Introduction
The law of demand and supply works in opposite ways in the sense that, when the prices of commodities change, demand and supply also change in the opposite direction holding other factors constant. The extent of adjustment of supply and demand is dependent on the type of the commodity in question. For instance, demand or supply of some commodities responds more than changes in price as compared to other commodities (McEachern 15).
This introduces the concept of elasticity of goods. The magnitude of the effect of change in price on the commodity depends on the price elasticity of the commodity (Sexton 41; Mishra 59). This paper reviews the price and income elasticity of commodities from Nike and Adidas companies. Specifically, the price elasticity or inelasticity will be discussed in relation to how sports apparel products react to changes in prices. Besides, the paper explores other issues of the two companies that influence the elasticity or inelasticity of their products.
Brief Synopsis of the Nike and Adidas Products
Nike Incorporation
Nike is an American company operating within the sports apparel market that was founded in the year 1964 in Oregon and operated in the free market. Nike Inc is one of the top sports footwear and accessories designers in the world. At present, the company controls a market share of 20% of the global athletic market and has annual revenues of 25.3 billion dollars. This company stocks sports balls, bags, and eyewear, footwear, and sports shoes for adults and children.
Nike’s strategy for operating in the oligopolistic market focused on the utmost premium brand quality that customers demand or may not know that they require at that time. For instance, in the year 2014, the company invested more than 100 million dollars on product research and development to improve its product line in a bid to gain dominance over other giant apparel brands. The strong market position has allowed the company to meet customer demand since it has a resounding knowledge of the global consumer trends (Guru 51).
Adidas Corporation
Adidas is a multinational company that was founded in 1949 in Germany and specialized in sports apparel within the free global market. The current operating income of the company is 1.202 billion Euros, with total equity of 5.489 billion Euros. Other subsidiaries of the company are Reebok and Runtastic that deal with products such as footwear, toiletries, sports equipment, and sportswear.
The Adidas Corporation has been strategic in product diversification to minimize cases of failure in this oligopolistic market characterized by a few strong brands in the market. The business approach of the Adidas Corporation is organic growth since its expansion has been necessitated by the increasing customer base and demand for different sports apparel product lines. From the inception of the company, the business strategy has always followed a strategic plan in physical growth and market growth within Germany and external markets in order to gain a better stand in the free global market (McEachern 19).
The company has enjoyed a global presence and is currently positioned to increase its current market share following the strategy of establishing other subsidiaries that operate independently of the mother company across all continents.
Research question
What is the relationship between price and income elasticity of Nike and Adidas products?
Research objective
The objective of this research paper is to establish how price and income elasticity affect the pricing of Adidas and Nike products. The findings will reveal the ideal pricing mechanism that the two companies should adopt in order to remain competitive in the dynamic apparel market.
Elasticity indicators for the main products offered by Nike and Adidas
Price elasticity of Nike products (Nike jersey)
Nike’s products are price elastic since they are categorized as luxury goods. For instance, the demand for the luxury Nike jersey product is very sensitive to price changes since potential customers can do without the product when it is considered too expensive. This is explained in the diagram below.
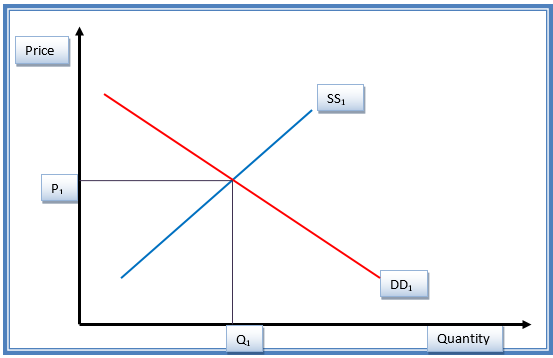
Figure 1.1 shows the initial equilibrium status of the Nike products before the changes in the price. DD1 shows the demand curve, while SS1 shows the supply curve (Guru 48). Equilibrium price and quantity are P1 and Q1, respectively.
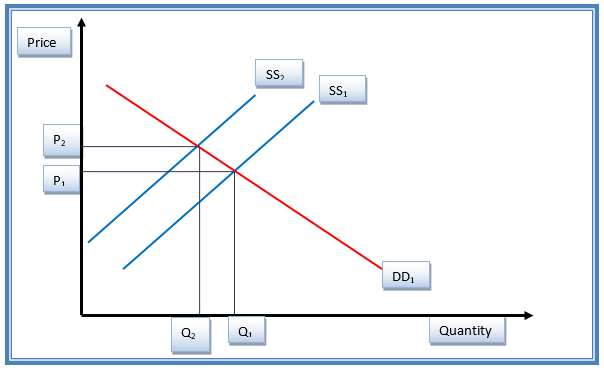
An increase in the price of Nike jersey with other perfect substitute products such as Adidas jersey causes an inward shift of the supply curve from SS1 to SS2, as indicated in figure 1.2. This gives a new equilibrium position. Price increased from P1 to P2 (Mankiw 56). This indicates reduced demand from the customers. The net effect of the increase in price is a contraction of the demand side. The price elasticity for Nike jersey product is pre-calculated at 0.7 (McEachern 23).
