Introduction
Tesla, Inc. is one of the leading manufacturers of electric vehicles, battery cells, and energy solutions. The company aims at building a complete vertically integrated production system to ensure an undisrupted supply chain management and product delivery to its customers (Tesla, 2021). Since its establishment in 2003, the organization managed to build facilities in several locations producing cars, batteries, as well as such products as Powerwall, Powerpack, and Solar Roof (Tesla, 2021).
The core of the technologies exploited by Tesla is lithium-based cells, and the organization has direct ties with lithium producers in different parts of the world (but mainly in Africa and Asia) (Olivetti et al., 2017). The company is famous for its innovative approach to the car manufacturing business with its vertical integration and direct sales to customers.
Tesla Supply Chain
The backbone of the company’s supply chain management is its focus on vertical integration, so the vast majority of Tesla’s suppliers are Tier 1 suppliers (see Figure 1). The organization under discussion collaborates with diverse companies providing materials to its manufacturing facilities (with major facilities located in the USA and China) (Naor, Coman and Wiznizer, 2021). One of the major strategies the company has used to reduce costs and lower down prices has been the design and production of batteries (Gianesello, Ivanov and Battini, 2017). This approach has translated into the company’s major competitive advantage, making Tesla cars expensive but still affordable.
The company is committed to the development of sustainable relationships with its suppliers to build a resilient supply chain. At present, a larger part of suppliers is US-based (40%), while 30% are located in China, Japan, and Switzerland (Wu and Yang, 2017). The rest of Tesla’s suppliers are located in different parts of the world (mainly Africa and Asia). Tesla attempts to encourage its suppliers to establish sustainable practices and often qualifies some of its partners providing certification (Wu and Yang, 2017). The organization has clear policies that are developed for suppliers who have to comply with high standards regarding environmental aspects and labor force factors.
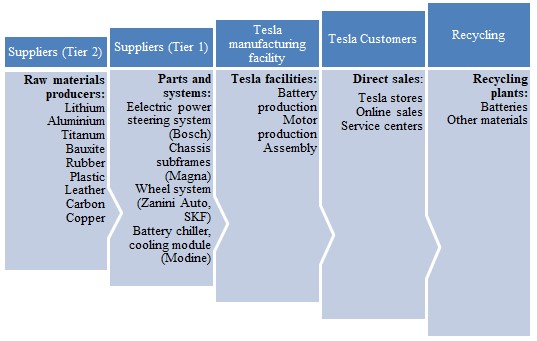
As far as sales policies are concerned, Tesla is famous for its Silicon-valley approach as it does not collaborate with distributors but sells directly to customers. This strategy has both advantages and downsides, but it, by all means, makes the organization stand out (Wu and Yang, 2017). On the one hand, this strategy enables Tesla to control prices and lower them down while developing close ties with customers.
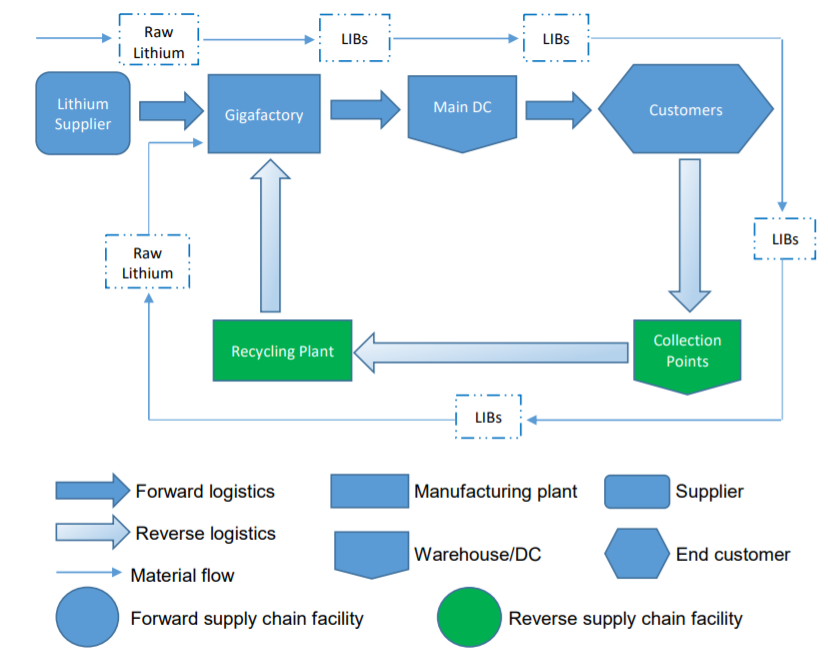
On the other hand, the company has to face litigation issues in some states as Tesla sales are banned in some parts of the USA. Online sales have become another innovation Tesla has tried to employ to win a larger market share. Service centers and collection points, as well as recycling facilities, are important elements of the company’s supply chain, making Tesla an innovative car manufacturer with arrays of loyal customers across the globe (see Figure 2).
