Introduction
Many companies are involved in the chocolate industry which has become very popular as many people enjoy its delicious taste. Some of the major companies in this industry include Cadbury, Mars, and Nestle. These companies are the major companies that rule the international market, although Mars Incorporated dedicates its business in another sector as well. Mars Inc. has been able to compete favorably in the chocolate industry without solely dedicating its efforts to the brand. Nestle, on the other hand, has expanded its market to achieve global operations and brand since it changed to chocolate productions in the 1920s. Their major aim is to satisfy their shareholders happy and to deliver high-value products.
Specific Strategic Operations
Mars Inc.
The operation strategies for Mars Inc. include monitoring its market throughout the world. Before the company launches any new product, it communicates to its customers and surveys to determine what the views their view on the product itself. They also inquire what the customers think about the brand name the company is proposing to give the product. They, therefore, depend on the consumers’ feedback to determine the direction of their business, especially in developing their marketing programs. It applies InfinityQS ProFicient software to monitor, control, as well as, to improve the quality of its manufacturing processes in its entire enterprise.
The company also provides products in various other categories which include snack foods, drinks, pet care, as well as, main meal food. It also produces electronic products and also deals in information technology. It focuses on consumer as well as the company’s competition in each of its separate regions in the confectionery industry. It, therefore, adopts standardization of its products where one factory produces several units of identical products. For the company to respond to consumers’ preferences, they have adopted product differentiation.
Mars Inc. applies the global brand strategy to reach its customers. According to Mclean (2009), its global brand strategy enables it to partner with distribution agencies to increase its efficiency in aligning its core global brands in the global market. Its agency partners help it in building its brands across major markets. This enables it to achieve a global communication platform in building its iconic brands.
Nestle
Nestle applies an integrated cost leadership/differentiation approach. Under this strategy, it provides a broad range of products that are in over 20 categories such as coffee, cereals, milk, pet foods, as well as, mineral water. In this case, a mass of market segment is served with a range of products. It, therefore, adopts ways of achieving low-cost operation by exploiting its scale of production, expanding and maintaining a wide scope of production, and by using high technology to produce highly standardized products. It has a large production plant that enables it to achieve high production output. This reduces the cost of production of its products. Its production plants are highly automated and are used to produce products in mass. The demand for its products is generated by forecasts which are derived from sales and marketing.
The forecast applies an ERP system known as the Globe. The ERP system is used to generate production which is then dispatched manually. It, therefore, focuses its efforts on innovation, design, and development as well as brand-marketing of its products to achieve product leadership. The company develops brand names which create an excellent image in the minds of customers. It combines its name with the product name when designing a brand name making it easily identifiable to customers. This helps it achieve customer loyalty in the market. Its product leadership enables it to adopt cost leadership in the market, thus allowing it to sell its products at different (higher) prices as compared to other companies such as Cadbury and Mars which also offer essentially the same products.
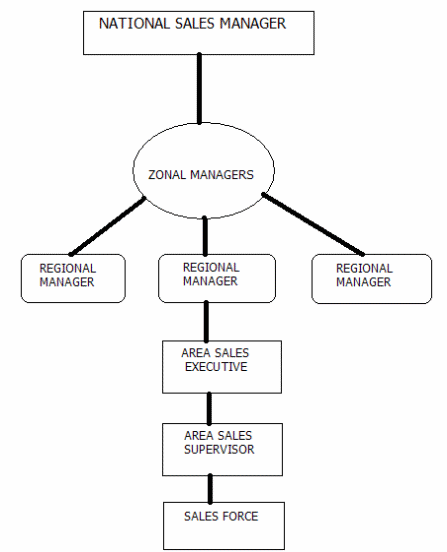
Compared to Cadbury and Mars Inc., Nestle’s sales strategy emphasizes more on the company’s sales force (Khan, 2007). It invests more on training its sales workforce. The management of the company believes that the performance of the company highly depends on the sales of its products. They, therefore, spend heavily on training their sales representatives before they are sent to the field. Their sales promotions are planned effectively and are quite rapid to meet the changing consumption seasons. Their sales management structure is as in the appendix. The structure helps them coordinate sales activity in each of their country of operation.
Nestle adopts a corporate strategy that is client-oriented. This strategy is beneficial to both the business and the consumers. It has an up to date ERP SAP which enables it to achieve efficiency in all its areas of operations which include purchasing of raw materials, forecasting, logistics, production, warehousing, as well as, sales (Khan, 2007). The software has been well integrated in all its operations making it able to manage all its progresses. The software enables it to produce superior quality products that command higher prices. These enable the company to achieve product and cost leadership.
Nestle adopts an international divisional structure. According to Khan (2007) under this structure, the company has created a separate division where all its overseas subsidiaries report. It is therefore easy to represent products, as well as, geographic interests at the same level. However, this structure also makes it hard for the company to coordinate information between its local and international product divisions.
