Introduction
Founded by Claud Hatcher in 1905 as the Union of Bottling Works in Georgia, RC Cola remains one of the leading soft drinks companies in the world. Just seven years after the noble course, the RC Cola little known in the soft drinks industry, started exploring the manufacturing line through franchised systems in the syrups and flavour sector (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015). With a series of branding and rebranding, the company entered the New York Stock Exchange as the Nehi Corporation with Cheri-Cola as the leading product in 1940. In 1958, the company acquired its current name, Royal Crown Cola Company (RC Cola).
Marketing strategies are dynamic. Each generation comes with new demands, needs, and preferences. Similarly, information and communication technologies set in. such factors revolutionise the branding, marketing, and advertisement strategies that various business entities use. RC Cola remains a relatively competitive soft drink entity with close competition with Coca Cola and Pepsi.
In order to stand global competition for the dynamic consumer needs, RC Cola employs dynamic, innovative, and creative marketing strategies that target specificities of consumers (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015). Equally, the use of technology, especially the internet in the marketing and brand promotion continue to spur RC Cola to success. This paper seeks to explore the strategic brand marketing systems that RC Cola employs to maintain the consumer base and keep up with competition from the players in the international soft drinks industry.
Brand Positioning and Values
Mental mapping
In this strategy in place, the products and brands aim at conquering consumer loyalty through artful advert presentation that seeks to arouse hope and desire among the customers. Mind maps are graphical ways of representing ideas, concepts, and information to a target audience. In the marketing sector, mind maps act as visual thinking tools that help customers to structure information in advert, gather such information, and comprehend the intended message.
Notably, mind maps enable consumers to synthesise the advert and generate ideas on the benefits of the product. In order to master this strategy, RC Cola presents adverts in unique and simple ways that remain attractive and mind provoking to the customer, thus increasing the desires of product purchase (Keller, 2003a).
Infographics, pictures, and artistic presentations offer the best method of developing adequate imposition of this strategy in the market. RC Cola through its strategic advertisement programme presents one of the most sophisticated artistic impressions on the bottles and cans containing their products.
These containers, often in the organisations red and blue colours, invoke customers’ desires for taste, thus increasing chances of purchases. In comparison to other players in the market, Coca Cola presents their can in relative red and black colours while Pepsi remain confined to the trademark blue colour limited conspicuousness in the marketing strategy (Keller, 2003a).
Competitive frame of reference
Introducing a brand in a competitive market environment remains a challenging marketing phenomenon. The difficulty increases in scope for entities making maiden entry into the market. Therefore, it is vital for companies and organisations to come up with new ideas or improve the existing products to win the hearts of customers. In a conventional market structures, customers stick to regular products unless better and improved brands and products come into the market.
Creating this new brand and product requires proper understanding of the existing products, their strengths, and weaknesses. In the snack industry, for example, creating a frame of reference entails understanding the positioning of the existing similar and dissimilar products. For instance, a new entity may focus on producing kids’ snacks, energy bars, or diet supplements as new products or improvements on the use and consumption of the existing products (Saddler, 2003).
Establishing a competitive frame of reference plays a vital role in developing a new brand. In drawing reference from the existing soft drinks giants such as Pepsi and Coca Cola, RC Cola developed a strategic frame of reference for effective competition. Chero-Cola as the maiden soft drink product explored competition with Coca Cola’s coke. As a soft drink within the thirst-quenching frame, Chero-Cola expanded the varieties of the thirst-quenching products in the market.
RC Cola in the dynamic world of energy drinks offers new and improved energy drinks targeting markets that Pepsi and Coca Cola continues to dominate. Engagement in such a wide scope of frame of reference increases product sales and market bases that translate to increased sales. RC Cola does not only focus on the American market, but also explores wider global markets to increase consumer base (Keller, 2003a).
Points-of-parity and points-of-difference
Making customers believe the new product is legitimate and genuine in the market place offers business entities an edge over competitors. Capitalising on the points within the existing market brands becomes important for the entry of new brands in the market. Even though establishing a new and unexplored brand presents high degree of innovativeness and creativity, understanding the gaps within the existing products in relation to customer satisfaction helps new brands penetrate the flooded market.
