Abstract
Leadership styles are adapted to the demands and the situations at hand. Leadership is more of the needs of the people and that of the organization and less of their personal needs. Leadership aims at guiding the organization towards a shared dream. Visionary leaders create an environment that allows innovation, sharing of ideas, and positive change in the organization. In the modern competitive business world, leadership should emphasize affiliation and democratize the running of the organization, promote teamwork, harmony, and ensure that people connect with each other. The following study focused on the leadership styles of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook in the Apple Company.
In order to gain insights into the leadership, a cross-sectional research design was used. The study entailed the use of secondary data, which was obtained by mining the information from purposely selected databases and management agencies. A quantitative examination system was utilized to test the hypotheses. The findings of the study revealed that leadership style has an impact on the performance of the organization.
For instance, effective leadership was found to be associated with job satisfaction, which in turn led to Apple’s high return on assets. In addition, effective leadership was correlated with high profits and the efficient use of resources. In conclusion, effective leadership helps an organization to manage risks, uncertainty and create a competitive advantage for the organization.
Introduction
Overview
This chapter covers the background to the study, problem statement, research objectives, hypotheses, and the significance of the study.
Background to the study
Leadership plays a significant role in the success of any organization, irrespective of its line of production. Excellent leadership helps individuals, groups, and the entire organization to adapt to the new changes and appreciate the prevailing conditions. Change is a great challenge for many organizations; therefore, good leadership is required to ensure that people cope with the new work requirements. In modern organizations, leaders are expected to be innovative and highly knowledgeable because this would help them survive in a highly competitive business environment (Maxwell 2007).
Leadership should leverage on knowledge and skill of the employees in order to create groups that are committed to the goals of the organization. According to Bernard (2003), employees committed to the company goals results in the successes of the organization. In the technology industry, Apple Company is leading in terms of service delivery and service quality. The company was founded and run by Steve Jobs, who was considered to be a visionary leader with excellent leadership skills and managerial prowess. The company is associated with innovation as one of the core values.
Steve Jobs’ leadership qualities were credited to the success of the company, which has dominated the technology industry for several years. As a leader, he devised various strategies aimed at steering the company to the next frontier (Keller 2006).
The primary aim of the study was to explore how effective leadership can lead to the success of an organization. Effective leadership is the backbone of any organization, and it is a recipe for the success of the organization (Schuttler & Burdick, 2010). A visionary leader focuses on the success and advancement of the organization. This is achieved by being both a leader and a manager. This study identified variables based on the explicit review of the current literature regarding the concept of leadership.
According to Keller (2006), efficient leadership means being inclusive and allowing followers to participate in the decision-making process of the organization. In addition, the leader is responsible for organizing training programs to enable the followers to be on par with the changes in the business (Malik, Danish & Munir 2012). An effective leader also champions innovation in the organization and also rewards the followers for a job well done (Sipe & Frick 2009).
A leader plays the role of assessing the performance of the followers in the organization and offers them rewards according to the efforts that they make to the organization (Kolenda 2001). It is also the duty of the leader to set up standards and objectives of the company that needs to be met by all the followers (Watson 2006). The leader also mitigates risks in the organization by efficiently allocating resources in order to achieve the desired ends. The productivity of the organization is enhanced by constantly training the followers of the organization in order to enhance innovation in the organization.
Statement of the problem
There are several studies that have taken place in relationship with styles of leadership and the effects they have on organizational performance. Leadership practices and the perception of the managers play an important role in job satisfaction (Rothfelder, Ottenbacher & Harrington 2012). Organizations that are successful usually ensure that there are systems that lead to organizational growth and employee job satisfaction.
Burke (2001) pointed out that job satisfaction involves the general contentment of all workers and top management. Even though there are many studies carried in relation to leadership, the studies have been general and aligned to specific leadership styles such as transformational and transactional. Therefore, the following research aimed at exploring the leadership styles with the main focus on the profile of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook in Apple Company. Apple’s case study plays a critical in ensuring that managers understand leadership styles that can increase the productivity of their employees and hence put in place strategic plans to gain a competitive edge.
Adetule (2011) noted that Apple’s prosperity is credited to the effective leadership strategies of Steve Jobs. Steve Jobs never made it through formal education; he was not considered to be an ‘A’ student. Thus, the study explored the performance of the organization in relation to leadership styles and the success of the organization. The study concentrated on Apple Company, which is in the private sector. Thus, there is still a gap that needs to be addressed in relation to public institutions, where bureaucracy leadership is commonly practiced. Nevertheless, the research provided a framework that forms the basis for organizational leadership styles.
Objectives of the study
Leadership entails influencing people and giving guidance to an organization that leads to increased productivity that is the basis for effective leadership (Batool 2013). An effective leader should be in a position to respond to work environment challenges and communicate the goals of an organization. The purpose of the research was to look into the functions of top management’s mode of leadership and the implication on the performance of Apple Company under the leadership of Steve and Tim. Thus, the specific objectives of the study included:
- To critically analyze the relationship between the type of leadership and the motivation of employees in an organization.
- To critically evaluate how visionary leadership relates to transformational leadership and the overall impact on the creation of competitive advantage for the organization.
- To critically evaluate the relationship between visionary leadership and the productivity of an organization by investigating a case example of Apple Company under the leadership of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook.
Research Hypotheses
In order to address the above-mentioned objectives and examine the relationship that is observed between leadership and the organization’s success, the following hypotheses were formulated and tested in the research:
- H1: There is a positive relationship between leadership type and the employees’ motivation and job satisfaction.
- H2: There is a kind of relationship between visionary leadership and transformational leadership styles.
- H3: There is a positive relationship between visionary leadership and creating a competitive advantage for an organization.
- H4: There is a positive relationship between visionary leadership and the productivity of an organization.
- H5: There is a positive relationship between visionary leadership and the organization’s profitability and return on assets.
- H6: There is a positive relationship between visionary leadership and abilities to manage risk and uncertainty in an organization.
- H7: There is a positive relationship between visionary leadership and the efficient use of resources.
Justification for the study
There are several studies that have taken place in relationship with styles of leadership and the effects they have on the success of an organization. For instance, studies have shown levels of inconsistency in relation to transformational and transactional leadership. Some studies have indicated an important relationship found between the style of transformational leadership and not the transactional style (Allen and Wilburn 2002). However, the findings are not absolute as the data obtained pointed that despite the leadership style, some organizations still have a marked level of success.
Any leadership that is considered to be proficient normally impacts the level of performance of an organization and business manageability in the midst of competition (Kang & Singh 2006). The study gave a basic assessment of whether the leadership style championed by Steve Jobs and Tim Cook was sufficient for the Apple Company. The findings of the study are of great value to policymakers. They will provide the policymakers with a wide exposure to leadership and change management. Thus, the study enables managers and policymakers in organizations to adopt the relevant strategies that are in line with the situation. The findings of this study also add to the body of knowledge of related studies concerning the usefulness of effective leadership styles.
Scope of the Study
The success of an organization can be determined by job satisfaction and commitment to the organization. Job satisfaction is a state of positive emotion that comes about as a result of an experience at the job. According to Johnson (2007), leadership influences the type of attitude that employees have concerning the firm. In addition, leadership is a critical determinant of the performance systems and strategies employed in an organization.
The study flowed in conformity with the main objective, which was to determine the usefulness of effective leadership in the performance of the organization. Secondary data and statistical techniques were applied to study and explain the variables related to the research objectives. Therefore, the study focused on the leadership styles of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook.
Structure of the Dissertation
The dissertation consists of five chapters. Chapter I is an introductory one, and it presents the overview of the whole dissertation, the background of the study, the problem statement that is focused on the study’s issues and significance, objectives of the study, research hypotheses, and justification of the study. In addition, this chapter also provides the scope of the research, as well as notes on the structure of the dissertation.
Chapter II proposes the literature review discussing the notion of leadership, the relationship between the leadership and management as it is presented in the scholarly literature, leadership traits, the models of the leadership, leadership styles and their impact on performance, the connection between leadership and organizational goals, as well as steps to set appropriate goals for the company. The chapter also discusses leadership theories and focuses on the leadership for innovation, referring to the example of Steve Jobs as a visionary leader.
Chapter III analyses the methodology used for the research while explaining the sampling strategies, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. Chapter IV analyses the findings and presents the discussion of the study results. The main focus of this chapter is on the analysis and interpretation of the statistical data related to the research problem and hypotheses. Chapter V is the concluding one, and it provides not only conclusions related to the study results but also appropriate recommendations to address the research problem. Finally, the learning statement is provided to explain the findings from the perspective of learning.
Literature Review
Introduction
The section assesses past investigations that have explored leadership styles, theories, and applications inside the organizations. Above all, the part mainly assesses the way in which visionary leadership has been tied in different organizations to create and force changes to be in force. As well, it highlights key variables and ideas that encompass the restorative system and the diverse ways that relate to the subject. Data included in this study were from dependable sources, principally from past works. In particular, there has been a sharp focus on the past studies distributed in books, diaries, and checked in articles. Some key databases sought the guidelines for incorporating emerald knowledge, leadership, and business diaries.
Leadership and Management
Leadership is a complex phenomenon that cannot be specified or described definitely (Gratton & Jones, 2004). There are many scholars who have undertaken to study the differences between leadership and management. According to Gratton and Jones (2004), the conflict between leadership and management is attributed to the organizational culture. Leadership defines and changes the culture of any arrangement. On the other hand, management affairs relate to the refinement of the organization. Thus, the arguments depict the extensive diversity in terms of the behaviors of the leadership and the managers (Avolio, Walumbwa & Weber 2009).
The relationship between leadership and management has been explored in capitalist economic organizations. The functions of the leader and the manager have been compared and contrasted with the intention of illustrating their differences. While the leader is the trailblazer, the director is the administrator; the leader originates the idea that is implemented by the director. The leader takes the risk to explore new ventures, while the manager’s role is to maintain the current venture.
The leader concentrates on the individuals everywhere while the manager lays down the organizational frameworks. A leader will make the best choice while the supervisor will choose the best. A leader creates an organizational culture while the manager operates within the culture. This already demonstrates that leadership is on another level as compared to management. There is no vivid definition of leadership that is universally accepted; this is attributed to the fact that leadership varies from one field to the other (Gratton & Jones 2004).
Leadership Traits
The leader of an organization plays the role of inspiring trust in the employees. The leader also has the privilege to transform the entire organization in line with his vision and passion. The actions of the leader empower the rest of the people; hence, making it possible to learn new ideas and concepts (Wanasika 2009). The leader is the first person to start any change process in an organization as the rest follow. The original definition of leadership is associated with personality, while the recent definition of leadership is associated with the ability of the person to influence.
