Abstract
Social media is a new marketing arena that has created excitement and intensified competition among companies, businesses, and brands to develop relationships, create news, and build communities in the global virtual space. This exploration seeks to understand the effect of social media on how the tech giant Google has adapted its promotion policies to include social networking. A qualitative study is performed by way of structured interviews with a total of 90 media experts. Results show that social media facilitates customer relationships within Google as well as the engagement of both existing and new customers. Therefore, by analyzing Google’s performance with the onset of social media, the research argues that real business progress in the contemporary business setting is realized with the utilization of websites such as Facebook, Linked In, and Twitter. Online public sharing is a game-changer for Google because companies that have previously invested in this marketing approach claim higher profits, with a prediction of greater returns in the future.
Overview
Social media is defined as a channel that helps to exchange ideas and essentially interact using highly accessible communication techniques (Fuchs, 2017). Essentially, social media helps companies harvest data from individuals using social media networks and use the acquired information for marketing and internet advertising (Fuchs, 2017). The overall benefit of integrating social media into a company’s marketing communication strategy is to establish a platform that attracts customers and prompts them to share their ideas regarding products and services of common interest. Hence, this paper seeks to examine how Google can adopt social media as an organizational performance measurement tool within the UAE market, with particular reference to customer relations.
The paper will start by reviewing previous work done by prominent researchers to understand how social media affects company performance. Then, the following section of the study will use a qualitative research methodology of semi-structured questionnaires and interviews to gather the necessary data. Then the final segment will deliberate the outcomes of the info collected and provide Google with recommendations on how to pursue a successful strategy in the UAE markets.
Background
Launched in 2011, Google+ was Google’s attempt to compete with Facebook and Twitter. In 2013, Google shifted its attention to YouTube and unsuccessfully tried to integrate it with Google+ to ignite participation in the platform. However popular YouTubers expressed their fury over the company’s attempt to leverage their success by using it to improve the crippling social network. The platform ultimately failed to win over people which prompted Google to shut it down in 2018. Nonetheless, Google has over the years managed to remain profitable through its various advertising sites such as Google Search and Google maps. In 2018, Google managed to acquire a revenue of $136 billion from its websites alone. Through the implementation of a social media strategy, Google will be better positioned to improve their company image and capture the interest of more people, thereby establishing a larger market share for themselves.
Research Questions
The research seeks to answer the following questions:
- How does Google use social media to improve business development by maintaining positive relationships with customers?
- How does Google use social media to enhance the company’s visibility and overall marketing strategy?
Literature Review
Social Media
Organizations in the modern business era have and continue to invest a vast amount of capital to gain the affirmative impacts of social networking sites to expand their enterprise both regionally and globally (Rodriguez, Peterson, & Ajjan 2015). In the sales context, Charoensukmongkol and Sasatanum (2017, p. 32) define social media as “a system based constituent of interaction, business, and affiliation building purposes of an organization, which leverages the collection of clients to boost value co-creation.” Furthermore, public network sharing has been described as web-based applications developed on technical foundations that undergo constant renovation in a collaborative routine (Wang & Kim, 2017). According to Meikle (2016), social media has defined a means by which individuals interact to exchange intelligence and thoughts in computer-generated groups and systems. Compared to the traditional marketing techniques, social networking has an extremely high degree of efficiency which has inspired organizations to join social media companies so that they can participate in the affluent virtual environment (Grayson & Hodges, 2017).
Social Network Sites for Marketing and Customer Service
Social networks are available in a variety of forms such as media-sharing sites, blogs, appraisal sites, and virtual domains (Go & Yu, 2016). Social media allows users to recommend their choice of products, services, and websites throughout web social networks and to stay in touch with a large community that may have proven difficult to obtain through traditional marketing channels (Tuten & Solomon, 2017). Moreover, Dahl (2018) explains that public networking sites enable users to share information with their friends and family regarding service and product brands. Social network marketing primarily establishes an honest relationship with customers, demanding manufacturers and service providers to disclose the truth rather than creating a false image for the product or service.
Stephen (2016, p. 20) makes it clear that in the modern business setting, customers are less concerned with style, well-informed, and more challenging; therefore, companies ought to be available and accessible at all times in every social networking site such as Twitter, Facebook, and Blogs. Felix, Rauschnabel, and Hinsch (2017) assert that enterprises should possess social networking knowledge to drive traffic to their site. Guesalaga (2016, p. 72) also states that users of online public networks in most instances use more than just one type of platform; it is much more opportune for a company to invite its Twitter friends to join the organization’s Facebook page. Customers regularly check social media networks to stay informed about a brand’s items and marketing campaigns (Ramanathan, Subramanian, & Parrot, 2017). Furthermore, purchasers view social networking websites as places where they can receive information during real-time interaction with company representatives. Social networking makes it easier to establish a connection with communities, but it can also separate people from business depending on the degree of honesty between the parties in business (Rodriguez et al. (2015).