Cadbury
Cadbury adopts a pricing strategy to help it achieve market growth. Developing an appropriate pricing strategy in the market enables it to create a mass market for its products. Their pricing strategy involves price cut-offs or reducing the weight of the products while maintaining the prices. For it to achieve its pricing strategy, Cadbury keeps limited numbers of unskilled employees, maintains high-level technology to streamline its operations process, and also keeps its old and outdated facilities at the lowest cost possible.
The company understands that the unskilled employees, as well as outdated facilities, can compromise the quality of its key process (Porter, 1998). Just like Nestle, it also offers various products in every category in the chocolate industry to help it expand its market. Its chocolate bars have similar designs and colors worldwide. Besides, the products contain more milk as compared to those from other companies. In its marketing strategy, Cadbury uses big boxes of chocolates that are stored next to checkout areas to enable it to attract impulse buying. Its products are always on the vending machines as well as inconvenient stores normally located next to the counter to attract impulse buying of their products. It also uses coupons in its sales promotion.
Cadbury has a multinational strategy and adopts a decentralized organizational structure. This structure allows Cadbury to grant its international subsidiaries to make their lower-level specific decisions which enable them to forge their path in every market. According to Hebert (2009), the confectionery industry matches well with this strategy since tastes are localized. Considering that Cadbury operates subsidiaries in different regions across the globe, this strategy allows it to react fast to trends.
Similar operation strategies
All the companies adopt similar distributive strategies/channels to make their goods available for customers. They all use retail outlets, as well as, wholesalers to make their products available to consumers in retail shops, supermarkets, and supermarkets. For example, Cadbury sells its products directly to wholesalers and retail network distribution networks. It has 2,100 distribution networks and 450,000 retailers (Hebert, 2009). After production, the products are shipped to their warehouses where they are later shipped or transported by road to customers on request. The customers are the distributors who supply them to retailers and consumers. Cadbury, Mars Inc., and Nestle also contract agencies and distribution partners to help them supply their products across markets. This enables them to achieve efficiency in their operations (Ellram, Fawcet & Ogden, 2007).
Cadbury, Nestle and Mars Inc. share a common warehousing strategy. All activities that are related to the handling of finished confectionery products to the point of sale are normally handled under warehousing operations in one complex. This occurs in all three companies in all their regions of operations. The warehouses are positioned in strategic places that help them with storage, as well as, logistics operations. However, their management systems differ. For example, Nestle applies System Application Product for Data Processing (SAP) to manage its warehouses (Khan, 2007). It uses SAP to manage its inbound and outbound operations as well as in stock management. The warehouses include internal and external warehouses.
They all focus on providing affordable brands and high-quality products to attract customers. Nestle’s low pricing strategy aims at providing relatively lower prices than those of foreign brands that exist in the local market (Khan, 2007). It focuses on A-class, and low pricing to enable it to attract customers who mainly depend on imported brands, as well as, potential customers.
All these companies adopt both modern and traditional methods of advertisement as their marketing strategy. They apply media mix for their promotions and advertisements, and these include the internet, television, radio, newspapers, and magazines. They use emotional appeals in their advertisements to attract customers. They ensure visibility through their internet websites and other organization’s websites. They also use social networks to reach their customers and to develop strong relationships with them through their feedbacks. They all sponsor events to maintain, as well as, to increase product awareness. Nestle and Cadbury adopts contests as well as free samples as a means of gaining familiarity and trust from their target market. They also focus on producing a broad range of chocolates to enable them to satisfy the customers’ taste as a means of expanding their market share. For example, Nestle and Cadbury focus on expanding their product line as a means of expanding their market. Again, Mars and Cadbury use the eye-level concept to ensure that consumers do not miss their products while shopping.
These companies also share a lot in common in terms of their positioning. They continually focus on driving innovations in the confectionery category, as well as, offering brands in different formats and pack sizes in line with the changing consumer trends (Khan, 2007). They also understand that their continued success depends on their ability to develop new products, as well as, brands.
In all these companies, quality is considered as the uppermost priority in the manufacturing strategy. It is, therefore, a key performance measurement for all the companies. Other performance indicators for all these companies include safety, time, defects as well as lost. They determine the demand for their new products by conducting surveys as well as through information sharing within their group of companies. For example, Nestle applies ERP SAP which Mars Inc. applies InfinityQS ProFicient software to improve and manage their product quality. This software enables these companies to execute process involvement initiatives in a user-friendly, as well as, flexible manner, and to make real-time decisions.
