Executive Summary
This study discusses the importance and relevance of employee engagement in 21st-century organisations. It traces the origins of employee engagement and how it has grown into a major aspect of organisational management. The study also analyses the key aspects of employee engagement, its importance, and relevance in details. Drawing from the case study of Google, the study highlights the best practices for an organisation to achieve high employee engagement. Among these practices are major enablers of employee engagement that have been discussed and which each organisation should strive to attain. These enablers include strategic narrative, engaging managers, integrity, and employee voice. Lastly, the study offers recommendations that organisations that aspire to achieve high levels of employee engagement should follow.
Introduction
With the current technological developments and globalisation, organisations are operating in an environment where competition does not just come from other local organisations, but from across all nations of the world. Such trends mean that organisations are increasingly finding themselves in difficult situations where they have to utilise their resources in the best way possible to ensure that they offer differentiated quality products, a slim workforce, effective services, and great customer relations approaches. The most vital resource in any organisation is the human resource, which is the key determinant of the outcomes of the various processes that are in place. In this case, organisations are increasingly putting in place measures of ensuring that the workforce is productive to remain competitive. A recent study indicates that over 70% of all workers are not productive in their workplace because they lack the necessary motivation, are in the wrong careers, or because they hate their jobs. Such statistical findings are even gloomier in developed countries such as the United States. They depict bad precedence for poor organisational performance and hence the lack of competitiveness in the respective industries.
To address such problems, organisations are focusing on the concept of employee engagement where measures are being put to ensure that employers are active and productive in their respective duties and other organisational activities at all times. Through employee engagement, organisations are keen on ensuring that employees are involved in all performance processes to ensure maximum productivity. According to Pettigrew, Woodman, and Cameron (2001), employee engagement is an important aspect of any organisation. It forms a solution to the increasing problem of low productivity, absenteeism, and burnout. The problem is affecting many organisations. Lack of employee commitment is a major problem that is facing both private and public organisations (Bhuvanaiah & Raya 2014). Hence, a study of employee engagement can offer important tips in guiding organisations in improving their employee engagement and productivity levels. This study seeks to explain employee engagement, its significance, how it can be applied in an organisation, trends in the industry, and/or how it can be measured. Further, the study will discuss the case of Google Inc., which is one of the most successful technology companies in the world, to investigate its employee engagement concepts. The paper will also identify and use important lessons from this company a recommendation for organisations that seek to put more efforts towards employee engagement.
Literature Review
Definition and the Origin Employee Engagement
Employee engagement can be defined as the process of harnessing members of an organisation to their work roles. In the process of engagement, people are free and willing to express themselves physically, emotionally, as well as cognitively in the process of performing their roles. In this definition, three concepts are evident. Firstly, cognitive aspects refer to employee perception of the organisation, its leaders, and working conditions. Emotional aspects relate to employee feelings regarding the organisation and their attitudes, positive or negative, towards the organisation and its leaders (Best 2009). The physical aspect refers to the material efforts that are essential to completing the set roles. Consequently, engagement requires the physical and psychological presence of the employees in performing their roles.
Scholars such as Bass and Avolio (1999) define employee engagement as the positive and satisfying work-related state of mind in an employee that is illustrated by his or her devotion, assimilation, and vigour. Further, Philbin and Sandra (1999) assert that employee engagement is the degree to which people value, take pleasure in, and/or believe in what they do in an organisational setting. Another definition presents employee engagement as a deep-rooted and a broad connection between employees and their organisations (Brajer-Marczak 2014). Such connection results in the willingness of employees to go above the ordinary step to ensure the success of their organisations. From the above expositions, it is evident that employee engagement has many definitions. This situation has resulted in even more approaches that various organisational management experts suggest for successful employee engagement.
The term employee engagement is a recent concept in the discipline of organisational management. According to Best (2009), it emerged in the 1990s. Early management experts such as Best (2009) recognised the word engagement as a crucial concept in the field of management. However, employee engagement gained popularity in the 2000s as evidenced by the emergence and use of employee engagement questionnaires to measure worker commitment. In further developments, there was more support and recognition of job commitment through the stressing of psychological frameworks for enhancing productivity at the workplace. In other words, more emphasis was put on the importance of positive psychology in ensuring employee engagement. Over time, employee engagement has grown to include various areas of the organisation such as employees, resources, workplace environment, and demands.