Leadership is a wide concept that is respected across the globe, and that is the reason the definition of leadership changes from one organization to the other. There has been a limitation associated with the studies on leadership that has been done since the early 1990s. This limitation has been attributed to the fact that the scholars who study leadership and the individuals who are the leaders have been unable to give a universal definition of leadership accurately (Abbas & Asghar 2010).
Leadership is the act of talking to people to follow a particular trend. It also entails the leadership to offer guidance and influence. Therefore, the actions that come with leadership include: guiding, influencing, overseeing, commanding, directing, and controlling (Avery 2004). The leader has the challenge of innovating creative initiatives that are to be followed by the rest; he has to demonstrate the capability to lead from the top.
The skills of the leader will enhance speedy decision making in the organization. Leadership has a broad depth because it is considered to be universal. Sakiru et al. (2013) argued that leadership and management are very close, but it should be noted that they are not similar. Every leader should demonstrate strong and articulate management skills (Maxwell, 2006).
There are numerous variables that characterize viable leadership. These variables include the culture in the organization, the behavior of the members of the organization, and the personality of the person entrusted to lead the organization. Many leaders who are considered to be successful have so many positive traits. Successful leaders are flexible, thoughtful, commanding, concerned, enigmatic, powerful, and confident. Steve Jobs possessed most of the listed traits.
Models of Leadership in Current Organisations
Abbas and Asghar (2010) argued that the current global business environment necessitates effective leadership. Wanasika (2009) noted that effective leadership recognizes progressions and enacts systems that lead to the expected outcomes. Abbas and Asghar (2010) further asserted that leaders who make the viable changes must demonstrate ownership of learning, aptitudes, ability, and capabilities required in mapping out the path towards accomplishing results that fulfill both the clients and the collaborators. Consistent change is inescapable in the current business atmosphere and shapes the leadership models (Kippenberger 2002). In relation to visionary leadership, Bass (2005) stated that it is linked up to imaginative methodologies that enable businesses to progress (Avolio, Walumbwa & Weber 2009).
The leadership and execution of the firm have been identified to be most related by numerous analysts (Keller 2006). Matha and Boehm (2008) argued that leadership entails authoritative techniques that help in inspiring employees to execute projects that align with the strategic goals.
Leadership Style and Performance
Many scholars have pointed out that leadership is a very important concept in any organization. Leadership has a great impact on organizational behavior and organizational culture. Rafferty and Griffin (2004), in their study of transformational leadership, argue that efficient leadership positively impacts the organization by fostering quality management and, in turn, better results. In the process of the advancement of any organization, leadership assumes an element part towards forming the eventual fate of the organization.
The excellent leader offers a sense of inspiration and motivation for the workers in the organization, and also at the same time, helps the workers to meet the organizational goals and targets (Avery 2004). Leadership is an element that is enshrined in the behavior of an individual; this helps the individual to mentor a group of individuals to accomplish a specific target that is shared by all of them (Gallos 2008)
Leadership consists of strategies that include motivating, inspiring, and encouraging individuals with the aim of stimulating growth and development (Watson 2006). It is always a philosophy that any leadership style directly reflects on the performance of a particular organization. Rafferty and Griffin (2004) pointed out that there is a direct relationship between leadership and performance. Today’s business environment has evolved, and it is highly competitive in nature. This calls for pragmatic and visionary leadership that can spur invention and innovation for the sustainability of the organization (Rafferty & Griffin 2004).
Many studies that explore the relationship between leadership and organizational performance have revealed that efficient leadership has a positive impact on the development of the organization and also on the performance of the organization. Leadership provides a dynamic platform that equips the organization to handle new challenges that might come along the organization’s operations (Abbas & Asghar 2010).
The performance of the organization is reflected through attaining maximum profits, producing high-quality products and services, efficient marketing strategies, and excellent financial returns. All of these are determined by the quality of leadership that is in place in the organization (Polelle 2008). The performance of the organization is what makes the organization stand out among other competing organizations in the same line of business or operations. In addition, the performance of the organization reflects the level of productivity of the workers. The level of output of the workers in the organization is determined by revenues and profits generated. The factors determine the growth of the organization and its ability to compete favorably in the complex business environment (Kouzes & Posner 2003).
Many researchers who have undertaken to study the concept of leadership have focused their researches on how effective leadership impacts the performance and the development of organizations. Therefore, it is very important to understand the relationship between the concept of leadership and its impacts on any organization (Adetule, 2011). Blanchard and Cathy (2002), in their study, argued that effective leadership is the engine that drives any organization. The organization should achieve economies of scale, and therefore, gaining a competitive advantage and stand out among its peers is the dream of any leader (Aquinas 2006).
In a study of the transactional leadership in an organization, Bass (2005) found that the leadership style has the impact of enticing the employees of the organization to meet the set objectives by availing the required necessary resources.
In this case, the job performance of the organization’s members will determine the number of rewards. Visionary leadership, on the other hand, involves looking at the future of the organization and strategically setting visions that create a sense of commitment and dedication among the organization’s members so that they work to achieve the goals (Avery 2004). Visionary leadership has an overall impact of inculcating a sense of togetherness, dedication, trust, and motivating the members of the organization. This, in turn, raises the level of performance of the organization (Gallos 2008).
It is the aim of organizations to efficiently perform so that they become better than the competitors (Collins 2001). This can be achieved by creating more emphasis on leadership. Thus, Bass (2005) asserted that it is the role of the leader to create a good working environment that strategically positions and shapes the mentalities of the members of the organization. Bell (2005), in his study, argued that the leader-centered approach in organizations has made it possible to define precisely the correlation between leadership and the performance of the organization. Other scholars have opted to investigate how to use the act of leadership effectively to impact the performance of the organizations.
This has mainly focused on how the leadership paradigms or behaviors can be changed to be in conformity with the vision of the organization to help improve the performance (Clawson 2011). The combination of leadership styles, organizational culture, employees’ competence, and the level of motivation is very effective in the performance of the organization (Daft 2005).
Most studies that relate to leadership point to similar conclusions. For instance, the style of leadership is highly correlated to the customers’ experience, the employees’ experience, and the financial growth of the organization (Ferch & Spears 2011). It can be noted that there is a research gap since many studies have not explored the concept of the relationship between leadership and the performance of the organization.
Many scholars have based their research on the relationship between the leader and the subordinates or their immediate supervisors. Other researchers have opted to investigate the entire organization and surroundings. Other researchers such as Fint (2012) have argued that the leadership styles that are used by the leader have a direct effect on the subjects and the entire organization. Hughes, Ginnett, and Curphy (2012) argued that not all previous studies have concluded that there is a positive relationship between leadership and the performance of the organization.
Leadership and Organisational Goals
Effective leadership involves strategically outlining the objectives of the organization by setting up well-designed organizational goals aimed at steering the organization to the next frontier (Gallos 2008). The organizational goals should be stated in terms of results rather than the process. Effective leadership emphasizes that the organizational goals should concentrate on the result rather than the formula to achieve it. Secondly, a well-designed goal can be calculated or counted; the goals will outline how the results are calculated and what to anticipate (Watson 2006).
In addition, a well-defined goal should be precise in regards to the set deadline; it clearly stipulates how much time it should take before the evaluation process begins. The other point is that the goal should be challenging but very easy for the organization’s members to attain. Highly set goals provide a sense of motivation for the organization, as opposed to lowly set goals that discourage rather than motivate. Lastly, a well-designed goal should converse with all the relevant stakeholders in the organization. Everybody in the organization should be well versed with the goals to avoid conflicts and confusion (Sipe & Frick 2009).
Steps in the setting of organizational goals for effective leadership
The setting of organizational goals is not just a one-time thing; it is a complex process that involves various stages. The first step is to analyze the mission statement of the organization. The distinguished objectives ought to plainly mirror the mission of the organization (Sipe & Frick 2009). The next step entails the evaluation of the accessible assets in the event that they are in a position to back the achievement of the objectives.
The third step is to decide the goals on a personal level or together with the colleagues. The goals must be specific, quantifiable, and appropriate (Matha & Boehm 2008). After that, the goals are written down and conversed with the appropriate stakeholders who are supposed to be versed in them. Writing the goals down emphasizes the relevance and value of the goals of the organization. The final step is to examine the results in regard to the performance of the organization. This will provide an opportunity to change or reset the goals that are not performing.
Theories of leadership
Leadership styles involve the development of a vision and direction that focuses on the future, along with strategies that are necessary to achieve the set goals (Northouse 2001). According to Burke (2001), although the subject of leadership has elicited a lot of argument from business scholars, there is no succinct understanding of leadership. Burke (2001) pointed out that leadership does not have the ultimate definition.
However, Burke (2001) agreed that all definitions revolve around the same basic characteristic of goal and group influence. Moreover, other scholars such as Harold and Fedor (2008) believe that leadership is a process of motivating which is aimed at influencing other people to work hard towards the achievement of the organization’s goal. For instance, transformational leadership involves the leaders identifying the desired change and subsequent creation of a vision to execute the change.
The concept of leadership styles is traceable in ‘Great Man’ theory that emphasized that leadership is based on hereditary factors. The “Great Man” theory supports that leaders are born (Northouse 2001). The theory points out that the inborn qualities in leaders are not transferable to other people. However, with time, studies on leadership have been advancing, and traits and specific qualities are used as the basis for understanding leadership styles (Chardan & Devi 2014).
According to Chardan and Devi (2014), leadership is all about decisiveness, ability to adapt, assertiveness, ambitions, as well as the possibility to show energy at work. Chardan and Devi (2014, p.5) discussed leadership from the perspective of behavior. This concept of leadership and behavior relates to the situational theory of leadership that postulates that leaders ought to make an analysis of any given situation so as to fit an individual’s behavior into the situation (Northouse 2001).
Chardan and Devi (2014) added that leadership style involves patterns that are used by leaders in an organization. On the other hand, Kolenda (2001) considered leadership styles to include interaction patterns that are evident in top management and their juniors. In the contemporary competitive business environment, more focus on leadership is based on the perspective of interpersonal and task relationships. Hence, the broad focus on transactional and transformational leadership styles forms the basis of many leadership studies. The two types of leadership styles have aspects that relate to other leadership styles.
For instance, visionary leadership can be described in relation to transformational leadership. According to Harold and Fedor (2008), transformational leadership takes into consideration the possibility of leaders offering incentives to employees as a way to encourage them. Transformational leadership style serves as a guide through idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation as well as individualized consideration. As such, transformational leaders consider the fundamental change of goals, values, and aspirations of employees.
