary Business, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Brown, R 1959, Statistical forecasting for inventory control, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Charry, S 1995, Theory and problems in Production and Operations Management, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, New Delhi.
David, F 1995, Distribution Planning and Control, Chapman & Hall, New York.
Everett, E & Ronald, J 1994, Production and Operations Management, Prentice-Hallof India Private Limited, India.
Hyndman, R 2009 Business Forecasting Methods. Web.
ICAB Tutorial, 2013 Theory of Operations Management. Web.
Joseph, G 2004, Theory and Problems of Operations Management, Tata.
McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi.
Joseph, G n.d., Operations Management, Tata McGraw-Hill International, New Delhi.
Kreitner, R 1983, Management, Houghton Mifflin, Boston.
Kumar, S & Suresh, N 2008, Production and Operations Management, New Age International (P) Limited Publishers, New Delhi.
Kumar, S & Suresh, N 2009, Operations Management, New Age International publishers, New Delhi.
Lawrence, K & Klimberg, R 2009, Advances in Business and Management Forecasting, Emerald Group Publishing, UK.
Morris, B 1978, Workshop: Management education and development. Web.
Pannerselvam, R 2004, Production and Operations Management, Prentice-Hall of India Private, India.
Porter, A 2011, Operations Management. Web.
Sahaf, G 2009, Strategic Marketing: Making Decisions for Strategic Advantage, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd, London.
Slack, N, Johnston, R & Chambers, S 2007, Operations management, Prentice Hall/Financial Times, New York.
Stevenson, W 2007, Operations Management, McGraw-Hill, London.
Tangient LLC 2013, Forecasting. Web.
The Restoration Resource 2009, Applying Basic Operations Management Concepts How to Avoid or Deal with Flood Damage. Web.
Torben, A & Winther P 2010, Strategic Risk Management Practice: How to Deal Effectively with Major Corporate Exposures, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
Turner, P 2002, HR Forecasting and Planning, CIPD Publishing, London.
