Introduction
The present report was commissioned by Paddy and John McGuiness. The report evaluates the current financial position of Lockdown Ltd and provides recommendations based on the analysis. The report is divided into three parts: company valuation, general advice based on the analysis of financial statements, and specific advice on the questions of interest. The first part includes detailed calculations of profitability, liquidity, gearing, efficiency, and investor ratios. The second part contains the highlights of the ratio analysis and recommended changes to improve financial performance. The third part includes recommendations on specific questions, such as suggested share price, potential threats, and delivery vans.
Analysis of Financial Statements
Company and Accounts
Lockdown Ltd is a private company that operates ten stores selling alcoholic beverages. The enterprise was established by brothers Paddy and John McGuiness in 2009, with only two stores run by each of the brothers. At present, the company has 20 full-time and 20 part-time employees apart from the McGuiness brothers. Lockdown Ltd currently has only two shareholders, with Paddy and John McGuiness holding 50% of shares each.
In 2019, the company started wholesaling to local pubs and restaurants using credit lines and purchased two additional restaurants. As a result, the company’s revenues increased from €4.2 million in 2018 to €4.85 million in 2019. Additionally, total assets increased from €10.24 million to €12.6 million. The majority of the increase in assets was attributed to non-current assets (€2 million). Thus, the extended customer base was beneficial for Lockdown Ltd.
However, the recent expansion of the company also had negative effects on financial performance. In particular, the company was forced to use debt to finance the increase in assets. As a result, the company’s long-term debt increased from €0 to €1 million, which caused interest expenses. Additionally, in 2019, the company experienced a significant increase in inventories (from € 180,000 to €650,000). This may be due to the fact that the company has not yet decided how to manage its current customer base and how many inventories it may need to avoid supply disruptions.
It is also crucial to notice that despite the fact that the revenues grew in 2019, net income decreased from €900 thousand in 2018 to €725 in 2019. This change is alarming and requires further investigation.
Profitability
Profitability analysis demonstrates how efficiently the company uses its resources to generate value for shareholders. The company’s profitability can be measured using several ratios, including Gross Profit Margin (GPM), Net Profit Margin (NPM), and Return on Capital Employed (ROCE). The present report will calculate all three of these ratios. All the profitability ratios are visualized in Figure 1 below.
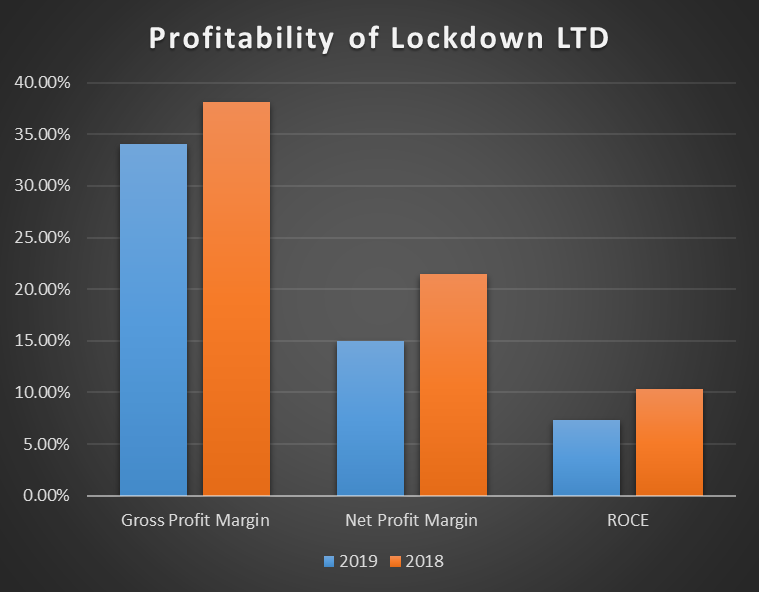
GPM is calculated by dividing gross profit by total revenues. The calculations are provided below:
![]()
![]()
The calculations demonstrate that GPM decreased from 38.1% in 2018 to 34.02% in 2019. This demonstrates that the direct costs of producing one unit of the product have increased. This may be a result of the need to hire additional store managers, which increased labor costs. Additionally, two newly purchased stores may not have started working at their full potential, which may be associated with decreased profitability. Thus, even though the decrease in GPM was significant (4%), it is not alarming, as it can be explained by the current needs of the company. However, if the new stores were purchased at the beginning of the year, this may be a sign of concern, as the cost of goods (COGS) sold grew disproportionately.