Electric Vehicle Industry Challenges
Tesla’s supply chain is rather resilient, and its vertical integration helps the company address potential disruptions. In some cases, these efforts are characterized by limited effectiveness. One of the major challenges the automotive industry (as well as the vast majority of industries) faced was the COVID-related restrictions (Cavaliere, 2021; Naor, Coman and Wiznizer, 2021).
The lockdowns countries chose as their response to the pandemic had adverse effects on the automotive industry. Electric vehicle production turned out specifically vulnerable due to the disruptions in lithium supplies. Car manufacturers and battery producers were unable to satisfy the existing demand as lithium suppliers had to halt their operations and needed time to retain their functioning. The industry has not recovered yet, and researchers note that more time will be needed to address the outcomes of lockdowns (Cavaliere, 2021). The supplies of other materials also suffered, but the associated supply disruptions did not have such detrimental effects on the industry.
In addition to the severe shock linked to the pandemic, the industry still faces its traditional challenges. The capacity of batteries remains one of the basic issues manufacturers are trying to address, as this factor has a considerable effect on purchasing decisions (Gianesello, Ivanov and Battini, 2017). Tesla cars are popular for their powerful batteries and luxury design. At that, the company is still trying to enhance its batteries capacity so that their (and other manufacturers’) electric cars could compete effectively with fueled vehicles.
At present, the latter is still faster and have an almost limitless range as the infrastructure is highly developed in all countries of the world. The networks of gas stations enable drivers to access almost any location in the world (as drivers can also bring fuel in tanks). These options are still unavailable to electric vehicles with quite underdeveloped infrastructures of recharging points and limited battery capacities.
Technological and Data Driven Supply Chain Communication and Information Requirements in Electric Vehicle Industry
Innovation is one of the primary features of the electric vehicles industry, so communication and information management play an essential role in organizations’ life cycles. Companies have to ensure proper analysis and management of big data to ensure the effectiveness of their supply chain. Producers utilize numerous applications and software products to manage big data and ensure the most effective use of resources. Blockchain technology is gaining momentum due to its focus on transparency and reliability. This technology is attractive to electric vehicle manufacturers because they can optimize their inventory flow (Raj Kumar Reddy et al., 2021). Blockchain technology is instrumental in building networks of reliable multi-tier suppliers and partners.
The automotive industry also benefits from the use of various software tools, such as simulations or decision-making facilitators (Gianesello, Ivanov and Battini, 2017). For instance, managers often try to forecast the availability of resources and potential disruptions. As far as communication is concerned, companies choose among a variety of applications. They use corporate information systems to ensure that internal communication is safe (Raj Kumar Reddy et al., 2021). Communication with partners also occurs with the use of safe channels and corporate information systems. Companies need to access certain databases and information systems to manage the flow of their inventory. The instant interchange of data is critical, which has become evident in the post-COVID business world.
Disruptions in the flow of materials and resources lead to major challenges in supply chain management, which can be illustrated by the current situation with battery production. The shortage of lithium has led to delays and companies’ inability to satisfy market demand (Cavaliere, 2021). The industry has undergone a number of shocks between 2020 and 2021 related to the maintenance of proper communication and interaction patterns with partners. Slow recovery is apparent, but many suppliers left the market, which made automotive producers develop new business ties.
Supply Chain Effectiveness Assessment
To evaluate a company’s progress and ensure its sustainable development, it is possible to utilize diverse assessment instruments. A balanced scorecard is one of the tools managers utilize to estimate whether their organizations perform well and manage to attain the established goals (Pearce II, Robinson and Mital, 2018). This measurement helps companies to identify weaknesses in the operations, improve their functioning, and ensure the achievement of strategic goals. The focus is on such areas as financial performance, internal business processes, learning, and customer service.
- Vision: Tesla aims at accelerating the “world’s transition to sustainable energy” (Tesla, Inc., 2021, p. 4).
- Strategy: Tesla’s strategy is characterized by a vertically integrated business model and a focus on user experience.
Based on the analysis of the balanced scorecard, it is possible to assume that Tesla is characterized by high performance and high potential to grow further. The company is one of the leaders in the market of electric vehicles in the United States, as its market share reached 72% of the U. S. electric vehicle market in April 2021 (Kay, 2021). Hence, the target of an 80-percent-share is attainable, making the organization’s supply chain strategy effective. The establishment of a Texas-based facility will have a positive impact on Tesla’s growth and enables the company to increase its market share through higher sales.
The new facility will also contribute to lowering down the costs that are planned to go down to $25,000. This goal has not been achieved yet, revealing some weaknesses of the existing strategy. The reduction of production costs can be instrumental in achieving this objective.
