Introduction
Introduction
Generation Z employees are joining the job market and their traits are significantly different from that of the older generations. According to Tulgan, a significant number of these young workers are graduating from colleges across the country. Managing these employees has become a major concern for leaders in modern organizations. Ngunjiri and Madsen argue that the totalitarian approach of managing employees, which was popular among the silent generation, has increasingly become unpopular among the younger generation. A leader must understand the needs and fears of followers and develop effective ways of addressing them. The ability of a manager to guide employees in achieving specific organizational goals depends on their level of motivation. When employees are highly motivated, they tend to make an extra effort to ensure that specific goals are realized. However, demoralized group of workers will always tend to avoid their responsibilities and would not be concerned about organizational goals. As such, current leaders have to understand specific traits of Generation Z employees, factors that motivate them at work, and what they expect of their leaders. The transition is coming at a time when women are becoming increasingly involved in leadership both in startups and in large corporations.
Women’s leadership has gone through a major transition over the past several decades. The concept of women leadership among the silent generation was frowned upon, as Tulgan observes. In fact, it was not common to find women in senior management positions in the corporate world. However, the trend has been changing consistently over the years despite the numerous challenges that they often encounter. Baby boomers encouraged girl-child education, which marked a major step towards women’s empowerment. Montes notes that the effect of girl-child education during the period of baby boomers became apparent when generation X joined the job market. Studies show that a new generation of ambitious young women committed to achieving corporate success despite the existence of numerous challenges emerged. When generation X entered the job market, they started embracing women’s leadership as it was becoming a common phenomenon despite the existence of numerous stereotypical beliefs that impeded career growth among female managers. Generation Z is joining the job market at a time when it has become evident that women have the capacity to offer quality leadership in the corporate world. The researcher considered it important to understand whether women can make better leaders than men when it comes to managing generation Z employees.
Background
The concept of leadership has been evolving over the years because of various changes in the socio-economic, political, and technological environment. According to Rhode, as generation Z enters the job market, managers are finding it difficult managing them using some of the traditional concepts of leadership. Scholars have found out that generation Z are restless in the workplace environment. They can easily consider switching jobs from one employer to another whenever they feel discontented at their current workplace. Their addiction to social media, especially Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram is another major issue. They spend a significant portion of their time on these platforms instead of engaging in meaningful economic activities. In a world where the concepts of activism and human rights have gained relevance amongst many people, leaders find it challenging controlling generation Z in the workplace environment. The ability of a firm to achieve success in the current competitive business environment depends on the effectiveness of its management unit to overcome these challenges.
Women are becoming increasingly engaged in leadership despite the existence of issues highlighted above. According to Kumar, the workplace environment has evolved over the years and women leadership is becoming increasingly acceptable in different workplaces around the world. Several Fortune 500 companies have now embraced women to be their chief executive officers. Mary Barra of General Motors Company, Ginni Rometty of IBM, Indra Nooyi of PepsiCo, Safra Catz of Oracle, and Vicki Hollub of Occidental Petroleum are some of the female chief executive officers of some of the largest global corporations. These female leaders have to deal with the emerging challenges in the current business environment. They have to create an environment where generation Z can find sustainability in order to improve their productivity. Some of these female generation Z employees are ambitious and keen on climbing the corporate ladder. Managing such an ambitious workforce depends on the ability of the leader to understand their needs and channel the energy towards the right courses. In this paper, the researcher seeks to determine the effectiveness of women’s leadership at a time when young workers in generation Z are finding themselves in the workplace environment.
Research Problem
Women are currently playing critical roles in various business entities, government agencies, and non-profit making organizations around the world. The former President Barack Obama even stated that women make better leaders when he was campaigning for former first lady, Hillary Clinton. As women position themselves as leaders, they have to contend with new challenges in the current society. Many economies in North America and Europe are growing, and unemployment rates are dropping. As such, it is easy for an employee to move from one company to another. The economic growth is of great benefit to companies keen on increasing their revenues, but it introduces a new challenge where employees feel that they do not have to struggle to earn a living. Some of the traditional leadership styles based on theory X of leadership are becoming ineffective in such a business environment.
Motivation and the ability to influence and convince employees have become more desirable leadership attributes than the ability to scare and force employees to deliver impressive results. Bungay argues that leaders have to find ways of charming their workers as a way of influencing their performance and ensuring that they spend most of their work time on activities assigned to them. At the same time, women are still fighting the stigma that they are not fit to be in leadership. Although some great leaders such as Margret Thatcher of the United Kingdom and Angela Merkel of Germany have proven that women can make some of the best leaders in the world, Tulgan argues that they still have to deal with the perception that they got favored to achieve their positions.
