Any government has the power to regulate the economy of the country and not only does it regulate the economy, it has a vital role to ensure that the economic condition remains stable. It is the responsibility of the government to ensure that all the aspects of the economy maintain a stable level so that the country can grow and expand. The government regulates many things in an economy including inflation, exports and imports, prices of many vital commodities, and many important economic aspects.
The government of England has entrusted the job of determining the monetary policy, in the hands of the Bank of England. Bank of England looks into many other big issues. One of the most important issues is that of ensuring monetary stability in the economy, which can be achieved through a combination of stable prices of goods and services across the economy coupled with a low inflation level and level of confidence of the investors in the currency of the country. The Bank comes out with the monetary policy to ensure certain key objectives like delivering price stability with a low inflation level coupled to support the Government’s economic objectives of growth and employment. Price stability is taken care of, by the Government’s usual inflation target of 2%. There is a need to contemplate the crucial and critical role played by price stability in achieving the aforesaid economic stability, and in providing just the right conditions for a sustainable and longer living growth in output and employment. Chancellor of the Exchequer announces the Government’s inflation target every year in the annual Budget statement. Though The 1998 Bank of England Act enables it to set interest rates independently, however, The Bank does hold accountability to the parliament and the wider public, which cannot be refrained from. The legislation provides the government the power to instruct the bank on the interest rates issues for a limited period during an emergency, for the sake of national interests. (How Monetary Policy Works).
The Bank of England has a monetary policy and it uses the same to regulate the mechanism of the economy. Like when it decides to change the interest rate, the government is trying to check the overall expenditure of the economy. A change in interest rates is mostly used to contain inflation, which is the result of lavish expenditure by the country. The bank sets a fixed interest rate at which it lends money to financial institutions and depending on this interest rate, individual banks and other financial institutions set up their interest rates, which apply to the whole economy. This step is of indispensable importance to the economy, as this is very widely used to contain inflation. The only purpose behind such a step is just to contain undue inflationary levels prevailing in an economy. The point to be noted here is that this interest rate set by the Bank of England is so effective and powerful that it chips in greatly to regulate the whole economy. It affects the stock and bond prices and also influences the asset prices throughout the country. This interest rate also regulated the savings in an economy, which eventually results in capital formation and reinvestment. It is noted that when interest rates are high, people prefer to invest money in government deposits that are less risky than the stock markets, and similarly, high-interest rates boost up the savings. Lower interest rates make asset and real estate prices go up, as people start ignoring conventional saving instruments and make use of the high-growth ventures like shares and houses, which pushes up their prices. Interest rate change also affects exchange rates, as an increase in the interest rate in the UK will yield better returns to the investors compared to their overseas ventures.
This research paper is addressed to all the people interested in knowing how the Bank of England works and how it keeps pace with the global changes taking place around the world. Bank of England is the central bank of the UK; the paper threw light upon the measures taken by the Bank of England to curtail inflation in the UK and other efforts taken by the bank to ensure growth and stability in the UK. I firmly believe that the audience will agree with the facts presented in the paper, the reality has been presented in the paper with the help of research and there are no two ways about whether or not the audience will agree with the facts, I believe they will agree with the facts presented in the paper because they all the facts have been retrieved from reliable sources mentioned in the reference section of the paper. The next part of the paper will elucidate the macroeconomic policies and the impact of the same on the US economy.
Subprime Mortgage Crisis
The purpose of this study is to bring to light the mechanism of an economy and banking system. The study focuses on the subprime crisis that has hit the US in the last two years. The study throws some light on the adverse effects of the crisis on the US as well as other economies of the world. The study also mentions the recent shutdown and take-over of Lehman Brothers and also the problems faced by AIG to borrow money.
Literature Review
One of the most important responsibilities for the Fed is that of ensuring monetary stability in the economy, which can be achieved through a combination of stable prices of goods and services across the economy coupled with a low inflation level and level of confidence of the investors in the currency of the country. The Fed comes out with the monetary policy to ensure certain key objectives like delivering price stability with a low inflation level coupled to support the Government’s economic objectives of growth and employment. To understand how the Fed monitors price-related regulations to keep a check on inflation, we may consider a small example of the regulation of house and property prices. To take any decisions related to interest rates keeping in mind the ongoing inflation rate, the Fed must be thorough with the booming property prices and must take steps to ensure that the prices are not artificial.
Government intervenes through its central bank to regulate the prices of many commodities, similarly, it also regulates the prices of houses like any other important commodity. Fed has the responsibility to keep a check on asset prices including the prices of houses. There can be several reasons why the prices of houses may shoot up, as the simple rule of demand and supply has a definite impact. (Demand and Supply for Housing).
