Paper outline
This paper is entirely focused on Tinapa Company’s 401(k) plan. It provides the plan of action that the company intends to utilize in implementing the plan and additionally highlights the guidelines and procedures that will guide the process. The paper also describes the funds to be availed as well as a highlight of the risks and returns associated with each individual fund. In general, it acts as a tool upon which interested parties can learn the basic on the company’s intended 4(k) plan.
Introduction
Purpose of This Summary
The purpose of this summary plan is to familiarize an employee/interested parties with important information concerning Tinapa Company 401(k) Plan (the Plan), which was developed by Tinapa Company (the Employer) on January 1, 2011. This summary, describes the important features of the Plan in non-technical language, and hence answers most employee’s/interested parties’ questions about the Plan. It replaces all prior announcements by the Employer about the Plan. Nevertheless, it is a summary, and if there is any conflict between the description in this summary and the terms of the Plan, the terms of the Plan will control implementation. If an employee has any questions/interested parties’ have any questions about the Plan that are not addressed in this summary, they should contact the administrator.
Administration of the Plan
The Plan is administered through a written trust agreement, and the trustees of that agreement are responsible for the Plan’s investment policy.
Plan summary
- Plan Effective Date: April 1, 1997
- Maximum Deferral: 15% of Salary
- Company Contribution: Discretionary
- Eligibility Requirements: Age 21 and 12 Months of Service
- Monthly Entry Dates: January 1st, & July 1st
- Change in Investment Mix: Daily
- Normal Retirement Date: Age 65
- Early Retirement Date: Age 55 and 10 Years of Service
- Vesting of
- Elective Contributions: 100% Immediate
- Employer Contributions: Begins from Date of Hire
- Years of Service Vested Percentage
- Less than 3 0%
- 3 but less than 4 20%
- 4 but less than 5 40%
- 5 but less than 6 60%
- 6 but less than 7 80%
- 7 or more 100%
- Death/Total Disability: 100% Vesting
- Hardship Withdrawals: of Your Elective Deferrals Permitted
- Loans: Permitted with a Minimum of $1,000
Transmittal Letter
Retirement Planning Officer,
Tinapa Company
P.O. Box 11234-001
Contact: 0234567-123
Dear sir/madam,
Based on the legal provisions on employee’s retirement’s savings and these letter present information of Tinapa’s 401(K) plan as may be deemed appropriate. The 401(k) plan fees included in this disclosure form represent the following: $250000 estimated 401(k) plan expenses for the period 01/01/2011 through 12/12/2011 Additional investment product information regarding fees may be obtained from the product prospectus, annuity contract or other similar documents. Additional information relating to plan administration services and expenses is contained in documentation provided by the service provider, including the contract for plan services. Other plan expenses may include legal fees for initial plan design and ongoing amendments resulting from changes in pension law or plan design and the cost of a mandatory annual audit.
Sincerely,
Signature of Retirement Planning officer
Date
Plan Participation
The Employer has assigned number 001 to the Plan; the accounting year of the Plan, called the Plan Year, begins January 1st and ends the following December 31st; and if it becomes necessary for An employee to bring legal action against the Plan for any reason, legal process can be served on either the Administrator, the Employer, or the Trustees.
Eligibility Requirements
The plan is designed to meet the requirements f the Internal Revenue Code. Accordingly there is no obligation to include all employees in the plan. While exclusion of certain employee categories is not the ultimate plan for the company, initial implementation will exclude hourly employees. This is meant to simplify initial administration of the plan. Additionally, to avoid costly non-discrimination testing, all the highly compensated employees will not be party to the initial plan. It is also important to note that all inclusion/exclusion criteria have been evaluated for qualification under the regulations promulgated by the Internal Revenue Service.
