Abstract
Research on organizational culture supports the belief that corporate customs are vital for efficient operations and profitability of the business. Even though various studies have examined the correlation between corporate culture and performance, experimental results appear to be mixed and indecisive. Additionally, limited studies analyze the connection between organizational culture and customer retention. The majority of the existing studies discuss the link between corporate culture and employee performance in commercial institutions. Few studies have examined non-profit organizations.
Most scholars agree that the promotion of flexibility-oriented corporate culture boosts employee performance and guarantees customer retention. Such a culture facilitates career development, which is an essential factor that contributes to employee commitment. A motivated workforce works towards the realization of organizational goals. In the process, it fulfills consumer needs, resulting in customer loyalty. This study will examine the impacts of corporate culture on employee performance and customer retention using both qualitative and quantitative methods. The research will utilize qualitative data from secondary sources. It will also rely on primary data gathered through in-depth interviews. The interviews will target employees working in different departments at the UN Secretariat.
Introduction
Understanding the correlation between corporate culture, employee performance, and customer satisfaction is paramount because it helps to boost a competitive edge of an enterprise. Businesses ought to establish corporate cultures that guarantee continuous development. According to Paschal and Nizam (2016), organizational culture is vital because it influences employee commitment and turnover.
Businesses that embrace flexible cultures experience low employee turnover. Such cultures provide a working environment that empowers workers, enabling them to operate with minimal interference. In return, the workers exhibit a high degree of job fulfillment and are devoted to their duties. An efficient corporate culture promotes organizational performance, which translates to customer satisfaction.
The objective of the Study
The primary objective of this study is to determine the impacts of corporate culture on employee performance and customer retention. The study seeks to identify how the United Nations uses corporate culture to boost employee performance and retain member states.
Structure of the Proposal
The proposal will constitute four chapters. The first chapter will comprise the introduction. The second chapter will consist of a preliminary review of existing literature. Chapter three will include the methodology of the proposed study. Chapter four will discuss the results of the study and outline the research timetable.
Background
The existing literature lacks a standard definition of organizational culture. Instead, scholars define the term from diverse perspectives. Belias and Koustelios (2014) confirmed that there was no single definition of culture or an agreement on how it should be studied and defined organizational culture as “a pattern of basic assumptions that a group has invented, discovered or developed in learning to cope with its problems of external adaptation and internal integration and has worked well enough to be considered valid” (p. 137).
On the other hand, Guiso, Sapienza, and Zingales (2015) defined organizational culture as a collection of universal norms and values of an enterprise’s employees. It comprises fundamental assumptions that business learns to address challenges attributed to external adaptation and adjust to the current environment.
Organizational culture impacts different corporate and employee-related outcomes. It influences employee behavior, creativity and innovation, learning and development, and knowledge management (Anitha, 2014). Numerous studies have analyzed the correlation between organizational culture and employee performance. Unfortunately, the findings of the studies appear inconclusive due to structural, design, and definition-related differences and challenges.
Nizam and Paschal (2016) assert that some studies cite reconciling impacts of aspects like knowledge management, organizational innovativeness, and knowledge conversion between corporate culture and employee performance. Hyland, Lee, and Mills (2015) allege that one requires considering the interactive character of processes, culture, and business outcomes when analyzing the association between organizational traditions and employee performance. The authors hold that organizational culture impacts employee performance and customer retention via mediate factors.
Employee performance reflects the degree of the realization of organizational goals. Companies use numerous objective and skewed measures to evaluate employee performance. Habib, Aslam, Hussain, Yasmeen, and Ibrahim (2014) contend that employee performance is widely featured in the majority of the organizational theory literature. Nevertheless, evaluation of employee performance remains a significant challenge to many researchers and corporate managers.
Researchers that analyze the link between organizational culture and employee performance utilize various measurements. Evaluating the relationship between culture and employee performance, Rahimi and Gunlu (2016) found that most institutions use growth and economic profitability as the units of measure. Such standards are difficult to use in non-profit organizations. Hogan and Coote (2014) maintain that scholars use indicators such as the number of clients handled and cost per service to evaluate employee performance in non-profit institutions.
Customer retention depends on the degree of an organization’s ability to fulfill the needs of its target clients. An organizational culture that emphasizes customer-oriented knowledge sharing, behaviors, performance-based rewards, and cross-functional teams contributes to customer satisfaction and retention (Homburg, Jozic, &Kuehnl, 2017). Such a culture ensures that employees offer products and services that satisfy consumer needs. In return, clients develop a positive impression of the company, thus opting to establish a lasting relationship with the organization. Corporate culture has significant impacts on human resources.
It determines the traditions, habits, and values that human resource exhibits. Pantouvakis and Ourania (2013) argue that organizational culture is essential in “establishing a unified organization, thus influencing the direction of human resource development and performance” (p. 51). On the other hand, human resource development and performance enable an organization to meet customers’ expectations and preferences, therefore facilitating their retention.
Public organizations have complex organizational cultures due to the nature of their operations. Dependence on governments for financial resources, external political influence, and rigorous formal legal restrictions affect the smooth running of public institutions. The United Nations (UN) organization is one of such bodies that have a complicated corporate culture. The UN runs multiple agencies with individual decision-making bodies that comprise many governments and associated constituencies. The governments have a significant influence on the operations of the agencies and budget approval.
Consequently, the agencies encounter challenges in decision-making as they have to please their financiers. Clarke (n.d) holds, “The budgetary process determines the resource allocation to different programs” (p. 126). Therefore, member states manipulate the process to suit their interests. Small countries that do not influence the UN Secretariat and agencies establish alliances to ensure that they benefit from budgetary allocations.
The UN agencies operate under the rule of neutrality that requires all employees to reign over political manipulations. Unfortunately, mixed loyalties dominate the agencies where employees are torn between abiding by the UN system and serving the interests of their home countries. Clarke (n.d)avers that at the agency level, the UN employees experience immense pressure to serve the interests of paymasters. The UN system and Secretariat are under the constant influence of the member states and the Security Council. The two evaluate the UN organizational performance based on political measures. Lack of a well-defined corporate culture hinders the efficiency of the UN.
