Executive Summary
A large number of pharmaceutical companies face problems when it comes to managing their supply chain. One of the main issues that affect the supply chain of these companies is product shortages. Pharmaceutical companies such as GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) are involved in managing sophisticated supply chains that pose a huge challenge in their effective management. This situation eventually affects the product supply that may result in huge losses for the companies.
However, as the paper reveals, technological advancements such as the Automated Robotic Warehousing system, Automated Guided Vehicle System, and Radiofrequency Identification have provided an ample solution to tackling supply chain shortages and related issues in pharmaceutical companies through improving the systems’ operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Introduction
The supply chain in pharmaceutical companies is often characterized by the complexity of operations and processes. Before a drug is made available in the market, it has to undergo a number of phases, which include research and development, manufacturing, and finally distribution. The most influential phases in the supply chain of a drug in a given market are the manufacturing and distribution stages. The manufacturing phase can be divided into primary and secondary manufacturing. Primary manufacturing involves the production of the active ingredient that is responsible for curing the disease.
This process is featured with long processes that may take time, thus necessitating a series of rounded shifts. In this regard, primary manufacturing involves a multiplicity of stages that may result in inventory being held up in-between stages. Additionally, materials must undergo time-consuming quality control tests before approval for every subsequent stage. These procedures may introduce extra delays in the system. On the other hand, secondary manufacturing encompasses further processing and packaging to the final products that are ready for the market. Primary and secondary manufacturing sites exist at separate locations, thereby introducing a possibility of delay during transportation. Wholesalers and retailers are significant players in the drug supply chain of pharmaceutical companies such as GSK since they act as intermediaries between the company and the final consumers/patients.
As-Is Processes in GlaxoSmithKline Supply Chain Operations
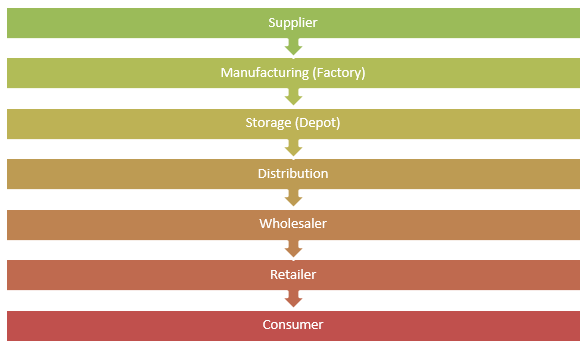
The company’s supply chain comprises suppliers, manufacturing sites, storage depots, distribution networks, wholesalers, and retailers.
Supplier Management
The company has adopted an online bidding platform where suppliers register for the online bidding process and wait for the approval. The company’s management claims that the adoption of this practice has translated into saving on the cost of up to 15 percent. The company subjects the suppliers through a vendor approval process before being allowed to supply it with any materials. Once approved, the successful suppliers are checked for improvement capability, progress, and a review of their performance throughout their contracted period (Chauthari, 2012). The company has adopted an electronic invoicing system where it can submit its purchase orders to its suppliers who are served with an electronic delivery note after transactions. This form of operations management has paved the way for real-time invoicing capability and status of payments, hence providing an advantage to the suppliers.
Manufacturing
The company has two sets of sites, namely, primary and secondary manufacturing platforms. Primary manufacturing sites, which are twelve in total, are responsible for the production of active ingredients. On the other hand, the secondary sites, which are 15 in number, are responsible for the conversion of the active products into finished goods. Therefore, primary manufacturing sites are responsible for supplying materials to the secondary sites for the final conversion to the finished products (Weyzig, 2004).
Storage and Distribution
The company has configured its supply network in a way that each of its manufacturing plants is tasked with the responsibilities of producing a small family of its products and distributing the finished products to the local and regional markets.
Wholesalers/Retailers
The company sells its products to wholesalers via its distribution centers that then sell to retailers and finally to the consumers. Before the company approves orders, the wholesalers must be validated as compliant with the company’s qualification standards.