The findings by Harold and Fedor (2008) do not provide a basis under which transformational leadership transcends to result in organizational performance. On the other hand, Rothfelder, Ottenbachers, and Harrington (2012) noted that the transactional leadership style focuses on leader-follower exchange with the follower abiding by the orders given by the leader. In this type of leadership, compensation of employees, whether positive or negative, is paramount. Employees under such leadership receive rewards for their work as it emphasizes that workers ought to complete the tasks that leaders give them.
The leaders offer motivational rewards to the employees (Rothfelder, Ottenbachers & Harrington 2012). In addition, Harold and Fedor (2008) pointed out that transactional leadership involves the recognition of employees’ needs and desires, along with offering the necessary platform for such needs. In discussing transactional leadership based on the reward system, Johnson (2007) pointed to the importance of the leadership style. However, Johnson (2007 did not relate to how the reward system, either positive or negative, influences the level of job satisfaction and organizational performance.
Lowe and Kroeck (2006) advanced the argument by noting that transactional leadership represents ordinary leadership, while transformational leadership represents extraordinary leadership. Transactional leadership involves a give and take situation, whereby the followers bring in their efforts, output, and allegiance. The leader, in turn, rewards them as per their contribution (Gratton & Jones 2004). On the other hand, transformational leadership is whereby the leader inculcates a sense of awareness and consciousness regarding the vision of the organization and offers a sense of motivation and inspiration to the followers (Kang & Singh 2006).
The performance of the followers of a leader is boosted by their emotions, intelligence, and morality; these enable them to accomplish goals and exceed their anticipations (Kantabutra & Avery 2010). The main difference between transactional leaders and transformational leaders is that the transactional leaders rely on the laid down strategies and procedures to manage the organizational culture, while transformational leaders manage the organizational culture in conformity with the new set of strategies and procedures (Keller 2006). Change in any organization is inescapable, and it is the obligation of the leader to launch and bolster this change process.
Transformational Leadership
The process by which a leader persuades the supporters draws the line between transformational leadership and value-based leadership. A transformational leader uses his personal attributes such as his character and his values to inspire and motivate the followers. On the concept of transformational leadership, the leader and the followers work together to elevate each other (Kline 2010). Motivation from the leader makes the followers trust the leader and be loyal and respectful.
Motivation also helps the followers prioritize by concentrating on the goals of the organization rather than their personal goals for the sake of the development of the organization. Transformational leadership is aimed at providing followers with a new mindset so that they change the ways and procedures of operations to achieve the desired results (Kolenda 2001).
Kouzes and Posner (2012) argued that transformational leaders have outstanding characters that set them apart. According to scholars, transformational leaders are charismatic, motivators, intelligent, and concerned. Being charismatic helps the leader to have a clear vision and a strategy for the organization and plants the same in the minds of the followers so that they can have the same mission. In the same way, charismatic leadership enables the followers to have confidence and pride in the organization and in the leader and, therefore, choose to serve the interest of the organization rather than their own personal interest (Kouzes & Posner 2003).
The second character of the leader, which is being a motivator, normally comes together with being charismatic. The leader is capable of setting up higher standards in the organization, which act as a source of motivation or inspiration to the followers. The followers, in turn, identify the leader as a reference for higher standards. The followers normally look up to the leader as he is the source of hope and confidence to them. The leader provides them with inspiration that increases their loyalty to the organization and enables them to understand the organizational goals better (Matha & Boehm 2008).
The leader offers inspiration to the followers by telling them success stories and also by being confident and hopeful about the future of the organization (Bass 2005). Therefore, transformational leaders encourage the followers that the future is always bright and that with hard work and dedication, all things can be achieved. This makes them be regarded as visionary leaders. Motivation comes from assigning the challenging task to the followers. These challenging tasks are aimed at opening up the followers’ minds and strategically positioning their mindset to open up for new ways of operations (Maxwell 2007).
The third attribute of a transformational leader is to be intelligent. The leader typically exhibits this by deliberately presenting and regulating new thoughts and ideas to the organization and, in the meantime, moving gradually from the old methods of doing things. Knowledge empowers the leader to grant to the adherents with key consideration, sensibility, and critical thinking abilities (Keller 2006). The followers will now be equipped with better ways of handling situations and examining the facts that had previously been under looked. The intelligence of the leader fosters invention and innovation, which are essential for improving the performance of the organization.
The fourth attribute of the transformational leader is being concerned with the welfare of the followers. The followers need to be empowered through appropriate training and mentoring programs. The leader is in a better position to be the mentor by providing exceptional leadership to the followers. The leader should understand the followers fully so that he can determine what kind of empowerment is relevant to them. The leader should treat the followers with respect and dignity and guide them to follow the correct path in order to attain both their individual goals and the organizational goals (Miller 2012). The show of concern for the followers will enable them to reach a certain level of maturity and increase their productivity in the organization.
Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership entails a scenario whereby the leader offers rewards to the followers with respect to the value-added to the organization. The followers are rewarded for their compliance and commitment to the goals and objectives of the organization. The leader directs and oversees the finish of undertakings in the organization by the devotees to guarantee that the objectives of the organization are met (Miller 2012). The transactional leader clearly spells out the correct path to follow in order to achieve organizational excellence. In addition, the leader puts mechanisms in place to eradicate all barriers and hindrances that might limit the followers from achieving these goals.
Transactional leaders normally demonstrate both profitable and remedial actions. Profitable actions involve rewarding the organization’s members, while remedial actions involve defining the code of conduct in the organization. The leader provides incentives that act as rewards to the followers because the followers expect to be recognized for exemplary performance. The setting and definition of the organizational goals clearly combined with the availability of proper incentives to recognize performance will motivate the followers to perform beyond the expectations (Northouse 2010).
Remedial actions involve defining the principles of compliance and how to handle mediocre performance. In addition, it entails a clear definition of what to do as a punishment for a job poorly done (Northouse 2010). Transactional leadership is a type of leadership that requires constant supervision to check for inefficiencies, mistakes, or faults and defining the remedial actions that are relevant to correct the errors. The excellent performers are adequately rewarded in proportion to their contributions (Polelle 2008).
Situational Leadership
Situational leadership is also called contingency leadership. In this case, the leader tries out various leadership styles so as to manage a situation at hand (Rafferty & Griffin 2004). The leadership style that will finally be adopted by the leader is the one that is supported by the followers and also relevant to the situation at hand. The followers should have an appetite for development, and their level of development will determine the direction of the leadership style. In addition, the personal traits of the leader will also influence the leadership style that is chosen in contingency leadership.
Therefore, in general, situational leadership is dependent on the relations between the leader, his followers, and the situation at hand (Sadler 2003). Some scholars have criticized situational leadership by arguing that it focuses much more on the production of the task at hand while giving less attention to the members of the organization (Schuttler & Burdick 2010).
Organizational Leadership
Organizational leadership is associated with teamwork because it is considered to be a collective team effort. Organizational leadership brings about innovation and the introduction of new concepts and ideas for performing tasks (Sipe & Frick, 2009). Organizational leadership starts with the individual’s abilities and traits as a leader. This enables the leader to garner trust and confidence from the followers who support him in all the ways. Organizational leadership makes it possible to formulate a strong organizational culture and increases the level of commitment of the organization’s members so as to achieve the organization’s goals (Miller 2012).
Leadership for innovation
Training and development are the chief instruments for breaking new grounds. Hence, conveying changes to an organization (Aquinas, 2006). The capability absorbed through expert preparation aids in getting acclimated to the novel innovation, additionally adds to the new upgrades (Avery 2004). The preparation of the expert must occur within a social organization of governance between the training officer, the organization’s overall, and the HR.
This assures that the preparation offered is as per all the partners’ perspectives and pursuits. In this model, preparing unites all the co-operators, and the normal hobby is distinguished and worked upon (Clawson 2011). According to Collins (2001), the general picture of the organization and the mentality of the supporters are additionally controlled by the level and nature of preparation and improvement.
In the contemporary business atmosphere, most organizations are confronted with firm rivalry for their quality staff (Matha & Boehm 2008). The experts in the department of HR underline the importance of putting in place measures to foster job satisfaction (Avery 2004). Keller (2006) noted that organizations that put resources into preparing the advancement of employees end up benefiting from an upgraded workplace. The measures taken in preparing the employees are credited for discouraging the level of staff departure (Ferch & Spears 2011). Furthermore, the measures create a platform for improved innovation, individual and team growth, gains, and authoritative execution of the organizational strategies.
In many organizations, the leaders dependably apply a top-down approach of leaders, which has worked out to be incapable in the organizations these days. For this position, the administrator outlines the strategies for success, sets points and goals, specifies time periods; designate the roles among different capacities without an interview. In such instances, the preparation office just executes obligations administered by the top leaders.
According to Watson (2006), the preparation and HR improvement ought to be a steady process as opposed to a rash procedure. Sadler (2003) argued that business directors should contemplate the occupation and comprehend the issue of change. Sipe and Frick (2009) added that directors are concerned about the specialists and their roles in the organizations. Thus, they contemplate how the management modifications ought to be taken care of to make ideal results.
Abbas and Asghar (2010) suggested that administrative measures must put in place the system that adapts to the organization’s environment. According to Avery (2004), organizations ought to put in place strategies to enhance progress and maintain extraordinary business outlines fit for exploiting their capabilities and business (Avery 2004). It is along these lines that it is a basic requirement basic for any leader to concentrate on thoughts or projects that ensure performance. In this manner, leaders have different techniques to utilize in order to promote progress in the organization. These techniques differ from organization to overseeing body because of the distinctive way of their needs. The best strategy is to create a tranquil domain in the work environment to fortify inventiveness and innovation (Kantabutra & Avery 2010).
Many researchers consider complacency to be one of the real impediments to the development of organizations (Bell 2005). Leaders work to prepare divisions as a convention in the wake of settling on all the key choices inside unreasonable due dates (Ferch & Spears 2011). Leadership and management assume an essential part of keeping up the qualities and theories of a business center.
Development accompanies a broad extent of hazards that are respected to be of vast significance and worth to the present-day business venture (Bass 2005). In any case, it is worth noting that in contemporary times, firms with leadership that does not encourage invention have been on the front line to start inventive exercises. The leaders here feel that everything ought to be performed subsequently just as to advance creative exercises (Collins 2001).