Literature Review
The absence of concrete data on different cultures complicates the understanding of theories of the corporate culture. Most employers prefer to recruit like-minded employees to ensure that they work together towards common goals. Liden, Wayne, Liao, and Meuser (2013) posit, “Theories on organizational culture typically have different overall corporate mind-sets, such as ethics, profits, or philanthropy” (p. 1438). The theories that explain corporate culture include consistency theory, theory X and theory Y, and the involvement theory, among others.
Theory X and Theory Y
The suppositions of theory X and theory Y are based on Maslow’s hierarchy of needs conjecture, which argues that the degree of employee commitment is pegged on their needs. Theory X is premised on the lower-hierarchy needs, while theory Y is founded on high-order needs (Arslan & Staub, 2013). Organizational leadership can use either of the needs to enhance employee performance.
Nonetheless, the most significant impact can be realized through the satisfaction of the higher-order needs. Theory X argues that employees cannot devote themselves to organizational goals without coercion and control by the management (Arslan & Staub, 2013). It holds that workers have inborn hate for responsibilities and tend to avoid them at all costs. Moreover, employees have to be threatened, directed, pressurized, and controlled to realize organizational objectives. The theory fails to appreciate that most workers have ambitions and commit themselves to corporate goals as long as they help them achieve their dreams.
Theory Y holds that Organizational leadership must facilitate employee development to boost commitment (Arslan & Staub, 2013). An organizational culture that promotes training and development helps to enhance employee performance because it motivates them to pursue their aspirations. The theory argues that employees exercise self-direction if allowed to make decisions on matters that affect their areas of specialization.
Moreover, a culture that promotes performance-oriented rewards enhances employee commitment. Arslan and Staub (2013) aver, “People are committed to objectives since they are a function of the rewards associated with their achievements” (p. 105). Intellectual creativity is critical to employee performance. However, it is imperative to acknowledge that it cannot be achieved through intimidation, coercion, or management programs. Instead, it is realized through the appropriate inculcation of cultural principles of individual responsibility and accountability. Traditional management practices and issuing directives cannot help to improve employee performance.
Consistency Theory
The consistency theory argues that organizational effectiveness is pegged on culture. Organizations with reliable, consistent, integrated, and well-organized cultures are successful. A steady and well-coordinated culture instills a set of core values in employees, which guides their operations. According to Ruiz-Palomino, Martinez-Canas, and Fontrodona (2013), organizational culture has a significant influence on employee behavior as their conduct is ingrained in core values. It enables corporate leaders and employees to overcome their differences and compromise for the sake of business. The consistency attributed to organizational culture promotes stability and a high level of conformity among employees, which supports seamless operations and boosts their performance.
Involvement Theory
The involvement theory is founded on the notion that participation and contribution instill a sense of ownership and accountability in employees, thus boosting their commitment and performance. Successful companies establish their institutions around teams, empower employees, and build human resource capacity at all levels (Strom, Sears, & Kelly, 2013). A corporate culture that promotes employee development and empowerment allows an organization to assemble a dedicated workforce. Managers, executives, and regular workers devote their energy to organizational goals because they feel like they own part of the company (Karatepe, 2013). Employees at all levels ensure that they contribute to decision-making processes, thus guaranteeing flawless operations.
Customer Relations Management
Customer relations management refers to an organizational strategy that aims at creating value for the primary target clients and establishing a lasting gainful relationship with consumers. Cultural factors influence the success or failure of customer relations management (Battor&Battour, 2013). A corporate culture that encourages customer-oriented behaviors, supportive relationships, innovation, high-risk taking, and teamwork is likely to facilitate efficient customer management, thus guaranteeing their loyalty (Park, Lee, & Kim, 2014).
The analysis of the organizational learning framework reveals a strong correlation between corporate learning culture and customer retention (Lukas, Whitwell, & Heide, 2013). A culture that gathers quality customer data helps to align organizational strategies with consumer needs. In return, an organization wins the trust of the target customers, thus retaining them.
Staff Management
Employees are a reflection of an organization. A workforce that understands its responsibilities and consumer needs enable an organization not only to attract clients but also retain them (Rahimi, 2017b). Marketing theorists agree that organizations, which pay attention to consumer needs and act in customer-oriented manners, do better and enjoy a substantial client base (Namasivayam, Guchait, & Lei, 2014). According to Eman, Ayman, and El-Nahas (2013), the interaction between consumers and employees augments customer satisfaction. Hence, employee behavior is paramount in promoting customer loyalty.
On the other hand, organizational culture influences employee behavior. Thus, it is essential to improving customer retention. Corporate leaders appreciate the significance of offering tailored services to consumers. Most organizational cultures encourage employees to accord consumers personalized attention (Martelo, Barroso, &Cepeda, 2013). It goes a long way towards winning the trust of customers and encouraging them to continue relating to a business. Many companies persuade their workers to address consumer needs in an on-the-job context. Such a culture helps an organization not only to meet consumer needs but also to gather customer feedback, which is vital in shaping the future operations of an organization.
Research Question
Limited studies have been conducted to establish the connection between organizational culture, employee performance, and customer retention. Moreover, the majority of the existing studies focus on commercial institutions (Rahimi, 2017a). The lack of studies that analyze non-profit institutions makes it difficult to ascertain the contribution of corporate culture to such organizations. In this study, the researcher will determine how non-profit organizations align their corporate culture with the capabilities of the workforce and consumer needs. Specifically, the researcher will evaluate how organizational culture helps to enhance employee performance in non-profit institutions. The study will assess the effectiveness of organizational culture in addressing the needs of the target population.
