The environment in business is the surrounding in which the organization will or is thriving, considering the social, technological, economic, and political factors put in place. The environment of business comprises both internal and external business environments, which affects the organization’s decisions, strategies, processes and performances. Generally, the environment consists of employees, customers and suppliers as well as external factors and forces such as economic environment, legal environment, political, cultural and technical environment.
PESTEL is an acronym that stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors that are applied in business evaluation.
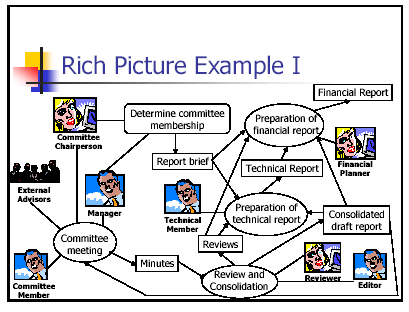
The environment of a business is affected by external factors, either positively or negatively. This depends on political factors which define the nature of specific international agreements political stability within a country and the neighbouring countries as well as trade partner’s countries. When there are conflicts within a country or the neighbouring countries arising either from socio-cultural differences, there is the possibility of a high level of immigration and delocalisation.
This will obviously affect the suppliers, demand and customers within those particular areas. If the business is located where these particular have migrated to, then high demand will be realised while on the other hand, the business situated in the parts where people are general competitiveness of moving from, low demand results. Other external factors like technology may threaten the organization by affecting its environment through the introduction of unique products which are low priced and attractive to the consumers. This will be embraced by customers; hence the environment is changed from its pre-existing position of good performance to a new environment that is not favourable for business performance.
Uncontrollable functions are those factors that affect the business environment, and they do occur naturally without being directly attached to human control and if they are beyond his power of control. Competition may be an example of an uncontrollable factor. This is simply because, in a country where there is freedom of business launch, anyone is given the right to begin a business; hence whoever thinks that he is able to do so creates a business. Competitor control becomes uncontrollable. Terrorism is one of the uncontrollable function which attempts to cause unrest within a country. Terrorism threatens the political positions as well as the government, which is the sole institution that is mandated with legal matters. Terrorism within a country leads to the strengthening of security and structuring of new laws that help in ensuring peace is maintained in a country.
Acts of terrorists create a bad image of a country and contributes to hatred among the two. If two countries had a good relationship before, this is broken, and restrictions are put that hinder a free or fair business environment. Whether political terrorism or non-political terrorism, terrorism aim is to create fear and oppression in many people while it’s carried by small and secretive people. This causes a lot of destruction to the manufacturers and middlemen traders together with the consumers.
Swot is an abbreviation that stands for strength, weakness, opportunities and threats. Swots methods are important in reviewing the present position of a business and its services. It applies the above four factors which enable an organization to conduct a structured analysis of its general operations.
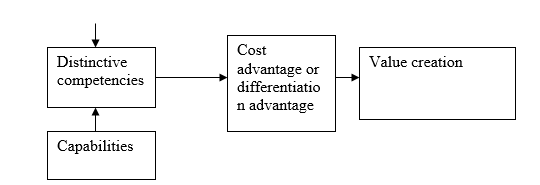
Competitive advantage is defined as the position that a firm occupies in its competitive landscape. This is attained when the firm sustains profits that exceed the average for its industry as compared to its rivals. There are two basic types of a competitive advantage which are identified as either cost advantage or differential advantage. A firm is considered to have attained a competitive advantage when it is able to deliver the same benefit as its competitors while offering them at a lower cost or when it delivers benefits that exceed those of its competing products.
These two advantages are referred to as positional advantages, for they define the company’s position of leading to get to the competitive advantage position, a firm has to defend itself against competitive forces and secure its own customers. This is achieved through prudent research on a particular strategy to apply. This must convince the customer, and the firm must therefore offer products and services of superior value. One of the strategies that firm apply is offering customers a good product at a lower price. They also do research so as to provide a different product which a better product that buyers think is worth a premium price.
Michael porter’s profile
The brand capability has a dramatic change in marketing a product. A brand with high performance does not need much effort in marketing. Customers find its essential good and buy it without much persuasion to accept its credibility. In order to produce a brand with higher performance, it is important that the design appeals to the customer and is of high quality. In addition to its higher performance, it has to have a sound design that addresses concerns on its trust and reproducibility.
Brand to gain recognition; one has to do every bit to see how it’s performing. This will include brand campaigns, brands and their performance form an integral part of brand management. Measuring brands and their performance entails considering brand equity and having brand evaluation, brand elements and assemblage.
Diagram of porter’s five forces
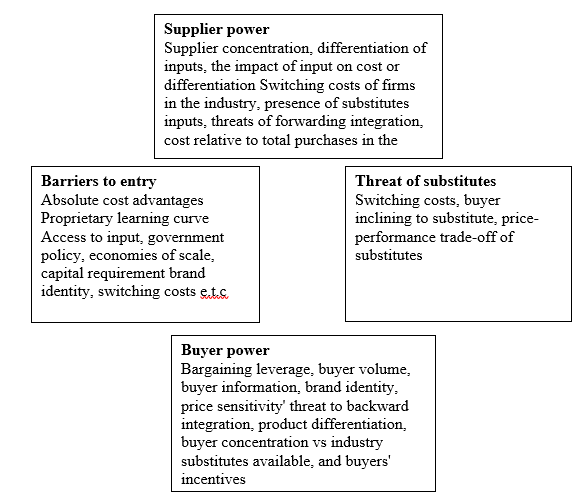
Strategic intent is the company’s vision of what it wants to achieve in the long term. It is a core statement of the means by which a company or organization aspires to achieve its vision. This creates a desirable future for a firm. It simply serves as a linkage between two states of the current design and ecosystem to a future business design and ecosystem. It is composed of the decomposition of exploration rules into the next level of detail, linkages to the exploration rules and transition rules that define how it will migrate from its current design and ecosystem to a future business design and ecosystem. Strategic reality would refer to the actual position of your business in the market. It gives the current competitive power of the company.
Reference
Brooks, I and Weatherston, J. (1997): The Business Environment, Challenges and Changes, Prentice Hall.

