The paper describes and analyzes the issues of H&M’s organizational processes and approaches to consulting and teamwork. It provides comprehensive conclusions and recommendations based on the highlighted problems.
Introduction
Organizational management is the key to achievement of a company’s objectives. The management is a complex role that contains two distinct roles namely decision-making and leadership (Srivastava, 2005, p.6), with the first role including the development of the organizational policies, operational strategies, and planning the implementation processes. Leadership involves how the top management reacts towards the changes in the environment as a move towards achieving company objectives (Kivipold & Vadi, 2010, p.4). Factors like environment will determine which major role to be adopted (Sisaye, 2001, p.8).
The labor market for skilled laborers is currently competitive and one key step towards obtaining a competitive advantage by an organization is to hire and retain the skilled employees. A lot of research is necessary to help organizations survive in the competitive world (Volberda, 1996, p.2). In addition, the satisfaction/dissatisfaction of the employees of an organization will determine the quality of their poor performance. Primarily, the dissatisfaction of the employees may stem from the working conditions that are prevailing in the organization (Srivastava, 2005, p.10), as well as from the personality in the leaders of the organization. Therefore, how leadership roles are defined in the organization and how the leaders relate with the employees can influence the level of satisfaction obtained by the employees.
Watson Company has a problem that primarily stems from the kind of leadership and management that is seen at the organizations. The management appears not to care so much about the significant contributions that the employees in the shop-floor can make towards the realization of company objectives. The culture that has been developed by the leader at the organization is one where the employees are only restricted in their areas and none is ready to lend a hand to an overloaded worker performing a related task within a given project. Another problem that can hinder growth and development in a company is lack of finance for inventions and innovation. This can also be a reason towards the slow growth witnessed at Watson Company and will continue to be a barrier towards development in the organization.
H&M has a better kind of organizational management, which has seen the organization grown extensively over the years. The operation of the company the goes internationally enables it to improve its global reputation and will ensure that the organization survives the strong competition in the global market. The kind of organizational culture and the leadership style that is provided by the current leaders are motivating the employees of the organization and this will eventually lead to further excellent organizational performance in the future.
Analysis of Issues
Organizational Design and Structure
The organizational structure in a company will affect its success (Fontaine, 2007, p.2). There is perhaps no specific organizational structure to be adopted by various industries. It will be determined by factors like the size of organization, as well as how the individual tasks are related (Graubner, 2006, p.36). The particular structure will depend on the company’s state of development, the organizational culture, the leadership style, and the kind of industry in question. The organizational structure will define ‘the hierarchy of the authority, the reporting relationships, and functional units and their responsibilities’ (Pang 2004, p.32).
There are two kinds of organizational structures adopted by the organizations – the mechanistic and organic organizational structures. The mechanistic kind of organization is characterized by a bureaucratic management system with each individual charged with a specific area of service leading to poor creativity (Pang 2004, p.32). The company leadership is characterized by a ‘formal hierarchy of authority’ (Pang 2004, 32). This also calls for a formal system of communication from the top management down to the lower-level implementers. It is also characterized by an autocratic kind of leadership that does not allow for much inventive and innovative ability by the employees (Pang 2004, 32). This form of organization is seen to be outdated in the current economy with a rapidly developing use of technology (Pang 2004, p.32).
On the other hand, the organic form of organization is flexible in the management and the authority is evenly distributed to many powers within the organization (Pang 2004, 32). The employees of the organization are often involved in the decision-making process by the top management as it involves participative leadership and decisions (Pang 2004, 32). Every employee has the freedom of expression and he/she is allowed to go beyond the predefined roles and jurisdictions as a way of improving inventions and innovations by the organization. The kind of communication is less formal in this form of organization. This is the kind of organization that is currently appropriate to be adopted by a competing organization. The management should constantly review the organizational structure to match the factors that prevail within an outside the organization (Pang 2004, p.33; Sanchez-Manzanares et al, 2008, p.1). A typical organizational structure is presented below. The structure will vary depending on the functions in the organization.