Significance of the Study
Women leadership and generation Z is an important topic because it addresses two critical issues, which are emerging in the current workplace environment. Generation Z forms a significant portion of newly recruited employees in many companies across North America and Europe. Their aspirations in life, motivation towards work and general mannerism is significantly different from that of the older generation. It means that when managing such employees, the leadership needs to take a unique approach to ensure that they remain motivated and committed to a firm. Women’s leadership has also become a major issue in the current workplace environment.
Affirmative action was seen as the only way of creating a platform where women could achieve success despite numerous challenges they face in the workplace environment. However, it has become less relevant in most of the developed economies as many consider it inappropriate because it creates the impression that women are disadvantaged. The concept of equal opportunity for all emerged, where entities are encouraged to base promotions on merit without any form of bias. Many women have demonstrated that given equal opportunities they can compete favorably against men and achieve success in the corporate world. However, they now have to face the challenge of managing generation Z. This study will investigate the capacity of women to lead in the modern corporate world and the manner in which they should manage young employees.
Research Question and Objectives
Generation Z currently form a significant number of newly recruited young employees from college. Managing these young employees requires a different approach, and women in leadership need to understand how to control them. In this section, it is important to develop a set of questions that would help in collecting data from different sources. The researcher developed a research question, which also formed the hypothesis for the paper, as follows:
Do women make better leaders for the generation Z employees?
The question was meant to offer guidance when collecting data from various sources. The researcher developed an objective based on the above research question, which was to be realized at the end of this study. The following is the objective:
- Finding a concept of women in leadership and its relevance in managing generation Z employees
Thesis Structure
The paper has five chapters, introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, and conclusion. The first chapter provides background information about the study and steps needed to achieve success. The research question and significance of the research are also discussed in this chapter. The second chapter provides a review of the literature. It was necessary to explore what other scholars have found out in this field. The third chapter is the methodology where the researcher discusses approaches used to collect, analyze, and present data. The fifth chapter provides a summary of the findings and recommendations that should be considered. The paper also provides a list of sources used in the study.
Literature Review
The previous chapter provided a detailed background of the concept of women in leadership and its relevance in managing generation Z employees. In this chapter, the focus is to review what other scholars have found out in this field, and grey areas that still need to be investigated. According to Schiefelbein, literature review plays an important part in any scholarly research. It makes it possible to gather secondary data based on the already published information. As such, it eliminates cases where one duplicates information that is already in existence. The review makes it possible to identify possible conflicts of information or issues that scholars feel should be addressed.
Generational Characteristics of the Workplace
The workplace environment has been changing over the decades because of the socio-economic and technological changes. Globalization has also had a massive impact on the workplace environment as people move from one part to another. The increased interaction and cultural integration have brought new realities to people in various parts of the world. Diversity in the workplace environment has also helped in transforming organizational cultures and practices, especially among transnational companies. According to Tulgan, the character traits that traditionalists exhibited about four or five decades ago are significantly different from that of the younger generations. The expectations, beliefs, and desires of people in different generations vary. As such, Ngunjiri and Madsen hold that the manner in which a firm handles baby boomers in the workplace should be different from the approach taken when handing generation X or Y employees. Trying a generalized approach may have a counterproductive outcome because of the difference in traits based on the age of these workers. The researcher considered it appropriate to analyze the traits of these different age groups to determine how they are different from generation Z employees.
A silent generation or traditionalists
The silent generation, sometimes referred to as the traditionalists, is a group of individuals who were born between 1922 and 1945. The majority of them are retired, and a few who are still active in the corporate arena are majorly running their businesses. The traditionalists were known for their strict adherence to rules and regulations set in the workplace. They are highly disciplined and respect authority. The trait meant that they could easily flourish in an environment of authoritarian rule. They did not find problems following strict instructions and working under pressure. They value gratitude and appreciation from both the junior and senior employees within the firm. According to Kadakia, another major characteristic that makes the silent generation significantly different from the younger workers is their simplistic lifestyle. They do not have the desire to show off their financial capacity even if they are financially empowered. They may purchase fancy products primarily to enjoy comfort instead of showing off their wealth. This group of workers highly believed in the separation of duties based on one’s gender. Grubb explains that they inherited a society where men were believed to be the breadwinners while women were expected to take care of their homes. When growing up, they embraced this tradition and did not believe in having women in leadership. Although women had started making impressive progress in various careers such as teaching and nursing, they were not active in senior leadership positions.
