Executive Summary
One of the principal components of any company’s success is the way it demonstrates the support in terms of social guarantees. However, the company under consideration experiences difficulties due to the lack of sick absence management. It is, therefore, necessary to develop specific HR practices for it to reduce the personnel turnover, improve the public image as well as the perceptions of employees about the provided social guarantees. In order to develop a common HR strategy for the company, three scholarly articles were reviewed.
According to the results of the study, the efficiency of sick absence management depends on several factors. They relate to the provision of different conditions for short-term and long-term sick leaves, the common practices of career promotion in the organization, and the use of programs facilitating the process of taking sick leave. Thus, the recommendations for the company include the improvements in career management practices, changes in the existing sick absence systems, and the provision of different options for sick leaves for different categories of employees. In this way, the company would be able to increase its performance and profits without losing personnel.
Introduction to Research
The thesis of this report is to evaluate social guarantees provided by the company to its employees in terms of short-term and long-term sick absence and study the practices that can be used for further improvements. As the provision of social guarantees plays a significant role in the formation of employees’ opinions towards managers, it is vital to reveal the areas that need to be improved and define the primary target groups. The results of this study would contribute to an understanding of what measures are efficient for various types of employees.
Stages of the Research Process
The first stage of the research process is a critical review of the articles related to the research questions. It would allow evaluating the status of the current knowledge on the topic, which is essential for underpinning the research questions, and provide empirical evidence from the results of the company’s policies assessment. The outcome of this stage would include the general description and analysis of the sick management practices used by other companies as well as their proved efficiency or inefficiency. Such an approach would allow selecting the components for further research and consideration for the benefit of the chosen company’s strategy intended to improve the provision of social guarantees for its employees at different levels. The three articles that I have selected for this purpose are:
A Novel Approach to Early Sickness Absence Management: The EASY (Early Access to Support for You) Way: by Evangelia Demou et al., Work.
Collaborative Case Management to Aid Return to Work After Long-Term Sickness Absence: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial: by Cassandra Kenning et al., Public Health Research.
Preventing Sickness Absence With Career Management Intervention: A Randomized Controlled Field Trial: by Salla Toppinen-Tanner et al., Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.
The second stage is synthesizing the results of the articles in order to gain a clear picture of what improvements related to sick absence management are applicable to the situation of the company. This information is reliable on the grounds of the inclusion of the experience of researchers and their strategies implemented within other organizations. The combination of knowledge from various sources would be beneficial in terms of provision of a better outcome for the chosen company as it allows diminishing the risks while implementing a new strategy aimed at improving the situation with sick absence management.
It is followed by the third stage, which refers to the development of a HR strategy and its further presentation to key stakeholders. The provision of extensive information on the chosen strategy and steps of its implementation would allow all the participants to understand their tasks and see a clear picture of what outcome is expected. The report would also identify the level interest of the stakeholders and the reason for it. As a result, the company would be able to provide sufficient social guarantees for its employees.
Data Collection Methods
For this study, I will use two different data collection methods. The first method is the engagement of various organizations and their employees in the process of introducing materials and training the personnel within an established period. The results would be considered in terms of the success or failure of such interventions in the companies’ activities. The second method is the comparison of indicators of companies before and after implementation of new sick absence programs to reveal the tendencies. The disadvantage of these methods is in their insufficiency when used separately. However, they are advantageous in terms of the provision of comprehensive data on the issue.
The main features of the first data collection method, the engagement of specified companies in similar experiments relating to the implementation of strategies for improvements in sick absence management, include several conditions. They refer to the defined number of participants from organizations, the structure of presented materials, and the intended outcome of such an experiment. As for the second data collection method, it is characterized by the availability of sufficient quantitative data for further analysis allowing to demonstrate the impact of specific changes on the company’s indicators.
Thus, for example, the first method is efficient in terms of provision of information on the current situation in the company whereas the second method is an excellent tool allowing to analyze the received data. The combination of qualitative and quantitative methods of data collection makes them beneficial for the purpose of research. The difference between them is in the fact that the first method does not provide for a clear structure and requires additional measures whereas the second one is quite the opposite as it ensures clarity but lacks extensiveness.
