Introduction and Background
Executive Summary
The key questions that are supposed to be answered here include the year of incorporation, business head office, product/service offered, business financing projected revenue and extra information regarding the marketing plan. For instance, business X is a start-up company, that planned to start operating in June 2016. The company will offer a wide range of products and services for individuals and businesses in a geographical area covering Abu Dhabi and other major cities within the UAE. The company expects to attain higher annual revenue in the next three years. The company is expected to achieve sales of $40000 in the next three years, and net earnings of $60000 in the same period. The company is also expected to maintain a 50 percent benchmark performance.
Company’s Goals
Key questions include:
- What are the organization’s main goals and vision? (an effective business has a course that all staff adjusts to, and a reasonable image without bounds)
- What are your objectives, goals, methodologies, and strategies? (what the business needs to do, why it is doing it, and by what method it will achieve this). For instance, business X’s goals include revenue maximization; establishment of a high-status retail presence in Abu Dhabi and its environs; expanding the market of its products through vigorous promotion and multi-channel marketing; and optimization of a company’s operations to reduce costs and satisfy customers.
Measurements
Key questions include:
- By what method will you quantify and track your outcomes? (Every goal ought to be quantified and the outcomes documented so as to trace what is working and what isn’t).
Ownership and Management
Key questions include:
- Who are the owners of the business?
- What is their contribution?
- How many employees will be hired?
For example, business X will be owned by partners. The partners will contribute equally to the day-to-day operations of the company. The company will also hire supervisors, helpers, marketing executives, procurers, accountants, officers, messengers, and watchmen. The owners will act as the managers.
Products
Product Description
Key questions include:
- What will be the company’s products or services? (list the products or services and ensure that the description is short and precise)
- What will be the core product?
- How will the customers benefit from the products?
For example, business X will focus on producing stylish and affordable products. The products will include products A, B, C and D. The demand for these products is increasing day by day, hence their prices. The company will make the products affordable to the general population. The company will make product D the core of its business and a source for referrals for other products and services.
Future Products
Key questions include:
- Is the business planning to expand its products or services in the future?
For example, in the future, the company plans to diversify its products. The production of others will require a considerably high amount of capital.
Environmental Analysis
Key questions include:
- What are the industry trends?
- Does the product or service have demand? (the business has to have a market)
- Has the company conducted a consumer need appraisal or survey regarding the product/service? (consumer needs and wants guides the marketing goals)
- Who are the potential clients and what are their demographics?
- Is the product or service in line with existing fashion and trends?
For example, the industry is also highly concentrated, with workplaces occupying nearly half of the market. Given a large number of small and medium-sized businesses, the product and services are in high demand. At the moment, customers are looking for real benefits of the products and are buying in relatively small quantities due to high prices. Furthermore, due to changing tastes and an increase in household income, consumers are now looking for quality over quantity. As a result, there is a general swing towards premium products (Cravens and Piercy 16).
The per capita consumption is high among adults aged between 15 to 34 years. They are considered to be the heaviest spenders. Therefore, they are the target market for most companies. Moreover, studies show that the current designs of products appeal more to the youths than older people (Federal Research Division 33). For this reason, the company must cater to this category of consumers. Moreover, many consumers in the UAE are very conservative and loyal to specific brands. Loyalty is brought about by the unique taste of certain brands (Aaker 22). They also value the quality of materials that goes into the product. For that reason, brand image and product quality are the most significant aspects. However, product prices are also becoming a significant factor. This is attributed to the high cost of living (Pitta and Katsanis 53; Federal Research Division 38).
The target market
Key questions include:
- Who are the target markets?
- How big are the markets?
- What proportion of the market does the business anticipate?
- How will the business pull in and maintain its market share or expand it?