The UN is one of the non-profit organizations with intricate organizational culture. Clarke (n.d) posits, “The UN promotes the official organizational values of integrity, professionalism, and respect for diversity among its staff” (p. 128). The fact that the UN hires employees from diverse backgrounds and runs multiple agencies makes it difficult to comprehend its corporate culture. In this study, the researcher will evaluate how the UN promotes an organizational culture in a diverse workforce.
Specifically, how do the different agencies embrace and ensure that they operate within the guidelines of the UN organizational culture? Moreover, the researcher will evaluate the impacts of the UN organizational culture on employee performance. The UN focuses on providing services to member countries. The developing states benefit most from the UN (Clarke, n.d). Therefore, the study will consider developing states as the primary clients for the UN. The researcher will evaluate how the UN organizational culture contributes to the satisfaction of the developing nations.
The study will analyze the nature of the UN organizational culture and how it is reflected in the various agencies. It will also investigate employee perception of the culture and how it assists them in their daily operations. An examination of the attitude of the developing nations towards the UN will confirm if the organizational culture helps to satisfy the needs of the target population. Currently, there is limited literature about the impacts of organizational culture on customer retention. Thus, this research will help to close the existing gap. The primary questions for the study are;
- What are the impacts of organizational culture on employee performance?
- What are the effects of organizational culture on customer retention?
Methodology
Researchers have numerous modes of data collection and analysis at their disposal. The method of data collection selected depends on the availability of information, finance, and time. Some of the widely used methodologies include triangulation, surveys, and case studies. Currently, there is limited information about the link between organizational culture and customer retention. Additionally, the existing data elucidate limited information about the corporate culture of non-profit institutions. Thus, to come up with general findings, there is the need to rely on the triangulation method. The researcher will use both qualitative and quantitative methodologies to determine the link between organizational culture, employee performance, and customer retention in the UN.
One of the advantages of qualitative research is its ability to offer multifaceted contextual interpretations of how people understand a specific research issue. The method captures data regarding the “human” side of a research question. According to Bansal et al. (2017), the qualitative methodology helps researchers to collect information about emotions, behaviors, opinions, relationships, and beliefs of people. It also assists in gathering data about subtle factors like social norms, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, which go a long way towards enabling the researcher to compile a comprehensive report. The primary limitation of qualitative methodology is that it cannot be used to gather universal information.
Quantitative methodology gathers numerical data, which helps to guarantee the credibility of a study. Numerical data is not vulnerable to misinterpretation. Therefore, it enables researchers to come up with reliable findings. Moreover, it allows pollsters to use different statistical methods to analyze data, thus gaining an in-depth understanding of the research issue.
The researcher will require both descriptive and numerical data to understand the impacts of organizational culture on employee performance and customer retention in the UN. Thus, this study will rely on in-depth interviews as the primary mode of data collection. Bansal et al. (2017) define an in-depth interview as a “qualitative research technique that involves conducting intensive individual interviews with a small number of respondents to explore their perspectives on a particular idea, program, or situation” (p. 226). Gathering data from multiple UN agencies is difficult. Therefore, the study will focus mainly on the Secretariat since it is the principal-agent.
The researcher will collect descriptive and numerical data regarding the number of clients that the agency serves, the current number of employees, and workers’ perception of the agency’s corporate culture. The researcher will also gather information regarding the number of new states (if any) that have joined the UN. Moreover, the study will inquire about the number of countries that have expressed their dissatisfaction with the Secretariat and their chief complaints (see appendix 1).
The primary objective of the study is to determine if the UN organizational culture helps to enhance employee performance. Thus, the researcher will decide if the UN corporate culture enables employees to discharge the mandates of the Secretariat without challenges. They will also examine the factors that hamper efficient operations in the agency. A total of 30 employees will be interviewed. The participants will be selected from different departments within the Secretariat.
The researcher will also rely on secondary data from existing literature. The secondary data will go a long way towards assisting the researcher in preparing the interview questions. According to Bansal et al. (2017), secondary data helps a researcher to identify existing gaps, thus knowing the right questions to ask during the interviews. Currently, there is limited data regarding the correlation between corporate culture and employee performance, and customer retention. The researcher will use the existing data to understand the research issue. Moreover, the secondary data will form a basis for verifying the findings of the in-depth interviews.
Limitations and Ethical Issues
Time constraint is a major limitation for this study. The researcher will not have adequate time to conduct a detailed study. Additionally, inadequate literature about the effects of organizational culture on customer retention is a major constraint for the study. The researcher will require maintaining the privacy of the participants. This will be realized by not disclosing the names of the participants. Moreover, no unauthorized persons will have access to the findings of this study.
Research Outcome
The primary objective of this study is to determine the role of organizational culture on employee performance and customer retention. Thus, the expected outcome of the research is a description of the UN organizational culture. The study should also describe the role of the organizational culture on employee performance and customer retention.
Contingencies
Numerous challenges may hamper the success of the study. For instance, some participants may fail to turn up for the interview due to changes in their working schedules. Additionally, some participants may fail to provide detailed information regarding the study questions, thus affecting the credibility of the results. To address these challenges, the researcher will contact the participants in advance to determine the time that they will be available for the interview. The researcher will also supply scorecards to all the participants to prepare them for the interview.
Research Timeline
Analysis of Research Data
Quantitative analysis
T-test
The research used a t-test to carry out a comparative analysis between the impact of culture on customer satisfaction and employee performance at the UN. The explanatory variables used in this analysis were the predominance of democratic, participatory, autocratic, and freestyle organizational cultures. As captured in table 1, the means of different cultural applications were derived with the respective standard of deviation and rank (see appendix 2). This shows that the highest mean was recorded under participatory organization culture (5.2939). The lowest mean was recorded under freestyle organizational culture (4.1757).
The finding is a clear indication that participatory organizational culture is predominant within the UN. The least practiced culture is the freestyle way of doing things. Moreover, the standard deviation indicates that there is variation in the application and impact of different cultures on employee performance and customer satisfaction. This finding addresses the research question that intended to establish the organizational culture that promotes optimal employee performance and customer satisfaction at the UN. A t-test was then used to establish the statistical significance of the above results on the basis of the following hypothesis.