Key Aspects of Employee Engagement
From the definitions and the origins of employee engagement, it is evident that various scholars understand and define employee engagement differently. However, from these definitions, it is evident that three key aspects are evident (Cadle, Paul & Yeates 2010). Employee engagement involves workforce, employers, and the interaction between employees at all levels of the organisation. The organisation should seek to create a favourable environment where such a partnership can occur and lead to a win-win situation for all parties. An organisation accommodates three types of employees. This knowledge forms an important basis for working towards a better employee engagement in the organisation. The first type of employee is “engaged” employee. Such a member of staff is very energetic in the organisation. He or she is always seeking to know and understand his or her roles and the performance expectations and if possible to exceed them (Tripon & Dodu 2005).
These employees are very passionate about their work and the organisation. Besides, they are always ready to use their talents and abilities to benefit the organisation. Their performance is always very impressive. Hence, they form an important group that has the potential to propel the organisation ahead. The second group of employees is referred to as “not-engaged”. This group refers to the employees who are always ready to do their tasks but do not have any outlook for the achievement of overall organisational goals (Mishra, Boynton & Mishra 2014). In other words, they are always seeking to complete a specific task at hand just for the sake of finishing it. According to Hamann (2007), such employees do not have solid productive relationships with their managers. They often feel that their inputs are not being appreciated. Lastly, there is the “actively disengaged” employee (McLean 2005). Actively disengaged employees are those that have extreme negativity on an organisation. They are constantly looking for an opportunity to make their displeasure known to all. They are very harmful to an organisation since they often discourage engaged workers by propagating elements of pessimism. It s the duty of ensuring that while the environment is conducive to employee engagement, the actively disengaged workers are not derailing the efforts that the organisation has put in place to achieve more robust workplace.
The Importance of Employee Engagement at the Workplace
Despite being a recent concept, employee engagement has emerged as a very important concept of organisational management, especially in the 21st century. According to Lambin (2007), employee engagement is a very crucial parameter in determining organisational performance, organisational outcomes, and employee wellbeing. Further, the engagement is a central tenet that managers must encourage and/or seek to achieve because disengagement is now considered the most significant reason for employee lack of motivation and commitment to the goals of an organisation (Bushe & Marshak 2009). For productivity in the workplace, employee engagement is very crucial. It has been linked to high profitability and customer and employee loyalty, which are important conditions for a successful organisation. Besides, it is very crucial in an organisation’s growth and in reducing employee turnover, which is a major problem that many organisations are facing.
Further study suggests that engagement promotes employee wellbeing as an important aspect of organisational productivity. Engaged employees feel more secure at work, are more energetic, and have a positive influence on an organisation’s reputation. Further, there is more commitment to duties at hand, as well as overall organisational goals. This situation can immensely contribute to success in the organisation (Cadle, Paul & Yeates 2010). However, employee engagement does not occur in a vacuum. It requires supporting management and environment, which the organisation must strive to ensure. With passion, commitment, and alignment, engaged employees can align their roles with the organisation’s strategies.
Important Factors that Lead to Employee Engagement
In light of this discussion on the importance of employee engagement, what should organisations do to encourage the concept at the workplace? What are the main elements that lead to an environment that fosters worker commitment? Various factors are important in ensuring a vibrant workplace environment where employees are highly motivated and engaged to perform to their level best (Mukherjee 2007). The following diagram represents these key factors.