Baby boomers
The baby boomers are individuals who were born between 1946 and 1964. They were born at a time when the United States and many western nations were experiencing impressive economic growth after the end of the Second World War. Many parents felt comfortable having multiple children because of the improving economic conditions. The baby boomers still form a significant number of the workplace population, although some of them are retiring from the corporate world. Espinoza and Ukleja explain that baby boomers currently dominate top leadership in large and mid-sized companies in Europe, North America, and other parts of the world. They are keen on exerting their influence when defining cultural practices and values in the workplace. They were strongly influenced by the silent generation, and they are often considered workaholics because they find it normal to spend more hours in the workplace. They value education and really emphasize on the quality of products or services delivered to clients.
Baby boomers value teamwork, especially when handling related tasks. Their strong work ethics have been attributed to the success of the majority of the current Fortune 500 companies. They are independent-minded and self-assured, a trait that has made them successful as modern-day leaders. According to Espinoza and Ukleja, this generation of workers is competitive and goal-centric. The competition between Bill Gates of Microsoft and Steve Jobs of Apple Inc in the initial years when the two companies were witnessing massive growth demonstrates the level of competitiveness of the two companies. The two leaders were keen on ensuring that their companies emerged as dominant players in the computer software industry. It is also important to note that these workers are often considered resourceful because of their experience and mentally focused. Caraher believes that baby boomers will continue to dominate corporate leadership for another decade.
Generation X
generation X is a group of people who were born during the years of 1965 to 1980. The majority of them are in mid-management, with a significant portion heading different sizes of companies around the world. Dunn explains that when growing up, generation X children revolted against authority, and they maintained these traits even after getting into the job market. They lacked the strict discipline and the ability to work for long hours as exhibited by the baby boomers. Connell noted that generation X workers are often skeptical of authority and they often show little respect to title, hierarchy, and status. Instead, they emphasize more on work-life balance more. While they will remain committed to their responsibilities, they also want their managers to respect the need for them to attend to family needs.
Most of them prefer working in an informal workplace where they can have fun without compromising on the quality and quantity of their output. They are self-reliant, and as such, do not believe in working under strict supervision. Unlike the older generation, these workers do not believe there is value in spending many hours in meetings and conferences. Instead, they prefer high productivity to help in completing tasks within the shortest time possible so that they can have their personal time with family and loved ones. According to Tulgan, the fact that generation X employees embraced the hands-off philosophy of management created a trend where some of them could work from home, a trend that was unheard of among workers in the previous generation. As emerging technologies continued to change the workplace environment, such practices started becoming common among this generation of workers.
Generation Y
Generation Y, often referred to as the millennial, is a group of people born between 1981 and 1994. They were significantly influenced by generation X employees. According to Ngunjiri and Madsen, these employees work in a highly diversified environment. They do not find it challenging working in such an environment because they went to school with people of diverse backgrounds. Madden believes that one in every three employees in the current workplace environment in the United States is a minority. The trend has also become common in many European cities such as Berlin, London, and Paris among others. Although discrimination is still a common problem among members of this group, the situation is not as bad as it was among employees of the previous generation. Generation Y employees are described as optimistic people who are confident and civil-minded.
Ngunjiri and Madsen believe that these people are committed to ethical principles and morality in the workplace environment. Employees in this group highly value effective communication in the workplace and will often avoid uncertainties. They value a management system where decisions are made within the shortest time possible and the outcome communicated to all the relevant parties using reliable systems. Schiefelbein notes that generation Y has embraced technology-based communication systems such as emails and other emerging platforms such as WhatsApp. They also cherish multitasking, especially if doing so would help them create time for personal recreation without compromising on quality. It is important to note that these individuals are materialistic in nature, which means that the amount of salary offered to them often defines their loyalty to the firm. However, they are open-minded and can easily embrace change as a way of improving their productivity and satisfying their clients.
Generation Z
The last group of employees in this classification is generation Z. They are individuals who were born after 1994. A good number of people in this class, especially those born between 1995 and 2000, have just completed college, and are joining the workplace environment. As Caraher observes, the number of these employees is expected to increase as the older generation retires. The traits of generation Z workers are significantly different from that of the older generation. Ngunjiri and Madsen emphasize the need to understand these characteristics to know how they should be managed in the changing corporate world. One of the most obvious characteristics of generation Z employees is that they are tech-savvy.
According to Espinoza and Ukleja, the majority of these people grew up in an environment defined by technology. They had access to mobile phones when they were young and social media platform was just gaining their foothold as a dominant means of communication. As such, most of them have been experimenting a lot with technology from a tender age. Among the silent generation, communicating through platforms such as social media is considered unacceptable when engaging in official duties. However, generation Z is very comfortable with such methods of communication in different settings. This young generation of employees is open-minded. They can easily embrace change, especially when it promises a better world. According to Montes, their flexibility makes them easy to work with when introducing new systems in an organization. According to this scholar, generation Z employees are entrepreneurial. A significant number of these young people have demonstrated their desire to start sustainable business ventures even at times when the older generation gets comfort in employment, which many consider social security.