Online Public Networks for Business Performance
Organizational performance refers to how well a company meets its financial objectives and market criteria (Bakotić, 2016). Likewise, Shin and Conrad (2017) defined organizational performance as the result of numerous entrepreneurial aspects such as leadership, job procedures, team effort, dialogue, and relations that facilitate innovation, policies, corporate culture, and loyalty. Baker and Sinkula (2015, p. 254) explain that organizational performance refers to the change of inputs into yields in an effort to attain certain results. Performance is measured by checking the organization’s cost-effectiveness against the achieved outcome (efficiency). According to Corvellec (2018), organizational performance creates three areas of business results: financial performance, shareholder benefit, and commodity market performance. Also, Valmohammadi & Ahmadi (2015) state that organizational performance is measured using two methods: financial (net earnings on investment) and nonfinancial (work process, commodity quality, and consumer satisfaction).
Relationship Between Organizational Performance and Social Media Usage
A number of explorations have been performed to study the effect and the rewards of social media as far as organizational performance is concerned. For instance, Parveen, Jafaar, and Ainin (2015) discovered that the use of online public networks has a profound influence on company performance, in aspects relating to cost minimization, enhanced information accessibility, as well as improved customer relations. Ali-Hassan, Nevo, and Wade (2015) found that social media marketing offers a significant amount of value to individuals since it facilitates interaction between employees and clients, particularly those who reside in diverse geographic zones. Ainin, Parveen, Moghavvemi, Jaafar, and Shuib (2015) goes on to explain that social media makes it possible for firms to engage in a direct and timely fashion with the end-consumer, at a reasonable cost, that ascertains a business higher levels of communication efficiency as opposed to traditional approaches. Furthermore, Sheer and Rice (2016), in a study to investigate the association between internet performance and organizational internet use, realized an upsurge in revenue expansion, cost reduction, relationship enhancement, and time lessening.
Agnihotri, Dingus, Hu, and Krush (2016, p. 177) elucidates that public networking “is more than just liking Facebook pictures and leaving trivial comments, it has meaningful impacts for companies during the process of knowledge management and sales and marketing as well. A research study by Khatib (2016, p. 49) titled: “The utilization of social networking sites attributes on procurement decision empirical investigation of Saudi consumers in Aseer region” attempts to find out how the stimulus of online network sharing is mirrored on customers’ buying decision and if this impact varies at the various phases of the buying process. Having gathered data from a sample of 310 people in Aseer Saudi Arabia, the study came to the conclusion that the effect of social media varies based on the diverse stages of the customers’ buying decision-making process (Khatib, 2016).
Santoro, Vrontis, Thrassou, and Dezi (2018, p. 352) conducted an analysis entitled: “The implementation of online social networks in creating and commercializing new ICT.” In the study, an integration structure developed from theory appraisal helps organizations to better comprehend their development procedure and practices that expedite the innovation and launching of products in new markets. Results indicate that the social media setting is a practical structure for conducting team workshops to teach members how to effectively use social media in creating and marketing new products.
Research Methodology
Research Philosophy
The research method combines both inductive and deductive approaches and undertakes the investigation as mixed with both the quantitative and qualitative approaches. According to Palinkas et al. (2015, p. 538), the mixed-method methodology is effective in researching human attitudes and behavior. Myers and Powers (2017) explain that deductive reasoning takes place when the inference is derived rationally from a list of ideas. Data acquired from both quantitative and qualitative techniques will satisfy the inductive method. Rahman and Areni (2016) argue that while emphasizing qualitative data, an inductive method will aid the researcher to pinpoint a theory, based on the information obtained.
Methods of Achieving the Research Objectives
In order to achieve the set research objectives, all the papers used in this work were selected by means of special filtering, and the principle of keyword search was utilized. As a core, such speech constructs were taken as “organizational performance,” “Google,” “social media,” “influence,” and “customer relations.” One of the main selection criteria was the relevance of academic sources, which is a significant aspect of sources’ credibility. All the resources were printed no more than five years ago, which testifies to their sufficient reliability. As a key database, the Google Scholar global platform was utilized, which is another valuable product of the company in question. In addition, standard search engines were involved, and based on the keywords and the research topic, some papers were excluded. The main reasons that influenced the rejection of some academic articles were their irrelevance (to an old publication period) and insufficient coincidence with the topic under consideration. As a result, the final sample comprised thirty sources that were used for this study as a theoretical background and tools for answering the research questions posed. Each of these works contains valuable information on the themes discussed.