Overall, it is possible to conclude that the company’s supply chain management strategies are effective and instrumental in achieving the established goals. The company develops close relationships with multiple suppliers across the globe to reduce costs and ensure the undisrupted delivery of vehicles and inventory. The construction of several major facilities in diverse geographic locations is also an effective strategy that can ensure the reduction of costs. The focus on staff training and a wide range of internship programs can contribute to enhancing the overall performance of each employee, each team, and the entire organization.
However, some gaps are yet to be addressed for the sustainable development of the company. Tesla should invest more in innovations as it should improve its batteries capacity and reduce vehicles’ prices to win a larger market share. This can be attained by using more efficient processes and more functional materials.
Recommendations
Stakeholders’ Engagement
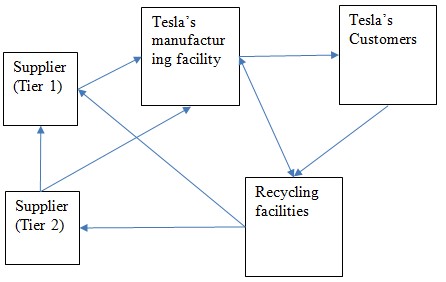
To address the weaknesses of the existing supply chain, Tesla should implement a number of strategies. The engagement of stakeholders in the supply chain operations is efficient but can be improved. As mentioned above, the company has Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers, although the latter are not numerous (see Figure 3). Moreover, suppliers (Tier 2) provide resources to Tesla, thus, becoming Tier-1 suppliers. Further vertical integration is important as it can minimize disruptions and reduce costs, which are critical goals for the company’s development (Pearce II, Robinson and Mital, 2018).
These stakeholders can also be engaged in recycling incentives, becoming a part of the corresponding cycle. After the recycling of some products, the produced raw materials can be sent to suppliers and Tesla manufacturing facilities. This strategy can contribute to achieving Tesla’s objectives regarding sustainability enhancement. The company articulates its commitment to a higher level of sustainability and reducing its environmental footprint. Recycling is one of the effective methods to attain this goal. Further investment into innovations will be needed to ensure the creation of the necessary technologies and approaches.
Participation in various sustainability projects, collaboration with local communities and authorities, and the issue of effective policies can be instrumental in enhancing stakeholders’ engagement. The company develops policies that encourage its partners to become more environmentally responsible (Tesla, Inc., 2021). The organization’s collaboration with local communities and authorities has proved to be effective as it has led to positive changes for the environment and the creation of a positive image of the company. The involvement of Tesla’s partners in such projects can make their outcomes more far-reaching and their effects more lasting.
Relationship Management
Relationship management is essential for maintaining proper links with customers and partners. Cross-sales can be utilized as a strategy to enhance the collaboration between Tesla and its customers and partners. Cross-selling involves the provision of additional products and services to other stakeholders (Pearce II, Robinson and Mital, 2018). The provision of recycling services can be seen as one of the forms of this collaboration.
Tesla offers its customers to recycle cars and components (with the focus on batteries), but these incentives can be further developed. Partners can also be engaged more effectively as participation in such projects can improve their image and help them gain certain benefits related to compliance with higher standards. The close interaction with authorities can be an important premise for the effective use of this strategy. The creation of the infrastructure to deliver components to recycling facilities is an illustration of the area for close partnerships with Tesla’s suppliers.
Counteracting the Challenges in the Electric Vehicles Industry
As mentioned above, the COVID pandemic unveiled some of the weaknesses of the existing supply chain management in the electric vehicles industry. Companies appeared to be vulnerable to the supplies of such vital raw materials as lithium (Cavaliere, 2021). Hence, it is essential to ensure the availability of such critical resources. Again, vertical integration is one of the ways to address this issue as internal policies and infrastructures can assist in building resilience to raw material supply disruptions (Wu and Yang, 2017). The company can better accommodate to potential restrictions and limitations as controlling internal processes and operations can be implemented while the collaboration with multiple partners is associated with higher risks.
To address another challenge typical of the industry, Tesla needs to develop close partnerships with other organizations working on increasing the capacity of batteries. This strategy has proved to be effective as the collaboration between Tesla and Panasonic has led to the development of innovative products and considerable advancements in the area of battery production (Wu and Yang, 2017). The car manufacturer should continue developing such relations and implement various incentives and projects with other organizations.
The focus should be on innovation and sustainability, which will have a positive impact on stakeholders, as well as the entire industry. Electric vehicles are still less attractive due to their limited range, so the creation of more powerful and reliable batteries, as well as the introduction of other innovations, will be beneficial for all companies operating in the industry. The cooperation with authorities related to infrastructural projects is another effective strategy to implement. The creation of effective networks of recharging points across diverse geographic locations is an important step, leading to the evolvement of the industry.
