Abstract
The adoption of best practices by multinational enterprises is a necessity because of globalization challenges such as stiff competition, diversity, and increased creativity and innovation. Starbucks is an international corporation that has achieved great success through the implementation of ethical business practices in the areas of human resource management, environmental conservation, ethics and compliance, and corporate social responsibility.
The company’s business practices are founded on key corporate values that are stipulated in its mission statement. Starbucks’ sustainability is founded on the application of ethical practices in dealing with employees, suppliers, consumers, and stakeholders. The processes of recruitment and hiring as well as employee training and development reflect the corporation’s values.
Introduction
Starbucks Corporation is a multinational enterprise that was founded in the United States of America in 1971. It grew from a few stores to more than 30,000 locations around the world. The corporation’s business practices are the major reason why it has grown tremendously over the past few decades to become one of the leading coffeehouse chains in the world. The firm sells a wide variety of products: hot and cold drinks, whole-bean coffee, evolution fresh juices, espresso, and snacks among others. Starbucks’s success can be attributed to effective human resource management, environmental sustainability, corporate social responsibility, and ethics and compliance practices.
Literature Review
Starbucks’ globalization strategy is augmented by business practices that reflect its corporate culture. Human resource management practices ensure that talented employees are hired and retained, and customers receive the best service (Akdeniz 52). The main goal of human resource management is to enhance organizational performance through effective recruitment and hiring, increased employee motivation, and reduced turnover. Starbucks engages in various human resource practices that are founded on corporate values, customer service, and the treatment of employees as partners (Akdeniz 54).
Its recruitment and selection practices are rigorous and are designed to promote the firm’s working culture. The organization has reward and employee-development policies that are aimed at improving human capital and retaining qualified individuals.
Sustainability is one of Starbucks’ main goals that reflect its organizational values and a commitment to environmental protection. In that regard, the corporation has a mission statement that aims at guiding environmental leadership in all business operations (Ferrell 34). According to the statement, the corporation is committed to developing innovative solutions for change, buying and selling environmentally friendly products, adopting environmental responsibility as a corporate value, and sharing information regarding environmental issues with partners. Components of the sustainability strategy include greener stores, reducing waste, promoting recycling and reusability of materials, and purchasing environmentally friendly coffee (Ferrell 34).
Discussion
Human Resource Management Practices
The Starbucks Corporation is popular for exemplary human resource management practices that facilitate the attraction and retention of experienced and talented employees. The company treats its personnel as an integral part of corporate growth. Enhancing diversity is one of the most important aspects of HRM practices (Mello 53). Employees are provided with various incentives regardless of their age, sex, sexual orientation, religion, race, or ethnicity (Akdeniz 65).
For example, they enjoy comprehensive health benefits (medical, dental, and vision care), stock options, and retirement plans (Ferrell 54). Open communication is encouraged in order to ensure that employees are informed about the firm’s operations (Normore 149). Management teams hold frequent forums to answer employee questions and solve any job-related issues. Starbucks believes that a good employee should be able to conduct their duties well, satisfy the customer, and possess an aptitude for social consciousness (Ferrell 57). This is contained in its mission statement that describes the major objective as to inspire and nurture the human spirit through quality service delivery.
Employee training is another HRM practice that Starbucks values highly. The company offers a variety of training programs that are aimed at instilling in employees, values that define the firm’s corporate culture (Leinwand and Mainardi 94). For example, workers learn how to foster the values in their service delivery. In addition, they are taught effective communication in order to create customer loyalty.
The corporation’s human resource practices encourage the development of better working relationships within the organization (Ferrell 64). Every individual is treated equally. For instance, part-time and full-time employees receive similar benefits that include saving plans, medical cover, income protection, discounts, and free drinks (Mello 67). The “Adoption Assistance Program” supports workers who adopt children by reimbursing a certain percentage of the costs incurred during the adoption process (Leinwand and Mainardi 99). The aforementioned benefits enhance employee motivation, increase the overall output, and decrease rates of turnover.
Recruitment and hiring are among Starbucks’ most important human resource practices because employees are an invaluable asset. In that regard, interviews are thorough and held over several locations with different managers (Lemus et al. 25). The interview process is reflective of the organization’s working culture. Personality is one of the aspects that managers look for during hiring (Flamholtz and Randle 86).