Analysis of Product shortages as an Issue in GSK’s Supply Chain
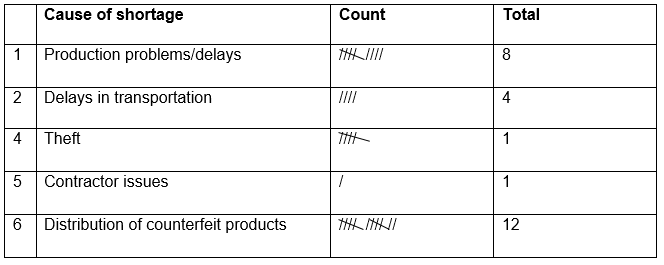
The following checklist illustrates the causes of product shortages in GSK’s supply chain
Production Problems and Transportation Delays
One of the main issues that cause shortages of products in the market is the company’s internal and external production process where products that fail to meet the standards of quality are rejected. As a result, the situation translates into shortages in the market. Additionally, the company faces a problem concerning product transportation from one location to another such as from the primary manufacturing site to another. This situation results in product manufacturing delay and eventually shortages in the market (Palmer, 2014).
Contractor issues
GSK faces a problem with one of its contractors, Xenoport. The company was outsourced to manufacture Horizant that was used for leg treatment. Xenoport accused GSK of breach of contract following manufacturing delays that resulted in product scarcity in the market (Palmer, 2014).
Theft
In addition, the company has reported a number of theft cases in its manufacturing and distribution centers. The issue has had a hand in the supply chain shortages (Ritchey, 2012).
Distribution of Counterfeit Products
Besides presenting a danger to patients, the distribution of counterfeit products by intermediaries contributes to shortages of genuine products in the market. Counterfeit products offer a cheaper alternative in terms of both transportation and price and hence their greater demand relative to genuine products.
Technology Appraisal
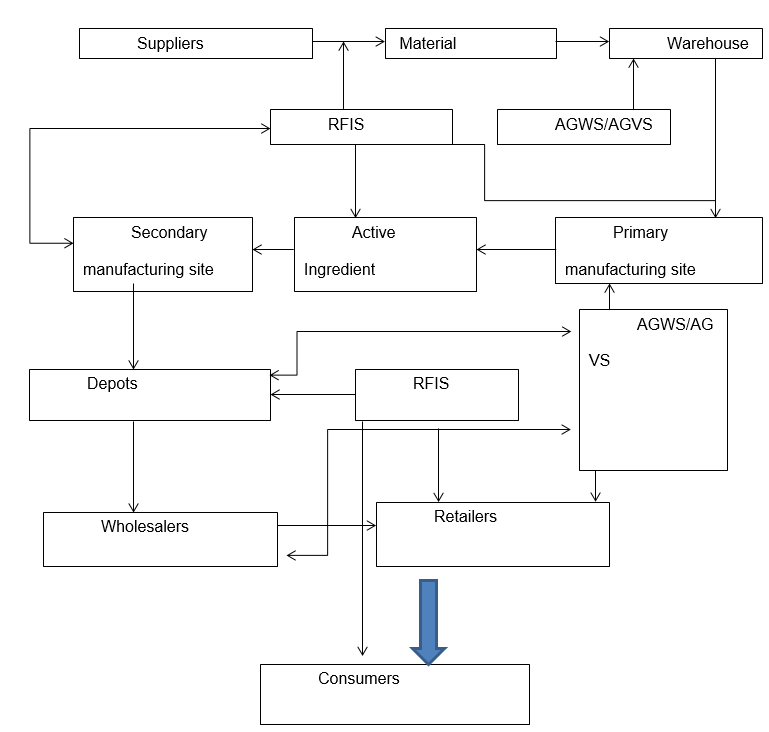
Automated Guided Vehicle System (AGVS)
AGVSs are fully automatic transport systems that are used to transport items from one location to the other. The advantage of using this technology is that it is capable of functioning without any kind of human intervention, hence its applicability in warehousing, production, distribution and logistics environment. Moreover, by integrating this technology, GSK will reduce shortages caused by inefficiencies in production, logistics, and distribution (Jula, 2011).
Automated Guided Warehousing System (AGWS)
Through the integration of this automated warehousing system in the distribution centers, GSK will reduce cases of shortages that are linked to poor warehousing practices by increasing the efficiency of its storage and distribution facilities. To optimize the use of this technology, GSK should customize the design of its automated guided technology to suit its specific storage needs (Schulz, Behling, & Buhrs, 2008).