NPM is calculated by dividing net profit (profit after interest and tax) by the total revenues. The calculations are provided below:
![]()
![]()
The calculations demonstrate that NPM decreased from 21.43% in 2018 to 14.95%, which is almost 6.5%. The decrease in NPM is attributed to the growing COGS, distribution costs, administrative costs, and interest. Both distribution and administrative costs increased by 33% in 2019, and interest expenses were €50. Such a drastic decrease in NPM a sign of concern, as administrative and distribution costs increased disproportionately with revenues from the new customer base. This may demonstrate that the new imitative of wholesaling buying the new stores may not have shown their full positive effect.
ROCE is calculated by dividing profit before interest and tax (PBIT) by the capital employed. PBIT can be calculated by adding interest expense to profit before taxation, and capital employed can be calculated by subtracting current liabilities from total assets. The calculations are demonstrated below:
![]()
![]()
The results demonstrate that ROCE deteriorated from 10.31% in 2018 to 7.31% in 2019. This implies that for every €1 invested, the company was able to generate 7.31 cents in 2019, which is a 41% decrease in comparison with 2018. This confirms that the profitability of the company is deteriorating at an alarming rate, which needs to be investigated in the future. Such a trend in profitability may negatively affect the attractiveness of the business to future investors.
Liquidity
Liquidity ratios demonstrate if the company has enough current assets to cover its immediate expenses. Liquidity is usually measured by two ratios, including the current ratio and the quick (acid) test. The difference between the two ratios is that the acid test does not take inventories into consideration, as they may be difficult to convert to cash. The results of the liquidity analysis are visualized in Figure 2 below.
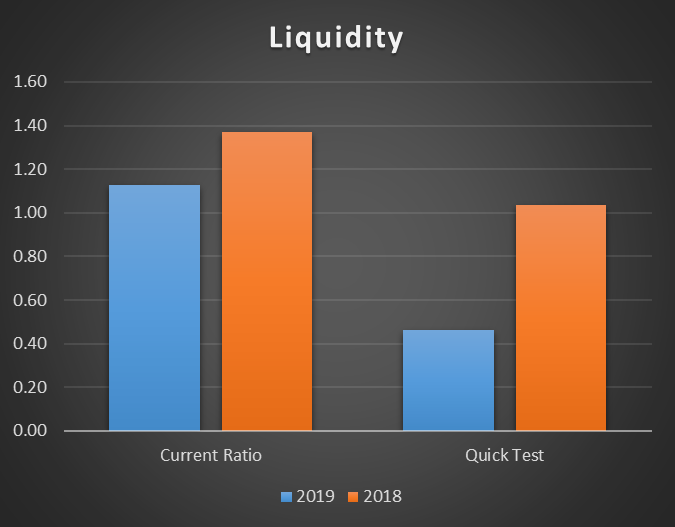
The current ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. The quick ratio is calculated by subtracting inventories from current assets and then dividing by current liabilities. The calculations are provided below
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The calculations demonstrate a significant deterioration of the company’s liquidity in 2019 in comparison with 2018. While the current ratio analysis shows that Lockdown Ltd had enough current assets to cover its expenses during both years under analysis, the acid test showed different results. In particular, the acid test ratio decreased from 1.04 to 0.46, which is a considerable concern for the company. The problem is that if the inventories are excluded from the equation, the company will need outside finances to cover its current liabilities.
Efficiency
Efficiency ratios demonstrate how well a company uses its assets to generate income. The efficiency of a company is usually calculated by the working capital cycle, which includes three ratios in the analysis: inventory days, receivable days, and payable days. The formula and calculations are provided below:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The results of the calculations are visualized in Figure 3 below.
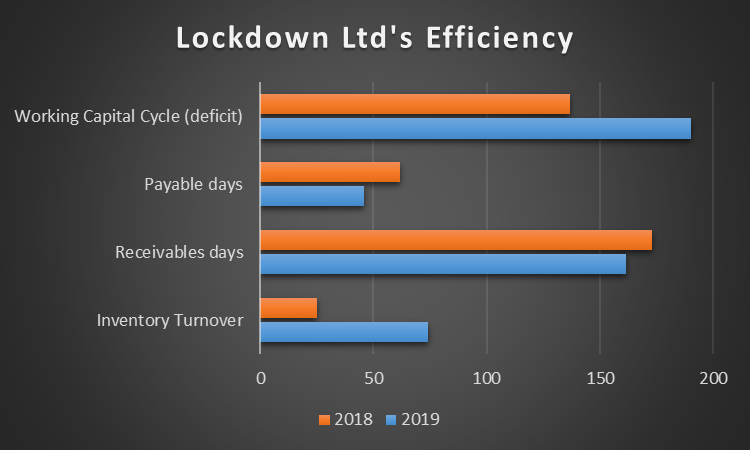
The analysis of the changes in Lockdown Ltd’s efficiency revealed a significant decline in all the parameters. First, the inventory turnover time almost tripled, as it grew from 25 days in 2018 to 74 days in 2019. This was a result of the disproportionate growth of inventories in 2019. Second, the time it takes to collect the payments from the customers also increased from 162 days in 2018 to 173 days in 2019.