Quality chain investigation guarantees extraordinary business operations and empowers the business base to contend and enhance its portfolio. Game changer investigation highlights different open doors that an organization can work inside its locale. It additionally gives different qualities that the organization holds, keeping in mind the end goal to argue in the ingenuity (Aquinas 2006).
It is with the information of a successful leader that an organization truly needs advancement and all the more inventively keeping in mind the end goal to look after itself. Progress is, in this manner, influenced, as the loudness of any framework that is sponsored by viable leaders. Leadership is an essential component of the perseverance of any representative body. Fair leadership pulls the domain unit in reverse as opposed to driving it ahead. An organization with a regular and effective leadership will be in a more upright spot to stay out front of the multitude of its rivals as for all aspects of the employment (Kang & Singh 2006).
In parliamentary law, to support a game-changer and maintenance of astounding associates, social orders must guarantee that preparation and improvement of their HR are not taken delicately (Gupta 2004). Giving careful consideration to expert preparation warrants the unfaltering quality and benefit in organizations (Gupta 2004). Inventiveness brings into the organization new thoughts that are extraordinarily valuable to the survival and the suitability of the organization (Gratton & Jones 2004). This can exclusively be achieved independently of anyone else arranging the procedures of the individual actors.
They perceived the motivation behind key arranging and the creation of systems since individual blunders may bring near the actual effect on the framework overall (Abbas & Asghar 2010). A standout amongst the essential facets of human asset improvement is helping representatives to end up more successful in the work and to be capable of adjusting different employments inside the company (Polelle 2008).
According to Gallos (2008), the strategies for enhancing performance in an organization involve effective outlining and execution of the preparation projects. The leadership should organize the measures and put in place systems that should produce the expected results (Fint 2012). Gupta (2004) argued that expert training helps organizations sustain a strategic distance.
Steve Jobs as a modern visionary leader
Successful organizations usually put in place leadership styles that aim at fostering employee satisfaction; poor job satisfaction is likely to cause an organization’s failure. Johnson (2007) pointed out that job satisfaction involves the general satisfaction of all workers and top management. As such, employees’ contributions to any organization are assessed based on job satisfaction and organizational commitment.
Johnson (2007) found that there are many contextual factors in an organization that affect employee job satisfaction. Some of these factors include workplace flexibility, job security, job autonomy, salaries, and leadership. For an organization to succeed and attain a competitive edge, employees’ satisfaction has to be enhanced (Johnson 2007). Bass (2005) stated that highly satisfied employees are likely to give a lot of effort in their work, thereby leading to the achievement of set goals and objectives.
A research carried out by Kipperberger (2002) established that leadership does not have a specific perspective of an application on employee satisfaction. However, Sakiru et al. (2013) are of the contrary opinion, and they point that different types of leadership can be looked at from the view of the social context and history. Gupta (2004) added that leadership should be investigated with respect to the context of the application and the influence they have on the employees. Sayeed and Shankar (2009) noted that there exists a constructive relation between job satisfaction and the transformational leadership style.
Furthermore, an empirical study on leadership styles and job satisfaction by Kippenberger (2002) indicated that there was a significant relationship between principal’s transformational styles of leadership with teachers’ job satisfaction.
Many organizations are concerned with how to build leadership capability that attracts and leverages the organizational talent and the development of employees. The current business environment is marked by increased competition that is driven by globalization and the knowledge economy; this has necessitated changes in leadership strategies in order to attain a competitive edge (Wanasika 2009). In the current work environment, leaders have to manage change, solve problems, set the vision, and manage production for the organization (Kafetsios, Kassotaki, Zammuner & Vouzas 2009). Key competencies that are required for leadership to achieve success in management include leading the self and leading others to allow effective management of teams in an organization (Batool 2013).
An effective leader should be in a position to respond to work environment challenges and communicate the goals of an organization. As a result, emotional quotient (EQ) has become a pertinent approach to visionary leadership. The emotional quotient measures emotional intelligence (Batool 2013). According to Kafetsios, Kassotaki, Zammuner, and Vouzas (2009), visionary leadership entails the ability of a leader to understand emotions and apply understanding to enhance collaboration and productivity. Emotional Quotient (EQ) is paramount in leveraging on personal self-awareness.
Thus, emotional intelligence leadership is anchored on four tenets of managing emotions, using emotions, understanding emotions, and perceiving emotions. Organizations oriented to emotional intelligence leadership have been found to be more successful.
Many scholars argue that the leadership skills of Steve Jobs started at an early age when he developed an interest in technology. According to Polelle (2008), Steve was so much obsessed with electronics and developed his management skills in line with his interest in technology. Steve had a winner’s mentality from a young age and performed the roles as a CEO with passion and dedication.
These skills helped Steve to transform Apple to be a global icon in terms of making computers. The company became huge both in size and value. Apple Company was the first company to create a Mac operating on a Windows platform. The mouse was also a creation of Steve Job. The use of the mouse has become popular globally among computer users (Jobs &Thomas 2011). In addition, Steve contributed to the field of movies by producing many blockbusters. Steve Jobs had a fighting mentality, which enabled him to endure cancer for a longer period (Polelle 2008). The fighting attitude was also demonstrated by his desire not to give up, even when he had failed in the past.
Steve Jobs is still regarded as a genius and an idealistic leader; this was enshrined in his personality. He had several outstanding personal traits that included: being open-minded, being a perfectionist, being passionate, being flexible, being charismatic, and being highly persuasive. An enormous company in the class of Apple needs the best leadership that is backed up by a strong organizational culture that created a sense of identity and uniformity in the organization. Steve Jobs managed to inculcate a distinct organizational culture that made it possible to identify any Apple employee at first sight (Jobs &Thomas 2011).
The culture of the company was founded on the personal traits that were possessed by Steve Jobs (Polelle 2008). Many people, including the employees and the customers of Apple all across the world, were very inspired and motivated by the success stories that were told by Steve Jobs. It was part of his philosophy to inspire and motivate people to work hard; this pushed the company far above the other firms.
Steve Jobs is identified in the same class as the world’s successful modern leaders. His personality influenced the way Steve discharged his duties. He had a group of very loyal employees who did not care even if Steve became rough on them at some times. This was because Steve was an inspiration to many of the employees as well as being a role model (Jobs &Thomas 2011). Steve never gave up on any, no matter how hard the situation looked like. In everything he did, there was an element of perfectionism. Steve is credited with creating an attitude of endurance in Apple Company by introducing the strategies of entrepreneurship, leadership, and invention, and innovation. Steve had simple ways of doing his work that produced great results, and, in the end, he took responsibility for either success or failure.
According to Jobs and Thomas (2011), Steve could push his employees to go the extra mile and accomplish the unmanageable; he achieved this through constant motivation and inspirational talks. These character traits point to the leadership employed by the leader. According to Batool (2013), the leadership style relates to emotional quotient leadership. The leadership is exemplified through the transformational leadership process. The leadership demonstrated by Steve relates to the argument by Gallos (2008) that leadership is an element that is enshrined in the behavior of an individual. The leadership traits thus enabled Steve to mentor Apple’s staff in order to achieve shared goals.
In summation, the leadership style of Steve Jobs can be portrayed as versatile, centered, visionary, and creative. He was impractical for the reason that he never upheld for copying what was at that period in the business sector, as he accepted that the organization held the capacity to present something fresh. Dissimilar to different leaders who assume that a standard thing could be possible in an unexpected way, Jobs had an alternate point of sight since he was sure that his representatives would dazzle the world with new things.
According to Miller (2012), effective leadership is enhanced by a good communication process that ensures that the workforce is motivated. In order to reach and motivate the employees, Steve was a strong proponent of face to face conversation because the communication is direct, reliable, and the feedback is instant (Polelle 2008). As a leader, Steve Jobs divided his team into small groups of top talents who were assigned challenging tasks but still managed to produce the desired results.
Leadership is a concept that gives much attention to many people all around the world. All the aspects of any organization depend on good quality leadership. The example of Steve Jobs’ leadership exhibits how any organization can benefit from having a visionary and transformational leader (Jobs &Thomas 2011). The success of Steve Jobs as a leader was constant. Unlike other leaders who just succeed on a one-time basis. Case in point, he supervised the improvement of an iPad, which has changed the itinerary in which organizations operate. Steve is broadly recognized for his discourse whereby he undertook:
“Everything around us that we call life was made up by people that are no smarter than you.” He went on to claim, “you can build your life that other people can live in, so build a life and don’t live one” (Jobs &Thomas 2011, p. 34).
Steve was an amazing leader who took the time to comprehend the client’s needs and make up an item to fulfill them by using the accessible assets in the organization (Sadler 2003). Then again, Tim Cook is a soul who trusts in the coordinated effort. Tim Cook took over that item; change is guaranteed through consistent testing. In one of the meetings with the Business Insider Magazine, he was cited stated that,
“You look for people who appreciate different points of opinion. People who care enough that they have an idea in the middle of the night want to call and talk to you about it. Because they’re so excited about it, they want to push the idea further, and they believe that somebody can help them promote the idea another step instead of them doing everything themselves ” (Polelle 2008, p. 39).
Conclusion
The literature review shows that there is a considerable relationship between employee satisfaction and leadership styles. Even though different studies were carried from different locations and with respect to a different context, it is evident that a relationship exists between the leadership style employed and the level of employee satisfaction. However, most studies based their facts on generalization and not aligned with the specific leadership styles.
In relation to Apple, Steve Jobs and Tim Cook have leadership traits that emphasize the conducive work environment that is fit for innovation. The engagement of the employees in the strategic goals of the organization ensured that Apple was in a position to create a platform for technological innovation. Based on the literature, it is arguable that leadership style has a crucial role in the performance of the organization.
It can be noted from the reviewed literature that there are still divergent views regarding the relationship between leadership and performance. There are proponents who believe that organizational performance is positively influenced by effective leadership, while there are opponents who argue that leadership does not determine the performance of the organization in any way.
The arguments are drawn from different studies that have explored the different concepts of leadership, which has led to divergent opinions, hence, creating a knowledge gap. This study was aimed to bridge that gap by closely re-examining the relationship between leadership and organizational performance by using a reputable leader (Steve Jobs) and a reputable company (Apple Company) as a case study. This was intended to add to the existing body of knowledge in the same field.
Research Methodology
The methodology involves the approaches that are applied in the collection of data. It also includes the approaches applied in the data analysis. According to Denk (2010), study methodology is the systematic planning of actions that are applied in the collection of information. It includes the subsequent analysis of data in a logical manner that helps in the realization of the research purpose. Study methodology entails the use of different research designs to inform the process of data collection (Bronfenbrenner & Evans 2000). Examples of the study designs include descriptive, cross-sectional, experimental, and explorative researches.