Null hypothesis
H0. There is a difference between the mean of the organizational cultures within the UN organization.
Alternative hypothesis
H1: There is a difference between the mean of the organizational cultures within the UN organization.
The researcher carried the t-test at the 95 % level of confidence, and the results were tabulated to establish an existing trend (see appendix 3). As summarized in appendix 3, it is apparent that the p-value (sig. (2-tailed) is actually greater than 0.05, which is the alpha value of the four organizational cultures. Thus, on the basis of this finding, the null hypothesis is accepted since it implies that the variances in the means for different organizational cultures are statistically significant at a 95% confidence level. Therefore, from a statistical view, there is a predominant organizational culture within the UN organization. The predominant culture is the participatory organizational orientation.
ANOVA analysis
A multivariate analysis was then applied to test the variances and existing relationships between different organizational cultural orientations within the UN. The three departments analyzed were Logistics, Finance, and Corporate Affairs, which fall under the domain of the secretariat. As captured in table 3, the information gathering was evenly distributed within the three departments to establish the predominant organizational culture practiced (see appendix 4).
On the basis of the mean and standard deviation, the findings summarized in appendix 4 indicated that the democratic organizational culture is predominant in the finance department within the UN. In the logistics department, the autocratic organizational culture was predominant, while participatory culture prevailed in the corporate affairs department. Therefore, it can be concluded that the prevailing organizational culture differed across different departments. The variances could be attributed to the structures and type of active stakeholders. Therefore, the ANOVA analysis was further carried out to establish if the variances in the application of organizational cultures across different departments had any statistical significance. The hypothesis of the ANOVA test is presented below.
Null hypothesis
Ho: µ1 = µ2 = µ3
The null hypothesis indicates that there is no variance in the application of different organizational cultures within the secretariat division of the UN organization.
Alternative hypothesis
Ho: µ1 ≠ µ2 ≠ µ3
The alternative hypothesis indicates that there is a variance in the application of different organizational cultures within the secretariat division of the UN organization.
The results of ANOVA analysis were tabulated to establish an existing trend (see appendix 5). As summarized in appendix 5, the F-value is 4.21 while the P-value is 0.001. Due to the fact that the p-value is less than 0.05 at a 95% degree of confidence level, it is an indication that there are variances in organizational cultures within the secretariat division. Specifically, the variances were noted within the finance, logistics, and corporate affairs departments. This is a clear indication that organizational cultural orientations vary from one department to another. Therefore, it can be concluded that the predominant organizational culture in any department might have an impact on the level of employee motivation or customer satisfaction.
Correlation Analysis
As a statistical tool, correlation analysis is important in measuring the degree of association existing between or among variables of the study (Mason, 2017). In this case, the researcher used correlation analysis to ascertain the existing relationship between organizational effectiveness and cultures applied. The organizational effectiveness was measured as a product of employee motivation and customer satisfaction.
There are indicators that provided information on the quality of the general organizational effectiveness. The indicators selected for correlation analysis were employee satisfaction, customer feedback, corporate image, and organizational growth (see appendix 6). As captured by the results summarized in appendix 6 from a sample of 30 respondents, the employee satisfaction level means had the highest score of 4.8094 followed by customer feedback at 4.6698. The least score was on organizational growth at a mean of 4.5383. The results above are an indication that there are high customer feedback and employee satisfaction levels at the UN.
This means that the organizational cultures applied at the UN have a positive impact on employees and customers. Since all the means fall within a single unit, it is a sign that the organization is effective in balancing different structural management principles for a positive outcome. For instance, the difference between the highest and lowest mean was recorded at 0.3. Moreover, the standard deviations for all the indicators are very low.
Specifically, the lowest SD of 0.9622 was recorded for the customer feedback indicator, followed by 1.2031 for the employee satisfaction variable. The low SD for all the indicators could also imply consistency in the responses and dependability of the sample space. Thus, on the basis of the above results, the researcher selected employee satisfaction and customer feedback as the proxies for organizational culture effectiveness. The null and alternative hypotheses are presented below.
Ho: There is no significant relationship between culture and organizational effectiveness.
H1: There is a significant relationship between culture and organizational effectiveness.
The researcher then carried out a correlation matrix between organizational cultures and the effectiveness of the UN secretariat division (see appendix 7). The results summarized in appendix 7 indicate that there is a positive correlation between organizational culture orientation and employee motivation/customer satisfaction. The highest correlation score was recorded for the participatory culture at 0.678, followed by democratic culture at 0.652. The positive correlation is a clear indication that organizational culture has a positive influence on customer satisfaction and employee motivation at the UN secretariat division. Moreover, the high correlation score between the predominant culture and organizational effectiveness, within the variables of customer satisfaction and employee motivation, suggests that the UN is an effective establishment with healthy organizational cultural orientations. Moreover, the findings suggest that the UN organization has a general pool consisting of well-motivate employees and satisfied customers.
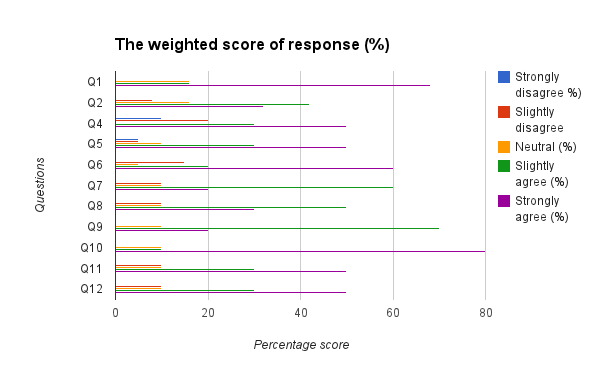
Answers to the Close-Ended Questions
As summarized in appendixes 8 and 9, the summary of responses for each question was tabulated.