Another reason behind a change in property prices can be Mortgages. A mortgage is the money borrowed to buy a house, as for most people buying a house is not easy. Over the years mortgage market has picked up greatly and the current scenario is different from the one that existed in the beginning. Mortgages were supplied only by the building societies. Building societies were non-profit institutions and encouraged only the members for the grant of loans, so the people who were members and had contributed to an extent for a considerable period got loans easily, and accounts with building societies became the only means to get mortgages. Soon these societies had to compete with the banks and other financial institutions specialized in granting housing loans. This price war resulted in a greater demand for owner-occupied houses and consequently, the demand for houses grew stronger, resulting in a substantial price increase. (The UK Housing Market – Factors Influencing the Housing Market: Mortgages).
Besides the above-mentioned factor of mortgages, there are other factors like stamp duty and planning that affect the market for housing. Mortgage interest relief at source (MIRAS) was a tax concession to owning a house. It reduced the house owner’s liability to income tax as the money spent on the interest on the mortgage was considered to be tax-free. This made borrowings cheaper and as a result, there was a huge demand for housing and the prices shot up. With the introduction of MIRAS in 1990, many people were exempted from stamp duty. (The UK Housing Market – Factors Influencing the Housing Market: Stamp Duty and Planning).
The central bank sets a fixed interest rate at which it lends money to financial institutions and depending on this interest rate, individual banks and other financial institutions set up their interest rates, which apply to the whole economy. This step is of indispensable importance to the economy, as this is very widely used to contain inflation. The only purpose behind such a step is just to contain undue inflationary levels prevailing in an economy. The point to be noted here is that this interest rate set by the Bank of England is so effective and powerful that it chips in greatly to regulate the whole economy. It affects the stock and bond prices and also influences the asset prices throughout the country. This interest rate also regulated the savings in an economy, which eventually results in capital formation and reinvestment. It is noted that when interest rates are high, people prefer to invest money in government deposits that are less risky than the stock markets, and similarly, high-interest rates boost up the savings. Lower interest rates make asset and real estate prices go up, as people start ignoring conventional saving instruments and make use of the high-growth ventures like shares and houses, which pushes up their prices. Interest rate change also affects exchange rates, as an increase in the interest rate in the US will yield better returns to the investors compared to their overseas ventures. This phenomenon usually makes US dollar assets attractive, which pushes up the value of the currency vis a vis other currencies, and a stronger US dollar would mean less money would be shed on imports and less quantity of exports will take place as there will a lesser demand for products made in the US because of the currency being strong. It is interesting to understand the process of how the bank sets interest rates.
The primary step in this direction starts with the estimates of the money flow that takes place between the government and the Central bank, and the Central bank and commercial banks. The Fed makes sure to rectify all the imbalances, which arise along the path daily. There can be two phases to the money flow that takes place between the system, first when more money flows from banks to the government and second when more money flows from the government to the banks. In the first case, Fed’s liquid assets come down, which affects the short-term instruments of the money market. And in the second case, the market finds itself with a cash surplus. The Fed is the bank of the government as well as the bank of all the financial institutions and commercial banks, so it chooses the interest rates for the funds to be provided each day, and this interest rate is passed through the financial system, which influences the interest rates of the country. (How Monetary Policy Works). The diagram given below explains better.
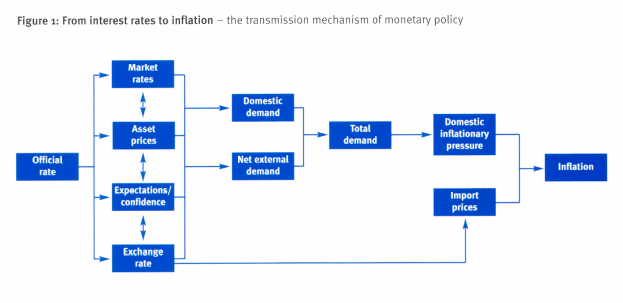
The above diagram explains the concept of system regulation. It shows that the official rate, which is set by the Bank of England, influences many parts of an economy such as market rates, asset prices including the house prices, expectations, and exchange rate. This gives rise to demand which is the total of domestic plus external demand which in turn gives rise to inflationary pressure resulting in inflation. Another important point shown, which deserves a mention is a relationship between the exchange rate and import prices, or the price paid for imports. As explained above, the stronger the exchange rate the lesser the price paid for imports, and the weaker the currency the higher the price paid for imports. (How Monetary Policy Works).
A change in interest rates is mostly used to contain inflation, which is the result of lavish expenditure by the country. When interest rates are high, people prefer to invest money in government deposits that are less risky than the stock markets, and similarly, high-interest rates boost up savings.