Discussion and Recommendations
Overview
This segment will discuss the outcomes of the data assembled through semi-structured interviews and questionnaires issued during the primary phase of the research. Results have been sorted according to their research category and the discoveries of the quantitative data have been exemplified with visual graphs.
Quantitative Research
As mentioned earlier, the study adopts a self-completed questionnaire, hand-delivered to every participator and collected at a later date. The finalized questionnaires were arranged in order to scrutinize the results of the feedback in charts and graphs.
Respondents job description in the company
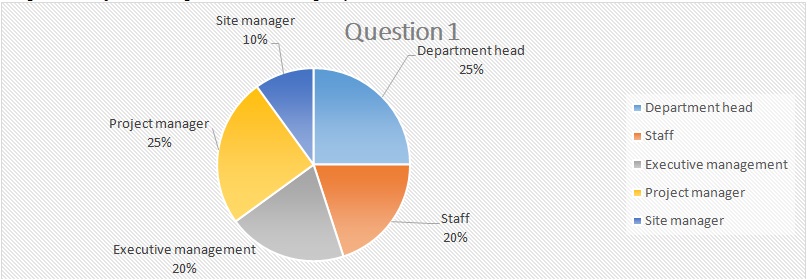
The first question asked each respondent about the job description held in Google and significantly most belonged to a station where they could remark on the social media situation within the company. 50 percent of respondents were in the head of departments category and 20 percent belonging to the executive decision-making group.
Respondents age group
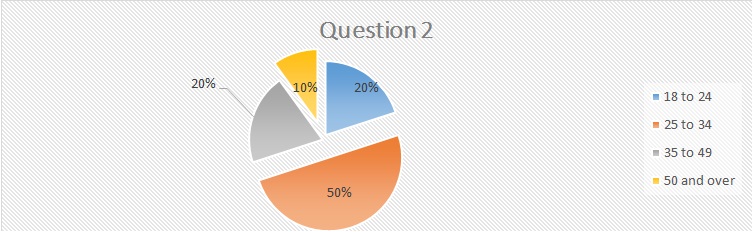
50 percent of the respondents identify with the 25-34 age bracket while 40 percent of the participants identify with the 35-49 and 18-24 age brackets. A minimum of 10 percent is above the 50 age gap. This chart is relevant to illustrate the preferences of individuals of diverse age groups in the company.
Personal social media profile
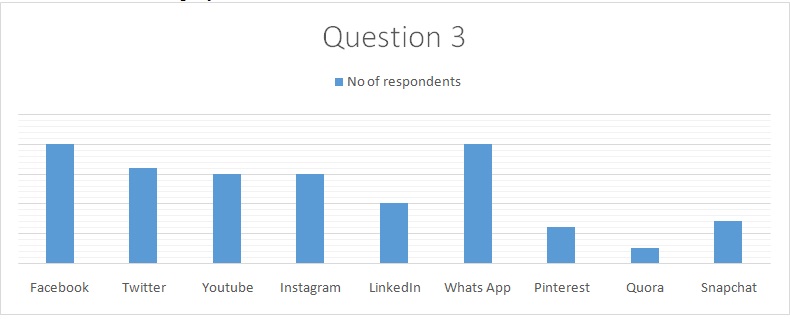
As expected, all the participants belong to at least one social networking site which is an apparent indication of the acceptance and popularity of online public networks among employees at the company, with WhatsApp and Facebook being the dominant platforms. Different groups share short videos and pictures with vital information, therefore enhancing team efficiency.
Questionnaire Discoveries and Analysis
Social media influence on business performance
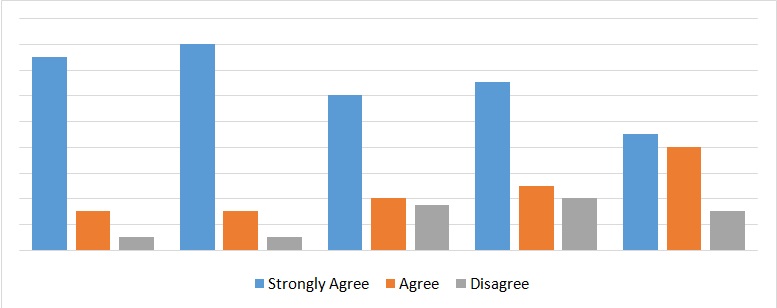
The above graph shows the effect of social networking on business performance. Most employees from different departments strongly agree that online public sharing has a positive influence on business performance. Companies use a considerable amount of time to seek out information on social platforms and create their own page which further illustrates the significance of social networking (Nguyen, Yu, Malewar, & Chen 2015).