Kothari (2005) defined research methodology as the process applied to solve a research problem systematically. According to Kothari (2005), research methodology entails studying the various steps that are adopted by a researcher in the investigation of a problem. Study methodology includes the logic behind the steps that are employed by the researcher (Kothari 2005). Research methodology thus involves the research methods (Mitchell & Jolley 2010).
The research methods are the techniques put in place by researchers in the process of executing a study. According to Neumann (2007), research entails moving from the unknown to the known in order to arrive at a solution to a specific issue being investigated. The process requires the drawing of data to be used for the correlations. Based on the understanding, research methods can be categorized into different groups. The first group includes the methods and techniques that are used to collect data. The second research method entails the techniques for statistics that are used to establish the correlations between the unknowns and the collected data. Finally, the third method of data collection entails the process that is used to determine the accuracy of the information collected.
According to Denk (2010), the data collected should be reliable and valid. The concept brings in the issue of ethical consideration in the collection of the data by the application of credible processes. Therefore, in order to execute the study and ensure that the objectives of the study are explored and correlations determined, various research methods were applied in the collection of the data and analysis.
The purpose of a scientific study is to discover answers to the research questions. According to Kothari (2005), it entails the use of scientific procedures to find out the truth, which has not been discovered. Neumann (2007) noted that the objective of the research is to gain familiarity with the issue being studied or to gain insights into a particular phenomenon. In the case of the current study, the phenomena under investigation are the leadership styles with the key focus on Steve Job and Tim Cook and their influence on organizational performance and change.
Therefore, the aim of the research methodology is to provide a platform for the discovery of the phenomena being studied. In addition, the study methodology provides the basis for testing the hypothesis and the establishment of the causal relationship between the various variables in the study. The common variables that are tested in a study include the dependent and the independent variables (Kothari 2005).
The research methodology entails different types of research that depend on the purpose of the study. The common types of research include descriptive, analytical, applied, fundamental, quantitative, qualitative, conceptual, and empirical. The basic approaches applied in research include the quantitative approach. The quantitative approach involves gathering empirical data that can be subjected to numerical manipulation (Denk, 2010). In the current study, the research will incorporate the quantitative approach. This will help to provide a comprehensive understanding of the leadership styles and their influence on performance.
There are many studies conducted in relation to leadership in different contexts. Most of the studies applied quantitative approaches in which empirical data was collected and analyzed. The studies used mixed methods of research in which both primary and secondary data were used. However, the current study relied on secondary data. This is in line with the argument by Neumann (2007) that research should be focused on a given aspect.
Thus, the quantitative approach and reliance on secondary data provided a platform in which the target users of the data will be well varnished with the empirical data. The data will be critically analyzed and correlations made by the use of statistical tools. For instance, the application of the SPSS analysis helps in ensuring that the inferences drawn depict a common perspective of leadership.
Research Designs
The research design applied in the study was a cross-sectional study design in which empirical data on the high-profit returns was collected and analyzed. A cross-sectional study helped in giving the snapshots of the performance of the Apple Company in the selected study period. The study period included the period from 2000 to 2013. Secondary data for the company’s performance in the selected period was used to analyze the implication of Tim Cook and Steve Jobs’ leadership styles.
The application of cross-sectional study helped in determining the influence of leadership on the performance of Apple Inc. Company. According to Vogt, Gardner, and Haeffele (2012), cross-sectional studies are carried out repeatedly to give pseudolongitudinal study. In the study, great emphasis was to collect substantive empirical data that was used for the analytical process.
Sampling
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of the target population (Sans, 2011). One of the key factors underpinning research methodology is to have a representative sample from which acceptable inferences can be drawn (Sreejesh & Mohapatra 2014). In order to arrive at a representative sample, the population being studied should be clearly defined, the sampling frame should be clearly specified, the method to be applied in the sampling should be identified, and the sample size should be determined. In the current study of leadership style, purposive sampling was used to select the Apple Company and the role of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook leadership styles.
The databases with credible information were also purposely selected. According to Sans (2011), purposive sampling is discriminatory as it gives the researcher the discretion to identify the subjects to be included in the study. As a result, there is the possibility of personal bias in the identification of the study participants. However, the method is paramount when specific information required can only be achieved from specific people. Thus, in the current study, Apple company has information that relates to the phenomenon being studied; hence, the reason to settle on the method.
Sample size
The determination of the sample size depends on the number of replication that can be applied in drawing inferences about the population/units. The type of data required for the research normally determines the sample size (Mitchell & Jolley 2010). Sample sizes are important in determining the precision of the study (Neumann, 2007). The sample size in this study involved the cross-sectional data covering the study period. The sample size included secondary data related to the performance indicators of Apple Company under the leadership of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook. The study was limited to the case of Apple under the leadership of the two leaders.
Data Collection Methods
There are varied data collection methods. According to Kothari (2005), the choice of the method to be applied in the data collection is determined by the strategy, the type of the variable being measured, and the point of collection. The mode of data collection to be applied in the study included the mining of data from the various databases. Therefore, the study relied on secondary data.
Data Mining
According to Sans (2011), the method of data collection is normally influenced by the research strategies, the point of collection, and the person to carry out the research. The main types of data collection methods used in the study included secondary sources of data collection. The secondary data was collected from databases (data streams) that contain margins and cash flow projections for Apple Company. Only credible databases were used in the study. This ensured that only reliable data was collected for the study. In addition, the selection of the data to be applied to the study was limited to the specific time during the leadership of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook. The use of credible data streams and the focus on given time ensured that the reliability and credibility of the data were upheld.
Gratton and Jones (2004) argued that the effectiveness of secondary data might be hindered by a low level of reliability and validity. Data was sourced from external sources. Thus, a review of diverse annual reports relating to Apple Incorporation, such as reports on corporate social responsibility and human resource management, was conducted. The secondary data was sourced from credible agencies such as KPMG, PricewaterhouseCoopers, and Deloitte & Touché. The choice of the agencies was informed by the view that they provide a comprehensive analysis of diverse aspects relating to organizations’ operations.
Secondary data was also collected from credible databases such as the Social Sciences Research Network [SSRN] and the EBSCO databases. Gratton and Jones (2004) asserted that secondary research could lead to the attainment of the actual data; hence, improving the accuracy with which the research questions are answered.
Variables
The dependent variable was effective leadership. The five independent variables under investigation were: the connection concerning effective leadership and higher profits, the relationship between effective leadership and the management of risk and uncertainty, the relationship between and the efficient use of resources, the relationship between effective leadership and return on assets, and the relationship between effective leadership and the creation of competitive advantage.
Reliability and validity
Reliability involves the consistency of the research instrument (Oladipo, Adenaike & Ojewumi 2010). The reliability of the research was achieved by using credible databases and agencies. They ensured that the data collected was consistent and reflected the outcomes of the leadership styles employed in the organization.
Validity measures the degree to which a research instrument collects the data that is supposed to be collected (Oladipo, Adenaike & Ojewumi 2010). The data collected related to the same time period, which ensured that the degree of external validity was achieved. Hence, the results obtained could be generalized.
Data Analysis Techniques and presentation
The data collected from the secondary sources were analyzed effectively in order to increase its relevance to the target stakeholders, such as organizational leaders. Moreover, data will be analyzed using Microsoft Excel and SPSS. By using these tools, the researcher will be in a position to undertake effective data analysis by incorporating diverse statistical analysis concepts such as percentages, standard deviation, variation, and correlation. Furthermore, these data analysis tools improved the effectiveness with which the findings of the study are presented. Subsequently, it will be possible for the target stakeholders to interpret the data effectively and efficiently.
Limitations of the study
According to Bell (2005), the relationship between leadership style and organizational performance is influenced by many factors. Therefore, the variables, namely, effective leadership, high profits, risk management, efficient use of resources, return on assets, and competitive advantage, may be affected by other factors. Thus, the findings of the study may not depict the actual influence of leadership on organizational change and performance. The other limitation is related to budgetary constraints. Therefore, future studies should take into consideration the other factors that may limit generalizations of results. In addition, budgetary allocations should have an allowance margin to cater for changes encountered during the actual study.
Findings, Data Analysis and Discussion
Introduction
This section covers the analysis of the data, presentation, and discussion. The results were analyzed using SPPS, regression, and correlation analysis. The empirical study was based on secondary data. The aim of the study was to find out the link between leadership style and organizational performance. The findings of the study were instrumental for academic purposes and were to serve a very crucial role for managers who intend to improve the productivity of their organizations based on strategic leadership. In addition, the study adds to the current knowledge. The application of the knowledge is critical for organizations that need to achieve a competitive edge and align with the strategic goals based on the adoption of effective leadership.
Findings
Table 1 is a summary of the findings. From the computation, it can be deduced that many employees believe that the effective leadership style of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook had a long-term effect. The leadership increased the profits and revenue of the organization; this is indicated by the higher value of the standard deviation. The findings suggest that the mean for the relationship between effective leadership and higher profits is 113.20 with a standard deviation of 14.30.
In addition, the calculated arithmetic means for the relationship between effective leadership and return on assets, efficient use of resources, and creating competitive advantage are less than the calculated arithmetic mean for the relationship between effective leadership and managing risk and uncertainty. Effective leadership has more effect in managing risks and uncertainty (Mean=127.21, SD=15.31) than creating competitive advantage (Mean=114.351, SD=14.221), efficient use of resources (Mean=103.11, SD=10.81), and return on assets (Mean=102.11, SD=11.31).
Table 1: Summary of the results.
Inferential statistics
The results of inferential statistics were used to establish the relationship that exists between effective leadership and the performance of the organization; inferential statistics were used to ascertain the connection among the variables. The results are summarized in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Pearson correlation matrix for the variables.
NOTE:
- * = p<0.05
- ** = p<0.01
The results in the table above show that there are major correlations between effective leadership and return on assets (r = 0.5981, p < 0.01), effective leadership and managing risk and uncertainty (r = 0.5852, p < 0.01), effective leadership and creating competitive advantage (r = 0.3861, p < 0.01) and between effective leadership and efficient use of resources (r = 0.2682, p < 0.05). There was also a significant relationship between effective leadership and higher profits (r = 0.2734, p < 0.05).
A regression analysis to analyze how the variables predict the effectiveness of effective leadership and the results are summarized in Table 3 below.
Table 3: Summary of regression analysis.
Table 4: Summary analysis for return on profits, assets, and risks.