Taking the existing product head-on with goals of maximum neutralisation of he established brands offers an alternative way of pursuing the points of parity in market penetration. RC Cola’s strategy for maximum capitalisation on the market parity by taking Coca Cola and Pepsi head-on in the soft drinks thirst-quenching frame of reference offered high competition and productivity in the market.
The strategy coupled with improved methods of advertisement and redesigned packaging techniques provided customers with new exploration, hence increasing the rates of sales. Increase in sale translates into high profits and improved market penetration (Saddler, 2003).
Core brand values
Identity
In the business, developing ambition and high vision for company management strategies play a vital role in ensure consolidation of consumer base. With a strong vision to lead in food and beverage production and distribution in the global market, RC Cola employs strategic brand values that conform to consumers’ demands and preferences.
Concentrated brand identify acts as RC Cola’s strategic brand value that focuses on mass market. Through this strategy, RC Cola places adverts and marketing tools in common places with wide range of customer view. Recto Manila boasts of a wide professional billboard designed by MacGraphics Carranz. Similarly, the company employs the use of television advertisement as evidenced by Eat Bulaga advert, which targets majority of the viewers (Scott & Dunn, 2002).
Affordability
Pricing in the business helps to manage and consolidate consumer base. Business entities must develop mechanisms for proper pricing that ensures the company maintains or improves profit margins while at the same time recruit and retain the highest number of buyers. RC Cola’s pricing values revolves around affordability with great taste, thus increasing consumer loyalty.
Providing affordable prices increase access to the company’s product and services. This coupled with available values in brand strategies of the company through increase in the number of RC Cola plants, ensure wholesalers and retailers have access to unlimited products and brands. Maintaining supply and distribution networks ensures stability and availability of brands and products in the market hence helping in consolidating consumer bases (Scott & Dunn, 2002).
Community service
In business, promotions act as enticement to lure customers into more purchases. As a brand value in RC Cola, promotions help to draw consumers’ attention to product, thus creating purchases contests. These in turn improve sales volumes further raising profit levels. Even though many business entities find it difficult to explore the corporate social responsibility strategies in branding and marketing, RC Cola continues to perfect the strategy to win the hearts of consumers.
Through community assistance and sponsorship programmes, the company does not only generate interesting consumers’ base, but also loyal and trustworthy clients. Corporate social responsibility creates a sense of reward and appreciation to customers that further improves their purchasing frequencies (Scott & Dunn, 2002).
Brand manta at RC Cola
Branding as a component of marketing strategy revolves around naming, terming, symbolising, and designing company product and services in a unique format that propels such products to superior statuses in comparison to those of their competitors. Brand mantra is a unique worded statement that drives the company’s branding strategies.
It seeks to make peculiar position in the minds of the target consumers, provoke their attentions, and create awareness. Likewise, brand mantra helps companies increase their sales demands through creation of positive image about company products and services (Scott & Dunn, 2002). This helps in attracting new consumers as well as consolidating the loyalty of already existing customers. For RC Cola, the mantra goes “Taste Change. Good Taste Doesn’t” (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015)
Brand marketing programmes for RC Cola
Mixing and matching of brand elements
Brand elements in marketing act as the unique features that differentiate a product and business entities from their competitors. In the contemporary consumer discourse, the importance of brand elements remains vital in developing competitive edges in the market. With consumers developing personal brands similar to commercial objects, mix and match branding among business franchises increase the level of appeal to consumers.
Due to these dynamisms in branding, companies must develop brand names and mantras taking into account both the consumers and manufacturers’ perspectives. RC Cola’s contour bottle and its red and blue colours act as unique symbols for identification and differentiation from other competitors (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015).
Companies choose brand elements to enhance brand awareness, and help in the formation of strong and enticing brand associations. In order to build a unique brand quality for adequate market competition, business units must develop brands with high quality in memorability, meaningfulness, and aesthetic appeals. On the same note, such brands can be conformed to transferability characteristics of the product, adaptability over time, flexibility in target audiences, and defensibility from other players in the market.