The maximum age entry is set at 21 years in line with the law while the minimum service duration is one year. A mandatory one year waiting period is provided for those employees who fail to get the initial coverage. It is mandatory for all eligible staff to satisfy eligibility requirements before being included into the plan. Employees who meet the aforementioned criterion and are presented at the day of the plans adoption will be considered eligible while those who fail to meet the guidelines provided as well those joining the firm will be subject to a awaiting period of one year before their eligibility is considered. This measure is meant to facilitate ease of information and data management.
Eligibility (Service years)
One must have served for 12‑consecutive month period amounting to not less than 1000 Hours of Service. An Hour of Service is any hour for which an employee has a right to be paid, including vacations, holidays, illness, back pay and maternity leave. Participation eligibility is pegged on the aforementioned duration and the corresponding hours of service. Employee’s first 12‑month computation period starts on employee’s employment commencement date. The second 12‑month computation period will overlap the first computation period and will start on the January 1st which occurs prior to the first anniversary of employee’s employment commencement date. Each succeeding 12‑month computation period will begin January 1st and end December 31st.
Break In Service Rules
Break in service arises in instances where an employee fails to meet 500 service hours and as such his/her participation in the plan will be ended. An employee will not incur a Break in Service if An employee are absent from work because of an authorized leave; and if An employee are absent from work because of illness or maternity leave, An employee will receive credit for up to 500 Hours of Service if necessary to prevent a Break in Service. An Hour of Service is any hour for which an employee has a right to be paid, including vacation, holidays, illness, back pay and maternity leave.
Entry Date
Participants join the plan on the first of January and July to coincide with the date upon which the respective employee meets the requirements necessary. Upon becoming a Participant, the Administrator will establish an Account to receive employee’s share of any Employer contributions and investment earnings and losses. Employees Account will consist of the following sub-accounts: the Elective Deferral Account, the Matching Contribution Account and the Non‑Elective Contribution Account.
Contributions and Allocations
Elective Deferrals
Employees can enter into a salary reduction agreement authorizing the Employer to withhold up to $10,000 of employees Compensation each calendar year. This amount is called an Elective Deferral, which the Employer will contribute to the Plan and allocate to the employees Elective Deferral Account. The exact amount an employee wishes to defer will be indicated in employee’s salary reduction agreement.
Salary Reduction Agreements
An employee can change his/her salary reduction agreement semi‑annually on dates determined by the Administrator. An employee can also suspend or cancel the agreement at any time upon reasonable written notice not to exceed 30 days. If employee cancels or suspends salary reduction agreement, he/she is not permitted to put a new agreement into effect until the next semi‑annual election period. If necessary to insure that the Plan satisfies certain non-discrimination tests, the Employer can also amend or terminate employee’s agreement. In any Plan Year in which an employee is not authorized the Employer to withhold from employees Compensation at the maximum rate permitted, An employee can authorize that a supplemental amount up to 100% of his/her Compensation be withheld for one or more pay periods. However, the amount withheld under salary reduction agreement plus the supplemental withholding cannot exceed 25% of employees Compensation.
Matching Contributions
The Employer may make a discretionary Matching Contribution each Plan Year. Matching Contributions made on employee’s behalf will be allocated to his/her Matching Contribution Account.
Allocation eligible participants
All staff employed prior to December 31st and who have completed a minimum of 1,000 Hours of Service during the Plan Year is entitled to employer allocations for that particular year. Participants who terminate employment before December 31st will only receive a contribution allocation (other than Matching Contributions) if they complete at least 1,000 Hours of Service before termination.
Top Heavy Contributions
This plan involves allocation of more than 60% of contributions by staff to key participant employees. For each year in which this Plan is top heavy, the Account of each Participant who is a Non-Key Employee and who is employed by the Employer on December 31st will receive a minimum top heavy allocation equal to the lesser of 3% of his or her Compensation or the percentage of Compensation allocated to the Accounts of Participants who are Key Employees.