Branding Strategy
Key questions include:
- Does the business have a logo? (a logo ought to be an exceptional, straightforward imprint that represents and brands the business)
- What will be the slogan of the business? (the slogan should be a unique, innovative articulation that tells the client what the business is all about)
- What will be the company’s positioning statement? (this assists in selling products or services because it distinguishes a company’s product from that of its rivals. The statement should explain what the company intends to do for the clients, how it will do it, and why it is better than its rivals)
The company’s core branding factors will be based on a logo-a portrait of a magical wand leaning on a dollar symbol. Instead of using cartoon images or clip arts, business X will not be shown in the images, but in a distinct symbol of the magic entrenched in the service, for instance, shiny lines and luminary bursts. These core elements will be used in stationeries, business cards, and business forms among others. Non-visual catchphrases “at your service” and “can do” will be used in telephone conversations and customer care service. The catchphrases normally vary according to the customer’s needs (Melewar and Wooldridge 330).
Competitors
- Who are the company’s rivals? How is the business well-positioned? (The business should position its products or services differently from the rivals)
- How exceptional is the business from the rivals? How does it differentiate itself from the rival? (The business should discover its aptitude and advantage)
- What will the business add to the industry that other businesses have not? (The business should come up with new products and strategies)
Image
Key questions include:
- How do the clients perceive the business? (Client perception is very critical and can be determined when the business and marketing strategies are working).
- What image does the business want clients to have? (List all the qualities, aptitude, and values and integrate them into marketing strategies).
SWOT Analysis of Business X
Key questions include:
- What will be the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats for the business?
For example, the long-term experience of the proprietors in the industry will give the business a competitive edge in the market. In addition, the proprietors have been undergoing constant training to be updated with the current markets and systems of production. As a result, the company will be able to provide high-quality and reliable services to its clients. Business X’s weakness will be attributed to its low status and inadequate publicity. In addition, the company will have a low contact network. Even though the company aims to explore social media to increase network coverage, it is still not sufficient to attain a high number of clients.
Nonetheless, the company’s opportunities lie in the advertisement of high-quality products and services on social media and print press. The company will enhance its network contact and market its services online by simply creating a Facebook and Twitter profile. The company will also increase its client base by offering competitive prices. Last but not least, business X’s major threat is the high number of companies within the target market offering similar services. As a result, competition is very stiff. Other threats include unhealthy competition from the large established companies (Rust, Zeithaml, and Lemon 114).
Marketing Strategy
Key questions include:
- How will the company promote its business? (This pertains to how the company will create consumer awareness about the products or services. The right message and medium should be used).
- What channel will be used and how will the company link products and services with the clients? (the media placement should be influenced by the target market)
For example, a business X marketing strategy will involve direct contacts with the clients and promotional activities. Promotional activities will encompass referrals, mass/print media, web marketing, and social networking. The promotional activities will also entail the provision of brochures and newsletters to enlighten potential clients. The newsletters will contain a brief cover letter, case statement, description of the ideal client, services offered, a number of case studies, testimonials, frequently asked questions, and a list of clients. In addition, the company’s sales strategy will principally be based on personal interaction with potential clients and internet marketing. The products and services will be scaled to meet the client’s needs. The key metrics will be averaged for each month and posted on the Gap control panel. The measurements will be used to keep track of the company’s goals.
Financial Analysis
Key questions include:
- What fraction of the available funds will be used for marketing? (Marketing cost encompasses promotional items, events, media adverts, and online portal among others)
- What are the current and prospective financial prerequisites? (The timeline should be around 3-5 years. The tables in the appendices show some of the key financial statements)
Marketing Science of Customer Behavior
Key questions include:
- What informed the marketing strategy?
For example, according to Rust, Zeithaml, and Lemon, it is cheaper to maintain the existing clientele to a brand than to acquire new ones (114). Therefore, the satisfaction of these clients will be on top of the company’s priority. The theory of electronic propinquity introduced by Korzenny describes the psychological feeling of nearness aroused by the use of diverse electronic media. The theory posits that interaction through electronic media tends to enhance closeness more than physical interaction. This explains the company’s inclination towards the use of online marketing (Korzenny 5).