Even though each brand element comes with different strengths and weaknesses, mixing and matching such brand elements help RC Cola to develop unique and competitive products that stand out amidst products from the global competitors.
The RC Cola Neo’s advert represents an example of an integrated use of brand elements in marketing (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015). Apart from the aesthetic values from the improved contour bottles, the graphics on the product container contain descriptions of the content with emphasis on reduced calories. These features do not only appeal to consumers, but also invokes their desire for taste.
Integrating brand marketing activities
Brand elements come in different formats. In order to help customers and clients identify and differentiate products and services, business entities in the global market employ the use of integrated systems of brand element equities. RC Cola, for example, uses names, symbols, characters, slogans, jingles, and packaging equities in developing unique structures for brand promotion. Integrating the use of different strategies in brand elements helps RC Cola build awareness and positive image, leading to a direct positive improvement on the impacts of brand equity.
RC Cola’s brand elements remain highly memorable and easy to recognise. This helps consumers to recall brands and products, thus improving purchasing frequencies. Equally, in brand element development, RC Cola ensures descriptive, persuasive, and interesting verbal and visual infographics. These elements help in invoking curiosity among new buyers, thus improving chances of earning new customers.
Creating anaesthetic sense and emotions among the consumers and flexibility in product use across large portions of population ensure RC Cola retains the consumer bases. Interrelated use of these characteristics in developing a brand ensures the companies maintain completive advantage over competitors in the global market (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015).
Leveraging of secondary associations
Secondary brand associations are strategies in which organisations use specific aspects and transferring entities of a brand to achieve brand equity. Such transfers may include co-branding strategies, ingredient branding, celebrity endorsements, and sponsorships deals. While making maiden entry into the Israeli market, RC Cola came in with a slogan – “RC: Just like in America”.
This helped to create a sense of association with America among consumers in Israel. Equally, American-loving residents of Israel draw some sense of emotional attachment from such slogans. In turn, more sales result and customer base widens. In the 2012/2013 fiscal year, RC Cola sponsored Marco Andretti of the Andretti Auto-sport during the IndyCar series. Such secondary associations help in creating advertisement platforms, hence improving chances of increased sales (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015).
Brand marketing plan and its implementation
Brand Resonance Pyramid present an amicable planning and implementation platform for improving sales and increasing customer. For RC Cola to implement such a strategy, an in depth understanding of the tenets of this pyramid helps the management team develop proper structures for implementation, monitoring, and evaluation.
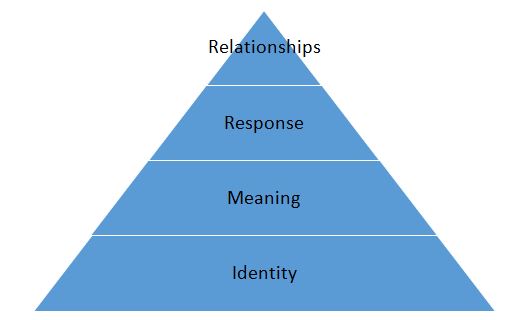
In order to create a significant brand quality, RC Cola requires strategies of reaching the peak of the above pyramid. The relationship level, also known as resonance level, requires clear and objective movements from the identify level through the meanings and customer responses. At the base of the pyramid is the brand identity that defines the brand salience and helps in ensuring brand awareness such as advertisement in billboards and televisions. At the second level of the pyramid is the brand meaning. In this level, product performance and imagery becomes vital.
Infographics, pictures, and memes help RC Cola in developing a strategy for ensuring appealing imagery. Customer feelings, judgments, and emotions redefine the demands and presentations of the brand (Keller, 2003b). Customers’ reactions and feelings before and after using RC Cola products help the company evaluate the performance of the brand in the market. At this stage, the company website and social interactive sites help RC Cola assess the brand’s performance in the market.
Interpretation brand performance for RC Cola
Brand value chain
Value chain is a series of activities and strategies that companies and organisations put in place to create and build brand value with the motive of recruiting new customers and widening consumer bases. Value chain brand affects the total value of revenues that a company generates. For that reason, developing adequate steps in creating value-chain brand remains a core factor in business success.