Roll-over Contributions
If an employee participated in another retirement plan before being employed by the Tinapa, he/she can transfer (or rollover) to this Plan any distribution received from that plan if all legal requirements (and any requirements imposed by the Administrator) for the transfer are satisfied. Employees are advised not to withdraw funds from any other plan or account until they have receive written approval from the Administrator to roll those funds over to this Plan. If an employee decides to make a rollover contribution and it is accepted by the Administrator, it will be kept in employees Rollover Account, in which an employee will have a 100% Vested Interest. Employees Rollovers can be withdrawn from the Plan at any time.
Benefit upon Retirement
An employee is entitled to receive 100% of his/her Account after reaching Normal or Early Retirement Age. Normal Retirement Age in this case refers to the date at which a staff reaches 65 years of age or reaches his 5thanniversary since joining the plan. Early Retirement Age is the date an employee reaches age 55 and completes 10 Years of Service. An employee can elect to postpone retirement and continue working, in which case an employee can either postpone receipt of his/her account until actual retirement, or an employee can have his/her account distributed while still employed. An employee’s account will be distributed in a lump sum as soon as administratively feasible after an employee request payment.
Benefit upon Disability
If an employee becomes disabled before Account is distributed, he/she is entitled to receive the Vested Interest in his/her Account. Disability within this reports definition means physical or mental condition which qualifies for receipt of disability gains withincontext of social security Act. Such qualificeations are howver subject to note having used drugs and other intoxicants, intentional infliction of injury, unlawful engagements and not having some in the military entitling one to military disability pension. If employee’s Vested Interest does not exceed $5,000, it will be distributed in a lump sum as soon as administratively feasible after becoming disabled.
If Vested Interest is over $5,000, An employee can elect to have it distributed as soon as administratively feasible after becoming disabled, or an employee can defer distribution until a later date; but cannot defer distribution beyond April 1st of the calendar year which follows the calendar year in which he/she reaches age 70. When distribution is made, Vested Interest will be distributed in a lump sum payment.
Benefit upon Death
If an employee dies before Account is distributed, beneficiary is entitled to receive the Vested Interest in employees Account. For married employee, the spouse is the bonafide beneficiary unless stated otherwise in writing. If not married, an employee can name anyone to be beneficiary..
Benefit upon Termination of Employment
If an employee terminates employment before reaching Normal or Early Retirement Age, or before death or disability, he/she will be entitled to receive the Vested Interest in his/her Account. Where vested interest is below $5000, it is distributed as a lump sum as soon as such distribution is administratively feasible at completion of the plan year of employment termination. If employees Vested Interest is over $5,000, An employee can elect to have it distributed as soon as administratively feasible after the last day of the Plan Year in which employment is terminated, or An employee can defer distribution until a later date; but cannot defer distribution beyond April 1st of the calendar year which follows the calendar year in which employee reaches age 70. When distribution is made, Vested Interest will be distributed in a lump sum payment.
Determination of Vested Interest
Employees Vested Interest is the percentage of employees Account to which an employee are entitled at any point in time. An employee will have a 100% Vested Interest in employees Account if an employee reaches Normal or Early Retirement Age prior to termination of employment, or upon employee’s death or disability prior to that date. The determination of employees Vested Interest at any other time, including termination of employment prior to employee’s retirement, death or disability, is described in the next paragraph.
Employees Vested Interest in all Elective Deferrals allocated to employees Account will be 100% at all times; but employees Vested Interest in all Matching Contributions and Non‑Elective Contributions will be determined by the number of Years of Service An employee have completed as indicated in the vesting schedule following this paragraph. An employee will for purposes of vesting calculations, a year is considered to have no less than 1000 service hours.
Years of Service Vested Interest
2………….20%
3………….40%
4………….60%
5………….80%
6………….100%
Hardship Distributions
Up to 100% of elective deferrals can be withdrawn. This is in addition to a 1000% of an employee’s vested interest in matching contributions as well as non-elective contributions if such an action is meant to finance hardships including:
- Eligible medical expenses meant for the employee or his/her family members;
- Employee’s residence purchase with exclusion of payment of mortgages;
- Payment of tuition fee within the coming 12 months of employee or a member of his family; or
- Payments to save employee from getting evicted from, or mortgages foreclosure of employee prime residence.