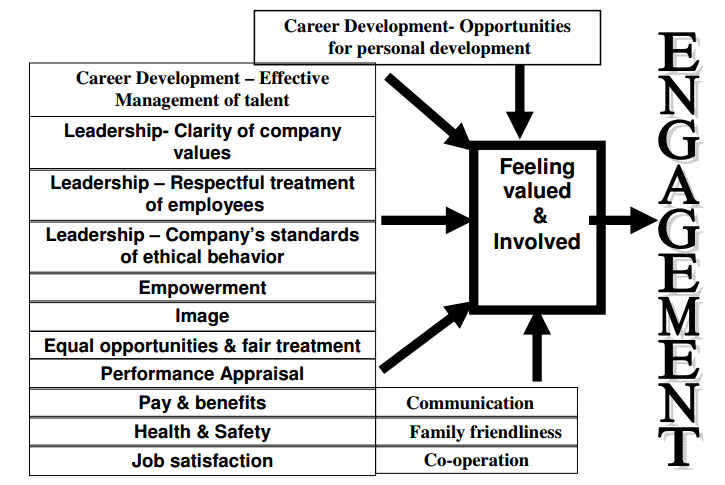
Firstly, in career development, an organisation must always provide opportunities for employees to develop their abilities, acquire new knowledge and skills, and realise their potential. Organisations that are actively engaged in planning and supporting the career paths of their employees invest in them. In return, the employees invest and purpose to benefit the organisation (McLean 2005). Secondly, occupational growth encourages the recognition and preservation of worker ability. It also fosters employee engagement as part of the learning process in the organisation.
The third most important factor in employee engagement is leadership, which encompasses three main factors. Firstly, employees are highly motivated when they feel that the core values of their company are clear and unambiguous. In other words, organisations should strive to ensure that their core values are straightforward. This situation gives employees the right motivation to work towards specific goals. Secondly, organisational leadership must always ensure respectful treatment of employees. This plan includes an appreciation of each employee’s qualities and contribution to the organisation, regardless of his or her position (Tikkanen et al. 2005). Thirdly, leadership ensures clear ethical standards that the company follows. This case, which ensures that employees feel protected from mistreatment or harassment, fosters engagement.
The fourth most important factor in employee engagement is empowerment. The organisation must put in place measures that allow employees to be actively involved in decision-making processes, especially when such decisions may affect their work (Tikkanen at al. 2005). Such empowerment fosters an organisational culture that accommodates trust and positive challenge for employees to innovate to ensure that the organisation is successful.
The fifth most important factor for employee engagement is an image. In this case, the perception of employees on the quality of goods and services that their organisation provides is a key determinant of the level of customer engagement. With employee engagement, employees are likely to own the processes of producing or offering the goods and services, thus leading to a better understanding of the company’s operations and products and belief in its activities (Lambin 2007). Such an environment fosters a good company’s image from within. This situation then leads to high levels of customer engagement. Other important factors include equal employment opportunities, fair treatment, performance appraisal, pay and benefits, health and safety, job satisfaction, communication, family-friendliness, and cooperation (Bass & Avolio 1999). Each organisation must put in place mechanisms for ensuring that these factors are reflected in the organisation since they play an important role in the process of fostering employee engagement.
Employee Engagement At Google Inc.: Analysis
Introduction to Google and Employee Engagement
Google Inc. is one of the world’s largest technology companies in the world with more than 55,000 employees worldwide. With a turnover of more $60billion, it is indeed important to have a case study on its employee engagement. Firstly, Google is very famous for the approaches that it uses towards encouraging employee engagement. Its concepts seem to be working well. In 2014, more than 80 % of workers at the giant search engine said they were satisfied at the workplace. This response was a great indicator of employee engagement in the company. The company’s approaches towards employee have been acknowledged. Many other corporate organisations are keen on understanding how Google manages to achieve such high levels of employee engagement. For instance, the company was ranked first in 2000, 2008, and 2012. It scooped the fourth position in 2009 and 2010 based on Fortune magazine’s survey that declared it the best company to work for. It was also nominated as the world’s most attractive company for graduating students by the Universum Communications talent attraction index (Rudnick & Kouba 2013).
However, how does such a large corporation manage to achieve such high levels of employee engagement? Many researchers who have asked this question have investigated it before coming up with different explanations for Google’s success. In this section, the paper carries an analysis of Google’s employee engagement strategy intending to understand the key strengths that have allowed it to attain its highly desirable model towards employee engagement (Cadle, Paul & Yeates 2010). Firstly, it is important to note that the company did not just wake and strike the cord to good employee engagement. However, its approaches have evolved to the current state. The company’s major success revolves around its HR where it applies what it refers to as the “three minds” mechanism. In this approach, the company’s human resource department is made of one-third of traditional HR personnel, another third by high-end strategy consultants, and a third by master’s and doctorate level analytical professionals. Such an approach ensures that the company offers a unique approach to human resource management.