This may be explained by providing credit lines for wholesale customers. Finally, the payable days decreased from 62 days to 46 days. As a result, the working capital deficit increased from 137 days to 190 days. This essentially means the Lockdown LTD needs to pay its creditors 190 days before it gets paid. This shortfall in cash is made up by the bank overdraft and is the reason why the company needs the overdraft. The company will need to pay interest on the overdraft, which will, in turn, further decrease its profitability. Thus, the company’s efficiency is a matter of concern.
Financial Gearing
Financial gearing is also called the level of financial leverage and determines how aggressively the company uses debt to finance its assets. The level of financial leverage is usually assessed using the debt to assets (D/A) ratio. The formula and calculations for this metric are provided below.
![]()
![]()
The results demonstrate that the company’s D/A ratio almost tripled in 2019 in comparison with 2018. If the company continues increasing its total debt, it may experience significant profitability problems due to increasing interest. Additionally, the company may become more sensitive to changes in the outside environment, such as interest rate increases. However, in absolute values, the level of financial leverage remains low, as the company finances its assets primarily with equity.
Investor Ratios
Investor ratios help to estimate the potential returns on the investments. These ratios demonstrate how attractive a company is for investors, which is a crucial question at this point, as Lockdown Ltd is planning to start selling its shares. The present report will use three ratios, including the dividend cover ratio, earnings per share (EPS), and price to equity (P/E) ratio. The calculations with relevant formulas are provided below.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The results are provided in Table 1 for visualization purposes.
Table 1. Lockdown’s LTD investor ratios.
The results demonstrate that the company’s ability to pay dividends decreased in 2019 in comparison with 2018 due to a significant rise in the number of dividends paid. Such a disproportionate increase in dividend payouts may lead to significant profitability issues. As for EPS, it also decreased by 24%, which means that the company is becoming less attractive to investors. Finally, the P/E ratio increased from 7 in 2018 to 8.97 in 2019, which implies that the company is becoming more overvalued, which decreases the confidence of the investors.
General Advice for the Company
The analysis of financial statements revealed significant problems with the performance of the company in almost all areas. The only positive changes the company experienced were an increase in total revenues due to the growth of the customer base and growth of total assets due to purchases of two new stores. However, almost all relative values had unfavorable changes in 2019 in comparison with 2018. Thus, the company needs to develop a series of measures to improve its financial performance:
- First, it is recommended that the company develops and implements strategies for decreasing the direct labor and material costs associated with the manufacturing of the product. One of the most feasible strategies for decreasing COGS is negotiating with suppliers to decrease the costs of materials. Since Lockdown’s customer base is increasing, the company’s bargaining power is also growing, which may result in significant discounts from the suppliers. The company may also conduct a search for other suppliers to compare the prices. Decreased COGS will improve the company’s profitability, which is crucial in its current position. However, decreased COGS will also negatively impact the efficiency ratios.
- Second, Lockdown LTD is encouraged to decrease its current administrative and distribution costs. The increase by 25% in both types of costs was disproportionate with revenue growth, which negatively affected profitability. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) can decrease its administrative costs by reducing traveling and entertainment expenses and by outsourcing (Wallo and Kock, 2018). SMEs usually outsource such services as accounting, human resources, cleaning, and forecasting.
- Third, the company is recommended to increase its control on receivables. Currently, Lockdown Ltd takes too much time (190 days) to collect the payments from the customers. This negatively affects the company’s liquidity and efficiency. Controlling receivables is crucial as the company offers generous credit lines to wholesaling partners. The receivables period can be decreased by being proactive in invoicing and collecting efforts, diversifying the client base, and offering early payment discounts. It should be noticed, however, that such discounts should be balanced, as they may negatively affect profitability.