An employee cannot make any Elective Deferrals for 12 months after An employee receive a hardship distribution, and the maximum amount An employee can defer for the calendar year after the distribution will be limited to employees maximum permitted deferral minus the amount An employee actually deferred during the calendar year in which the hardship distribution was made. A hardship distribution will be made in a lump sum.
Investment of Contributions
An employee will be able to direct the investment of employees Account. With regard to employees directed investments, An employee will be allowed to choose from a range of mutual funds and related investments approved by the Trustees. All earnings on the funds an employee invest will be credited to employees account. An employee will be able to switch between funds at such times as permitted by the Employer by contacting the Trustees or their designee in writing or through an 800 number which will be made available to an employee.
Any change an employee wishes to make to employees investment alternatives will go into effect as soon as practicable after the change is received by the Trustees or their designee. In addition, an employee can invest in any investment alternatives approved by the Trustees, including but not limited to stocks bonds and mutual funds.
The Trustees maintain the right to limit employee’s choice of investment vehicles and firms. All earnings on employees directed investments will be credited to employees Account. An employee will be able to switch between these alternative investments as often as permitted under the investment vehicles an employee choose. This Plan is in compliance with Section 404(c) of Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. It therefore allows employees independent control over his accounts assets. It follows then that plan’s fiduciaries, who include trustees, administrators and employer are free from any losses resulting from employee’s exercise of such powers
Plan Benefits Tax withholding
Distributions Not Subject To Withholding
Distribution eligible for roll over and consequently transferred directly to other qualified schemes or IRA’s are not subjected to tax withholding. Generally, any part of a distribution can be rolled over to another qualified plan or an IRA unless the distribution
- is part of a series of equal periodic payments made over employees lifetime, over the lifetime of An employee and employees beneficiary, or over a period of 10 years or more; or
- is a minimum benefit payment which must be paid to An employee because An employee have reached age 70. There are additional distributions that are not eligible to be rolled over.
Distributions Subject To Withholding
If an employee choose to have employees Plan benefit paid to an employee and the benefit is eligible to be rolled over, an employee only receive 80% of the benefit payment. The law requires that the administrator holds 20% of the benefits and remit the same to the IRS as an income tax. Where an employee receives distribution prior to 59 years of age, he/she may be subjected to 10%.
An employee cannot elect out of the 20% withholding. The possible alternative is for the employee to leave benefits within the plan or move it to an IRA or other scheme which allows rollovers. Roll over can still be done by the employee by simply putting the eligible distribution into IRA and if seeking 100% rollover, find alternative ways of funding the withheld 20%. Due to the complexities and frequency of changes in the federal tax law that governs withdrawal penalties and taxes, an employee should consult employees tax advisor to determine employee’s personal tax situation before taking any distribution from the Plan.
Other Information
Claims for Benefits
If an employee is not satisfied with a decision made about employees Plan benefits, an employee should submit a written claim to the Administrator. An employee will be notified on benefits denial within forty days upon application. If employees claim is denied, an employee can have the denial reviewed by making a written request to the Administrator, which along with a written statement explaining employees position must be filed within 60 days of the date an employee were notified in writing that the claim was denied. The Administrator may (but is not required to) provide an employee with a hearing, but must decide employees appeal within 60 days and give written notice of the decision.
Non‑Alienation of Benefits
Employees general creditors cannot garnish or levy upon employees Account and an employee cannot sell, transfer, assign, or pledge employees Account..
Amendment or Termination
Despite the plans implied permanency, it is subject to amendments or even termination by the employer. Upon termination of the plan, all participants are allowed access to 100% vested interests of their respective accounts of which are distributed in lump some. A written notification must be submitted to all employees in case of termination.
ERISA Rights Statement
ERISA entitles all the schemes participants to various rights and protections. It provides for all participants entitlement to non-chargeable examination of all plan documents which include insurance contracts, collective bargaining agreements and all such copies filed by the US Department of Labor. These may include well detailed yearly reports, objectives of the plan. This entitlement is exercised upon the employee making a formal request to the administrator.