Measuring Employee Engagement at Google
To understand employee engagement, various approaches can be used to measure it. According to Best (2009), various tools have been put forward towards the measurement of employee engagement. According to McLean (2005), if an organisation manages to get right all negative factors that tamper with employee dedication, it is on a path to employee engagement. Workplace employment relations study questions can be used to measure employee engagement at Google for each enabler.
The first enabler is known as the strategic narrative. A strategic narrative is defined as a strong and transparent organisational culture that allows and enables employees to have a light of sight for their job objectives and to align them with their organisation’s vision and aims. An emphasis on the role of leaders and managers is made, especially on their role in setting the strategic narrative. To measure the strategic narrative at Google, a question about the levels of employee engagement and sharing of the company’s values is used. From this question, it is evident that more than 90% of Google employees share the company’s values as a good sign of employee engagement.
The second enabler of employee engagement involves engaging managers. Engaging managers offer clarity and appreciation of employee contributions and efforts towards the success of the organisation (McLean 2005). Besides, they go a step further in ensuring efficient and effective work organisation, which guarantees that employees feel valued, equipped, and supported to undertake their jobs perfectly. Engaging managers facilitate and empower workers, rather than controlling and restricting them (Philbin & Sandra 1999). The approach covers behaviours, approaches, and actions of supporting, engaging, and promoting employee wellbeing. It ensures that the organisation gets the best out of the workers’ input. At Google, by asking the question of how each employee can describe his or her relation with managers, the majority of the employees felt that they had a good relationship with their managers.
The third enabler of employee engagement is the employee voice. Employee voice refers to an environment where employees’ views are not only heard but also sought out by the organisation (Bushe & Marshak 2009). The organisation needs to ensure that it establishes an environment where employees are listened to whilst allowing them to feel that their opinions count and that they make a difference in the organisation. Such an environment allows workers to challenge their bosses when appropriate. Further, the atmosphere allows staff members to pay attention and/or react to comments. This setting is very important in ensuring innovativeness and high employee engagement. A good organisation does not just engage its employees. Rather, it actively encourages them to express their views and consequently act on them when possible (Jeaw-Mei et al. 2006). Further, such an environment allows both individual and collective voices to be heard since they are equally important in ensuring employee engagement.
At Google, it is evident that employees are satisfied with the level of engagement with their employer and the level of their engagement in decision-making processes. For instance, an analysis of the company shows that the company actively seeks views of employees or their representatives (Rothbard 2001). Also, the company does not just listen but also where appropriate response to employees whilst allowing employees or their representatives to influence the final decisions (McLean 2005). For instance, one of the most notable activities in Google Inc. is the innovation time off where employees are encouraged to spend 20% of their time in coming up with innovative ideas. Such a strategy has allowed Google to come up with record-breaking concepts such as Gmail, Ad Sense, Google news, and Orkut among many others that are influenced by these private endeavours through the innovation time off (Rudnick & Kouba 2013).
The fourth enabler of employee engagement is integrity. Integrity in an organisation refers to the perception among employees that the organisation lives up to its values. Further, it also indicates the trust that employees have in an organisation that adheres to the laid out norms. When there is a disconnection between an organisation’s values and its real-life occurrences, there are high chances of mistrust and employee disengagement (Rudnick & Kouba 2013; Ahmad et al. 2014). On the other side, in an organisation that aligns its values with its reality, employees are likely to trust it, thus leading to productivity and engagement. To measure this aspect, a question on employee engagement seeks to know the level of employee trust that managers will keep their promises and whether managers deal with employees honestly. At Google, it is evident that trust is very high in the organisation and that employees express that they trust their managers to keep their promises and to deal with them honestly.
Other important measures of employee engagement include employee loyalty, sense of achievement, and discretionary effort (He, Zhu & Zheng 2014). In terms of loyalty, Google employees express high levels of commitment to their organisation and willingness to go the extra mile to see it succeed (Pettigrew, Woodman, & Cameron 2001). In terms of achievement, Google employees express higher levels of satisfaction with their achievements since they are recognised and motivated in that direction. Lastly, discretionary efforts indicate the willingness of employees to carry out tasks as their initiative (Tripon & Dodu 2005). At Google, the innovation time off is a prime example of how employees are willing to put individual effort on their initiative to come up with important ideas and innovations that can help the organisation to grow its stand as a world’s largest technological company.
