Introduction
All business organisations are established to make profits by focusing on delivering quality and competitive products and services. The competitive nature of most business markets make it necessary for the management of business organisations to focus on obtaining optimal quality.
Business organisations do not ensure quality simply to respect production and operational standards but to ensure positive consumer perception and high consumer loyalty. Quality assurance is more common in organisations that offer products than those that offer services but the level of competition in service industries makes it necessary for service providers to integrate Total Quality Management (TQM) gestures into their operations.
The aim of this paper is to propose research that will be designed to investigate the role of total quality management in business services. The proposed paper will analyse the availability of quality management in service organisations and the influence of TQM on the efficiency of these organisations’ services. The proposed research focuses on the role of quality management on the Information and Technology (IT) businesses because of the current increase and popularity of such businesses.
The importance of the IT industry cannot be overemphasized. Organisations that initially operated only through physical outlets are operating online services and this has increased the importance of IT services. The advantage provided by IT services is accompanied by a responsibility because business managers must ensure that they maintain total quality management in their IT operations.
IT services expose consumers to faster interactions with products and services and enables consumers to discuss the quality and experience offered by the products. Consumer satisfaction is not based only on the experience of the products and services but has shifted to the experience of the IT platform a company offers. The paradigm shift has created the need for managers to focus on total quality management when delivering their IT services.
Background and research problem
Quality Management
The increase in competition across various industries has made business organisations adopt TQM strategies. Researchers suggest that managers may perform TQM in any business across all segments of the market including service provision, government, and manufacturing (Tari, Molina, & Castejon, 2007), and that quality management improves services, consumer satisfaction, employee retention, better financial performance, improved competitive strength, and better output (Zu, 2009).
Businesses that implement a TQM strategy concentrate on achieving and maintaining superior outputs by applying management traditions for quality performance.
Feigenbaum, an early propagator of TQM explained the significance of the quality philosophy as a necessary performance ingredient for transforming business organisations (Zu, 2009). Quality management is defined as a group of standards and management strategies implemented by the management of an organisation to increase effectiveness and productivity.
Research studies have identified a correlation between quality management practices and organisational productivity, but these findings are inconsistent across research studies. The findings propose a positive association between quality management practices and organisational productivity and between other factors including excellence, performance, consumer perception, quality variables, cost effectiveness, and consumer satisfaction.
Most findings suggest a positive relationship between quality management and organisational performance (Zu, 2009; Kaynak & Hartley, 2005; Sila & Ebrahimpour, 2005; Prajogo & Sohal, 2003), while some are yet to draw conclusions on the relationship between the two variables (Nair, 2006; Agus, 2003).
Business performance in Information Technology
Many business organisations have applied Total Quality Management to achieve consumer retention, enhanced quality of services, profitability, and financial productivity. In the proposed research, three fundamental variables of business productivity will be considered namely consumer satisfaction, employee retention, and service excellence.
In business, especially in the IT sector, consumers’ expectations and opinion of services may continue varying due to dynamic IT business needs. Consumers will become more dissatisfied with the services offered by business organisation due the level of competition characteristic to the IT business. IT business organisations must work hard to enhance consumer customer retention because a single failure in the IT service may lead to consumer dissatisfaction.
A business’ ability to achieve employee retention indicates of effective quality management in businesses. Business firms seek to keep their employees satisfied (Oshagbemi, 2003) because business productivity is a function of employee satisfaction.
Similar to other businesses, IT firms may have some unsatisfied employees since people have different responses in work environments. Research suggests that different variables such as workplace environment, communication with superiors and contemporaries, equality, promotion prospects, pay, equality, job description, and benefits.
Many services, especially IT business services require direct interaction between consumers and employees and include interaction and social communication, which entail specific abilities and practices of workers that represent the business. Quality of service may also be viewed as operational efficiency. Some variables of quality service in the IT business include:
- User-friendliness, which defines the extra characteristic that improve the fundamental application of IT services, which include readability, speed, interphase smoothness.
- Conformance, which defines conformity of the IT business to various standards.
- Reliability, which describes the consistency in the performance of the IT service.
- Durability, which defines the level to which an IT service may perform constantly without failing.
- Serviceability, which describes ease of maintenance activities when necessary.
- Aesthetics, which defines interactive features including appearance, user-friendliness, and audio/visual systems.