Critical Review of Information Sources
The efficiency of the company’s performance is directly connected to its employees’ attitude towards management practices, especially the ones related to social guarantees. One of the essential guarantees is compensation and conditions for sick absence. Therefore, it is necessary to adapt the HR practices for the company to eliminate the current issues concerning sick absence management and thereby increase the employees’ satisfaction. Such measures would also allow managers to reduce personnel turnover in the long run. Therefore, my research question for the purposes of this study is:
Primary question: Does the company need to improve the compensation scheme and conditions for sick absence?
Secondary question: How do the current compensation scheme and conditions address these areas?
- Provision of social guarantees.
- Sick absence management.
- Engagement and collaboration.
- Retention.
Area of HR Practice for Investigation
The principal challenge for the company is its inability to provide similar conditions and compensation of sick leaves for all employees. Its cause is the lack of sick absence management and the use of legislation as the only guidance. This situation results in the lack of engagement of employees in the company’s activities and consequent decisions to leave the company in search of better options.
Analysis of Information Sources
A Novel Approach to Early Sickness Absence Management: The EASY (Early Access to Support for You) Way: by Evangelia Demou et al., Work. Managing sickness absence is a challenge for any company due to the existence of numerous causes deriving from varying conditions of its employees. It is, therefore, necessary to consider all the cases on an individual basis and, what is more important, identify a common compensation and management strategy for the improvements in employer-employee relationship. The failure to develop an HR strategy relating to sickness absence and its compensation might result in lost productivity as well as poor health of its employees.
This issue is a multidimensional one in terms of its impact on employees, employers, the healthcare system, and society as a whole, and therefore requires a complex approach. For this, it is vital to consider various circumstances, including cultural and occupational factors, the working environment, and others. This stage is required for both public and private companies to make early interventions in the case of sick absence. For this, the researchers proposed a model called EASY, which stands for Early Access to Support for You (Demou et al. 597).
This initiative is a completely new approach to sick absence management. The authors disagree that such programs as Sick Absence Management (SAM) project, Health and Work Assessment and Advisory Service, or NHS (The National Health Service) are sufficient for proper management (Demou et al. 598). They can be efficient in terms of finance, but they do not eliminate the necessity for early prevention of sick absence. The EASY model is the response to such challenges, and it addresses the issue by involving medical personnel, organizing health promotion activities, and making work modifications for the employees with specific health conditions.
This program also aims to facilitate communication between managers and employees in terms of sick absence. The EASY service is used from the first day of absence and provides support and guidance for employees in terms of overcoming illness as well as returning to work (Demou et al. 597). The EASY stuff gathers and records all the information so that the company does not need to assign a manager for it. According to the data from questionnaires designed for the companies who used the EASY services, they contribute to the introduction of preventive measures and gradually reduce the number of sick leaves (Demou et al. 601). As a result, the companies observe the reduction in sickness absence. However, not all health conditions can be covered by this program, but it can be considered as a ground for the company’s sick absence management.
My analysis: Sick absence management is a primary task for any company, fully agree. The failure to provide specific social guarantees without affecting the company’s profits would lead to ill-health retirement and, consequently, the need for new talents. This case demonstrates the greater effectiveness of preventive measures such as proper sick absence compensation and other conditions in comparison to the greater involvement of HR managers in constant search for potential employees. Moreover, frequent turnover would destroy the image of the company for new workers. Needless to say that it would be cost-ineffective in comparison with proper sick absence management. The results of the study are valid for any company that intends to improve its performance by facilitating the process of taking sick leaves.
Collaborative Case Management to Aid Return to Work After Long-Term Sickness Absence: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial: by Cassandra Kenning et al., Public Health Research: The level of employment is considered to be an indicator for the current labor market situation, but it describes it only in quantitative terms. However, to turn quantity into quality, one needs to provide specific social guarantees for all employees, either potential or existing. Such a policy would allow not only increase the engagement of employees and facilitate their return to work but also reduce the costs for all the actors involved in the matter. The conducted research considers the data of patients with long-term conditions for further use of sick absence management intervention (Kenning et al. 2). Nonetheless, such a measure requires specific personnel training and adaptation as the recruitment of employees after extended sick leave absence would be the sole responsibility of the company’s managers.