Subprime Crisis and Its Effects
The subprime crisis started with the subprime lenders lending at higher rates than usual to the borrowers with bad economic history and lesser ability to pay back. The sub-prime lending functions on the principle of no collateral and higher interests. These debt instruments are then traded and are passed on to other banks or institutions which are ready to take them for the higher interest they get out of them.
Effects on the US and World Economies and Recent Shutdowns
Due to the passing on of the debt instruments some prominent hedge funds have failed to declare their current asset values. The problem has led to a total crunch of liquidity in the US. The markets witnessed BNP Paribas announced that it had frozen 3 of its hedge funds due to evaporation of liquidity, totaling around 1.6 billion pounds. The reason was that the bank couldn’t value units of the funds due to the effect of the US subprime market on them. The funds contained the bundles of subprime loans, the demand for which have fallen drastically over the last few months. Banks around Europe feared a total liquidity crunch as they feared that they might run out of cash to sustain day-to-day lending. ECB went to the extent of injecting 155 billion pounds to ease the system. Investors around the world started backing off from the markets fearing the ill effects of over-exposure to the mortgage markets. (How the US Subprime Mortgage Crisis Affect Irish Markets).
The high liquidity crunch faced by the US has made the Fed cut key interest rates several times over the last year. The liquidity crunch that the US has witnessed had also done bad to the commodity prices and the willingness of the banks and financial institutions to lend each other or even to the consumers. The Bank of England has also cut rates to 4.5 percent in its latest monetary policy. This would also result in the housing prices falling in the UK as the buyers will not be able to raise mortgage finance and sellers will be forced to cut down their asking prices. The collapse of Bear Sterns has affected their London operations with over 2,000 jobs in London. (Q&A: How will the financial crisis hit us?) Another unfortunate incident that took place a few days back was of the 158-year-old firm Lehman Brothers filing for chapter 11 bankruptcy due to the credit crunch. Financial institutions around the world have recorded $ 500 billion in credit losses and write-downs due to the subprime crisis. At the end of August, the company is believed to have had assets worth $ 600 billion funded with equity of just $ 30 billion. (Lehman Is In Advanced Talks To Sell Key Business).
AIG also faced a liquidity crunch due to the crisis and approached the Fed for funds as a temporary measure. American International Group was hit to the tune of $ 18 billion in losses over the last 3 quarters due to the guarantees they wrote on mortgage derivatives. (AIG, Facing Liquidity Crunch, Reaches Out to Regulator).
The problem has also had a very deep impact on the equity markets across the globe, which have tumbled down to their lowest levels in as many as 6 years. Dow Jones had plunged to below 8,000 levels for the first time after 2003. The latest story on the crisis is that of the US government making available $750 billion to bail out distressed institutions that have been reporting abysmal earnings quarter on quarter due to write-downs they have faced in the property market. The Fed seems determined to stem the subprime problem and is prepared not to stand down until the crisis is fully resolved, but it remains to be seen whether the rescue measures will have any impact on the economy in the medium term, for the short term though, it seems like the crisis will take at least a couple of years to clear itself. It will be long before the US economy starts to revive and look up once again.
Best way to make the use of today’s Economy
The stock markets of almost all the countries are at an all-time low, a person can certainly make the most of this wonderful opportunity. This can be done so by investing in the right shares and at this point, all the shares are the right shares. The blood bath which has taken place in the market is brutal and has affected the lives of many investors. This is the most appropriate time to make good money. Almost all the shares are at an all-time low, investing little money can give huge returns.
The subprime crisis goes to show how the economy of the world has been affected. There is an opportunity in every adversity is a very popular saying by a big businessman. If we catch the opportunity we can certainly make the most of it. So the opportunity here is the stock market. It can make millions of dollars for a person whose brain works in the right way. A classic example is the legendary Warren Buffet; he made billions of dollars from the stock market and any clever person can make a good amount of money from it, if not billions of dollars.
So to conclude it is an amazing opportunity for those who want to make the most of the recession. Investing in shares right now will prove very beneficial in the long run and it is highly advisable.
Works cited
“AIG, Facing Liquidity Crunch, Reaches Out to Regulator” CNBC. 2009. Web.
“Demand and Supply for Housing” tutor2u. 2009. Web.
“How Monetary Policy Works” bankofengland. 2009. Web. Bank of England.
“How the US Subprime Mortgage Crisis Affect Irish Markets”. Irish Mortgage Brokers. 2009. Web.
“Lehman Is In Advanced Talks To Sell Key Business”. CNBC. 2009. Web.
“The UK Housing Market – Factors Influencing the Housing Market: Mortgages” 2009. Web.