Radio Frequency Identification System (RFID)
The company can use RFIS to track specific product batches from manufacturing to their places of storage concerning time and safety. Moreover, through these devices, the company can track its product in the market, hence optimally reducing the cases of shortages because of the counterfeiting issue (Li, 2006).
To-be Processes as Solutions
Characteristics of Order Qualifiers and/or Order Winners
Automated Guided Vehicle System
The Automated Guided Vehicle System technological solution is an order winner because it allows fast and efficient management of both raw materials and finished products in the warehouse. According to Schulz et al. (2008), besides having a cost-saving advantage, this technology is highly reliable because of the system’s capability of transporting items from one location to another at a very low expense.
Automated Guided Warehousing System
An automated warehousing system qualifies as an order winner since it reduces the limitations associated with human labor such as slowness, inaccuracies, theft, and labor expense. For instance, by reducing human inaccuracies, the company may increase its delivery speed and precision to its distribution centers, thereby reducing cases of shortages that are associated with such limitations. Moreover, the system is reliable, efficient, flexible, and high performing.
Radio Frequency Identification System
RFDIS technology allows the company to track its raw materials and finished products throughout the supply chain. Therefore, it minimizes cases of shortages because of counterfeit products. This technology is not only reliable and fast-tracking but also guarantees precision in delivery. It also promotes uniqueness in the sense of reducing counterfeit products in the market.
Project Critical Appraisal
Automated Guided Vehicle System
The AGVS has been proven to address concerns associated with standardization, modularity, energy, navigation, and safety. In terms of safety, the navigation system has an automatic warning system installed that warns drivers to avoid issues of collisions. Due to automation, AGVS has been shown to enhance modularity in the reduction of production delays and delivery times. This situation ultimately ensures that the issue of product shortages associated with production and warehousing inefficiencies is minimized (Schulz et al., 2008).
Automated Guided Warehousing System
Poor inventory management of depot and/or distribution centers leads to episodes of stock-outs that ultimately cause shortages in the supply of the company’s products in the market. Fortunately, the integration of an automated warehousing system by warehouses and distribution centers has illustrated an improvement in inventory management that has resulted in a positive reduction of stock-outs in these centers. Moreover, the system has a storage and retrieval system that guarantees efficient management of the warehouse (Parthasarathy, 2010).
Radio-Frequency Identification System
Through tags, stakeholders such as consumers and hospitals can authenticate genuine drugs and easily identify the fake ones that fail the substantiation test. Additionally, the system has mitigated cases of product theft that may eventually result in the shortages of drugs in the supply chain.
Conclusion
Supply chain shortage is the main issue that is affecting GlaxoSmithKline. The problem is associated with production issues/delays, contractor issues, counterfeiting, theft, and increased demands that lead to stock-outs. Automated Guided Vehicle System, Automated Guided Warehousing System, and Radio Frequency Identification System qualify as winners in providing a solution to the issue of supply chain shortages. Additionally, the appraisal illustrates positive results from their integration. Thus, the paper recommends the three technologies as a solution to address the issue of supply chain shortages.
Reference List
Chauthari, A. (2012). Quality in supply chain & after sales. Anil M Chaudhari, EVP quality – GSKCH South Asia GSK Consumer Healthcare Ltd. Web.
Jula, I. (2011). Advanced material handling: Automated guided vehicles in agile ports. Los Angeles, LA: Center for Commercial Deployment of Transportation Technologies. Web.
Li, S. (2006). Radiofrequency identification technology: Applications, technical challenges and strategies. Web.
Palmer, E. (2014). Are price caps contributing to drug shortages in India?. Web.
Parthasarathy, S. (2010). Enterprise information systems and implementing IT infrastructures. Hershey, PA: Business Science Reference. Web.
Ritchey, D. (2012). Solving the Eli Lilly drug theft. Web.
Schulz, L., Behling, S., & Buhrs, S. (2008). Automated Guided Vehicle Systems: A driver for increased business performance. Web.
Weyzig, F. (2004). GlaxoSmithKline company profile. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Somo. Web.