In the article, the authors argue that there are several health conditions, such as back pain or heart problems, which result in a long-term sick absence of employees, but these issues should not prevent people from working. Therefore, the implementation of HR policy should aim at assisting employees in returning to work and hiring new employees regardless of their state of health if they are qualified and able to perform the required tasks (Kenning et al. 3). It should include specific modifications for recruitment methods and the training of personnel to demonstrate the necessity of new measures.
The development of a collaborative case management program as a part of the study encountered certain difficulties. The principal challenge was the recruitment of personnel and the engagement of companies in it. However, the people absent from work were not willing to participate in the study (Kenning et al. 17). Therefore, it can be concluded that organizations should provide social guarantees, which would motivate the employees to return to work and outweigh the benefits provided by the government. Further research is possible only in the case of an increase in the participation of both employers and employees.
My analysis: The development of HR policies on sick absence management should be the primary task of the company. However, such programs as EASY are not enough for its successful implementation, and there is a need for consideration of other factors. Thus, the development of various compensation and aid programs without proper assistance in return to work would not produce good results. On the contrary, it would result in a continued loss of staff and damage to the public image of the company. As can be seen from this study, the company’s support should be equal or similar to the government’s support of people with long-term illnesses. Since the results of the research are limited by an insufficient number of participants, they cannot be considered as reliable, but allow managers to make another valuable assumption. Hence, the provision of various benefits for employees returning to work as well as assistance in the process would be a good complementary to such programs as EASY, which does not promote motivation to work.
Preventing Sickness Absence With Career Management Intervention: A Randomized Controlled Field Trial: by Salla Toppinen-Tanner et al., Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine: The prevention of future sickness absence seems to be a beneficial approach for a company. The authors of the article claim that one of the most efficient methods in terms of decreasing the number of long-term sick absence is group intervention (Toppinen-Tanner et al. 1202). It allows the company’s managers to prevent sick absence from turning into permanent disability. There is a direct connection between long-term sick absence and career management, and it allowed the authors to develop the idea of health-safe promotion.
The future behavior of employees significantly depends on the HR policies of the company in terms of social guarantees provision and career promotion. Thus, the more attractive benefits they receive, the fewer people would be willing to take an extended sick leave (Toppinen-Tanner et al. 1202). It leads to the conclusion that career management group intervention is the right mechanism for controlling the sick absence time of the company’s employees. Moreover, such measures allow managers to reduce repeated sick leaves of the personnel.
However, career management group intervention does not seem to have an impact on short-term sick absence. In this case, the company needs to provide sufficient compensation for its employees to make sure they are in good health that would allow them to continue work. It implies the need for demonstrating the career perspectives primarily to the employees on short-term sick leaves. Some employees would be unable to perform the tasks at work and therefore leave the company anyway. Hence, the focus should be on the ones who can return, and it will result in the reduction of personnel turnover.
My analysis: I agree that career management interventions, together with proper social guarantees, increase the probability of employees’ return to work after a sick absence. The correspondence of the planned and the actual amount of participants allows to conclude the study’s’ authenticity and validity. However, it applies mostly to short-term sick leaves. The combination of these two provisions would allow the company to eliminate the risks contained in introducing beneficial programs for returning from sick absence and thereby increase the employees’ motivation to return to work.
The hypothesis is that the extensive use of the EASY program or any other similar option in combination with measures on ensuring the return of employees after sick leaves would be beneficial. Together with preventive measures, they would create a positive work environment and social guarantees for all employees. The implementation of such programs and measures would be a costly process, which would provide benefits for both employees and employers over time. However, it would not take more than 2-3 months to fully introduce the new policy within the company and improve the conditions and compensation for sick leaves.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The researchers of sick absence management focus on various aspects of this type of social guarantees. Such aspects include the development and introduction of special programs intended to facilitate the collaboration of managers and employees during their sick absence. They also consider possibilities of continuing work for employees with chronic illnesses and the prevention of sickness absence through career management intervention. However, the measures mentioned above do not provide a clear picture of what sick absence management in a company should be. Hence, it is vital to combine their findings in one study to develop a strategy for the development of sick absence management practices.