An organisation can drive its operations towards an excellent IT system by developing an office of information technology that knows and applies the Total Quality Management standards. The theoretical background highlighted in this section of the proposal exposes the quality management features of IT businesses.
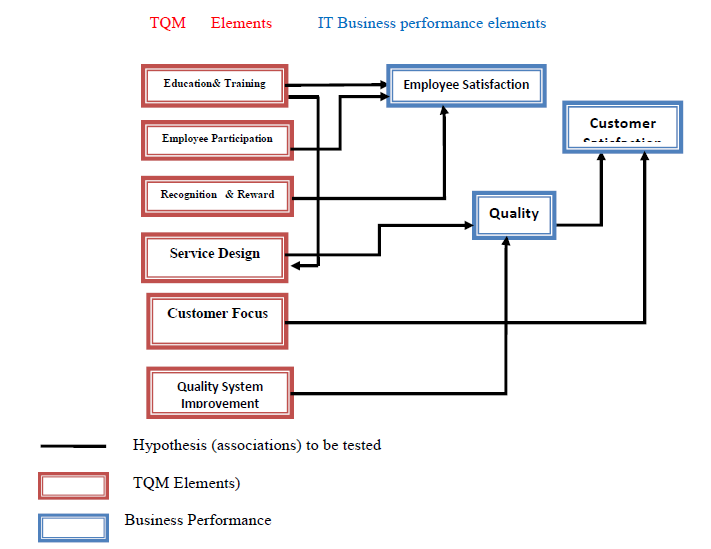
From the literature reviewed, it is observed that the elements of Total Quality Management (TQM) influence the variables that indicate performance in IT businesses. The literature indicates that consumer focus, employee retention, and quality of service contribute to the consumer satisfaction, while employee retention is a function of employee inclusion, benefits, recognition and development. Service quality and service design is based on system development and knowledge transfer, respectively.
Research question and objectives
The objective of the proposed research will be to investigate the relationship between quality management and service organisations and the objective will be achieved by analysing the relationship between variables that represent total quality management and the variables that influence service organisations. The proposed research will focus on the influence of total quality management on the productivity of IT service business organisations. The research objective will be achieved by responding to the following proposed research questions:
- What is the influence of total quality management on consumer satisfaction in IT business organisations?
- What is the influence of total quality management on employee retention in IT business organisations?
- What is the influence of total quality management on the quality of service in IT business organisations?
- What is the influence of total quality management on the quality of knowledge management in IT business organisations?
- What is the influence of total quality management on systems development in IT business organisations?
Research design (type of study)
The proposed research will employ a quantitative study. Quantitative studies involve numerical data used to draw conclusions to during research. The quantitative study will be hinged on a theoretical model which will include the different implementation variables of total quality management, and three variables of business productivity. The main hypothesis will be applied to investigate how total quality management influences business service quality.
Figure 1 illustrates the framework of the research design. The projected result for each variable will indicate the significance of the variable based on quality management and service quality. The links between the elements illustrates the potential relationship between the variables to be analysed during the study. The questionnaire will be developed according to the proposed research design and will comprise the variables and their links to be categorised by the participants’ opinions.
Figure 1: Framework for the Proposed Research Design
Data collection and analysis
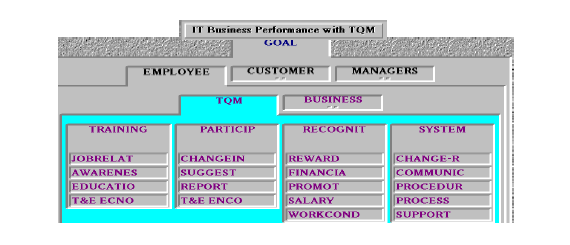
Data will be collected using the Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) model. The model will help the researcher study the factors that influence efficient service delivery as related in business firms. The AHP model is illustrated in the diagram below, and comprises five hierarchical levels.
The first hierarchical level is the goal level, which represents the performance of quality IT services. The second hierarchical level is the actors, which represents consumers, workers, and IT consultants. The third hierarchical level is the objectives, which refers to total quality management and business productivity. The fourth and fifth hierarchical levels are sub-measures of the third hierarchical level and comprise numerous variables.
