Introduction
Google Incorporation is one of the largest internet-based companies in the world. The company’s headquarters are in California. The company deals in areas such as software vending, search engine, and internet marketing. In the recent past, the company has added cloud computing to its products line. The company has grown through product differentiation, acquisitions, and merges in the last ten years. Google has a workforce of more than 47,000 employees based in its 52 offices across the globe. Google’s motivation strategy, called the ‘Innovation Time Off’, has been critical in ensuring optimal performance within its labour force. This research paper reviews several economic and business concepts as applied at the Google Incorporation.
Oligopolistic market
Reflectively, several firms in the internet related service industry have the same monopolistic power as is the case of the Google Corporation. However, Google Incorporation has unique operational strategies which can be equated to the ideals of oligopolistic strategies. For instance, Google Incorporation has consistently increased its production and diversification of products in the market instead of reducing output with the intent of increasing prices. A critical review of the software market indicates that the products of Google Incorporation are readily and easily available as compared to those of its numerous competitors.
Unlike a monopolistic firm that would manipulate the quality and prices for its products with the intent of increasing its returns, Google Incorporation did not adopt this strategy. The company had to preserve competitiveness to avoid the pressure as a result of monopolistic control of the market. In the ideal, a monopolist firm has the potential and capital base to fully exploit the market through lowering quality, cost of inputs, and increasing the prices for its products in order to attract higher profits than other firms that operate in a perfectly competitive market. Google Incorporation was afraid of being labelled the monopolistic venture ready to take advantage of sole control of the market to manipulate the forces of demand and supply (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
The recent performance of its main competitor called Yahoo has taken the monopolistic accusations off its operations. Despite having the opportunity to use its monopoly power to manipulate prices and quality of its products to increase the profits, Google Incorporation concentrated on product improvement through innovations. Over the years, Google Incorporation has managed to dominate the software market despite competition from Yahoo. Since Google Incorporation operates in a dynamic industry that experiences constant technological innovations, it has channelled heavy capital investment in the product research and development to counter its main competitors.
In contrast with the fallacious arguments by different groups, it is not palpable that a firm which is a market leader is undoubtedly a monopolist establishment. In the ideal, a monopolist firm has the potential and capital base to fully exploit the market through lowering quality, cost of inputs, and increasing the prices for its products in order to attract higher profits than other firms that operate in a perfectly competitive market. However, Google Incorporation does not fit in the above description. Thus, it exhibits oligopolistic tendencies.
Price elasticity of demand for Google’s products
The extent of change in supply and demand is dependent on the commodity in question. It is because the quantity of demand and supply of various commodities changes by a different magnitude when the price of the commodity changes. Some commodities respond more than others, and this creates the concept of elasticity of goods. Price elasticity measures the extent by which either quantity demanded or supplied will change when the price of a commodity change (Baumol & Blinder, 2011).
Demand and supply are the fundamentals of economic analysis as the interaction of the two forms a market. The law of demand and supply works in opposite ways in the sense that, when the prices of commodities changes, demand and supply also change in the opposite direction holding other factors constant. Since the extent of change in supply and demand is dependent on the commodity in question, the pros of raising prices of products of Google would be increased profit and better returns. However, the cons of increasing prices would be reduced demand and reduced supply, as explained in the diagrams below.
Demand and supply of Google products before changes
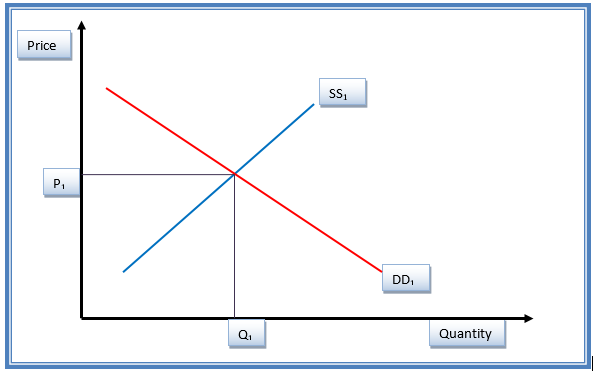
Explanation
Figure 1.1 shows the initial equilibrium status of Google products before the changes in the price. DD1 shows the demand curve, while SS1 shows the supply curve (Baumol & Blinder, 2011). Equilibrium price and quantity are P1 and Q1, respectively.
Demand and supply of Google products after changes in the price
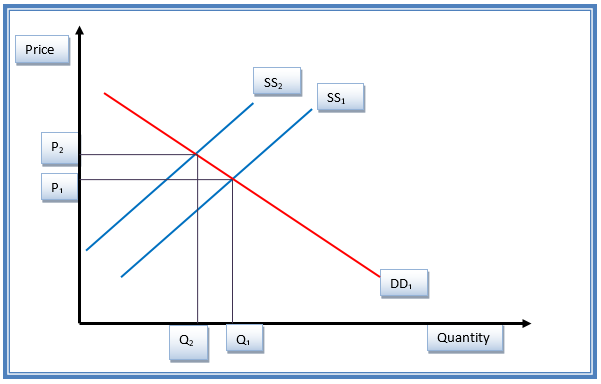
Explanation
An increase in the price of Google products causes an inward shift of the supply curve from SS1 to SS2. This gives a new equilibrium position. Price increased from P1 to P2 (Baumol & Blinder, 2011). This indicates reduced demand from the locals. The net effect of the increase in price at Google is a contraction of the demand side.