Analysis of Each Question
- To what extent are you knowledgeable or aware of different organizational cultures as practiced within the UN secretariat division?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree on q6.
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- Chart 1 in appendix 10 indicates that 90% of the respondents were aware of different organizational cultures practiced within the UN secretariat division.
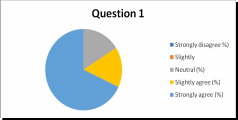
- Does your department have a unique culture in managing its operations?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- In response to the second question, 87% of the respondents acknowledged the existence of a unique organizational culture within their department, as captured in chart 2 in appendix 11. However, 6 respondents were indifferent.
- Is the primary focus of the organization’s culture towards efficiency effective, in your opinion?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- 92% of the respondents confirmed that the primary focus of the organizational culture in their departments was effective, as captured in chart 3 in appendix 12. However, 6% of the respondents were not convinced that the current culture is effective.
- How do you grade the organization culture in terms of being good and reflective of the actual motives of your organization?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- 95% of the respondents graded the organizational culture as effective and relevant to the motives of their respective departments, as captured in chart 4 in appendix 13. However, the rest of the respondents disagreed.
- Is it true that the success of your organizational culture is based on the strategy of performance or not?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- 80% of the respondents correlated the success of the organizational culture to the current success and effectiveness in strategy application, as captured in chart 5 in appendix 14.
- What do you think of the organizational culture in terms of its effectiveness in employee motivation (general)?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- As summarized in chart 6 in appendix 15, 87% of the respondents related the success of the organizational culture with their department as a dependent of the UN multi-global management approach. However, 2% of the respondents were neutral, while the rest disagreed.
- Do you agree with the content of the organizational culture now that you are one of the employees within the UN secretariat division?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- The findings indicated that 84% of the respondents were convinced that the content of their organizational culture was efficient and effective. However, 7% of the respondents were indifferent, as captured in chart 7 in appendix 16.
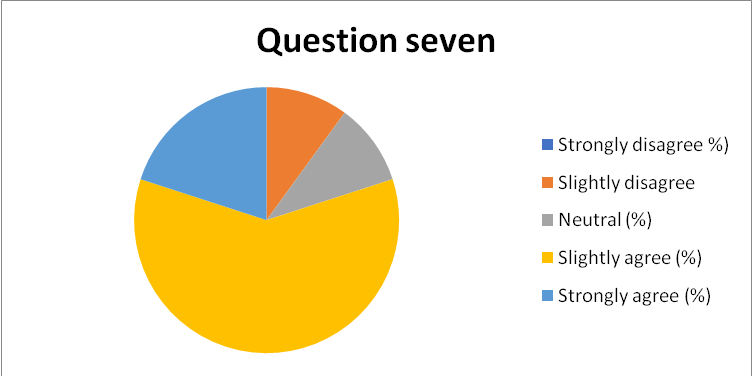
- Generally, the organizational culture in our organization is successful since it has empowered the employees to freely discuss opinions and thoughts as an active part of the organizational operations.
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- 91% of the respondents recognized their organizational culture as successful in integrating their opinions and thoughts as part of the secretariat division, as captured in chart 8 in appendix 17. However, 6% of the respondents were not satisfied by the current culture in promoting their interaction with the operations of each department.
- To what extent are you aware of the level of customer satisfaction with the services and products your department offers? I am aware that customers are satisfied.
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- 97% of the respondents recognized that most customers are satisfied by the services and products they offer at the departmental level, as captured in chart 9 in appendix 18. The high positive response could be associated with an effective organizational culture or effective service delivery charter. Only 3% of the respondents were indifferent.
- What do you think of your department’s organizational effectiveness in terms of representing the UN customer-employee corporate balance?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- 94% of the respondents agreed that their respective departments’ organizational effectiveness was representative of the UN customer-employee corporate balance. However, 3% of the respondents slightly disagreed while the rest remained neutral, as captured in Appendix 19.
- Do you think that the current organizational culture is effective in motivating the employees and guaranteeing customer satisfaction?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
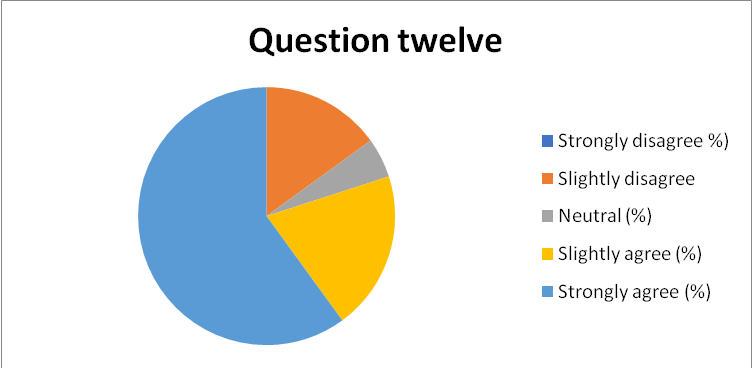
- 89% of the respondents were convinced that the current organizational culture is very effective in promoting employee motivation and guaranteeing customer satisfaction. However, 6% of the respondents were neutral while the rest slightly disagreed, as captured in Appendix 20.
- Do you think that the current organizational culture promotes proactive stakeholder participation?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
87% of the respondents could associate the current organizational culture to a high level of stakeholder participation in their respective departments. The rest slightly disagreed or adopted the indifference position as captured in Appendix 21.
Discussion, Conclusion, and Recommendations
The findings indicated that organizational culture influences the performance of the employees and customer satisfaction. Apparently, the respondents indicated that the UN organizational culture promotes a holistic and healthy work environment. Moreover, there are attractive remuneration packages for different sets of relevant skills. The employee promotion structure is also standardized. In addition, the organization respects diversity, and there is a policy in place for addressing any employee concern.