Figure 2: AHP Model
Data collected from the questionnaire will be transformed to the AHP model based on the projected results. The projected results will provide the mean values of sub-measures to be assessed and compared with the other levels. E(x), the projected result of the random variable x will be calculated as indicated in the equation below.
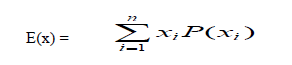
Where:
- n = number of x (random variables) values = 5
- xi = i
- i represents the variables, which include = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
- P(xi ) = xi probability
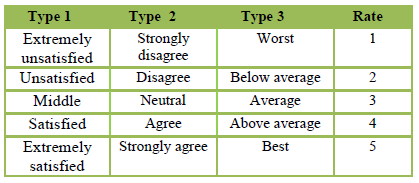
- xi = the values 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 used to compute different sets of five linguistic measures illustrated in the table below.
Table 1: Linguistic Measures
The suggested AHP framework has a broad structure and may reorganised to suit any business organisation, quality management variables, organisation strategic traditions, and significant factors influence business productivity.
Case Study
The research will involve a case study performed for an IT business organisation, which will have more than 100 workers grouped into the six major categories as illustrated in the diagram below.
Figure 3: Proposed Organisational Structure for the IT Service Business
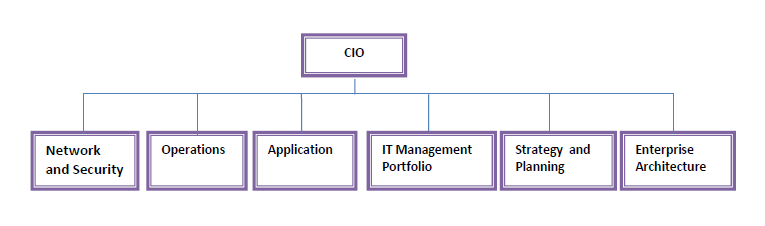
The case study will be designed to apply the idea of total quality management and to establish some applicable suggestions, standards, and recommendations for providing quality, which subsequently influences consumer satisfaction positively. Basically, gaining satisfying and competitive services, which may be provided by total quality management standards and methods, will theoretically be included in all functions and departments within the organisation.
The literature indicates the major concerns of IT businesses are consumer satisfaction and service quality. The proposed research will consider an IT business organisation proficient in diverse practices at the first and second hierarchical levels. During the research, the organisational structures of the selected IT organisation will be modified to improve its performance.
Possibly, including total quality management standards will enhance the quality of the records of the software but this may negatively influence the time necessary for product delivery since the procedure will extend the magnitude of each activity.
Including quality management standards will require some alterations in the business structure and the information department’s procedures. A guess and check method will be used to test the potential provisional keys for correcting the barriers. The feedbacks from consumers will be used to evaluate the effect of each modification process made by the selected IT service company.
Findings and Conclusion
The findings from the proposed research will be communicated textually and diagrammatically. The mean values of the total quality management variables and the IT business productivity variables will be presented on a chart. The Statistics for Social Sciences (SPSS) software will be used to perform an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) experiment to compare mean values for the two groups of variables (quality management variables and IT business performance variables).
The results of the analysis will be used to determine the relationship between quality management and service organisations. The analysis of each variable’s behaviour will be used to identify the variables with the highest and least correlation among other variables.
The analysis of the results will also be performed regarding the AHP model. The perception of the important variables from each hierarchical level will be considered. The analysis will be performed to identify the level of significance for the variables considered during the research.
The participants’ responses to the questionnaire will be the source of the input data and this may lead to an elimination of possible findings. The elimination of these findings will be negligible and will not significantly affect the results of the research. The result of the analysis will influence the researcher’s recommendation of where quality management needs to be improved. Quality management may be improved by modifying the organisational structure or the service delivery procedure.
Quality management may be improved by modifying the organisation’s structure because TQM is an incorporated system that affects all areas of the service providing organisation. The management of the organisation can effect change in its quality management system by modifying some aspects of the organisational structure.
Possibly the principal stride that the management of the organisation can take to create a standard TQM system, will be to create a suitable organisational system that maintains uniformity of the communication of quality standards across each department and every worker within the company. For example, the management may need to shrink some elements of the organisational structure, and increase other elements, to enhance service delivery speed amongst the shareholders and offer independence to the consultants.