The following is a questionnaire that applies to the study of employee engagement at Google.
Employee Engagement Questionnaire-Google Inc
Enablers of Engagement
Instructions: The questions by ticking [Ö] where appropriate
- What is your gender?
- Male [ ]
- Female [ ]
- Where does your age lie?
- 20-25 [ ]
- 26-30 [ ]
- 30-40 [ ]
- 40-55 [ ]
- >55 [ ]
- Which is your department?
- HR [ ]
- Finance [ ]
- Communications [ ]
- Monitoring and Evaluation [ ]
- Other [ ]
- How frequently do you play a part in the different activities carried out by the company?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
- How many times has it happened that you were so much into the job that you lose the track of time?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
- How often does it happen that your mind wanders off from the task that you are performing on the job?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
- How often do you think that the most exciting things for you are getting involved with things happening in this organisation?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
- How often does it happen that you are not interested in the activities going on in the organisation?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
- How often does it happen that being a member of this organisation makes you come alive?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
- How often do you think that you are highly engaged in this organisation?
- Seldom [ ]
- At times [ ]
- Frequently [ ]
- All the time [ ]
To understand employee engagement, the above questionnaire was given to 50 Google employees in the Middle East-Dubai Office. The findings were as discussed below. Firstly, the first three questions covered the characteristics of the participants such as their gender, their age, and their departments of work at the organisation. To ensure fairness of representation of the respondents, an equal number of males and females was selected. For the analysis of the other questions of the questionnaire, the Likert Scale options were used. The table below shows the Likert Scale options:
Also, the colours that are used in the charts represent an option of the Likert Scale where blue colour represents ‘seldom’, green represents ‘at times’, Fon represents ‘frequently’ while purple represents ‘all the time’.
The fourth question of the questionnaire prompted respondents to record how often they participated in organisational activities. Out of the 50 respondents, 21 of them, representing 42%, participated in the activities all the time. Another 20 respondents frequently participated in such activities. The remaining nine participated in the activities at times.
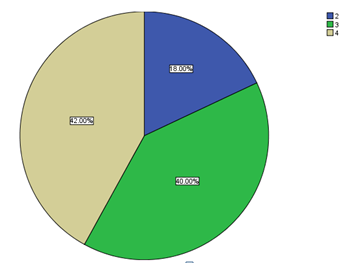
The fifth question sought to understand employees’ concentration at work. To measure this aspect, the questions were framed to ask respondents on whether they lost track of time during their working hours. The findings showed that 22 of the respondents forgot to keep track of time all the time. This finding was an indication of their deep involvement in work. 20 of the respondents frequently lost track time while the remaining 8 respondents lost track of time in some instances.
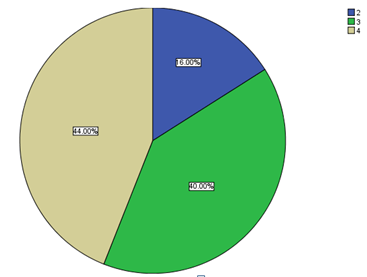
The sixth question sought to know whether the respondents ever found themselves in situations where their minds wandered from the current tasks to other things. The findings revealed that 21 respondents constantly had situations where their minds wandered from the task at hand to other issues as compared to 20 who frequently found themselves in such situations. Nine respondents indicated that they at times found their minds wandering off the tasks at hand.
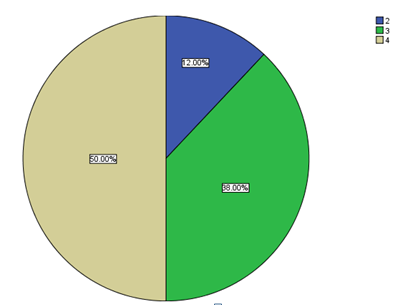
The seventh question on the level of excitement of employees on different activities at the organisation revealed high levels of excitement at Google Inc-Dubai Office. 46% of the respondents were constantly excited in addition to a further 42% who were frequently excited. Only 12% recorded being excited at times.