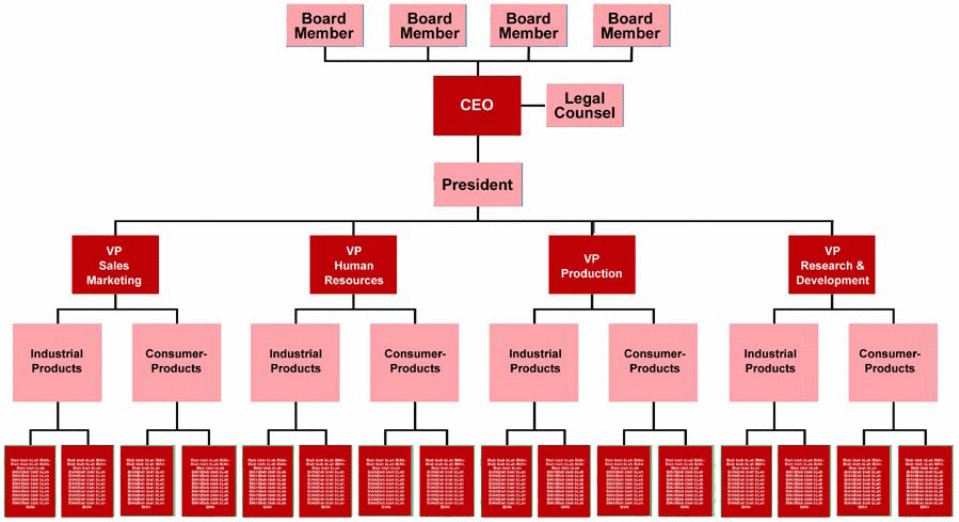
The organizational structure that is witnessed in Watson Company is the traditional old-fashioned hierarchical system with a descending authority (Case study). The company has 40 managers serving in different fields of management. This is not proportional to total number of the employees that are within the organization. Besides, the company is family-owned with Gordon Watson being the Managing Director. Below the MD is the operations director to whom the Managing Director has assigned the responsibility of overseeing the production activities in the shop floor.
There are managers at the various departments of the organization that are charged with various responsibilities. The departments are seen to perform their functions independently despite the firm’s requirement that there be a liaison between related departments like the Manufacturing and marketing departments. The marketing department is seen to handle the customers independently without involving the manufacturing department.
Besides, it has also been noted that the decision-making process in many departments of the organization is performed by the top management without involving the other staff in the department. This ignores the fact that the staff in the shop floor is better placed and it understands the appropriate ways of making improvements to the operations of the organization. The mechanistic organizational structure is seen when the workers in the shop floor are not flexible and cannot move in between the different activities in the production process (Case study 1). This implies a kind of structure where the management had defined to the individual employees their particular roles with little emphasis to flexibility in the roles carried out by the employees (Pang 2004, p.32). An employee is thus not in position to learn and acquire new skills. Neither does this allow a possibility to come up by new ideas by the employees.
On the other hand, the organizational structure that is seen at H&M Consulting is the organic type with the top management empowering the staff and other employees to try innovative procedures (Case study 2). It has the hierarchy in leadership but with less authority on the top management. The firm has a Chief Executive Officer who is charged with the overall responsibility of managing the operations of the firm. The managers have a loose relationship with the other staff and the means of communication is less formal. The staff members and other stakeholders in the organization are always involved in the decision-making processes. The employees are also flexible in the activities that they can perform within the organization. They are allowed to try new techniques if only that could be of some good to the organization. This has made the operations successful at the company.