The respondents noted that customers of the organization are generally satisfied, considering the positive feedback. Moreover, the compliments outweigh the complaints in the ratio of 8:1. The cultural practices identified by the respondents as responsible for retaining and attracting customers include quality service charter, constant client engagement, and a healthy customer-organization relationship matrix.
The findings indicate that organizational culture has a direct impact on employee performance and customer satisfaction. Specifically, an effective organizational culture should integrate the aspects of human sustainability to create a dynamic work environment for optimal employee performance. As a result, the highly motivated employees will offer optimal services to customers, thereby increasing the magnitude of positive feedback from the clients (Dasgupta, Suar, & Singh, 2013).
When the organizational culture is structured and policy-oriented, as is the case with the UN secretariat division, it is possible to track the interpersonal relations, work environment, and working conditions, among others. Moreover, it is within reach to quantify the perceptions of the employees on the effectiveness of each matrix. For instance, as observed by the majority of the respondents, the nature of information exchange and supportive work environment has inspired the employees to perform optimally. As a result, customers get optimal services in all sections of the administrative pyramid of the secretariat division.
In order to effectively inspire proactive employee performance, it is necessary for an organization to balance the dimensions of personnel satisfaction and skill set for optimal output for every bundle of inputs. As established in Theory X and Theory Y, striking a perfect balance has the potential of minimizing the magnitude of inequality in the fulfillment of employee and customer expectations (Harrison & Wicks, 2013).
In relation to the secretariat division of the UN organization, there is a perfect balance in employee motivation and skillsets for optimal performance. For instance, the current leadership of this division has embraced a high power/distance score as a strategy for bridging any existing gap between supervision and employee expectations. As a result, there is an internalized culture of teamwork for optimal inter and inter-departmental performance.
Moreover, the decision environment is friendly to the needs of the employees and is customized to serve the needs of all stakeholders. The tailored decision-making process has created an inclusive and flexible group culture that supports a proactive communal connection between the organization and employees or customers (Obeidat, Masadeh, & Abdallah, 2014). The current organizational culture also promotes a healthy and holistic interaction between employees to internalize harmony and balance the group dynamics. Apparently, the findings suggest that this strategy is responsible for the high score in terms of customer satisfaction and employee performance.
As part of the cultural organization dimension, it is important to balance the internal and external management dynamics to ensure that the duties and expectations are perfectly matched to the skills of each employee. This means that the dimension should integrate transformational leadership and organizational ideologies to create a superior work culture. As a result, it will be easy for such an organization to promote inclusivity, self-actualization, creativity, and equality among the employees (Suma & Lesha, 2013).