Price elasticity of Adidas products (Adidas jersey)
Adidas’ products are also priced elastic since they are categorized as luxury goods. The demand for Adidas jersey product is sensitive to price changes since potential customers can do without the luxury product when it is considered too expensive (Mishra 29). Therefore, when the price of Adidas jersey increases, customers will respond by buying less or switching to perfect substitute products deemed as more affordable. This is explained in the diagram below.
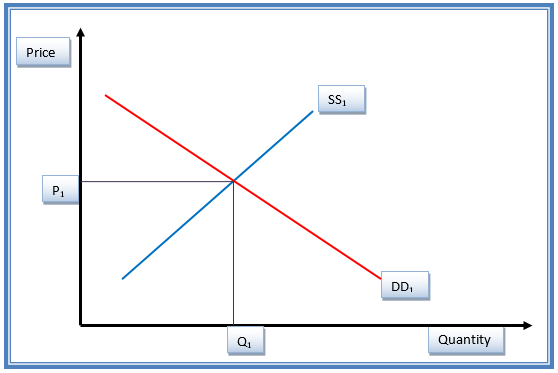
Figure 3 shows the initial equilibrium status of the Adidas products before the changes in the price. DD1 shows the demand curve, while SS1 shows the supply curve. Equilibrium price and quantity are P1 and Q1, respectively.
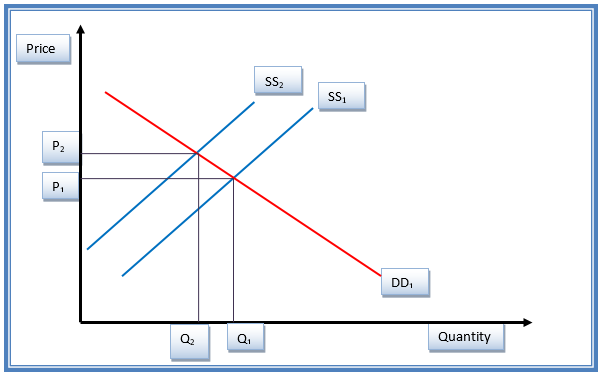
An increase in the price of Adidas jersey with other perfect substitute products such causes an inward shift of the supply curve from SS1 to SS2, as indicated in figure 4. This gives a new equilibrium position. Price increased from P1 to P2. The price elasticity for Nike jersey product is pre-calculated at 0.5 (Sexton 19).
Comparative analysis
According to Guru (2015), “it can be argued that goods that account for a large proportion of disposable income tend to be elastic. This is due to consumers being more aware of small changes in the price of expensive goods compared to small changes in the price of inexpensive goods” (p. 49). In this case, Nike and Adidas products are price elastic. These products have elastic supply since their prices determine their ease to be purchased in the market.
Besides, when the demand for the same fall, the supply responds almost instantly to the market. Considering an event in which the prices of Nike and Adidas products increase, the demand for the same products will decrease by the same magnitude triggering the supply to decrease in the long run. On the other hand, the reduction in the price of Nike and Adidas products will influence the demand to increase as more customers will prefer the products (McEachern 43; Mishra 22).
Income elasticity
Income elasticity of Adidas products (Adidas jersey)
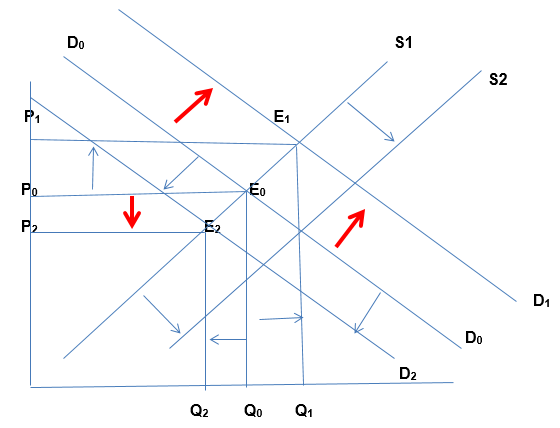
Since Adidas jersey is a luxury product, it is income elastic. That is, an increased income of a household would translate into more demand for the product since the household will have more disposable income to purchase the product. The reverse is also true. For instance, when the income of a household increases, the demand for Adidas jersey will increase. This leads to an outward shift in the demand curve for a product from D0 to D1, and a new equilibrium is achieved at point E1 with price P1 and a higher quantity Q1. Conversely, when income reduces, individuals’ disposable incomes reduce (Guru
51). Given that Adida’s product is a luxury commodity, the demand will decline, resulting in the drop of quantity of products demanded. The income elasticity of Adidas jersey is pre-determined at 0.4 (Mankiw 29).The corresponding price will fall from the initial P0 to P2. A new equilibrium will be achieved at point E2. This is ilustrated below.