Does social networking foster brand reliability among customers?
In figure 5 below, 60 percent respondents of firmly endorse the idea that social networking boosts brand loyalty while 20 percent simply agree with this discernment. Nevertheless, 15 percent fail to agree with the idea that social media enhanced brand loyalty and another 5 percent strongly reject the idea.
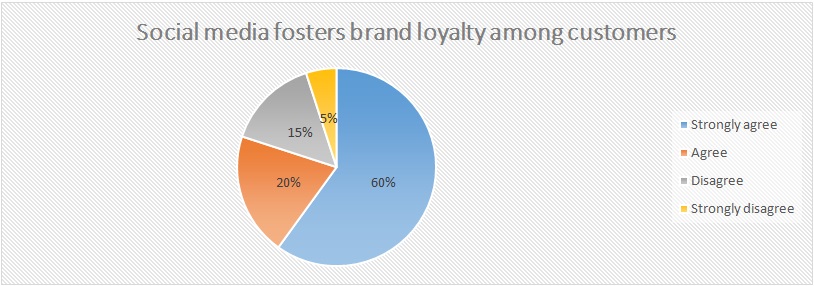
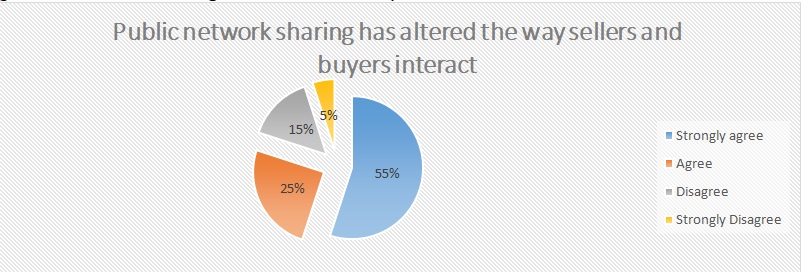
Figure 6 below illustrates that 55 percent of the participants strongly agree with the perception that social networking has changed how sellers and buyers interact and 25 percent confer with this notion. However, 20 percent of the respondents disagree. The idea of immediate feedback has revolutionized the way businesses approach customer service. The home page of online public networks such as Twitter, Facebook, Pinterest, Linked In, and Instagram allow customers to leave their feedback.
Has social media changed how sellers and buyers interaction
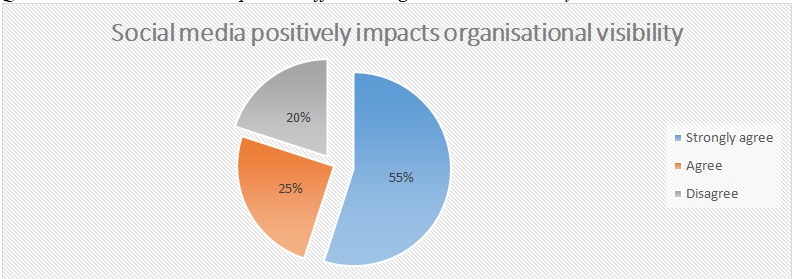
In figure 7 below, 55 percent of participants strongly agree that social media enhances organizational visibility, making it a majority 80 percent of respondents that concur and another 20 percent disagreeing with this fact. Social media can, therefore, be considered as a worthwhile investment to spend time and money on, to enhance wider organizational acceptance among followers.
Does social media have a positive effect on organizational visibility?
Qualitative Research – Research Outcomes of the Semi-Structured Interviews
- Social networking experience – As far as social media experience is concerned, the findings of the semi-structured interviews give the indication that all interviewees are present on the internet and are also frequent users owing to the easiness of use. For instance, the first interviewee explained that “I use Facebook frequently to look up new products and reviews on the same items from individuals who have previously used them.” Another interviewee said that “I have always witnessed that if a user happens to post the right video or picture on Facebook the likes, shares and views rises drastically.”