According to Baumol and Blinder (2011), “it can be argued that goods that account for a large proportion of disposable income tend to be elastic. This is due to consumers being more aware of small changes in the price of expensive goods compared to small changes in the price of inexpensive goods” (Baumol & Blinder, 2011, p. 34). In this case, Google products are price elastic. These products have elastic supply since their prices determine their ease to be purchased in the market. Besides, when the demand for the same fall, the supply responds almost instantly in the market. Considering an event in which the prices of Google products increase, the demand for the same products will decrease by the same magnitude triggering the supply to decrease in the long run. On the other hand, the reduction in the price of Google products will influence the demand to increase as more customers will prefer the products (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
Income elasticity of Google’s products
When consumers income increases, the total disposable income increases. Consumers can afford to pay for Google products. For this reason, they demand more products from the company. This leads to an outward shift in the demand curve for Google’s products from D0 to D1 and a new equilibrium is achieved at point E1 with price P1 and a higher quantity Q1. Conversely, when income reduces, individuals’ disposable incomes reduce (Baumol & Blinder, 2011). Given that Google’s products are services with series of perfect substitutes, the demand for the products wills declines, resulting in the drop of the quantity of products demanded from Google from the initial quantity, and the corresponding price falls from the initial P0 to P2. A new equilibrium will be achieved at point E2. This is summarised in the graph below.
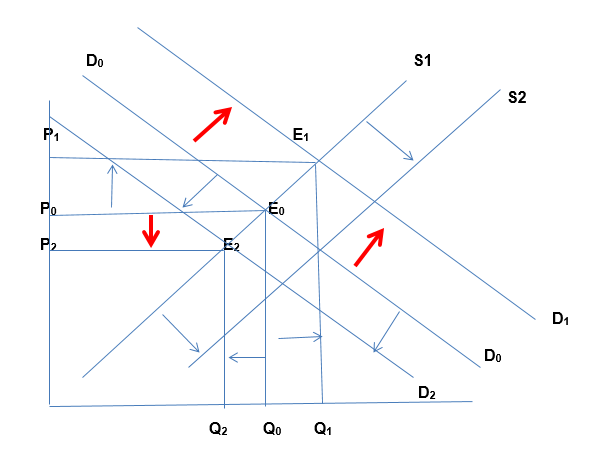
Closest competitors
There are several players such as Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, and Linkedln operating in the same industry with virtually all of them dealing in a variety of internet based products, which can perform similar functions as the products of Google. With many customers looking for good value for their money, usability and affordability of the products have remained the main basis upon which customers make their final decision to purchase products in the volatile industry. All the players in the industry are putting measures in place to ensure they attract more customers and therefore expand their market share.
Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, and Linkedln pose the greatest threat to existence and business performance of Google in this industry. These companies have been in the industry for long period and are well established. The Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, and Linkedln have the same products and sometimes offer big discounts to customers. In the US internet services industry, loyalty to a brand plays an important role in customer behaviour. Therefore, Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, and Linkedln have remained as the main challengers of Google Incorporation.
Existence of substitutes and compliments
When there are more substitutes besides a product, chances of shifting to these substitutes are higher. Therefore, availability of a substitute may lead to decrease in demand when the price for a product increases. When the price increases, the household might be opt for the best alternative especially when doing the same will positively affect savings or add value to the disposable income. Therefore, several available substitutes in the case of Google make the demand curve to be responsive to changes in price since the consumer behaviour will not remain the same. Several available substitutes make the demand curve to be highly elastic as responsiveness to changes in price of the same attracts immediate change in customer behaviour such as purchasing pattern. A small change in price in elastic Google products leads to a greater change in quantity demanded as customers will opt for substitutes that have cheaper price tag or are more affordable in long run (Baumol & Blinder, 2011).
Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, and Linkedln have the ability to offer an alternative perfect substitute to customers who may be unsatisfied with products offered by Google. Unsatisfied customers have other alternatives from where they can get same services that Google Incorporation sells. However, the threat of substitutes is moderate since changing a brand is very expensive for customers in terms of initial settings and difference in operation systems (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
Growth of demand for Google’s products
The demand for Google products is growing every day. From its inception, the Google’s product line objective has been to provide quality products at the convenience of the clients. The services offered by the company include online advertisement, browser engine support, and software development. The Google has a product or service to anyone who uses computer. The company has expanded from the US to all other continents due to its customer-centricity business model. Since users of computers have been growing in the last two decades, it means that the demand for Google products also grows in equal proportion.
Labour force training to increase productivity and lower production costs
The Google Incorporation has a very unique organization structure. The company exhibits distinctive and unique organization configuration that is shaped by the organization’s goals. In advancing organizational learning, the system helps the business to avoid learning disabilities besides being proactive in organization thinking through continuous employee training. Therefore, Google should exhibit flexibility in its employee training arrangement to enable jobs to be redesigned to facilitate work-based innovations. Since training engages in active process of learning through skill evaluation, facilitation, and rewarding collective learning results, the ideal model for quantifying success will rely on the set objectives.