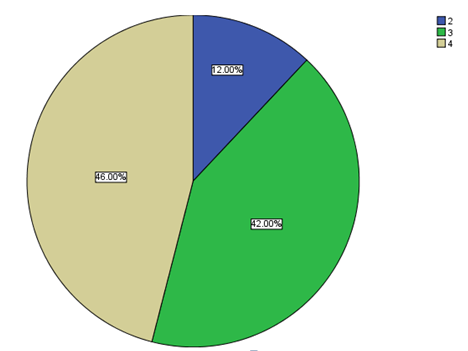
The eighth question required respondents to record their level of disinterest in organisational activities. One of the respondents rarely got interested. 8 respondents, 20 respondents, and 21 respondents chose the option of at times, frequently, and all the time, regarding their level of not being interested in organisational activities. The following table and chart show the responses to the question:
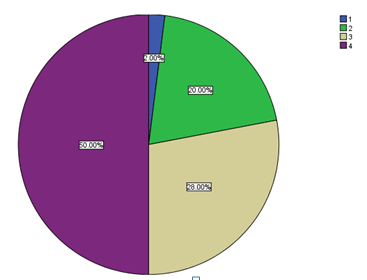
The ninth question asked clients on their level of liveliness as members of Google Inc. 44% of the respondents always felt that being members of the organisation made them feel alive. Another 26% often felt alive, while only 16% sometimes felt alive. Only 4% of the interviewees confirmed that they rarely felt alive. The following table and chart summarise the findings.
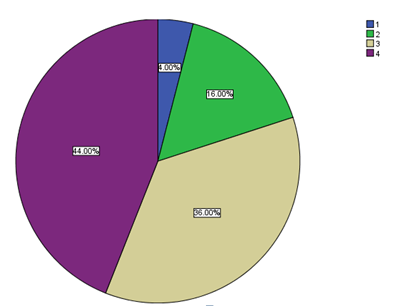
The last question asked the respondents on their level of engagement at the organisation. 48% or 24 of the respondents felt that they were always engaged. 38% felt that they were often engaged while 12% and 2% felt engaged sometimes and rarely respectively. The following is a summary of the responses:
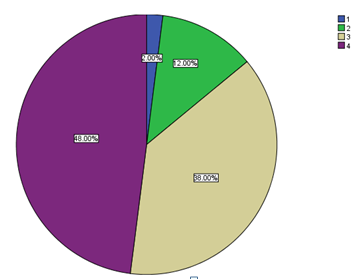
Recommendations
The human resource is a very important and critical aspect of any organisation especially in the present time when globalisation and technological development have stimulated cutthroat competition in all segments of the market. Without a high-level employee engagement and input, all other aspects of the organisation’s processes are in vain and hence the need for this process. Achieving a high level of employee engagement requires the organisation to put efforts towards developing a culture of trust and employee initiative among other factors as discussed above. For organisations to ensure employee engagement, the following recommendations should be considered:
- Organisations must also ensure that they use effective employee engagement tools that guarantee the establishment of a comprehensive database on the status of employee commitment
- Organisations must purpose to make employee engagement a priority through an encouraging culture that supports employee commitment
- The organisation should create open channels of communication through which employees can communicate and engage with each other and the management
- At the job level, organisations must strive to ensure that jobs are clear and that their respective tasks are meant to foster employee interest and concentration
- They must address the issue of ambiguity of job descriptions and tasks to ensure that employees focus on their respective roles
- Also, the jobs must be challenging and competitive as a way of ensuring that employees are motivated to put more efforts
- It is very important to put in place just and fair appraisal systems, which recognise and reward excellent performance
- The organisation should also encourage employee accountability at all times
- It is also very important to ensure that employees are involved in decision-making and planning of activities for their organisation
- Encouraging organisation ownership and a sense of belonging in employees is also very important in promoting employee engagement
- Compensation and benefits also play a key role in promoting employee engagement. Hence, organisations should ensure reasonable benefits at all times
- The organisation must ensure that it has strong ethical standards for all employees. In this case, it is important to guarantee trust, respect, and honesty among employees and/or between employees and the management.