Reasonable charges may be imposed on the employee for purposes of making the necessary copies. Other entitlements to the employee include summary of Plan’s annual financial report and a copy of the Administrator’s summary annual report. In addition an employee is entitled to a statement indicating whether he/she has a right to receive a pension at normal retirement age and any such benefits accrued if he/she stops working immediately. A formal request must be made for such a statement.If an employee lacks pension rights; the statement shows him/her the number of years before he/she becomes pensionable. To get pension, working is a necessity.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERITA) bestows obligations on the persons charged with the plans operation. They are refer to as fiduciaries and are obligated to act prudently and in the interest of the participants. The rights bar any persons from engaging in acts intended at stopping an employee from seeking pension benefits. When claims of employees are either partly or wholesomely rejected, employee is entitled to a formal explanation and the employee is entitled to demanding a review and reconsideration of his/her claims. ERISA provides clear guidelines of steps at the employee’s disposal in case of discontent.
For instance, if plan materials are not availed on time (within 40 days) even after formal request for the same, the employee may enter a federal suit against the administrator.similalry misuse of funds and mismanagement by fiduciaries can be brought before a federal court or the United States Department of labor as may be deemed appropriate by the employee.
It is then upon the court to decide which of the parties incurs the legal costs and fees incurred. Where the employ emerges victorious in the suit, the person sued may be order to handle the costs of suit while in case the opposite occurs, the employ may be obligated to pay the legal costs and fees. This may occur when claims made by the employ are found to be frivolous. Additional information on employ rights and entitlements are available at the U.S. Labor Management Services Administration, Department of Labor.
Mutual funds to be offered
Stock mutual funds are presumably the riskiest type of investment, although tend to yield the highest earnings in the long run. It’s important to note that not all investment in stock market is equally created. Some funds bear more risk and outperform the others in rewards. Most mutual funds are managed funds. There is a professional fund manager (or team of managers) that chooses the securities that are contained in the fund. The fund manager also decides when to buy and sell securities in the fund. Various options of mutual funds are availed for employees to choose from.
Conservative mutual funds
The funds basically use stocks, bonds and cash as a means of appreciating capital and revenue. They will however hold smaller positions in stocks as compared to average portfolios. Normally, 20% – 50% of such assets are directed to equity investments while 50-80% is channeled on assets with fixed income and cash. The funds will be directed through T. Rowe Price Personal Strategy Income Fund whose returns are as indicated below;
Trailing Returns
These funds are often the most attractive to investor considering that they bear minimal risks. Typically, investors are often interested in investing in areas where their investments are not only secure but also yield some level of returns in the long term duration. Investment of these funds is premised on steady growth corporations and excellent dividend payout history. They not only include stocks but also bonds which are often considered secure and relatively stable compared to stocks.
Despite not earning the large amounts associated with stocks, they are generally immune to volatility. It is estimated that they usually pay an interests rate of between 5 and 8 % and offer increased security. However, this does not imply their entire freedom form effects of stocks up and downs; it only implies the focus of administrators and managers on companies with enhanced stability.
Index funds: These funds mirror the market. They comprise of various stock which match market satiation. The funds change alongside the market changes i.e. when market goes up, they rise along and similar when the fund goes down, they too go down. They are often cited as the safest way to achieve steady return on investment. This is based on the assumption that the future is takes similar paths as defined by the past, a factor which is not guaranteed. The target index funds investments are as shown in the table below
Growth funds
This involves purchase of stock with increased likelihood of substantial growth in value. Various sub-categories are available under this option. These include aggressive growth funds which focus on areas of potential risks but highly rewarding in terms of returns, moderate growth fund which adopts a blend of stocks of moderate risks and value funds which focus on purchase of stock with relative stability but with lowly paying dividends. The fund however has flexibility in investing where best opportunities are presented. 65% of the funds are to be invested in common stocks. The funds may also be directed into convertibles, preferred stocks and security bond.