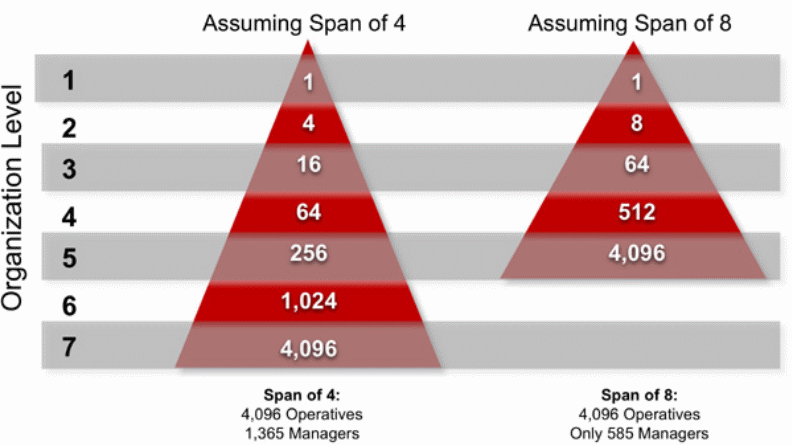
The organizational structures witnessed at the two companies can be likened to the Flat and Tall organizational structures illustrated by Crag W. Fontaine (2007), a psychologist and professor at Northeastern University.. The study illustrated the effect of having different levels of management in an organization as shown in the figure below. A span of 4 implies that four people report to a manager in the hierarchy.
Teamwork
The issue of teamwork has not been taken seriously in Watsons Company. It is a quality that is mainly inherited from the management (Adeniyi, 2007, p.10). This is observed when the production manager, Ahmed Khan, saw the need to incorporate computerized production technology in order to survive in the competitive global market. To achieve this, the production manager had proposed that the work force be organized into self-managed teams with various skills that can work as a group towards one achievement. This is leadership quality that promotes teamwork (Naoum, p.81) However, his proposal has not been taken seriously and there are little chances of success in it. There are also dangers associated with the use of information technology in coordinating activities (Markus & Robey, 1988, p.15).
Lack of teamwork and co-operation is also evident when the technical staff is glued to specific production machines partly because they have no adequate skills to operate the different machines and partly because there are no particular incentives for such a shift (Case study 1). This leads to some of the employees being overworked, as others do not work to the maximum capacity. Besides, even in teamwork, the success of the team will depend on task itself, the laborers, and the coordination within the team (Molleman & Slomp, 2006, p.2). The operations of the teams should be managed from within the teams (Guzzo & Dickson, 1996, p.19). This is definitely not possible at Watsons.
Use of teamwork is very strong in the operations at H&M Consulting. The organization that employees about 13000 staff and operates across several countries in the world works on different projects at a given time. In order to carry out the activities of the projects effectively, the management of the organization including the departmental heads forms project teams that draw individuals with different expertise. The firm has been ready to partner with other organizations (Dowd, 2006, p.1). There is organizational flexibility and the less formal system of communication allow for the coordination of the programs to be effective. The managers have the responsibility of advising the various teams during the execution of a particular project. Moreover, teamwork helps the projects to be completed in the shortest times possible as it has been seen to be associated with high production rates (Srivastava, 2005, p.19).
Leadership and Management Approach
The leadership style that is used by an organization greatly affects the ability of the organization to achieve its objectives because management is a corporate responsibility (Kivipold & Vadi, 2010, p.2). The kind of relationship that is developed between the top management of an organization and the workers of the organization will determine the job satisfaction and job performance by the employees (Srivastava, 2005, p.1). The performance of an employee often correlates with the job satisfaction that he/she derives from the job. Cases of dissatisfaction of employees have been seen to slow down the organizational productivity due to strikes and/or slow job performance by the workers.
The low-level employees are also excluded completely in the decision-making processes often do not feel a sense of belonging to the organization thereby lowering their performance. A good approach is then to have a decentralized decision making process of by providing effective means of communication from the top management to the low-level employees and including their opinions towards the proper management practices to be adopted (Fontaine, 2007, p.7). Proper decision-making alone cannot be a key to the success of the organization. Leaders should be role models that set standards to be adopted by the employees (Adeniyi, 2007, p.4).
The poor leadership quality at Watson is evident when the company struggles to obtain and retain its employees (Case study 1). There is very little employee satisfaction often due to the kind of leadership. The top management does not relate well with the employees. The HRM is not able to make a resolution due to the poor relations with and his inability to deal with the trade union. On the other hand, the leadership quality that has been demonstrated by the CEO of H&M is the desirable leadership style that can promote the quality performance by the work force.