Value chain, as a concept in business, separates useful activities that propel companies to superiority over competitors from the wasteful activities that often drive companies and organisations off the competition (Keller, 2003b). RC Cola boasts of focused value branding activities that range from affordable products, flexible and appealing brands to emotional brand images.
Brand chain consists of different facets at RC Cola. RC Cola in the outbound components of value chain depends on high number of points of sales, increased wholesalers and retailers, and convenient distribution agents (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015). Likewise, the company employs the use of professional advertisement agencies and celebrities to ensure irresistible appeal to consumers. The service department maintains close contacts with consumers by monitoring the satisfaction levels in the post-sale markets.
Brand value chain takes a steps-like format in realisation. Value stage exists in a series of four steps. In between these steps, lies the multiplier components that seek to push up the progress of the values stages. It takes into account the product, communication, trade, and employee plights in the value chain. In ensuring complete movement to the customer mind-set stage, multiplier components of programme quality set in. Markedly, it aims as ensuring clarity, relevance, distinctiveness, and consistency in the two consecutive value stages.
Customer mind-set stage takes into account consumer awareness, associations, attitudes, emotions, and feelings of attachment. The next stage of value chain is the market performances that evaluate the prices, market shares, business expansions, expenses, and profit levels.
Between stage two and market performance structures exist the market place conditions such as competitive reactions, channels support, and customer base. The last level of value chain is the shareholder value that evaluates the stock prices and market capitalisation. Market dynamics, growth potentials, risks profiles, and brand contribution under investor sentiments as a multiplier components exist between market performance and shareholder values (Keller, 2003b).
Brand audits
Brand audit is a comprehensive review, analysis, and assessment on the progress of brand in the market. It helps uncover sources of equity, identify areas that require improvements and components that drive company success. In carrying out brand audits, RC Cola assesses brand vision, mission, promises, and values set out during the development of the brand. Similarly, the company evaluates and monitors the brand position in the market, its personality, and the performance based on related and competing brands (Keller, 2003b).
Effective brands improve the company revenue levels since they inspire, captivate, and engage customers and target audiences. Developing a strong and effective brand, therefore, calls for frequent reviews and monitoring to assist in coming up with adequate measures of maintaining performance. Conversely, weak and disjointed brand leads to falling customer numbers, reduced sales, and increased losses.
RC Cola, as an international soft drink player, carries out brand audit to ensure they remain competitive in the dynamic markets. Brand audits help the company in evaluating brand resource strengths, brand value, popularity of the brand in the market, and deficiency of the brand. Likewise, RC Cola understands and explores the emerging trends and market capabilities based on the outcomes of the brand audits.
Outside threats, new product development and future channel profitability, perceptions, image, reputation, and attitude about a brand come out at the brand audits stage, enabling RC Cola to develop adequate measures for improvement in market capitalisation. Brand audits helps in developing new strategies for brand management, thus improving productivity and profitability of the business entity (Keller, 2003b).
Brand audit seeks to reveal how customers view a product or service. Similarly, it assesses the performance of the brand against the competing brands. In this line, the outputs of brand audits seek to support improvement and refocusing of brand management efforts and efficacies.
Outputs of audit help in enhancing and improving employees brand awareness leading to improved ambassadorial roles among employees. In the assessment of performance of the brand against the competitors, brand audits provide insights in developing improved brand architecture, efficient strategies, and viable brand portfolios, hence helping the organisation evaluate and refocus brand positioning in the market (Keller, 2003b).
Brand tracking
Brand tracking in the business field enables business leaders to assess the progress and track down areas that require improvement in a particular branding strategy. Tracking allows managers to trail effectiveness of advertisements, brands, and markets in relation to other market players. From tracking activities, business leaders stand high chances of developing effective marketing strategies to improve profitability.