Targeted Equity Holdings
Percent of net assets
Large cap funds
Large cap funds will seek to appreciate capital and create secondary revenues. It will be invested in assets in large cap securities. The choice of investment companies will be based on their respective considered values with respects to comparable players within the market. The investments will basically be directed to companies with a proven record of paying out dividends. These will include the following corporations from which members may choose:
Small and medium cap funds
This fund is intended to attain long-term growth through investment in small and medium sized capitalization companies in the United States and to some extent Canada. Most of the companies to be invested in have a history of paying out dividends. Among the companies of focus for these funds include:
Sizes of the companies are defined through market capitalization rather than physical size of the company. Basically this is a measure of a company’s stock value. It is a product of the outstanding shares of a company and per share prices of the stock. Small caps are mainly invested in companies with less that $1 billion capitalization. Although they normally yield high returns, they are fairly risky.mid caps funds are invested in corporations with a capitalization value of between $1 billion and $8 billion. They are less risky than cap funds but yield relatively lower returns over the long term duration. Large cap funds on the other hand involve investing in companies of over $8 billion capitalization value and often similar to index funds. They are less risky but have relatively lower returns compared to mid-caps and small caps.
Aggressive growth funds
These funds entirely concentrate of capital gains optimization. The funds are invested in different security type’s e.g. stock sales on short term, as well as long term options. However though, these funds experience unfathomable volatility.
It is important to note that each stock investment options presents its own set of risks and returns and hence choice on which options to adopt should not be spontaneous but rather factual based. The graph below provides an overview of the risk versus returns associated with the proposed investment options.
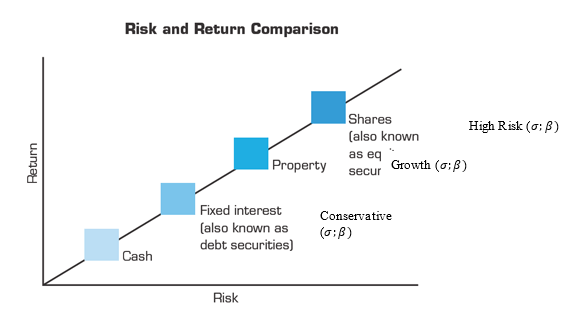
These funds are held in separate account to and invested through a number of alternatives.It basically seeks capital appreciation as well as current revenue growth. The table below highlights the choice of aggressive funds investment options available
Choice of investment funds
Choice of investment of options is guided by the risk return situation that an individual is willing to undertake. While individuals often want to obtain the highest possible returns, thy must also be willing to accept the risks associated with high return options. However, other than risk return situation, the amount of money an individual is willing to engage in investments and for what duration always comes into play. For instance, a person who wants quick returns and have his invested amount back would go for options with more speedy returns though of high risk? For safety, it is often advisable to choose a mix that is as protective of an individual’s investment as possible.
Often it would be advisable to put a large part of the investment in conservative investment options and a fairly good amount in growth funds. High risk investment just like the name suggests have increased risk of investment loss and hence should be allocated reduced amounts in order to safeguard ones investment. Perhaps it is important to mention that such an arrangement ensures that when loss occurs, its effect is rather minimal and the investor can easily overcome it. Putting a large percentage of investment in high risk investment is almost as true as gambling in the hoe that you will be the ultimate winner. On this basis, I would choose an investment portfolio bearing 55% conservative funds, 30% growth funds and 15% high risk funds.
This decision is basically on basis of assessing financial situation aspects including:
- How Much Have I Saved?
- How Much Money Will I Need?
- Risk Tolerance
- Market & Inflation Risk
- Time Horizon
- How many years until I retire
Risks associated with stock market investments include:
- Market Risk
- Short Term
- Risk of losing money due to market fluctuations
- Inflation Risk
- Long Term
- Risk that your investments won’t earn enough to maintain purchasing power.