- Fourth, the company is encouraged to decrease its current inventories. This can be achieved by improving the forecast accuracy by using the latest quantitative methods. For instance, Petropoulos, Wang, and Disney (2019) recommend using exponential smoothing as the primary statistical method of controlling inventories. Additionally, Tliche, Taghipour, and Canel-Depitre (2020) recommend controlling the supply chain using high-level quantitative methods. These approaches to forecasting inventory, however, can be very complicated, which may mean hiring a forecasting expert or using the services of dedicated companies.
- Finally, the company is recommended to revise its dividend policy, as the current level of dividend payments increased disproportionately. Such high dividends may scare potential investors, as the interest cover ratio suffered. Additionally, high dividends harm the company’s profitability and undermine its ability to develop using equity instead of debt.
Recommendations on Specific Questions
Share Price Advice
When listing a company on the stock exchange market, it is crucial to select the right price. A good starting share price can ensure that the company raises capital and establishes functional relationships with investors. Share prices are usually based on both qualitative and quantitative methods. The quantitative methods include a comparison of financial performance with competitors (Gad, 2020). The qualitative methods are associated with assessing the company’s history to make projections about future developments (Gad, 2020).
In terms of financial performance, FY 2019 was associated with a significant deterioration of the financial performance o the company, which was discussed in Section 1 of the present report. Such a negative tendency may make the company less attractive to investors. However, the story of the company is a story of success, and the fall in performance can be explained by the fact that the effect of recent expansions is not yet felt. Thus, if the company can explain all the changes in financial performance, the share price can be estimated by matching with competitors listed on the stock exchange.
Research demonstrated that a similar company is currently listed in the stock exchange at the price of €3.30 and a P/E ratio of 12. A simple equation can be created to estimate the most appropriate price using the calculations from Section 1.6 of the present report:
![]()
Thus, the recommended price for listing Lockdown Ltd is around €4.4. However, this price should be used only under the condition that a narrative of the company’s success is created.
Delivery Vans
When speaking about purchasing delivery vans, it is crucial to understand the benefits and financial implications of the innovations. On the one hand, purchasing such vans will increase the distribution convenience and corporate image. On the other hand, the purchases will negatively affect the financial performance of the company. In particular, the endeavor will increase the distribution costs due to maintenance, fuel, and personnel costs. This will negatively affect the company’s profitability without adding financial value.
Considering the fact that the company’s distribution costs in 2019 increased disproportionately, further growth of distribution costs is unfavorable. Additionally, the vans will need to be purchased using debt, which will impair the company’s leverage and profitability. Thus, it is not recommended to purchase the vans in 2020. Instead, the company should consider outsourcing the transportation costs.
Potential Threats and Future Plans
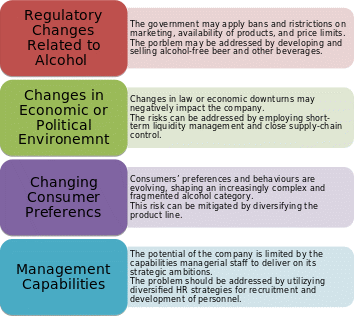
The potential threats that Lockdown Ltd can face are similar to the companies from the same industry. Thus, threats that Heineken (2020) may encounter in the future are applicable to Lockdown Ltd. The list of potential threats with future plans of mitigating the risks is provided in Figure 4 below:
Conclusion
The analysis of the financial performance of Lockdown Ltd revealed significant issues. In 2019, changes in all types of ratios in comparison with 2018 were unfavorable. The points of major concern were profitability, liquidity, and efficiency.
The company needs to implement measures to improve its current position by optimizing COGS and other costs, controlling receivables and inventories, and revising the dividend policy. The company is also recommended to avoid investing in delivery vans for at least a year to see how the newly-established customer base influences profitability. In conclusion, the company should pay close attention to the possible threats and establish action plans to mitigate the identified risks.
References
Gad, S. (2020). How an initial public offering (IPO) is priced. Web.
Heineken (2020) Annual report 2019. Web.
Petropoulos, F., Wang, X., and Disney, S. M. (2019) ‘The inventory performance of forecasting methods: Evidence from the M3 competition data’, International Journal of Forecasting, 35(1), pp. 251-265.
Tliche, Y., Taghipour, A., and Canel-Depitre, B. (2020) ‘An improved forecasting approach to reduce inventory levels in decentralized supply chains’, European Journal of Operational Research, 287(2), pp. 511-527.
Wallo, A. and Kock, H. (2018) ‘HR outsourcing in small and medium-sized enterprises’, Personnel Review, 47(5), pp.1003-1018.