They recruit individuals with qualities such as customer service skills, competency, and the ability to communicate effectively (Normore 151). Starbucks treats employees as partners. Therefore, new personnel must possess pleasing personalities that augment their qualifications, work experiences, and achievements. Howard Schultz (Starbucks founder) once stated that the key to success is hiring people who have similar values to those of the organization. This belief guides the recruitment and hiring processes.
Environmental Conservation
Sustainability is one of Starbucks’ priorities, and it involves environmental conservation, mitigation of climate change, and the utilization of renewable energy. The company is committed to reducing the environmental impact of its operations in order to attain organizational sustainability goals. In that regard, it closely scrutinizes all business operations in order to find ways of integrating new solutions that can create a sustained change (Leinwand and Mainardi 111). For example, green stores, greener cups and packaging, green power, and climate change strategies are aimed at enhancing sustainability (Flamholtz and Randle 74).
Starbucks’ Greener Stores program encompasses the construction of more than 10,000 environmentally friendly stores across the world in the next 6 years (“Environment”). One of the program’s objectives is the generation of solar and wind energy that will run stores in Canada and the United States of America (“Environment”). The firm is working with experts such as the World Wildlife Fund and SCS Global Services to attain this goal (Flamholtz and Randle 74). Starbucks aims at producing coffee and serving it sustainably to customers. The design and construction of the stores will focus on energy efficiency, renewable energy, water stewardship, a healthy environment, and waste diversion (“Environment”).
The company’s sustainability strategy also involves the reduction of waste and the encouragement of recycling and reusability of materials. It aims at doubling recycled cups and packaging materials by 2022 after attaining a goal of serving 5 percent of its beverages in personal tumblers by 2015 (see fig. 1).
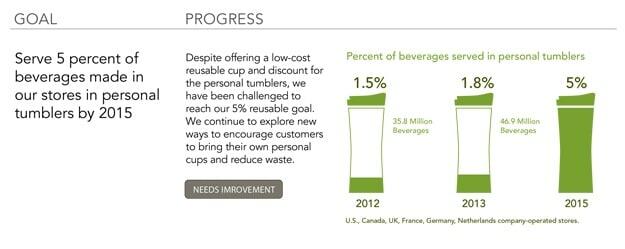
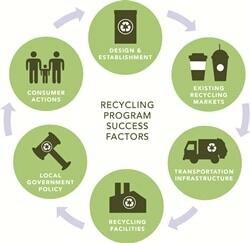
Cup innovation, reusable cups, and the development of recycling infrastructure are among the company’s initiatives that are aimed at reducing the impact of waste materials generated at its stores (“Environment”). The success of the recycling program depends on factors such as government regulations, consumer actions, development of infrastructure, and tapping into existing recycling markets (see fig. 2).
Starbucks advocates for model legislation and best practices as part of an initiative to encourage recycling. The main goal is to create recyclable and reusable cups that will reduce waste and promote sustainability. Starbucks is committed to playing a key role in mitigating the global challenge of climate change (Flamholtz and Randle 64). A climate strategy has been in place since 2004, and it includes various aspects: renewable energy, climate adaptation, energy conservation, and mitigation programs.
Starbucks only hires suppliers who adhere to its environmental mission statement and environmental purchasing policy. They have to share in the company’s values that are stipulated in the mission statement (“Environment”). The organization’s environmental purchasing policy requires all suppliers to meet relevant regulatory standards, encourages the purchase of environmentally friendly products, and promotes the use of materials that are easy to recycle.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Starbucks defines corporate social responsibility as the commitment to conduct business in a manner that generates economic, social, and environmental benefits in the communities in which it operates (Leinwand and Mainardi 122). Generally, it refers to the commitment to be responsible to all stakeholders. In contemporary society, there is an increasing awareness among companies of the need for corporate responsibility. On one hand, consumers are interested in more than being associated with a company’s brand. On the other hand, employees are looking for firms that have strong values and corporate cultures.
Shareholders invest in an organization that has a good reputation (Leinwand and Mainardi 65). Investing in communities is one of Starbucks’ social responsibility agendas that is achieved through corporate cash contributions, in-kind donations, and the Starbucks Foundation. Partnerships with organizations such as Conservation International (CI), Calvert Community Investments, and CARE ensure that cash contributions are used appropriately in the development of communities. Community-based programs that Starbucks funds include Make Your Mark and Choose to Give.