Supply Chain Communication and Information Requirements
The latest developments in communication technologies offer multiple opportunities to electric vehicle manufacturers. One of the opportunities Tesla can benefit from is the use of blockchain technology. This IT advancement can help Tesla in locating and building proper relationships with suppliers and other partners. As mentioned above, the minimization of the risk of supplies disruptions is one of the central goals, so companies need to have detailed background information about their partners.
Tesla should incorporate blockchain technologies to choose the most reliable suppliers, which is specifically important with raw materials providers (Raj Kumar Reddy et al., 2021). Blockchain technology is associated with transparency and reliability, which can help make evidence-based choices regarding partnerships.
It can be advisable to use the latest applications to facilitate the decision-making process. Various software products are now available to manage communication internally and externally, so companies can benefit from the use of the most advanced information systems that are safe and efficient (Pearce II, Robinson and Mital, 2018). Tesla needs to keep in touch with various companies of different sizes. The level of integration and collaboration also differs, which has to be considered when making decisions, regarding the use of a communication channel.
Communication with customers is also an important aspect related to supply chain management. Tesla pays specific attention to this area as the satisfaction of customer’s needs is a part of the company’s mission (Tesla, Inc., 2021). The organization (as well as its leader) is active on various social networks, which is essential for developing rapport through a high level of transparency and openness.
Tesla’s communication with customers during the pandemic and in the post-COVID environment was instrumental in enhancing clients’ loyalty and attracting new customers. It can be recommended to adhere to this approach and continue being an active communicator via social networks. This communication channel has become an integral part of human life in the modern world, so the company can articulate its messages effectively using this channel.
Supply Chain Strategy
Based on the analysis of Tesla’s performance, it is possible to identify the major challenges the organization has to face. One of the goals for the organization under consideration is to retain the leading position in the market of electric vehicles, where competition is steadily intensifying. One of the operational objectives to attain is associated with the number of deliveries as the company is still struggling with implementing its plan of 500,000 deliveries. Tesla’s establishment of two new facilities located in the United States and Europe is one of the effective strategies to address the issue. These facilities will ensure the company’s presence in the American ad European market and contribute to the rise of sales.
At the same time, it can be advisable to utilize the Six Sigma approach to manage supply chain operations. It is vital to identify the most vulnerable aspects of the production process and the existing supply chain operations (Pearce II, Robinson and Mital, 2018). The chosen solutions should become the basics of the new facility’s functioning. Planning and effective implementation are central to the effective implementation of this strategy. Further investment into innovations and the development of new solutions is also necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is possible to note that Tesla remains one of the leaders in the industry of electric vehicles, but it should constantly evolve and develop innovative strategies to retain this status. The company has faced certain losses and challenges related to the COVID pandemic and growing competition in the field. The market is becoming more competitive, so it is important to ensure the use of effective supply chain management instruments. Tesla aims at increasing the number of delivered vehicles and the reduction of its products’ price. The opening of gigantic facilities, the use of efficient software facilitating supply chain management and relationship management, and being active on social networks are instrumental in achieving the set goals. Tesla should invest into innovation to come up with new products and services.
Reference List
Cavaliere, V. (2021). ‘Elon Musk says Tesla prices are increasing because of supply chain disruptions across the auto industry’. Insider. Web.
Gianesello, P., Ivanov, D. and Battini, D. (2017). ‘Developing a blockchain framework for the automotive supply chain: a systematic review’, International Journal of Inventory Research, 4(4), pp. 257-280.
Kay, G. (2021). ‘Tesla’s global market share fell to its lowest level in over 2 years as electric car competition heats up’. Insider. Web.
Naor, M., Coman, A., and Wiznizer, A. (2021). ‘Vertically integrated supply chain of batteries, electric vehicles, and charging infrastructure: a review of three milestone projects from theory of constraints perspective’, Sustainability, 13, 1-21.
Olivetti, E., Ceder, G., Gaustad, G. and Fu, X. (2017). ‘Lithium-ion battery supply chain considerations: analysis of potential bottlenecks in critical metals’, Joule, 1(2), pp. 229-243.
Pearce II, J. A., Robinson, R. B. and Mital, A. (2018). Strategic management: planning for domestic and global competition. 14th edn. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
Raj Kumar Reddy, K., Gunasekaran, A., Kalpana, P., Raja Sreedharan, V. and Arvind Kumar, S. (2021). ‘Developing a blockchain framework for the automotive supply chain: a systematic review’, Computers & Industrial Engineering, 157, pp. 1-14.
Tesla. (2021) About Tesla. Web.
Tesla, Inc. (2021) Annual report on form 10-k for the year ended December 31, 2020. Web.
Wu, L. and Yang, W. (2017) ‘Tackling supply chain challenges of Tesla Model 3’, Operations Management Education Review, 11(1), pp. 5-34.