- The positive influence of social networking on organizational performance – All respondents suggested that social networking is empowering companies to perform better, based on the strategy employed. One participant said “Image constructing is the key motive to building a social media profile and this reason is proven every time we post on our Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook pages. This happens each time we uploaded videos and pictures after the inauguration of new offices in Dubai and Abu Dhabi.” Another respondent explicated that “I feel that organizations can lower their advertising expenses by being present and active on social media sites because it offers major publicity as well as brand visibility. Since social media followers share a common interest within an industry it is more important than ever that we address our target audience.”
Discussion
Both the qualitative and quantitative data were gathered to illustrate the importance of online public sharing to performance. The research objective narrows down on customer relationship as well as marketing and visibility to show how social media improves the performance of Google within the UAE market.
Some of the questions asked during the semi-structured interviews include the respondent’s personal experience with social networking, the positive influence of online public sites on business performance, and the participant’s overall perception of social media and its merits. Having provided their job description and age group, the respondents made it clear that they all are active users of at least one social media platform. The overall quantitative outcome of the questionnaire revealed the employees’ endorsement of the idea that social media participation is critical to the performance of an organization through the creation of brand loyalty, enhancement of interaction between organizations and the customers, and improving organizational visibility.
The investigation centered on customer relationships because Google is a globally recognized company which makes it necessary to keep consumer service at optimum levels amidst the stiff competition by the quickly rising social media giant, Facebook. Google is, by all means, the company with the largest number of loyal customers due to its wide-ranging services such as the Google Search Engine, Google Chrome, Gmail, and YouTube. If Google decides to develop a new social media platform, the company can leverage its massive number of loyal customers.
Also, social media enhances performance by facilitating smooth and relatively inexpensive communication between buyers and sellers. Accordingly, companies like LinkedIn, Instagram, Snapchat, Twitter, and Facebook have been successful in facilitating communication between buyers and sellers. For example, Facebook for Business allows both small and large companies to promote services, boost recognition, and increase customer support (Driver, 2019). Google also facilitates business communication on YouTube but it doesn’t come close to features offered by LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook (Dehghani, Niaki, Ramezani, & Sali, 2016).
Recommendations
Considering the observations made, the examiner advocates the following:
- Opportunities – Social media is a prodigious platform for mass engagement that can offer unparalleled opportunities for organizations. Accordingly, it is crucial for companies within the UAE to establish their presence on various social networking platforms while being careful to appropriately post and comment at precise times.
- Content matters – UAE organizations ought to have control over the content published on social media to avoid tarnishing the company’s reputation. Content is synonymous with the impression that an organization hopes to establish in the public sphere.
- Focus – It is necessary for companies in the UAE to identify which social media platforms are more popular in the region. Such data can be determined by computing the number of likes, comments, and followers to enable the organizations to prioritize on the suitable platforms that will be efficient in reaching a high number of potential shoppers.
- Control & Sustain – Companies in the UAE should allocate key staff the responsibility of implementing the social networking strategy and also manage postings, maintain the selected social platforms, and keep up the tempo so as to maintain consistent activities on the sites, which will ultimately intensify visibility and brand worth of the enterprise.
Conclusion
Organizations in the 21st-century workplace need to realize the potential behind social networking technology to ascertain their survival in the ever-competitive global business setting. This research sought to analyze how Google can adopt social media to ensure its performance within the UAE market and concentrated on marketing, visibility. This research has exemplified a favorable situation for enhancing organizational performance by responding to the queries that companies receive on their social media pages. The investigation reveals that a strong brand presence on social media leads to customer loyalty, increased company visibility as well as an enhanced relationship between organizations and customers.
Hence, both primary and secondary types of research illustrate that maintaining a positive relationship with customers on social media is an integral part of company performance. The researcher, therefore, recommends that UAE companies should explore the various growth opportunities that social media has to offer while also exercising caution on the type of content published on social networks. The researcher once again advocates for a keen sense of Focus for UAE organizations while identifying the social media handle that favors corporate goals. Finally, the study informs UAE companies on the necessity of appointing the main employees to manage the organization’s social media pages.
References
Agnihotri, R., Dingus, R., Hu, M. Y., & Krush, M. T. (2016). Social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales. Industrial Marketing Management, 53, 172-180.
Ainin, S., Parveen, F., Moghavvemi, S., Jaafar, N. I., & Mohd Shuib, N. L. (2015). Factors influencing the use of social media by SMEs and its performance outcomes. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 115(3), 570-588.