Starbucks views corporate social responsibility as an investment. In that regard, the organization invests in sustainable business practices that encourage the production of high-quality coffee. In communities where they purchase their coffee and offer their services, they invest in local organizations that help to improve the lives of the people (Lemus et al. 29). Competitive wages and benefit structures are also part of the company’s social responsibility program.
For instance, they offer employees opportunities for stock ownership as one of the ways to attract and retain qualified individuals. Starbuck’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) has on many occasions stated that these practices give them a competitive advantage with regard to the attraction and retention of employees (Flamholtz and Randle 87). They aid in reducing the costs associated with hiring, training, and turnover. Starbucks is known for corporate involvement in volunteer work in communities where it operates.
Ethics and Compliance
One of Starbucks’ corporate values is ethical business operations. Maintaining transparency in all activities is one of the factors that have fueled organizational success (Lemus et al. 31). The company’s Ethics and Compliance statute protects its reputation and promotes the creation of an organizational culture that is based on principled leadership and integrity (“Ethics & Compliance”). The Standards of Business Conduct policy provides guidelines regarding the legal and ethical standards that employees are required to follow. The Coffee and Farmer Equity (CAFÉ) Practices policy offers guidelines that ensure the ethical purchase of coffee from farmers (“Ethics & Compliance”).
Starbucks partners with other organizations with similar values to ensure that they make a difference in coffee-origin countries. One of the strategies used to enhance the sustainability of the farms is to purchase organic coffee (“Starbucks Ethical Sourcing”).
The company’s commitment to this objective includes the purchase of Shade Grown Mexico and Fair-Trade Certified coffees. The Fair-Trade system allows farmers to join cooperatives and sell their produce to buyers that offer favorable prices (“Starbucks Ethical Sourcing”). Organic products ensure that the firm sells coffee that has not been produced with the utilization of synthetic chemicals (“Starbucks Ethical Sourcing”). The business partners with Conservation International in order to ensure that farmers cultivate shade-grown coffee that has a less environmental impact.
Conclusion
Starbucks is a multinational enterprise that has grown immensely in the past two decades. The success can be attributed to its business practices in areas that include human resource management, environmental conservation, ethics and compliance, and corporate social responsibility. Human resource practices are aimed at recruiting and hiring qualified individuals, motivating and developing employees, lowering turnover, and ensuring that customers receive high-quality service. Corporate social responsibility practices promote the welfare of the communities in which Starbucks operates.
Environmental conservation practices aimed at reducing the environmental impact of the company’s operations and mitigate climate change in order to enhance sustainability. Ethics and compliance practices involve the development of quality relationships with suppliers and the promotion of moral business practices.
Works Cited
Akdeniz, Can. More than Coffee: The Secrets of Starbucks Success. Can Akdeniz, 2014.
“Cup and Materials.” Starbucks. Web.
“Environment: Pioneering Sustainable Solutions.” Starbucks. Web.
“Ethics & Compliance”. Starbucks. Web.
Ferrell, Linda, et al. Business Ethics: Ethical Decision Making and Cases. 11th ed., Cengage Learning, 2017.
Flamholtz, Eric, and Yvonne Randle. Growing Pains: Building Sustainably Successful Organizations. 5th ed., John Wiley & Sons, 2015.
“Greener Cups and Packaging.” Starbucks. Web.
Leinwand, Paul, and Cesare Mainardi. Strategy that Works: How Winning Companies Close the Strategy-Execution Gap. Harvard Business Review Press, 2016.
Lemus, Edel, et al. “Starbucks Corporation: Leading Innovation in the 21st Century.” Journal of Alternative Perspectives in the Social Sciences, vol. 7, no. 1, 2015, pp. 23-38.
Mello, Jeffrey. Strategic Human Resource Management. 4th ed., Cengage Learning, 2015.
Normore, Anthony, et al. Handbook of Research on Effective Communication, Leadership, and Conflict Resolution. IGI Global, 2016.
“Starbucks Ethical Sourcing of Sustainable Products.” Starbucks. Web.