NOTE:
- * = p<0.05
- ** = p<0.01
The result found out that the multiple R-value is 0.6022. The R-Square value of 0.361 indicates that 36.1% of the variables explained the dependent variable. The F-statistic (5.305) is statistically significant at the 0.01 level, meaning that the economic variables significantly enlighten 36.13% of the variance in addressing the effectiveness of leadership. Efficient use of resources is the best predictor of the effectiveness of good leadership as it has a beta coefficient value of -0.0.3190 and is statistically significant at the 0.01 level.
In addition, return on assets, higher profits, and creating competitive advantage are statistically significant at 0.05. The negative value of the beta coefficient of creating competitive advantage indicates that effective leadership has a greater effect in bigger organizations, for instance, Apple Company, than in smaller organizations. In the like way, the negative beta value of the higher profits coefficient shows that effective leadership is really important in uplifting the performance of the system.
Analysis and Interpretation
The success of a business is usually based on strategies that the management and leadership put in place. The business environment has been rapidly changing. Thus, the success of the organization depends on the preparation for the future. The leadership of an organization is supposed to put in place measures to prepare for the unforeseen future. Visionary leaders should put in place transformative strategies that lead to improved performance. The strategies are normally in terms of products, the process of work, and business model. The driving forces for the visionary leaders are to increase the profits of the organizations, to compete favorably, and promote the productivity of the employees.
Based on the findings, the leadership of Steve and Tim led to the profits of the organizations improving significantly. In addition, the utilization of resources was optimized. Hence, Apple Company managed to gain a competitive edge. Besides the visionary leadership demonstrated by the two leaders, internal and external factors contribute to the performance of the organization (Carneiro 2008). The factors include the nature of the organization, the technological and global factors. Leaders and managers are tasked with putting in place strategies to ensure that their organizations succeed.
The visionary leadership of Steve and Tim in Apple Incorporated innovative approaches helped the company to be effective and hence the high returns as depicted in Tables 2 and 3. For instance, in Table 2, the study applied Pearson’s correlations to analyze the profits, return on assets, and efficient use of resources, management of risks, and creation of competitive advantage. All the correlations were positive. The results point to the effectiveness of the leadership style employed by the leaders. Leaders normally take the prevailing business factors into account. In the past, leaders were tasked with creating and availing the resources to the firm so that it may perform well based on the present situations (Carneiro 2008).
Discussion
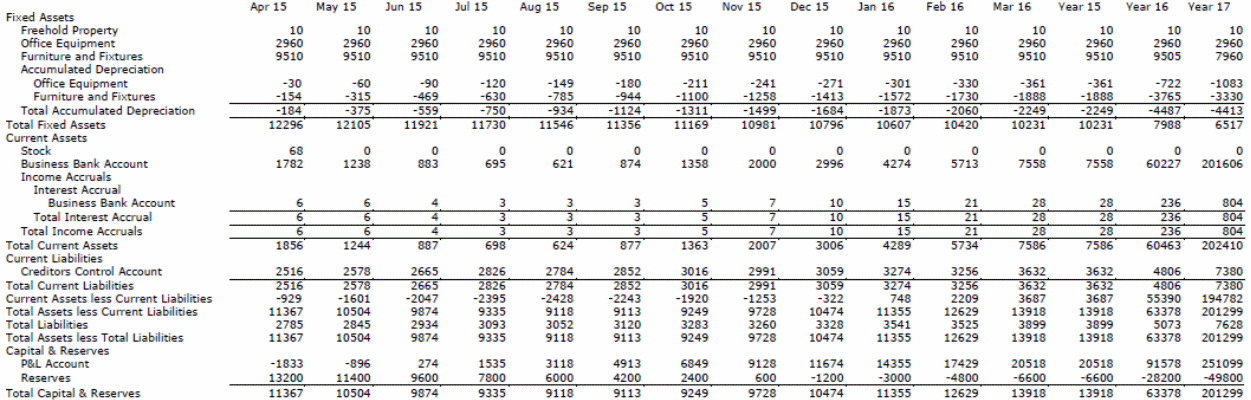
The type of data collected for the study was secondary data. It included the return on profits, the use of resources, the management of risks and uncertainty, and profits (see Appendix 1 to 4). In order to determine the impact of leadership in the context of Apple Company, the data was analyzed, and correlations are drawn to determine how the leadership style employed by Steve and Tim translated to increased productivity for the organization. The correlations were based on strategies put in place by the visionary leaders and their effect on creating a competitive advantage. The data were analyzed using statistical tools such as SPSS.
Based on the findings, the leadership styles employed by Steve Jobs and Tim Cook contributed to Apple’s high profits. This was achieved by the strategies they put in place, which in turn had an impact on managing risk and uncertainty. The type of leadership employed by an organization also influences the use of resources. Appendix 1 to 4 points to Apple’s projected cash flow, balance sheet, and profit and loss account for the company. The projections point to the growth of the company. Therefore, this points to leadership effect on return on assets and utilization of resources.
In any organization, the top management and leadership are expected to ensure maximum utilization of the available resources. The main aim is to ensure that the organization remains competitive in the marketplace while still sustaining the profitability of the organization’s position. Many studies carried in the past indicate that the available leadership styles affect employee satisfaction in different ways (Allen & Wilburn 2002). However, Wood (2010) postulated that an effective structure presents a greater extent of commitment and satisfaction of the job with respect to the applied leadership style.
In a situation whereby the employees are not satisfied, there will be negative implications for the organization (Rothfelder, Ottenbacher & Harrington 2008). For instance, low profits increased cost, withdrawal behavior, plus customers’ dissatisfaction. As the sector grows, so does the increase in competition. In the study, the leadership style employed in Apple Company by Steve Jobs and Tim Cook was correlated to employee satisfaction.
The high profits indicated the success and the return on assets, as outlined in Table 4.2.1 and 4.2.2. According to Burke (2001), several factors are responsible for the employee level of satisfaction. Such factors include communication, independence, accomplishment, wages, team environment, job security, co-workers, working conditions, and the acknowledgment of the employees. These factors are directly correlated with leadership employed in an organization.
Allen and Wilburn (2002) noted that the leadership style put in place plays the greatest role in determining the employees’ satisfaction levels in any organization. Therefore, there is a need to establish a relationship among workers that promotes satisfaction based on leadership styles. In a leadership situation whereby the employees are not satisfied, results that are adverse will be shown, such as low profits, growing cost, withdrawal behavior, high labor turnover, and customers’ dissatisfaction. Apple Company has been recording steady growth in the technology sector. The company has remained to be a leader in the smartphone industry. As the sector grows, so does the increase in competition. Effective leadership is supposed to provide directional leadership to overcome the competition.
The purpose of the study was to find out if there is any relationship between the type of leadership and organizational performance. The findings showed a significant link between the performance of the organization and leadership styles. The results related to earlier studies conducted in different contexts. For example, a study carried out to investigate employees’ job satisfaction in the Malaysian public sector revealed that there is a strong correlation between the style of leadership and job satisfaction (Kippenberger 2002).
In addition, Kippenberger (2002) indicated that there was a significant relationship between principal’s styles of transactional leadership and teachers’ job satisfaction. In a similar cross-sectional study targeting 100 organizations in the banking and manufacturing sectors, Malik, Danish, and Munir (2012) examined the correlation between leadership style and performance of the organization. The study established that leadership determines the strategic goals and the ability of the employees to work as a team to attain the set goals.
In relation to the current study, Steve Jobs and Tim Cook demonstrated inclusive leadership. This pointed to the transformational leadership that was responsible for the exemplary performance of the organization. As noted by Kouzes and Posner (2003), transformational leaders are charismatic, motivators, and intelligent. Thus, the two leaders demonstrated leadership that enabled the followers to have confidence and pride in Apple and thus translated to the growth.
Organizations that are successful usually put in place leadership styles that foster the success of the organizations (Johnson 2007). Based on the above findings, managers are supposed to put in place leadership styles that best suit the industry operation and employee’s welfare. The understanding of the environment of operation and employee job satisfaction increases the productivity of the organization.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusion
From the case of Apple Company, it is apparent that the type of leadership has a great implication on the productivity and performance of an organization. The strategies implemented by Steve motivated the employees and hence created an organizational culture of innovativeness. The strategies revolutionalized the company. For example, they led to new technologies and designs that created the iPhones and iPods. The products resonated with the technological and lifestyle needs of many people. As a result, Apple Company attained a competitive edge in the electronic market that it has been enjoying. Thus, the leadership strategies put in place by Steve had a strong relationship with the performance of Apple, as depicted in the findings.
Effective leadership is an important factor in any system. The findings of this research have revealed that effective leadership has a critical role on the performance of an organization. Enactment of proper and effective leadership in contemporary business operations can translate to a high return on assets. As demonstrated in the case of Apple, the effective leadership of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook is linked to the high profits and effective utilization of resources. Effective leadership also helps an organization to manage risk and uncertainty and also creating a competitive advantage for the organization. Effective leadership is associated with the setting of goals and objectives. Goals are very important to the organization because they provide clear direction to steer the organizational progress.
According to Martindale (2010), satisfied employees are likely to work as a team and hence drive the organizational change. Based on the research findings, it will be prudent for the management of the organizations to adopt leadership that are result oriented that contribute to job satisfaction. In addition to the research findings, the literature review showed that satisfied employees have chances of giving their best in terms of efforts that translate to high organizational productivity. However, it is important to note that the study results are limited to Apple Inc. Thus, generalizations made based on the findings could be biased. Extensive research that incorporates other private and public sector organizations could be essential in order o draw inclusive inferences.
The study established that there is a strong relationship between leadership style and organizational performance. Leaders play a crucial role in providing directions for the employees. They also help in designing performance management systems. In the case study, a strong relationship was evident between visionary leadership exhibited by the two leaders and the performance of the organization. With the ever-increasing competition in the private sector, human resource capital is integral to driving strategic changes and ensuring that the organizations remain profitable and competitive. Therefore, for the management and leadership of the organizations to achieve the goals, they need to put in place leadership strategies that motivate employees and hence contribute to organizational growth.
Recommendations
There are different types of leadership that vary, depending on the type of organization. For instance, in government institutions, bureaucratic leadership is commonly practiced in which chain of command and procedures are the most preferred norm (Woods 2010). Though the study was extensive, it focussed only on leadership styles employed by Tim Cook and Steve Jobs. This could have led to overlooking management strategies incorporated by line managers in the organization.