These companies also share some similar characteristics in their corporate strategy. Their business ethics have been designed to protect consumers from being exploited. Their business ethics also ensure they target to achieve a cleaner environment through environmentally friendly processes and products (Khan, 2007). They are committed to achieving environmental sustainability since they understand its significance to their business.
Ares of conflicts between different stakeholder groups
It is always normal for different stakeholder groups to have conflicting interests with a company’s business operations. It is difficult to balance the interests of all the stakeholders of an organization, and therefore most companies try to prioritize the interests most powerful as well as, vulnerable groups. In the confectionery industry, there are several conflicting interests among different stakeholder groups at Cadbury, Nestle and Mars Inc. either across the board or in a single company.
To achieve its pricing strategy, Cadbury maintains a limited number of unskilled workers, and instead, invests more in advanced technology and information technology to conduct its business operations. This means that most unskilled employees are being laid off as it continually invests in more advanced technology. The company is forced to compromise the welfare of existing unskilled workers. Besides, they have minimized the hiring of unskilled workers. This means that unskilled workers in Cadbury and even other companies such as Mars Inc. and Nestle which have also adopted high-level technology, fear for their job security. Thus, a considerable number of unskilled workers from the major companies in the confectionery industry are forced to look for another alternative employment.
Cadbury’s pricing strategy could also raise conflict of interest between the company and consumers. The company’s pricing strategy is such that it reduces the quantity of products while maintaining the price. This, it does to meet an increase in production cost which may result from an increase in raw materials, maintenance of technology or even an increase in expenditure on expert human resource. On the other hand, such reductions in quantity usually lead to customer satisfaction.
Again, in this situation, the company has to compromise the quantity of its products to achieve its core business objective. Such a strategy may cause some customers to turn to another brand or raise strong complaints due to misunderstanding of the situation. This means that as the management of the company tries to satisfy the interest of the shareholders, it compromises the needs of the consumers. In some cases, the consumers may read such instances to result from low moral values in the management team since most of these quantity reductions are not done transparently. Customers are normally not informed of the reasons leading to the weight reduction before it is conducted. Some customers would feel betrayed by the company to gain additional financial benefits.
There could also be conflicting interests between the management group of any of the companies and the shareholders. While the managers would focus on strategies that meet the long-term goals of the company, shareholders may not be willing to forgo a large part of the revenue which should form part of their dividends to be used to restructure and align the company’s operations. It, therefore, becomes very difficult to meet the company’s long-term objectives and the core of the business. Managers have to deal with the rising stiff competition especially in the confectionery industry which has many players including Hershey which is also a major player in the international market. The interest of a company’s executives is always to implement strategies and achieve quality productions which would help expand the company’s market share and therefore achieve sustainability of the company’s business operations. However, this is not possible without the financial support from the shareholders.
Again conflict of interest may arise between a company’s executives or managers and the shareholders especially where an audit project is conducted to give advice on some aspects of the project implementation and to give its results. This means that the executives who commission the auditing project may fail to disclose vital details of the project to the shareholders. As a result of this, the shareholders are therefore not accurately and fully informed of the progress or the real situation as regards the project.
Mars Inc. collects the views of its stakeholders who are the consumers about what they think of their new products or brand names before they finally release them into the market. In situations where the customers interviewed do not favor the new product, a conflict of interest is likely to rise between the company’s management group and consumers. The capacity to redevelop the product as per what the interviewed consumers favor may not be available.
Companies in the confectionery industry which adapt the centralized organizational structure usually use the same products in every region of their operation. Such a structure would certainly create a conflict of interest between the management group and the consumer group. The management group would favor the structure due to the cost-savings associated with it, while on the other hand, consumers view the global market structure as a barrier to obtaining local preferences (Chambers, Johnson & Slack, 2009).
Conclusion
Companies operating in the confectionery industry apply several similar operation strategies. These include areas of corporate, manufacturing, marketing, positioning, distribution and warehousing strategies where Cadbury, Nestle and Mars Inc. share similar operation strategies. However, there are distinct differences in their operation strategies particularly in organizational structure, pricing strategy as well as product range.
Reference List
Chambers, S, Johnson, R, & Slack, N. (2009). Operations management, 6th Ed. New York: Prentice Hall.
Ellram, L. M, Fawcet, S. E, & Ogden, J. A. (2007). Supply chain management from vision implementation, 1st Ed. New Jersey: Pearson.
Hebert, S. (2009). Market strategy and organizational structure: Three companies. Web.
Khan, S. A. (2007). Operational strategy of Nestle Beverages in Pakistan. Nottingham: The University of Nottingham.
Mars. (2011). Global brands. Web.
Mclean, V. A. (2009). Mars, Incorporated to refine global creative structure for biggest brands. Web.
Porter, M. E. (1998). On competition. Boston: Harvard Business Review, Boston.
Appendix
Nestle’s sales management structure.