Different business entities employ different tracking mechanisms to assess the performance of their brands. RC Cola engages in tracking all the brand strategies put in place for enhancing sales. Tracking brand image in the market in relation to other products in the market gives RC Cola a competitive advantage over competitors such as Coca Cola and Pepsi. On the same note, assessing and evaluating brand performance in relation to the specific retailers, distributors, and wholesalers given the close contact the company enjoys with these groups of people enables the management team to develop new strategies of conquering markets (Keller, 2003b).
Demographic play a vital role in business continuity. Different groups of people have different tastes and preferences. Assessing the customer satisfaction from brand products enables RC Cola to evaluate the attitudes, emotions, and feelings its brand arouse among the different demographic regions and groups (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015).
Complaints and suggestions help RC Cola in developing new strategies for improving its service and product delivery methods. In the advertisement perspective, tracking brand enables organisations to assess the effectiveness of different types of adverts and promotions put in place for brand marketing. Tracking advertisements assess the ability of the type of advertisement to create awareness, provoke consideration, and appeal to customers to increase purchases. Similarly, tracking advertisement help an organisation to assess the level of re-purchases customers undertake (Keller, 2003b).
Brand tracking survey must take into account brand usage to ensure productivity. In this facet, the tracking survey evaluates the frequency of purchases that consumers make overtime. At the same time, it relates the frequencies to the competing firms. For example, RC Cola requires an assessment to its use in relation to those of Coca Cola and Pepsi. Assessing the usage level enables companies to strategize the means of conquering consumers using products of the competitors. Likewise, tracking enables RC Cola assess the purchasing intentions of consumers.
This helps in managing the levels of quantity of products released into the market (Keller, 2003b). Brand attributes in tracking enable organisation to assess the satisfaction levels among customers. Similarly, attributes help business entities to evaluate consumers’ expectations in the market. In the end, the organisation makes products in relation to the demands, preferences, and priorities of the customers. Even though pricing and availability trends affect the level of customer satisfaction, some people value product conveniences in terms of utility.
Brand equity management system
Brand management takes place through a series of component tenets. Brand name management, logo management, design and packaging management, and advertisement management are vital components in brand equity management. Brand equity management helps in defining the expected roles and aspirations of specific products’ brands. In developing adequate understanding of brand equity management in RC Cola, brand equity pyramid comes into play.
Existing in three levels, the fundamental and uppermost part of the pyramid represents the brand that often remains fixed over time, such as the desire for production of quality affordable soft drinks. In the middle tier is the brand style, depicting brand core in terms of cultures, personality, and images. It offers the infographic representation of the real drivers of marketing brands. Brand themes with specific target audience occupy the base level of the pyramid.
Examples of such themes include physical aspects such as colour, logo, packaging designs, reflective aspects such as advertisement ambassadors, and target relationships such as glamour and prestige (Keller, 2003a). These themes represent the most flexible aspects in the pyramid and depict the methods that the brand employs in communicating its desires to customers. Markedly, advertisements and packaging designs fall in this category.
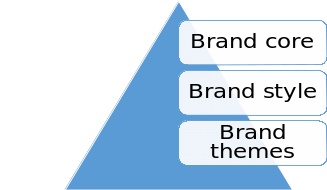
Growth and sustainability brand equity for RC Cola
Brand-product matrix
Characterisation of product and branding strategies that different companies employ in the market helps in understanding the expected management units of such companies harbour.
In such analysis, brand-product matrix act as an assessment tools that clearly defines the product qualities in relation to consumer expectations. Brand-product matrix organises all business products and brands in rows and columns, thus helping marketers and other business analysts in understanding existing brand lines as well as in exploring existing opportunities (Keller, 1999). RC Cola brand-product matrix based on Ansoff’s growth share matrix evaluates the productivity and profitability of the existing products in new markets, new products in existing markets, and new products in new markets.
Brand portfolios and hierarchies
Different brands share portfolios in many organisations. However, in cases where management lacks proper ways of managing such differences, collective grouping of brands into one portfolio often causes confusion in consumers’ minds. This calls for proper order and purpose to the entire organisation to develop clear and distinct values and qualities for products that share the same portfolio. RC Cola portfolios include RC Cola, RC Cola Neo, RC Q, RC Zero, Mulberry Farms, and Ben Shaws. Brand hierarchy in RC Cola exists in the horizontal format in which RC Cola, RC Cola Neo, RC Q, and RC Zero fall under RC Cola (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015).