Income elasticity of Nike products (Nike jersey)
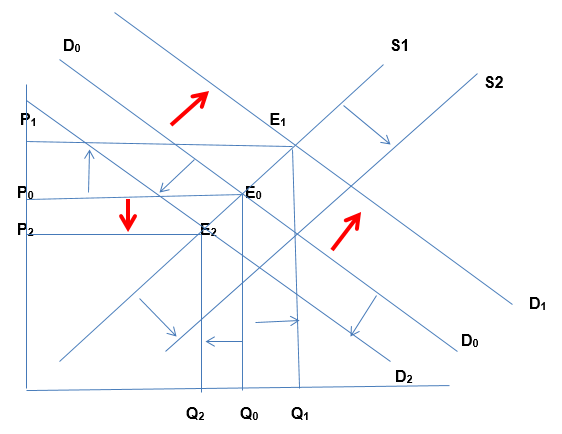
Nike jersey is a luxury product, which is income elastic. When income of a household increases, the demand for Nike jersey will increase. This leads to outward shift in the demand curve for product from D0 to D1 and a new equilibrium is achieved at point E1 with price P1 and a higher quantity Q1. Conversely, when income reduces, individuals’ disposable incomes reduce (Guru 48). Given that Nike product is a luxury commodity, the demand will decline, resulting in the drop of quantity of products demanded. The corresponding price will fall from the initial P0 to P2. A new equilibrium will be achieved at point E2. The income elasticity of Nike jersey is pre-determined at 0.5 (McEachern 33). This is ilustrated below.
Cross Price Elasticity
Basically, Nike, Adidas, and major players in this oligopolistic market have similar income elasticity behavior since the luxury products are the same and within similar price range. For increase, an increase in price of Nike jersey by 5% will result in an increase in demand for Adidas jersey by 10%, meaning that the cross price elasticity for these two substitutes and other products in the same categy is 2 (Sexton 19; Mishra 39).
The cross price elasticity of demand between the products of Nike and Adidas and competing products is 2 since market conditions are constant for all the players in the sports apparel industry (McEachern 54). However, Nike has higher price elasticity of 0.7 and income elasticity of 0.5 as compared to 0.5 and 0.4 respectively for Adidas. This means that Nike has higher price and income elasticity that Adidas.
Apparently, Nike and Adidas have perfect substitute products and operate in the same industry. Since the products of the two companies are categorized as luxury goods, they are considered price elastic since any change in the prices results in a proportional change in the demand. The two companies have potential for future growth due to their global brand image dominance as a result of product diversification, competitive pricing mechanisms, overzealous marketing, and strategic brand positioning.
Conclusion and Recommendations
As indicated in the analysis, it is apparent that Adidas Corporation has better income and cross-price elasticity in the apparel markets that Nike Incorporation. The existence of more subsidies and products in Adidas would translate into higher returns on investment than in Nike Incorporation. When there are more substitutes besides a product, chances of shifting to these substitutes are higher. Therefore, availability of a substitute may lead to decrease in demand when the price for a product increases.
When the price increases, the household might opt for the best alternative, especially when doing the same will positively affect savings or add value to the disposable income. Therefore, several available substitutes in the case of Adidas will make the demand curve responsive to changes in price since the consumer behavior will not remain the same.
In the case of the sports apparels market, several available substitutes will make the demand curve highly elastic as responsiveness to changes in price attracts immediate change in customer behavior such as purchasing pattern. A small change in price in sports apparel leads to a greater change in quantity demanded as customers will opt for substitutes that have cheaper price tag or are more affordable in long-run. As indicated in the above analysis, Adidas and Nike
Have product demand curves that are highly elastic due to existence of many alternatives in the market.
The two companies should create strategic limit pricing to ensure that they remain competitive in the midst of many perfect substitute products. However, the two companies are poised to benefit from the aspect of sylos postulate functionality. The concept of sylos postulate functions on a naïve and broad assumption that in the market, an incumbent will always maintain its pre-entry output levels in any event of a new entrant in that market segment (Mankiw 38).
Thus, if a new entrant decides to establish in the market, the incumbent may not really feel the threat as perceived by the sylos postulate view. Thus, this view is irrelevant since a new entrant will have to struggle to operate within full production module while the incumbent products of Nike and Adidas will have production at optimal. Besides, the new entrant will have to deal with sunk costs while the incumbents are enjoying competitive advantage.
Basically, in line with the above reflection, the sylos postulate as an example of limit pricing strategy may constitute anti-competitive behavior to the advantage of the strong brand names associated with Adidas and Nike. Before limit pricing, the forces of demand and supply may set the equilibrium prices for the sylo functionality in the two companies. In the short-run, the limit prices set will be inelastic. However, in the long-run, the limit prices will be elastic.
References
Guru, Simon. “Main Factors which Determines the Price Elasticity of Demand for a Commodity.” The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 9.18(2015): 47–77. Print.
Mankiw, Gregory. Principles of Economics, Volume 1. Alabama, Al: Cengage Learning, 2008. Print.
McEachern, William. Economics: A Contemporary Introduction. Alabama, Al: Cengage Learning, 2011. Print.
Mishra, Rajan. Industrial Economics and Management Principles. New York, NY: Firewall Media, 2008. Print.
Sexton, Roberts. Exploring Economics. Alabama, Al: Cengage Learning, 2015. Print.