Thus, it is recommended that further studies should focus on finding out the impacts of leadership on performance with the focus on other organizations that have excelled in different sectors. The studies should also explore departmental management that may result in changes in the performance. For instance, there is a need for researchers to conduct investigations that include the organizations that practice hybrid leadership styles, i.e., changing leadership depending on the circumstances or fusion of the different types of leaderships.
In the course of the study, there were challenges related to budgetary allocations and access to credible secondary data. Therefore, future studies should include sufficient budgetary allocations. In relation to the credibility of the data, future studies should review the databases before the actual study in order to gauge their credibility. Finally, effective leadership is important for the sustainability of any organization. This study highly recommends that the goals and objectives of any organization should be aligned with the strategic mission. This will include the management boards of the organizations to vet different leadership styles and choose the most appropriate leadership that conforms to their industry of operation.
Learning Statement
The theoretical philosophies of leadership and leadership approach are related to the corporate world in many ways. Effective leadership has a direct effect on the performance of the organization. The concept of leadership is very important and is required to be incorporated into the school’s curriculum so as to train the students at a very early age on fundamental principles of leading. Leadership is a concept that should not be taken lightly by today’s society as the younger generation are the leaders of tomorrow.
Steve Jobs is a role model and inspiration to many young people, and the youth need to challenge themselves to emulate the philosophies of great leaders like Steve Jobs. Based on the development of this study, I have focused my career on being a chief executive officer of my company in the future. This will enable me to exercise my leadership principles and qualities that I have learned in my various stages of development. For me to achieve this, I need to study more on the philosophies of the renowned successful leaders so as to equip me with the additional relevant skills that are needed for my pursuit.
The leader of an organization acts as the function of inspiring trust from the multitude. The leader has the exclusive right to transform the entire organization in line with his vision and warmth for the organization. The actions of the leader empower the rest of the people, hence, making it possible to learn new ideas and concepts. The leader is the first person to initiate any change process in an administration as the rest comes after.
The original definition of leadership associated it with personality, while the recent definition of leadership associated it with the power of the soul to determine. Leadership is a broad concept that is valued across the world, and that is the cause of why the definition of leadership changes from one system to the other. There has been a limitation associated with the written reports on leadership that has been practiced since the early 1990s. This restriction has been ascribed to the fact that the students who study leadership and the people who are the leaders have been unable to render a general definition of leadership accurately (Abbas & Asghar 2010).
Leadership is an essential ingredient in any organization. Many organizations have the goal of providing the best quality services or goods to the final consumers by using the minimum cost of production and the process of earning greater revenue. Effective leadership enables this to occur. From the study, I have discovered that job satisfaction among employees is critical to the success of any organization.
A crucial aspect that stemmed from the study is that Apple Company has had enhanced performance due to the initiation of policies that promote the welfare of employees. Karakas and Lee (2004) noted that leadership that puts that takes care of workers results in increased organizational productivity. In addition, effective leadership strategies are manifested by employees’ overall sense of harmony in general life (Karakas & Lee 2004).
According to Schulze (2006), leadership that provides intrinsic rewards and social orientations increases job satisfaction. The interactions of the employees provide the social aspect while the physical conditions inherent in the job influence the individual to achieve either job satisfaction that is paramount for innovation. Employees take part in most functions in relation to the day-to-day running of the business (Arnolds & Boshoff 2001). Many organizations strive for a type of human resource group that is best suited to propel the organization to achieve its goals and objectives.
The expectation is that the top management leaders should make maximum utilization of the available resources such as the employees to ensure that they remain competitive in the market. Arnolds and Boshoff (2001) pointed out that a trained workforce understands the vision, mission, and goals of the company. The factors that enhance the wellbeing of the employees improve their motivation and strengthen the performance of the organization. Therefore, from the employee’s perspective and studies by different scholars, job satisfaction is based on multiple factors. The factors include policies that affect leadership, social integration of the workforce, community service, and programs that enhance personal growth, such as remuneration and sense of belonging to the organization.
I have learned that effective leadership involves proper planning and formulation of relevant strategies for the sake of steering the organization forward. The goals of the company, therefore, reflect the anticipated results of the organization. With this, my company will be provided with a clear direction towards the attainment of the objectives. Therefore, it is important for organizations to envision the anticipated results before devising plans to meet them.
Many written reports have emphasized the apparent correlation between a thoroughly designed and strategic preparation and the overall success of the organization (Keller 2006). In the contemporary business climate, most companies are confronted with stiff competition for their quality staff (Matha & Boehm 2008). The specialists in the arena of human resources emphasize that companies should highly invest in grooming development and earnings from an enhanced working environment.
A depressed level of staff exodus as well as enhanced creativity, innovation, productivity, and organizational performance increase productivity (Chardan & Devi 2014). Thus, I have learned that any leadership involves the vision and direction development that aims at the future, along with strategies that are necessary to reach the set goals.
Effective leadership involves setting up of goals of the organization. In addition, it entails outlining in detail the strategy to employ in order to realize the set goals for the organization. Planning involves creating activities that are in conformity with the activities of the organization. These activities normally justify the result that has been created by the means. Effective leadership involves a good planning process that can be divided into two categories, for instance, informal planning and formal planning. Informal planning is an abstract design that is executed without being written down. It focuses on the short term as it is so specific to an area of the organization. Formal planning, on the other hand, is the kind of planning that is written down in advance. It focuses on the long-term objectives of the organization as it entails the shared goals of the organization.
Based on what I have learned, I intend to start a business venture in which I will put my leadership skills into practice. I plan to start a sandwich company that will be known for the best breakfast sandwiches and lunch sandwiches. My vision is to start just with one outlet, but with time expand to several outlets all over the world till I establish my brand of production. I will name it Weiss Sandwich Company Limited. My unique identity will be to produce sandwiches with natural ingredients and the best quality of bread.
I hope to establish a dependable following by providing tasty and fresh sandwiches produced from local ingredients available. The local providers will supply the ingredients. The ingredients will be prepared on-site with the aim of giving the customers a natural fresh taste. The reason for using local suppliers is to personalize them, thereby making our sandwich experience more exciting and unique. We also plan to carry out a contest for customers to showcase their talents by making their sandwiches in our outlet so that we can evaluate them and check on what we can add.
I plan to make an initial investment of £15,000. With this, I will set a target of £30,000 as the profits for the first year of production. Through my leadership qualities, I intend to ensure that this profit doubles in the second year and triples in the third year. Through my leadership, the company is projected to grow by at least 6 percent bi-monthly. With such visionary leadership, my company will be provided with a clear direction towards the attainment of the objectives. Thus, it is important for organizations to envision the anticipated results before devising plans to meet them.
My program is attainable and can be carried out by formulating the relevant strategies that can guide my business ahead. Through transformational leadership, I will take on traits of being open-minded, being a perfectionist, being passionate, being elastic, being charismatic, and being highly persuasive. I will manage the affairs of society. I will also wait for a team of followers to whom I will act as a source of divine guidance and motivation.
Breeding and development of the company’s workforce will be very important issues for our fellowship if the value and potential of the human resources are to be harnessed and developed. It produces a great opportunity for the members of the organization to devise new thoughts that can supercharge the execution and the operations of the organization. As a potential leader, I will want the best from their followers; therefore, I will plan for breeding activities for them.
My business idea and business plan have been confirmed through market research that we bore out. The sandwich market in the US is growing rapidly, and it is highly valued. Very many people will have a sandwich for lunch. Our location will be very strategic to capture the attention of the surrounding residents and businesses. We will offer the best sandwich prices than our competitors, which enables us to earn good revenue. The basis of the market research is to make us stand out among the other sandwich outlets. The market research focused on the competitors, whereby we looked at their pricing, products, customer service, and the general business.
The profile of the local area where the business will be set up is as per the government records. The area has a total population of 259,536 people, of which 125,473 are males, and the rest (134,063) are females. 48,697 individuals are aged 0 to 15 years. 191,158 individuals are aged 16 to 75 years. There are 111,243 households with residents with an average size of 2.33 family members. There are many large business complexes; therefore, many organizations are accommodated. The various organizations that are provided in the business complex include shops, restaurants, banks, shopping malls, and many offices. In addition, the area has a local university. The transport system in the area is also effective as there are both a bus station and a railway station.
The findings of the market research pointed out to the fact that the area is a prime location for our sandwich outlet. For instance, there is a large population of residents. The sandwich outlet will be located along a busy street that is our local area, and we have a better understanding of the residents. In addition, the people living in the location have high income; thus, a higher propensity to consume the sandwiches. The other sandwich shops are also located along the busy street; this will enable us to compete on the same level. An analysis of the street was also carried out with the aim of monitoring the human traffic in the morning hours and the afternoon hours. The morning traffic was monitored between 7:30 and 11:00 in the morning, and the afternoon traffic was monitored between 12:00 and 3:00 pm.
From the case study of Steve Jobs and Tim Cook, I have learned that a good work environment plays a crucial role in promoting performance in the organization. Therefore, proper strategies and leadership strategies that put into consideration the needs of the customers will be critical to ensuring the success of the business. The incorporation of practices that motivate the staff in the business will also help in increasing productivity. Motivated employees will ensure that the needs of the customers are taken care of in the best manner. I addition, the leadership strategies will be designed in a manner that will encourage innovation and the generation of new ideas.
References
Abbas, W & Asghar, I 2010, ‘The role of leadership in organizational change: Relating the successful organizational change to visionary and innovative leadership’, Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, vol.41, no. 2, pp. 1-49.
Adetule, J 2011, Handbook on management theories, Author House, Bloomington.
Allen, D & Wilburn, M 2002 Linking customer and employee satisfaction to the bottom line, ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee.
Arnolds, C & Boshoff, C 2001, ‘The challenge of motivating top management: a need satisfaction perspective’, Journal of Industrial Psychology, vol. 27, no. 1, pp 39- 42.
Aquinas, P 2006, Organizational behaviour: Concepts realities applications and challenges, Excel Books, New Delhi.
Avery, C 2004, Understanding leadership, Sage Publications, London, UK.
Avolio, B, Walumbwa, F & Weber, J 2009, ‘Leadership: Current theories, research, and future directions’, Annual Review of Psychology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 421-449.
Bass, B 2005, Transformational Leadership, Simon and Schuster, New York.
Batool, B 2013, ‘Emotional intelligence and effective leadership’, Journal of Business Studies quarterly, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 85-94.
Bell, J 2005, Doing your research project: a guide for first-time researchers in education, health and social science, Open university press, Maidenhead.
Bernard, M 2003, ‘The future of leader in learning organisations, Journal of Leadership and Organisational Studies, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 19-31.