Same as the principles of involvement and consistency theoretical inclinations, the secretariat division of the UN organization has managed to create an environment of proactive attitude, respect, and freedom of expression among the employees to influence positive performance. In order to continue with the positive trend in employee performance and customer satisfaction, the current organizational culture should be modified to integrate the aspect of constant employee training and an effective customer care orientation.
These aspects will ensure that the skill set of the employees is at par with their performance targets. Moreover, the customer care improvement will give the clients the opportunity to follow-up on their orders and make suggestions based on the results (Wilkinson & Redman, 2013). The division can then use these suggestions to further improve on customer satisfaction level.
Area of Future Research
This research was focused on establishing the impact of organizational culture on employee performance and customer satisfaction within the secretariat division of the UN organization. The entire research was angled on the determinants of employee performance and customer satisfaction on the basis of policy and structural orientation of the UN organization. Therefore, there was no focus on the aspects of constraints and rationale for the application of different cultures on the side of controls and strategic activities of the secretariat division.
Hence, there is a need for further research to be carried on the significance of incorporating the organizational culture constraints and rationale before making the final conclusion on the determinants of organizational effectiveness as influenced by existing culture. Moreover, the sample space of thirty respondents is not adequate to establish a scientific trend for an organization with more than 3,000 employees per region. This means that future research should expand the sample space to at least 200 respondents to capture a better picture of how organizational culture impacts employee performance and customer satisfaction.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Interview Questions
Appendix 2: Prevalence of organizational cultures in the UN
Appendix 3: Summary of the t-test results
Appendix 4: Organizational cultures practiced across different departments
Appendix 5: Results of the ANOVA analysis
Appendix 6: Correlation analysis results
Appendix 7: Correlation matrix between organizational culture and effectiveness
Appendix 8: Summary of the responses
Appendix 9: The distribution of the closed-ended questions percentage score
Appendix 10: Pie-chart 1: Summary of response to question 1
Appendix 11: Pie-chart 2: Summary of response to question 2
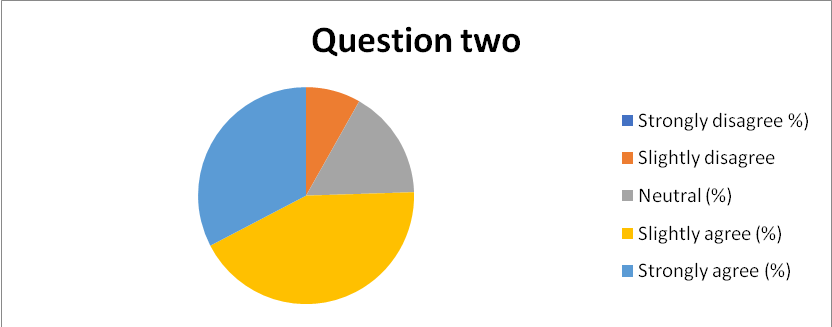
Appendix 12: Pie-chart 3: Summary of response to question 3
Appendix 13: Pie-chart 4: Summary of response to question 4
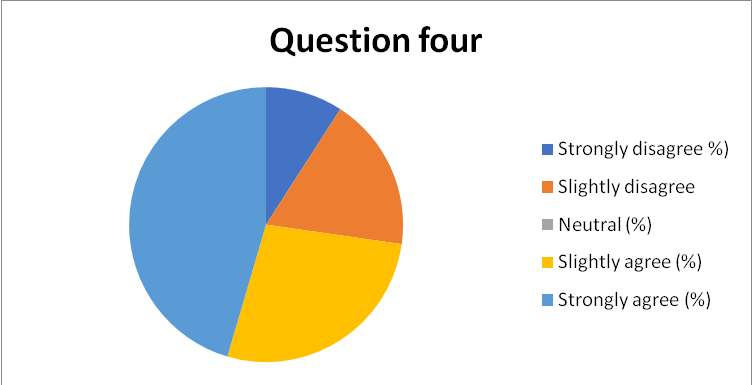
Appendix 14: Pie-chart 5: Summary of response to question 5
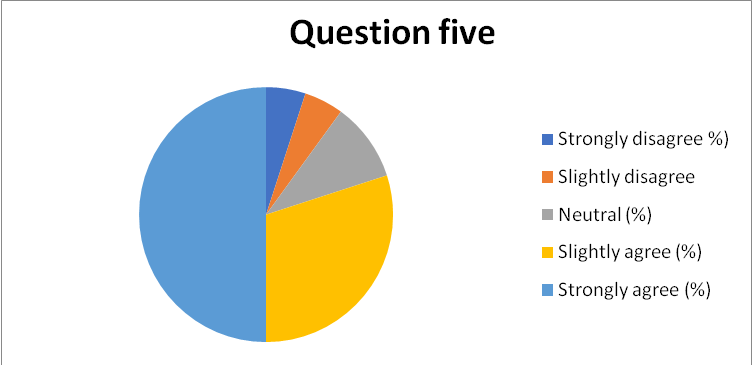
Appendix 15: Pie-chart 6: Summary of response to question 6
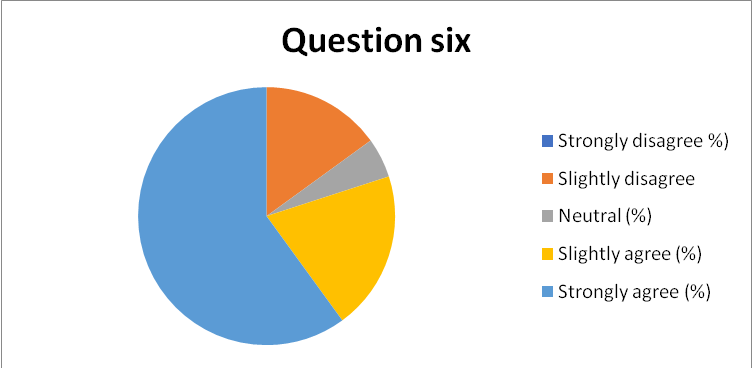
Appendix 16: Pie-chart 7: Summary of response to question 7
Appendix 17: Pie-chart 8: Summary of response to question 8
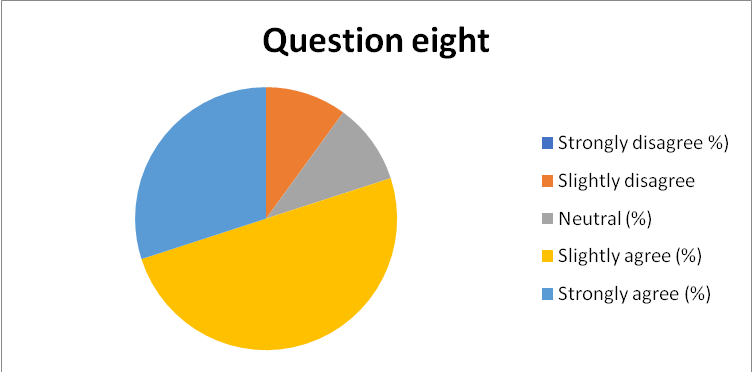
Appendix 18: Pie-chart 9: Summary of response to question 9
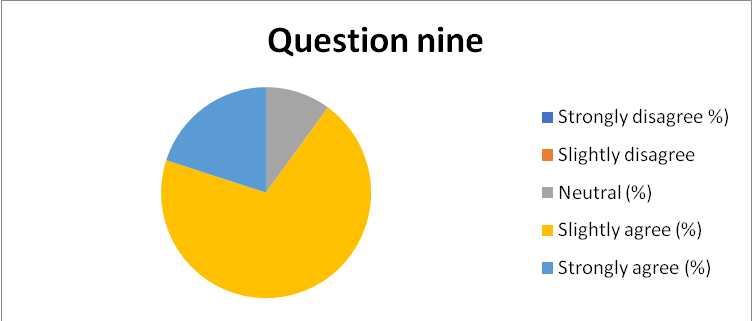
Appendix 19: Pie-chart 10: Summary of response to question 10
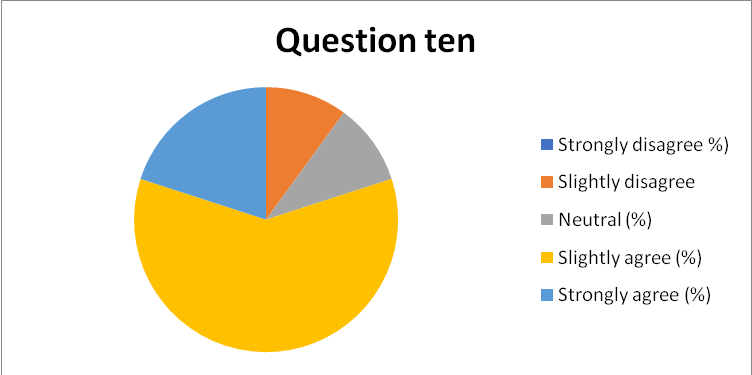
Appendix 20: Pie-chart 11: Summary of response to question 11
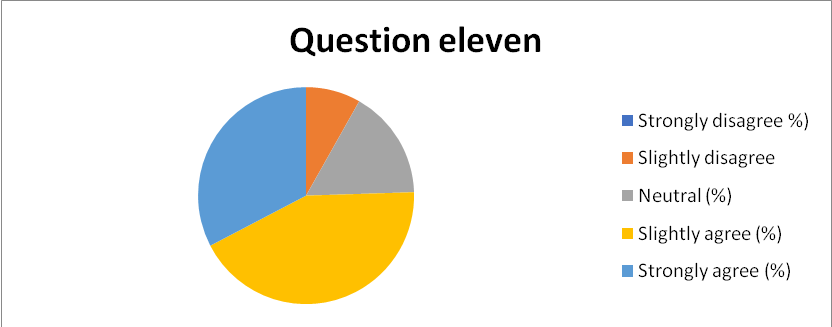
Appendix 21: Pie-chart 12: Summary of response to question 12
References
Anitha, J. (2014). Determinants of employee engagement and their impact on employee performance. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 63(3), 308-323.