First of all, the company needs to facilitate the procedure of taking sick leaves in the case of short-term absence. If employees have no issues with understanding the system, and it is easy for them to use, the company would be able to reduce the risks of losing personnel due to complications of their health conditions. Thus, short-term sick leaves would not turn into long-term ones that might result in employees’ resignations.
Second, there is a need for the motivation of employees through career promotion and the provision of other benefits at work. Hence, the company needs to complement the system of short-teams sick leaves with specific training and programs to demonstrate the benefits of work for it. Third, the creation of a flexible schedule or opportunities to work out of home for people with chronic illnesses would allow the company’s managers to maintain a high level of performance for all employees. The implementation of the measures described above would not only contribute to the creation of a unique sick absence management practices in the company, but also improve its public image, efficiency, and, as a result, profits.
Business Report for Stakeholders
Table 1. The Key Stakeholders of the Company.
The creation of new sick absence management practices provides for the involvement of principal stakeholders of the company. Employees and line managers demonstrate the highest level of interest in it as the provision of social guarantees would consequently increase the performance. The interest of line managers and owners in the matter is medium as they are indirectly related to HR management processes (see table 1). However, all of them would participate in these practices.
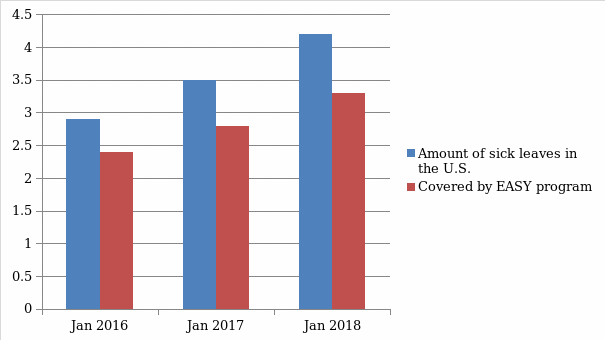
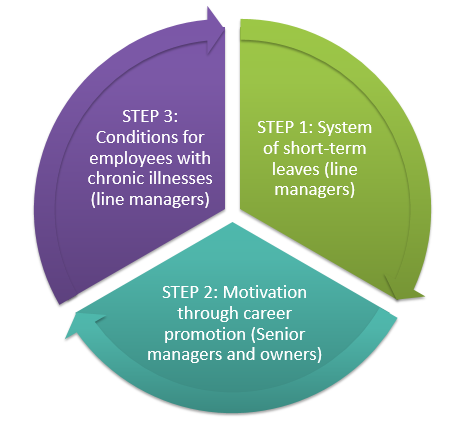
Thus, line managers would develop the systems for short-term and long-term leaves corresponding to steps 1 and 3, and senior managers and owners would motivate the employees through career promotion (see fig.2). The effectiveness of EASY services for increase in the amount of workers who reported the intention to take sick leave is shown on the example its possible implementation in the United States (see fig.1). The combination of such measures would ensure efficient control over the employees’ health conditions and sick absence management practices in order to increase the company’s profits.
Works Cited
“4.2 Million Workers Have Illness-Related Work Absences in January 2018”. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2018. Web.
Demou, Evangelia, et al. “A Novel Approach to Early Sickness Absence Management: The EASY (Early Access to Support for You) Way.” Work, vol. 53 no. 3, 2016, pp. 597-608. Web.
Kenning, Cassandra, et al. “Collaborative Case Management to Aid Return to Work After Long-Term Sickness Absence: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial.” Public Health Research, vol. 6, no 2, 2018, pp. 1-48. Web.
Toppinen-Tanner, Salla et al. “Preventing Sickness Absence With Career Management Intervention: A Randomized Controlled Field Trial.” Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, vol. 58 no. 12, 2016, pp. 1202-1206. Web.