Conclusion
The above discussion has identified the core tenets of employee engagement and its centrality in an organisation’s success. Although it is very recent, the concept has gained a lot of popularity. It will be detrimental to an organisation to ignore it. Looking at Google, it is evident that the organisation is a step ahead of the rest. Its employees are highly engaged and productive, a fact, which has led to the success of the organisation. With the realisation of the importance of employee engagement, organisations must therefore actively strive to create an enabling environment where employees feel appreciated. Such an environment allows employees to strive to achieve the organisation’s values. Among many recommendations, achieving employee engagement is a very critical aspect, which can easily give an organisation a competitive advantage over others. Concisely, with the various employee engagement measurement procedures, each organisation has the opportunity to get it right and create a highly effective and productive human resource, which can offer it the much-needed success in the highly competitive world of today.
References
Ahmad, N, Iqbal, N, Kanwal, R, Javed, H & Javed, K 2014, ‘The mediating role of employee engagement in relationship of internal branding and brand experience: Case of service organisations of Dera Ghazi Khan’, International Journal of Information, Business & Management, vol. 6 no. 4, pp. 26-41.
Bass, B & Avolio, J 1999, ‘Two decades of research and development in transformational leadership’, European Journal of Work and Organisational Psychology, vol. 8 no. 1, pp. 9-32.
Best, J 2009, Market-Based Management: Strategies for Growing Customer Value and Profitability, Prentice Hall, New York, NY.
Bhuvanaiah, T & Raya, R 2014, ‘Employee Engagement: Key to Organisational Success’, Journal of Indian Management, vol. 11 no. 4, pp. 61-71.
Brajer-Marczak, R 2014, ‘Employee engagement in continuous improvement of processes’, Management, vol. 18 no. 2, pp. 88-103.
Bushe, G & Marshak, R 2009, ‘Revisioning Organisation Development: Diagnostic and Dialogic Premises’, The Journal of Applied Behavioural Science, vol. 45 no. 3, pp. 348-368.
Cadle, J, Paul, D & Yeates, D 2010, Business analysis, British Informatics Society, Swindon.
Hamann, H 2007, What Is Organisational Development From A Process Work Perspective? The Process Work Institute, Portland, Oregon.
He, H, Zhu, W & Zheng, X 2014, ‘Procedural Justice and Employee Engagement: Roles of Organisational Identification and Moral Identity Centrality’, Journal of Business Ethics, vol. 122 no. 4, pp. 681-695.
Jeaw-Mei, C, Mein-Woei, S, Mei- Jong, L & Shieh, F 2006, Organisational Change and Development, National Chengchi University, Shanghai.
Lambin, J 2007, Market-Driven Management: Strategic and Operational Marketing, Palgrave Macmillan, New York, NY.
McLean, G 2005, Organisational Development Principles, Processes, Performance, Berrett-Koehler Publishers, New York, NY.
Mishra, K, Boynton, L & Mishra, A 2014, ‘Driving Employee Engagement: The Expanded Role of Internal Communications’, Journal of Business Communication, vol. 51 no. 2, pp. 183-202.
Mukherjee, K 2007, Customer Relationship Management: A Strategic Approach to Marketing, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi.
Pettigrew, A, Woodman, R & Cameron, K 2001, ‘Studying Organisational Change and Development: Challenges for Future Research’, Academic of Management Journal, vol. 44 no. 4, pp. 697-713.
Philbin, A & Sandra, M 1999, A Framework for Organisational Development: The Why, What and How of OD Work, Mary Reynolds Babcock Foundation, Winston-Salem, NC.
Rothbard, P 2001, ‘Enriching or depleting? The dynamics of engagement in work and family roles’, Administrative Science Quarterly, vol. 46 no. 4, pp. 655-684.
Rudnick, M & Kouba, W 2013, How the Google Effect is Transforming Employee Communications and Driving Employee Engagement, Watson Wyatt, New York, NY.
Tikkanen, H, Lamberg, A, Kallunki, P & Parvinen, P 2005, ‘Managerial cognition, action and the business model of the firm’, Management Decision, vol. 43 no. 6, pp. 789-826.
Tripon, C & Dodu, M 2005, Change Management and Organisation Development, University Press, New York, NY.