Ali-Hassan, H., Nevo, D., & Wade, M. (2015). Linking dimensions of social media use to job performance: The role of social capital. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24(2), 65-89.
Baker, W. E., & Sinkula, J. M. (2015). Market Orientation and Organizational Performance: A New Product Paradox? In G.A. Churchill & J.P. Peter (Eds.), Creating and Delivering Value in Marketing (pp. 254). Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Bakotić, D. (2016). Relationship between job satisfaction and organizational performance. Economic research-Ekonomska istraživanja, 29(1), 118-130.
Charoensukmongkol, P., & Sasatanun, P. (2017). Social media use for CRM and business performance satisfaction: The moderating roles of social skills and social media sales intensity. Asia Pacific Management Review, 22(1), 25-34.
Corvallis, H. (Ed.). (2018). Stories of achievements: Narrative features of organizational performance. London, England: Routledge.
Dahl, S. (2018). Social media marketing: Theories and applications. London, England: Sage Publications.
Dehghani, M., Niaki, M. K., Ramezani, I., & Sali, R. (2016). Evaluating the influence of YouTube advertising for the attraction of young customers. Computers in human behavior, 59, 165-172.
Driver, Saige. (2019). Facebook for Business: Everything You Need to know. Business News Daily.
Fuchs, C. (2017). Social media: A critical introduction. London, England: Sage Publications.
Go, E., & You, K. H. (2016). But not all social media are the same: Analyzing organizations’ social media usage patterns. Telematics and Informatics, 33(1), 176-186.
Grayson, D., & Hodges, A. (2017). Corporate social opportunity! Seven steps to make corporate social responsibility work for your business. London, England: Routledge.
Guesalaga, R. (2016). The use of social media in sales: Individual and organizational antecedents, and the role of customer engagement in social media. Industrial Marketing Management, 54, 71-79.
Khatib, F. (2016). The impact of social media characteristics on purchase decision empirical study of Saudi customers in Aseer Region. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 7(4), 41-50.
Meikle, G. (2016). Social media: Communication, sharing and visibility. London, England: Routledge.
Myers, K. K., & Powers, S. R. (Ed.). (2017). The International Encyclopedia of Organizational Communication: Mixed methods (vols. 1-11). Kings College, London.
Nguyen, B., Yu, X., Melewar, T. C., & Chen, J. (2015). Brand innovation and social media: Knowledge acquisition from social media, market orientation, and the moderating role of social media strategic capability. Industrial Marketing Management, 51, 11-25.
Palinkas, L. A., Horwitz, S. M., Green, C. A., Wisdom, J. P., Duan, N., & Hoagwood, K. (2015). Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 42(5), 533-544.
Parveen, F., Jaafar, N.L. and Ainin, S. (2015). Social media usage among businesses: A website content analysis. Asian Journal of Information Technology, 12(10), 342-348.
Rahman, K., & Areni, C. S. (2016). The Benefits of Quantifying Qualitative Brand Data: A mixed-method approach for converting free brand associations to a brand equity index. International Journal of Market Research, 58(3), 421-450.
Ramanathan, U., Subramanian, N., & Parrott, G. (2017). Role of social media in retail network operations and marketing to enhance customer satisfaction. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 37(1), 105-123.
Rodriguez, M., Peterson, R. M., & Ajjan, H. (2015). CRM/social media technology: impact on customer orientation process and organizational sales performance. In K. Kubaki (Ed.), Ideas in Marketing: Finding the New and Polishing the Old (pp. 636-638). Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Santoro, G., Vrontis, D., Thrassou, A., & Dezi, L. (2018). The Internet of Things: Building a knowledge management system for open innovation and knowledge management capacity. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 136, 347-354.
Sheer, V. C., & Rice, R. E. (2017). Mobile instant messaging use and social capital: Direct and indirect associations with employee outcomes. Information & Management, 54(1), 90-102.
Shin, D., & Konrad, A. M. (2017). Causality between high-performance work systems and organizational performance. Journal of Management, 43(4), 973-997.
Stephen, A. T. (2016). The role of digital and social media marketing in consumer behavior. Current Opinion in Psychology, 10, 17-21.
Tuten, T. L., & Solomon, M. R. (2017). Social media marketing. London, England: Sage Publications.
Valmohammadi, C., & Ahmadi, M. (2015). The impact of knowledge management practices on organizational performance: A balanced scorecard approach. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 28(1), 131-159.
Wang, Z., & Kim, H. G. (2017). Can social media marketing improve customer relationship capabilities and firm performance? Dynamic capability perspective. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 39, 15-26.