Brand expansion strategies
Repackaging
Repackaging presents a relatively cheap method of consolidating consumer loyalty. For the conventional contour bottles, RC Cola continues to develop new and aesthetic bottles and cans with increased appeal to consumers.
New packaging designs introduce new visual appeal responsible for provoking consumers’ thoughts while maintaining brand quality and characteristics (Mozota, 2003). Similarly, developing different packaging quantities help access different levels of consumers. RC Cola’s introduction of the 1.5 litre and 800 millilitre containers help vary the consumer trends while taking into account the purchasing power of different members of the consumer base.
Discounting
Price reduction acts as an incentive to consumers; it increases purchases. Designing new and effective pricing strategies in an existing market helps the company reach out to consumers with low purchasing capabilities while maintaining the relatively rich customers (Keller, 1999). Even though the discounting option does not work out well in promotions and during festive seasons, it helps RC Cola increase sale levels translating to profitability. During the off peak seasons, lowering prices by a 50 cents margin in relation to competitors prices helps RC Cola appeal to new markets and consolidate its customers leading to improved sales.
Re-branding
Even though re-branding needs calculated strategies to ensure maintenance of existing consumers, it offers a strategy for renewal of efforts for profitability. Ranging from packaging, re-design to product renaming, RC Cola employs this type of strategy in order to access new markets, as well as contain competitors in the existing markets. From Royal Crown Cola, Ice Cold Royal Crown Cola, Diet Rite Cola, Royal Crown Cola to RC Cola, the company continues to undertake great strides in re-branding of products to maintain a strong consumer base (Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International, 2015).
Overseas exploration
Even though the company started as simple family business into a multinational firm within the US, its numerous services across the globes continue to earn it more customers, leading to increased sales. RC Cola produces brand with life across the entire globe. Expanding production to unexplored markets helps the management team to consolidate profit levels and customer bases. Despite the associated costs, exploring international markets helps RC Cola withstand competition from international competitors like Pepsi and Coca Cola.
Brand reinforcement and revitalisation
Brand reinforcement and revitalisation seek to maintain brand quality amidst dynamic competition levels. Aimed at ensuring consumers retain desired qualities in products and brands, reinforcement revitalisation seeks to maintain brand image, prestige, and clamour (Mozota, 2003).
Even though in some cases reinvention and revitalisation strategies fail due to emerging technological demands in the market, changing towards customers’ emerging tastes and preferences offers RC Cola an edge over other competitors. Developing quality and maintain brand equity require proper analysis of the root drivers and core values of RC Cola’s brands and products.
Conclusion
Strategic brand management and high quality marketing structure play vital roles in propelling business entities to higher levels. In cases where an organisation produces high quality products but lacks proper marketing and advertisement mechanisms, the chances of business failure remains high. Strategic business management calls for adequate marketing strategies to improve sales volume and customer loyalty. RC Cola remains one of the noble international soft drink manufacturers with sophisticated marketing designs and improved advertisement structures.
References
Bottling Opportunities: RC Cola International. (2015). Web.
Keller, K.L. (1999). Managing Brands for the Long Run: Brand Reinforcement and Revitalisation Strategies. California Management Review, 41(3), 63-73.
Keller, K.L. (2002). Strategic Brand Management: Best Practice Cases in Branding. Mason, OH: Prentice Hall.
Keller, K.L. (2003a). Strategic Brand Management. Mason, OH: Pearson Education.
Keller, K.L. (2003b). Strategic Brand Management: Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity. Mason, OH: Prentice Hall.
Mozota, B. (2003). Design Management: Using Design to Build Brand Value and Corporate Innovation. New York: Allworth Press.
Saddler, P. (2003). Strategic Management. New York: Kogan Page Publishers.
Scott, D., & Dunn, M. (2002). Building the Brand Driven Business. New Jersey: Jossey- Bass Publishers.