The three building blocks of training evaluation include learning intra personal performance, learning processes, and practice leadership that reinforces performance. Better performance translates into organization growth, especially when the training process is continuous. In the end, the employee will perform optimally and efficiently use the resources of Google to minimize wastages that increase the production costs (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
Profitability of the Google Company
The Google Incorporation has remained profitable since the time of inception, which is more than a decade ago. The company has been experiencing an average growth rate of 15% per annum. Due to profitability, the company has managed to expand and currently owns more than fifty branches across the globe despite having been in the market for just ten years. At present, Google is the global market leader in the internet-based product and services industry.
Sustaining profitability of the Google Company
Business-to-Business platform
Google has employed the laggard activism strategy to capture the global market through the Business-to-Business (B2B) platform. As a result, the company has penetrated the global market due to a balance in factors such as the Western business style, global business approach, and flexible organizational structure. In order to penetrate the expanding global market, Google’s business platform was modified through introduction of services such as premium customer experience, compact support from the community, and low charges for small businesses. Besides, the company has managed to balance the elements of intangibility, inseparability, and heterogeneity in the 4Ps of its market mix due to improved product visibility for each target customer segment (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
Strong brand
Google Incorporation has established a brand image that enables it to attract customers with less effort as opposed to most of its less established rivals. The entrants have to invest heavily in promotion and advertising for them to attract new customers and maintain their customers. The established brand image has enabled the company to cut on its cost and get increased levels of profitability (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
Steady commitment to quality
Strong commitment to quality and product innovation enables the company to get the right experience for their customers. This has been possible through the recruitment of employees with the right skills and knowledge. These employees are further trained to understand the company production strategies. Moreover, the company conducts more market research to ascertain customer thoughts and changing demands (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
Expanded market
Google Incorporation has an active presence in all over America with an expanding presence in emerging markets including China, Japan, and Europe. In the past five years, revenues from sales doubled annually and the company expanded steadily. Having been in the internet-based service industry for over 10 years, Google Incorporation has acquired enough experience to compete favourably in the industry. It has had sufficient time to learn from its weaknesses and develop long-term strategies that will anchor it through the future of the market. As a way of adopting the emergent technological changes, Google Incorporation has invested in technological creativity to suit its consumer changing needs (Witcher & Chau, 2010). Finally, the company has been able to win more customers with its strategically-placed and ambient stores with conspicuous features.
How Google can make its profits to grow
Operational efficiency
Operational efficiency and market niche provide an indication of how well the company manages its resources, that is, how well it employs its assets to generate sales and income. It also shows the level of activity of the corporation as indicated by the turnover ratios. The level of activity for Google has remained relatively stable despite threat of competition, constant change of taste, and varying preference. In order to stay afloat, the company should streamline its operational costs and introduce freelance marketers paid on a commission. The marketers will operate from their homes to save the company daily expenses of running its business. Through implementing this proposal, the company will reduce its wage bill and seal cost loop holes (Witcher & Chau, 2010). This will translates into increased profits.
Consumer Centricity
Properly designed online marketing and product distribution management facilitate the success and sustainability in online marketing. To increase credibility and maintain professionalism, the current channels of reaching the consumers at the Google Incorporation should be tailored to encompass processes and features that flawlessly facilitate a healthy and a lifetime relationship between the business and its clients. Essentially, the success of e-marketing depends on proper alignment of a functional team that is responsible for the creation of flexible and quantifiable measurement tracking tools for periodically reviewing results (Witcher & Chau, 2010). This strategy will ensure that the business is sustainable through increased revenues.
Product concentration
The Google Incorporation should ponder concentration to its products in countries which do not have strict laws that protect the business, when expanding further to other foreign markets. Countries like China do not have strict rules which protect business entities from being copied by competitors. This will help in safeguarding its products’ brands and making sure that it targets specific market segments. This will ensure that Google introduces measures in its operative process that would make it distinct in the market from any firm. The introduction of product concentration should be applied while ensuring that the targeted markets, especially in Europe, have customised products that are unique to that region (Witcher & Chau, 2010). Therefore, product concentration will position the Google Incorporation as a strong incumbent brand in the global industry since the revenues will grow.
Vertical integration
The Google Incorporation may partner which medium businesses retailing products similar to those of its competitors. The objective of vertical integration is to expand Google’s market and make it easy for customers to access the products. The above objective can be achieved through created on in-house production, supply chain, and marketing strategies. When properly implemented, the company is likely to counter the strategy of its competitors of reaching the customers through proxy retailers. The choice of vertical integration is driven by the need to create that perception of reduced inventory costs. Reduced inventory costs translate into increased profits (Witcher & Chau, 2010).
References
Baumol, W., & Blinder, A. (2011). Economics: Principles & Policy. New York, NY: Joe Sabatino. Web.
Witcher, B., & Chau, V. (2010). Strategic Management: Principles and Practice, Alabama, Al: Cengage Learning. Web.