This leader leads by example and is a role model to many of the employees. His leadership has established a set of organizational values that advocate for teamwork and consultations in the operations within the organization. This has enabled proper management of the organization that operates internationally. It is an employee-owned organization and the kind of corporate governance used is essential in managing managerial discretion (Su 2010, p.5). He has empowered the staff to work independently and put in new approaches that can help in improving the operations of the organization.
Organizational Culture
The culture of an organization defines the set of values and principles that govern the performance of the employees towards the achievement of company goals (Barry, 2000, p.105). It includes the mission that the organization has and the techniques that define the procedure of achieving the mission. It is also defined in the history and leadership that has been seen in the organization (Barry, 2000, p.105). It greatly affects the reputation of the organization (Elsbach, 2006, p.18).
The culture at Watsons Company is not very well defined. The Managing Director of the company has a motto that: ‘If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it!’. This means that if a deal seems not possible to work, then it should not be forced. In such a case, the workers are set to develop laziness as there may be no means of determining if something cannot really work out properly. Besides, every one in the organization appears to be only interested in his/her predefined roles. The Human Resource Manager has noticed there is a problem of absenteeism and retention among the staff but feels that it is up to the supervisors to check on that. There is also a spirit if hereditary leadership in the organization. This is evident since top position is yet to be vacant and chances are high that a serving staff member is to be promoted to the position. A good approach in the recruitment of employees is to consider all applicants for a given job in an organization.
H&M Consulting has the mission of ensuring customer satisfaction through a professional excellence in its operations. It also aims at ensuring a job satisfaction and fulfillment of the employee needs. To achieve this, the organization has developed culture that is best defined by the acronym PRIDE; Progress, Respect, Integrity, Drive, and Excellence (Case Study 2). The organization is out to perform activities that promote economic development in the community. Organizations should respect the diversity that exists among the work force and ensure an equal representation of employees during the recruitment processes (Bratton & Gold, 2001, p.12).
The organization also promotes the spirit of integrity among the employees. It has a principle that it cannot promise a customer something that may not be achieved or accomplished in time. The spirit of ‘Drive’ implies the commitment of the organization to continued improvement of it operation. The employees are always expected to exceed the expectation of the organization. They should be committed to the company’s activities more than personal issues (Baumgardner et al. 2004). Such a commitment should also be coupled with excellence in performance by the employees. Thus, the organization relies entirely on the employees for the achievements of its company objectives.
Conclusion
The proper management of an organization is the key towards the achievement of the organizational objectives. There is need to make appropriate decisions by the management of the organization and to have the kind of leadership that allows for the implementation of the strategies that have been developed by the organization. The organizations are currently faced with the problem of hiring and retaining potential employees. A good level of productivity in an organization will only be achieved if the employees of the organization are satisfied by the working conditions. The level of job satisfaction and employee satisfaction will greatly affect the productivity. The satisfaction of the employees is also influenced by the leadership qualities in the leaders and how they relate with the employees. The organizational structure within the organization will have a big impact on the employee performance.
The cases study that was conducted happened to shed light on two organizations with different organizational structure. The difference in the systems adopted has seen the two organizations have different rates of growth. Watsons Company has the traditional hierarchal organizational structure with a central power. The organization is family-owned with the top-management position held by a family member. There are managers in various departments of the organization and each work independently of each other. There is little communication between the departments and neither are the staffs in the department involved in company decision-making processes. The workers in every field are strict to their roles and cannot provide an overlap to reduce the laden role that can be bestowed on the others. This kind of organizational management has led to poor growth of the organization. It is not able to expand its operations and provide more services. It is not able function across several countries and neither is it able to attract and retain many potential employees.
On the other hand, the management at H&M Consulting is that which allows for the quick growth of the organization. The decentralized power and the less formal means of communication that is allowed within the organization are the key towards the successes that have been witnessed in the organization. The employees are free to try new ideas in the organization. They are not restricted to an individual responsibility environment. Rather, a spirit of teamwork is developed in them that allow them to have a collective responsibility towards a particular objective. The leaders at the organization act as role models to the employees and they have set out the fundamental principles and practices that define the culture of the organization.