Blanchard, H & Cathy, S 2002, The generosity factor: Discover the joy of giving your time, talent, and treasure, Zondervan Press, Grand Rapids.
Bronfenbrenner, U & Evans, G. 2000, ‘Developmental Science in the 21st Century: emerging Questions, Theoretical Models, Research Designs and Empirical Findings’, Social Development, vol. 9, no. 1, pp.115-125.
Burke, W 2001, Full leadership development: building the vital forces in organizations, Human Resource Development Quarterly, vol. 12, no.1, pp. 99-102.
Carneiro, A, 2008, ‘When leadership means more innovation and development’, Journal of Business Strategy Series, Vol. 9, no. 1, pp.176-184.
Chardan, C & Devi, R 2014, ‘Leadership Styles’, Research Journal of Management, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 2-10.
Clawson, J 2011, Level Three Leadership: Getting Below the Surface, Prentice Hall, New York.
Collins, J 2001, Level 5 leadership: The triumph of humility and fierce resolve, Harvard Business Review, Boston.
Daft, R 2005, The leadership experience, Thomson South-Western, Mason, OH.
Denk, T 2010, ‘Comparative multilevel analysis: proposal for a methodology’, International Journal of Social Research Methodology, vol.13, no.1, pp. 29-39.
Flint, B 2012, The journey to competitive advantage through servant leadership: Building the company every person dreams of working for and every president has a vision of leading, West Bow Press, Bloomington.
Gallos, J 2008, Business leadership: A Jossey-Bass reader, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Gratton, C & Jones, I 2004, Research methods for sport studies, Psychology Press, Chicago.
Gupta, V 2004, ‘Impact of socialization on transformational and transactional leadership: Role of leader member exchange’, South Asian Journal of management, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 2-17.
Harold, D & Fedor, D 2008, ‘The transformational and change leadership effect on employee’s commitment to a change’, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 93, no. 2, pp. 346-357.
Hughes, R, Ginnett, R &Curphy, G 2012, Leadership: Enhancing the lessons of experience, McGraw-Hill Irwin, New York.
Jobs, S. &Thomas, A 2011, The business wisdom of Steve Jobs, Skyhorse Publishers, New York.
Johnson, T 2007, ‘The Principal Leadership Styles Impact on Teacher Motivation and Job Satisfaction, Human Resource Development Quarterly, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 2-19.
Kafetsios, K, Kassotaki, A, Zammuner, L & Vouzas F 2009, ‘Emotional intelligence abilities and traits in different career paths’, Journal of Career Assessment vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-17.
Kang, L & Singh, R 2006, ‘Stress at Work: An Assessment of the Magnitude of Various Organisational Stressors’, Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 190-202.
Kantabutra, S & Avery, G 2010, ‘The power of vision: statements that reason at’, Journal of Business Strategy, vol.31, no. 1, pp. 37-45.
Karakas, F & Lee, M 2004, ‘A qualitative investigation into the meaning of family well-being from the perspective of part-time professionals’, Equal Opportunities International, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 57-77.
Keller, R 2006, ‘Transformational leadership, initiating structure & substitutes for leadership: A longitudinal study of research & development project team performance’, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 91, no.1, pp. 202-210.
Kippenberger, T 2002, Leadership Styles, Capstone Publishers, London.
Kline, J 2010, Ethics for International Business: Decision-Making in a Global Political Economy, Routledge, New York.
Kolenda, C 2001, Leadership: The warrior’s art, Army War College Foundation Press, Carlisle.
Kothari, C 2005, ‘Contemporary methods of quantitative data collection and analysis in literacy research’, Reading Research Quarterly, vol. 39, no. 1, pp.94-112.
Kouzes, J &Posner, B 2012, The Leadership Challenge, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Kouzes, J &Posner, B 2003, Encouraging the heart: A leader’s guide to rewarding and recognizing others, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Lowe, K & Kroeck, Y 2006, ‘Effectiveness correlates of transformational and transactional leadership’, The Leadership Quarterly, vol. 7, no.3, pp. 385-425.
Malik, M, Danish, R & Munir, Y 2012, ‘The role of transformational leadership and leaders emotional quotient in organisational learning’, World Applied Science Journal, vol 16, no. 6, pp. 814-818.
Martindale, N 2010, ‘Leadership styles: how to handle different personas’, Strategic Communication Management, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 32-35.
Matha, B & Boehm, M 2008, Beyond the babble: Leadership communication that drives results, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Maxwell, J 2007, The Maxwell leadership Bible: New King James Version, Thomas Nelson, Nashville.
Miller, K 2012, Organisational communication: Approaches and processes, Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Boston.
Mitchell, M & Jolley, J 2010, Research design explained, Wadsworth, Belmont.
Neumann, W. L 2007, Social Research Methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Journal of Research, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 35-44.
Northouse, P 2001, Leadership; Theory and Practice, Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks.
Northouse, P 2010, Leadership: Theory and practice, Sage Publications, Oakland.
Oladipo, S, Adenaike, F & Ojewumi, A 2010, ‘Establishing the reliability and validity scale’, IFE Psychologia, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 1-23.
Polelle, M 2008, Leadership: Fifty great leaders and the worlds they made, Greenwood Press, Westport.
Rafferty, A & Griffin, M 2004, ‘Dimensions of transformational leadership: conceptual and empirical extensions’, The Leadership Quarterly, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 329-54.
Rothfelder, K, Ottenbacher, M & Harrington, R 2012, ‘The transformational, transactional and non-leadership styles impact on employee job satisfaction, German hospitality industry, Tourism and Hospitality Research, vol.12, no. 4, pp.201-214.
Sadler, P 2003, Leadership, Kogan Page Ltd, London.
Sakiru, O, D’Silva, J, Othman, J, Silong, A & Busayo, A 2013, ‘Leadership Styles and Job Satisfaction for Employees in Medium and small Enterprises’, IJBM, vol. 8, no. 13, pp. 122-143.
Sans, W 2011, ‘Sampling methods and market Surveillance’, Economic Quality Control, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 2-11.
Sayeed, O & Shankar, M 2009, ‘Emotionally intelligent leaders and Transformational leadership styles’, Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 593-610.
Schulze, S 2006, ‘Factors influencing the job satisfaction of academics in higher education’, SAJHE, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 318-335.
Schuttler, R & Burdick, J 2010, Laws of communication: The intersection where leadership meets employee performance, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ.
Sipe, J & Frick, D 2009, Seven pillars of servant leadership: Practicing the wisdom of leading by serving, Paulist Press, New York.
Sreejesh, S & Mohapatra, S 2014, Mixed research methods design: an application in consumer brand relationships, Springer, New York.
Vogt, W, Gardner, D &Haeffele, L 2012, When to use what research design, Guildford Press, New York.
Wanasika, I 2009, ‘In search of global leadership’, Journal of International Business and Cultural Studies, vol. 1, no. 1, pp.2-16.
Watson, T 2006, ‘Motivation: That’s Maslow, isn’t it’, Management Learning, vol. 27, no. 10, pp. 447-464.
Woods, A 2010, ‘Democratic leadership: Drawing distinctions with distributed leadership’, International Journal of Leadership, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 3-36.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Projected cash flow
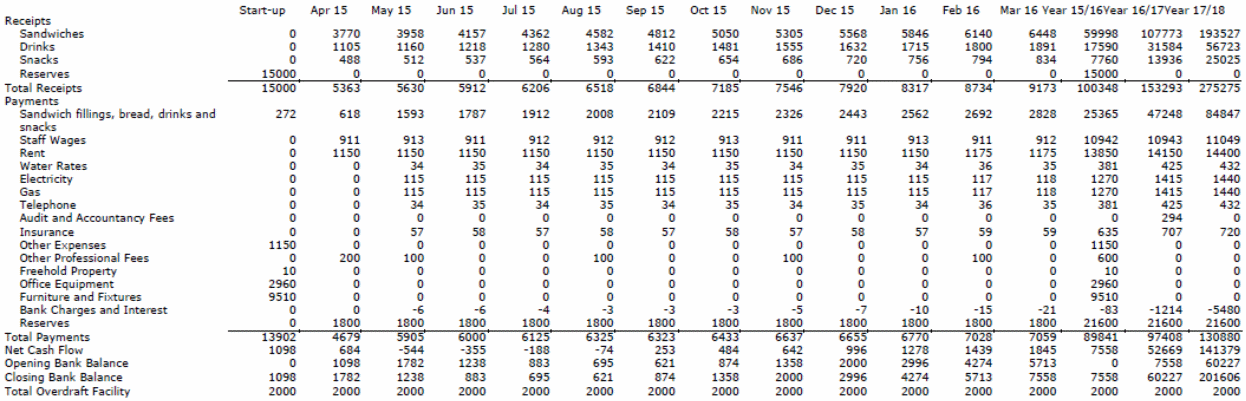
Appendix 2: Projected profit and loss
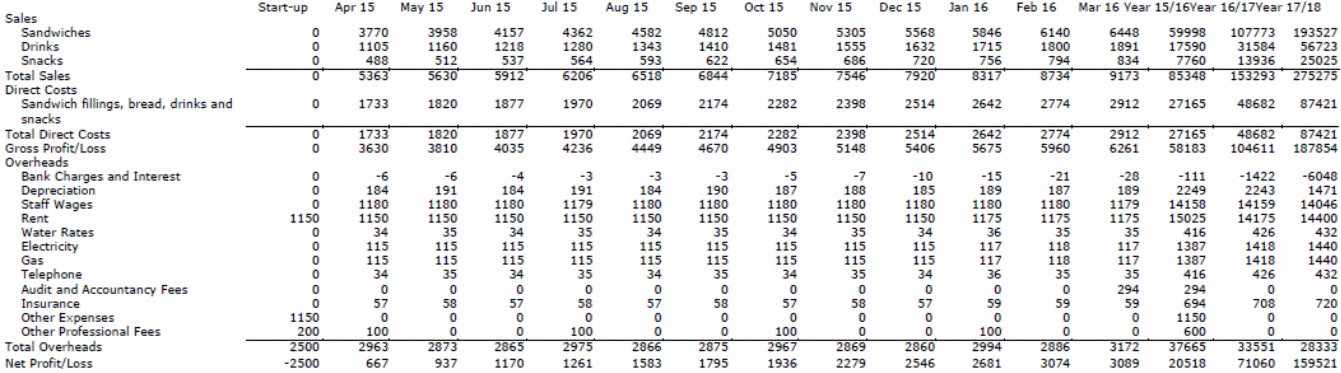
Appendix 3: Projected balance sheet