Arslan, A., & Staub, S. (2013). Theory X and theory Y type leadership behavior and its impacts on organizational performance: Small business owners in the Sishane Lighting and Chandelier District. Social and Behavioral Sciences, 75, 102-111.
Bansal, H., Eldridge, J., Haider, A., Knowles, R., Murray, M., Sehmer, L., & Turner, D. (2017). Shorter interviews, longer surveys. International Journal of Market Research, 59(2), 221-238.
Battor, M., & Battour, M. (2013). Can organizational learning foster customer relationships? Implications for performance. The Learning Organization, 20(5), 279-290.
Belias, D., & Koustelios, A. (2014). Organizational culture and job satisfaction: A Review. International Review of Management and Marketing, 4(2), 132-149.
Clarke, E. (n.d). Organizational culture, system evolution, and the United Nations of the 21st century. Insider’s View, 127-133. Web.
Dasgupta, A., Suar, D., & Singh, S. (2013). Impact of managerial communication styles on employees’ attitudes and behaviours. Employee Relations, 35(2), 173-199.
Eman, M., Ayman, Y., & El-Nahas, T. (2013). The impact of corporate image and reputation on service quality, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty: Testing the mediating role: Case Analysis in an International Service Company. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 8(1), 12-33.
Guiso, L., Sapienza, P., &Zingales, L. (2015). The value of corporate culture. Journal of Financial Economics, 117(1), 60-76.
Habib, S., Aslam, S., Hussain, A., Yasmeen, S., & Ibrahim, M. (2014). The impact of organizational culture on job satisfaction, employee commitment and turnover intention. Advances in Economics and Business, 2(6), 215-222.
Harrison, J., & Wicks, A. (2013). Stakeholder theory, value, and firm performance. Business Ethics Quarterly, 23(1), 97-124.
Hogan, S., & Coote, L. (2014). Organizational culture, innovation, and performance: A test of Schein’s model. Journal of Business Research, 67(8), 1609-1621.
Homburg, C., Jozic, D., &Kuehnl, C. (2017). Customer experience management: Toward implementing an evolving marketing concept. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45(3), 377-401.
Hyland, P., Lee, A., & Mills, M. (2015). Mindfulness at work: A new approach to improving individual and organizational performance. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 8(4), 576-602.
Karatepe, O. (2013). High-performance work practices, work social support and their effects on job embeddedness and turnover intentions. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 25(6), 903-921.
Liden, R., Wayne, S., Liao, C., & Meuser, J. (2013). Servant leadership and serving culture: Influence on individual and unit performance. Academy of Management Journal, 57(5), 1434-1452.
Lukas, B., Whitwell, G., & Heide, J. (2013). Why do customers get more that they need? How organizational culture shapes product capability decisions. Journal of Marketing, 77(1), 1-12.
Martelo, S., Barroso, C., & Cepeda, G. (2013). The use of organizational capabilities to increase customer value. Journal of Business Research, 66(10), 2042-2050.
Mason, J. (2017). Qualitative researching. London, UK: SAGE.
Namasivayam, K., Guchait, P., & Lei, P. (2014). The influence of leader empowering behaviors and employee psychological empowerment on customer satisfaction. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 26(1), 69-84.
Nizam, I., & Paschal, A. (2016). Effects of organizational culture on employees performance: Case of Singapore telecommunication. International Journal of Accounting & Business Management, 4(1), 19-25.
Obeidat, Y., Masadeh, R., & Abdallah, B. (2014). The relationships among human resource management practices, organizational commitment, and knowledge management processes: A structural equation modelling approach. International Journal of Business and Management, 9(3), 9-26.
Pantouvakis, A., & Bouranta, N. (2013). The link between organizational learning culture and customer satisfaction: Confirming relationship and exploring moderating effect. The Learning Organization, 20(1), 48-64.
Park, J., Lee, H., & Kim, C. (2014). Corporate social responsibility, consumer trust and corporate reputation: South Korean consumers’ perspective. Journal of Business Research, 67(3), 295-302.
Rahimi, R. (2017a). Customer relationship management (people, process and technology) and organizational culture in hotels: Which traits matter? International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 29(5), 1380-1402.
Rahimi, R. (2017b). Organizational culture and consumer relationship management: A simple linear regression analysis. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 26(4), 443-449.
Rahimi, R., & Gunlu, E. (2016). Implementing customer relationship management (CRM) in hotel industry from organizational culture perspective: Case of a chain hotel in the UK. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 28(1), 89-112.
Ruiz-Palomino, P., Martinez-Canas, R., & Fontrodona, J. (2013). Ethical culture and employee outcomes: The mediating role of person-organization fit. Journal of Business Ethics, 116(1), 173-188.
Strom, D., Sears, K., & Kelly, K. (2013). Work engagement: The role of organizational justice and leadership style in predicting engagement among employees. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 21(1), 71-82.
Suma, S., & Lesha, J. (2013). Job satisfaction and organizational commitment: The case of Shkodra municipality. European Scientific Journal, 9(17), 41–52.
Wilkinson, A., & Redman, T. (2013). Contemporary human resource management: Text and cases (4th ed.). London, UK: Pearson Education.