Recommendations
The success of the system that has been adopted by H&M Consulting clearly shows the kind of organizational structure that needs to b adopted. There is need to adopt an organic, flexible kind of organization. The workers in a given organization should be charged with certain roles. However, the provision should not be so rigid that the employee will now sit and relax when another one is working to death simply because that is another role altogether. They should be capable of moving between various activities in the organization.
There should be less formal kind of communication between the management and the employees. The usual reporting relationship adopted in a hierarchical structure often slows down the action process. An issue could be raised from the low-level implementers that is crucial and needs to be addressed urgently. However, the procedure that it will follow may make the organization make a substantial loss. There should be free flow of information between the management and the employees.
There is need to have proper coordination between various departments within an organization. The different departments in an organization should work towards the achievement of similar objectives. For instance, the human resource department should liaise with the other departments during the recruitments of the employees in the provision of incentives to retain the employees in the organization.
The decision-making process should not be done by the top management alone. The low-level workers seem to better understand the company operations and problems than the management do. They happen to understand the kind of adjustments that are necessary and, therefore, should be involved in the decision –making process.
The leaders should have good relation with the trade union to understand the needs of the workers. The trade union is the tool through which the employees can communicate their problems to the management. There is need for the management to listen to and solve the problems raised by the employees that make their working environment poor. This is achievable if there is a strong trade union that is recognized and has good relations with the management.
A culture should be developed in the organization that promotes teamwork and co-existence in multicultural environment. The workers and the management should be sensitive to their cultural diversity among the work force and the customers of the organization.
References
Adeniyi, M., 2007. Effective leadership management: An integration of styles, skills, and characters for today’s CEOs. Bloomington: Authorhouse.
Baumgardner, J. et al. 2004. How to be a winner with your boss. Good Housekeeping, Vol. 239, Issue. Web.
Barry, J., 2000. Organization and management: a critical text. London: Cengage learning EMEA.
Bratton, J. and Gold, J., 2001. Human resource management: theory and practice. London: Routledge.
Dowd, M., 2006. Instinet Adds H&M Consulting Group as Retail Research Partner. New York. Web.
Elsbach, K., 2006. Organizational perception management. London: Routledge. Graubner, M., 2006. Task, firm size, and organizational structure in management consulting: an empirical analysis from a contingency perspective. Oestrich-Winkel: DUV.
Fontaine, C., 2007. Organizational Structure: A Critical Factor for Organizational Effectiveness and Employee Satisfaction. Northeastern University College of Business Administration. Web.
Guzzo, R and Dickson, M., 1996. Teams in Organizations: Recent Research on Performance and Effectiveness. Annual Review Psychology, 47:307–38. Web.
H & M Consulting Limited. 2010. H & M Consulting Limited. (Online). Web.
Kivipold, K and Vadi, M., 2010. A measurement tool for the evaluation of organizational leadership capability. Baltic Journal of Management, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2010 pp. 118-136. Web.
Markus, L and Robey, D., 1988. Information Technology and Organizational Change: Causal Structure in Theory and Research. Management science, Vol.34, No.5. Web.
Molleman, E and Slomp, J., 2006. The Impact of Team and Work Characteristics On Team Functioning. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing, Vol. 16 (1) 1–15. Web.
Naoum, S., 2001. People and organizational management in construction. London: Thomas Telford.
Pang, P., 2004.Essentials of Manufacturing Engineering Management. Lincoln: iUniverse.
Sanchez-Manzanares, M. et al. 2008. Designing Organizations: Does Expertise Matter? J Bus Psychology, 23:87–101. Web.
Srivastava, S., 2005. Organizational Behaviour and Management. New Delhi: Sarup & Sons.
Sisaye, S., 2001. Organizational change and development in management control systems: process innovation for internal auditing and management accounting. Oxford: Emerald Group Publishing.
Su, L., 2010. Ownership structure, corporate diversification and capital structure: Evidence from China’s publicly listed firms. Management Decision, Vol. 48 No. 2, 2010 pp. 314-339. Web.
Volberda, H., 1996. Towards the flexible form: How to remain vital in a hypercompetitive environment. Organization science, Vol.7, No.4, pp.359-374. Web.