Work instructions
Work instructions consist of detailed work documents such as instructions for performing the job. The IT department should develop various work instructions so all tasks can be conducted consistently. Work instructions are referred to the procedures and give precise details of how individual operations are to be carried out to enable them to be performed to the required quality. Work instructions should be easy to understand and not cause confusion.
To achieve this, every department should be involved in drawing up relevant work instructions. Every activity in the department should be examined in greater detail before the work instructions are made. In fact, this study cannot provide a detailed process of work instruction due of the limitation of the words. It is recommended that the company can hire a management consultant for assistance of the strategy and planning department to setup a work instruction.
The results of the research may recommend employee and consumer inclusion to improve total quality management service. During the survey, employees in the selected service organisation will be interviewed to gain their opinion on what they consider absent from the company’s quality management system. The responses of the employees can be analysed and used to proffer recommendations.
Consumer responses will serve as an important source of analysable information for providing recommendations. The research will seek different forms of critical responses for consumers, and will develop a centralised critical record structure, which will document all consumer complaints. The management of every service company must understand the effectiveness of responding to consumers’ complaints and the must develop a system that receives and examines consumer complaints for quality improvement.
Service organisations that fail to react to consumer complaints reduce the opinion of their consumers. The availability of online forums makes it easy for consumers to share their opinions with current and prospective consumers. The quality service management of every organisation must consider all consumer complaints since it makes it possible for organisations to increase the superiority of their services.
When the complaints of consumers are received, the service organisation must determine the important complaints which require extensive research to identify their fundamental reasons and to correct those reasons. Direct interaction with consumers is closely related to an emphasis on value and consumer service.
The results of the analysis will be presented textually and diagrammatically to illustrate the opinions of the consumers regarding different service quality variables. The diagrams used in this section of the analysis will illustrate the variables with the highest and lowest quality levels based on the perceptions of the consumers. Possibly, an increasing the significance of the business purpose, instead of the total quality management variables, will cause an increase in accepting consumers’ service quality.
Total quality management variables in the IT service sector have been reviewed and various total quality management variables and business productivity factors. The AHP model will be utilised to gain an understanding of the conditions for analysis due to the perception of consumers, IT service company workers and IT consultants.
Possibly, different variables will affect the outcome of the proposed research. For example, the results of the research may be affected by the opinions of the participants. The participants’ opinions may vary from other workers in the selected IT service firm. The research findings may be influenced by the academic qualifications and working experiences of the participants. Some participants may respond to the questionnaire to deliberately indicate a positive/negative condition in the organisation.
The suggested AHP framework will comprise various levels of total quality management variables and IT business productivity factors and individuals who will assist effective interactions with the variables but it will endure hierarchical difference between the participants.
The suggested model may be improved and restructured using a different network procedure that will allow all the variables to interact before they are affected by any limitations. The questionnaire may be restructured. Additionally, since the influencing standards may be ambiguous in IT based systems, the interactive variables may be considered by using ambiguous factors. The results may then be evaluated within the prearranged ambiguous group of the variables.
References
Agus, A. (2003). The Structural Linkages between TQM, Product Quality Performance, and Business Performance: Preliminary Empirical Study in Electronics Companies. Singapore Management Review, 27(1), 87-105.
Kaynak, H., & Hartley, Janet L. (2005). Exploring Quality Management Practices and High Tech Firm Performance. Journal of High Technology Management Research, 16(14), 255–272.
Nair, A. (2006). Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Quality Management Practices and Firm Performance – Implications for Quality Management Theory Development. Journal of Operations Management, 24(6), 948-75.
Oshagbemi, T. (2003). Personal correlates of job satisfaction: empirical evidence from UK universities. International Journal of Social Economics, 30(12), 1210-1232.
Prajogo, D.I., & Sohal, A.S. (2003). The Relationship between TQM Practices, Quality Performance, and Innovation Performance: an Empirical Examination. International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, 20(8), 901-918.
Sila, I., & Ebrahimpour, M. (2005). Critical Linkages among TQM Factors and Business Results. International Journal of Operations and Production Management, 25(11), 1123-55.
Tari, J. J., Molina, J. F., & Castejon, J. L. (2007). The Relationship between Quality Management Practices and Their Effects on Quality Outcomes. European Journal of Operational Research, 183(2), 483-501.
Zu, Xingxing. (2009). Infrastructure and Core Quality Management Practices: How Do They Affect Quality? International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, 26(2), 129-149.