References
Aaker, David. Leveraging the Corporate Brands, Carlifornia:California Management Review, 2004. Print.
Cravens, David, and Nigel Piercy. Strategic marketing, Boston:McGraw Hill, 2006. Print.
Federal Research Division. Country Profile: United Arab Emirates (UAE), Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress, 2007. Print
Korzenny, Felipe. “A theory of electronic propinquity: Mediated communications in organizations.” Communication Research 5 (1978):3-24. Print.
Melewar, Tim, and Adrian Wooldridge. “The dynamics of corporate identity: A review of a process model.” Journal of Communication Management 5.4 (2001):327-340. Print.
Pitta, Dennis, and Prevel Katsanis (1995). “Understanding brand equity for successful brand extension.” Journal of Consumer Marketing 12.4 (1995): 51-64. Print.
Rust, Roland, Valerie Zeithaml and Katherine Lemon. “Customer-Centered Brand Management.” Harvard Business Review 14. 3 (2004):110-118. Print.
Appendices
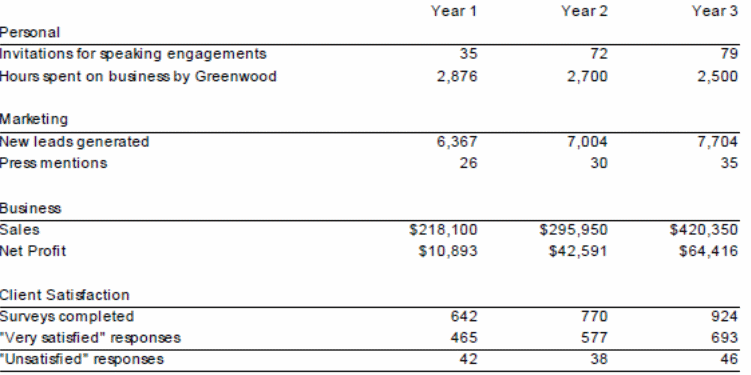
Appendix 1: Key Marketing Matrix
Appendix 2: Marketing Expenditure Plan
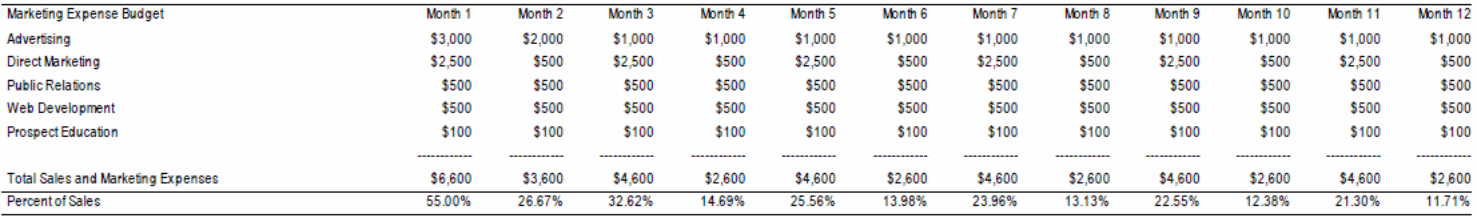
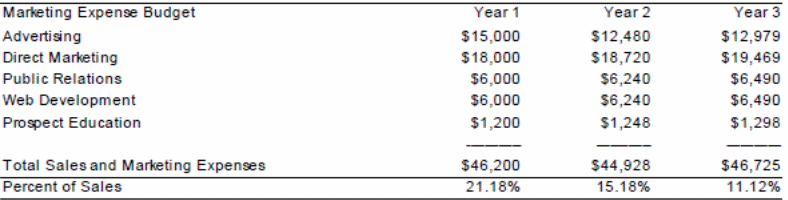
Appendix 3: Sales Projection
Appendix 4: GAP Dashboard