Young individuals are willing to forfeit such security to engage in business ventures. Some scholars have described this generation as being down to earth, which is a major shift from generation Y employees keen on showing off their wealth. They are also agile people; a trait that many believe has pushed them to consider venturing into business instead of settling for employment. Espinoza and Ukleja believe that generation Z has become sensitive to environmental pollution. They believe in science and are concerned about climate change. They have the fear that the older generation may leave them with the serious environmental challenges that they might be forced to address when it may be too late. As such, many of them are embracing environmentally sensitive policies as a way of preserving the earth. They also prefer working in companies with elaborate programs on how to manage the emission of greenhouse gases, industrial effluents, and other wastes, which have a direct impact on the environment. Table 1 below summarizes the character traits of the five generations of employees.
Table 1: Generational characteristics in the workplace
The comparison above shows that there has been a generational change of character of workers over the past several decades. The character and values that were embraced by the traditionalists are significantly different from that of the millennial and generation Z. According to Tulgan, a leader must start by appreciating the changing forces in the environment to determine the appropriate approach of leadership that would be appropriate when handling a specific group of workers. Knowing what they expect of a leader and the values that they uphold helps in defining principles and policies that a firm should embrace. Women in leadership need to understand how to manage generation Z despite their unique traits.
Gen Z and Start-Ups
In the section above, the unique traits of a different generation of employees, including that of generation Z have been discussed. It is important to focus on the relevance of these unique traits in startups. According to Madden, the high rate of failure of small and medium-sized start-ups is significantly attributed to the ineffectiveness of the management and commitment of the employees. The ability of these firms to succeed depends on skills, level of commitment, and effective communication amongst employees. The input that every worker makes in the specific area of assignment affects the overall performance of the firm. Many startups find it more desirable to hire young agile employees instead of the aging population. The traits discussed in the section above make them more desirable for these small companies. According to Kadakia, when a firm is starting its operations, one of its unique traits is often flexibility. During those early years, several mistakes would be made, and the ability of a firm to achieve success would be defined by the speed with which it can correct such mistakes. Flexibility is, therefore, critical in such situations. Generation Z is known for its flexibility. They can change from one approach to another as long as they are offered the necessary support and promised that such changes would create a better workplace environment for everyone involved.
The generation Z employees, unlike those of generation X, are not excessively materialistic. According to Montes, one of the common challenges that small startups face in their early years of operations is financial constraints. Most of these firms struggle to meet numerous needs relating to their operations. Working with materialistic employees who value attractive remuneration over everything else can be dangerous. Generation Z makes the best bet for a small firm that has limited financial resources. A significant number of these young employees are not burdened by family needs. The majority are yet to start families, which means that they can be contented with the salary that would be offered to them. It is easy to align their corporate goals with the company vision. The aim of the manager would be to ensure that the firm grows and reaches a level where it can pay its employees attractive salaries. On the other hand, these young employees are motivated by a promise for a better future.
The analysis of traits of these young employees shows that they are open mindset and agile. These characteristics are important for a small company that is starting its operations. Connell explains that in the modern business environment, it is common for a firm to use unconventional approaches to meet customers’ needs. For instance, large corporations cannot afford to give their numerous customers personalized services. However, small entities are embracing this approach of serving customers by trying to understand the individual needs of each client and providing services that meet these specific requirements. The younger generation is open to new ideas for meeting unique customer needs. Their agility means that they can easily understand emerging trends in the market. They can offer advice to the management on how to manage the changing market forces.
The analysis shows that this young generation of employees has embraced gender equality and women leadership. A study by Rhode shows that a significant number of new startups are headed by women. These leaders must understand that they can only achieve success in the market if they hire competent workers who also respect women as leaders. Having a team of highly qualified workers who do not value having a woman as their leader can lead to problems for the management. Dunn notes that generation Z employees have demonstrated their commitment to gender equality and do not have problems being led and directed by women. They focus on the competence and commitment of the leader instead of their gender. Female entrepreneurs would, therefore, find it easy working with these young employees. These employees will get the respect they deserve from these workers as they try to find ways of achieving success with their firm.
Ngunjiri and Madsen also note that the young generation of workers often embraces chances to learn from one another. The trait is crucial for a startup that is trying to learn the market trends to define its position in the market. As they learn the new market trends, they gain experience that would enable their company to achieve success in the market. Companies and leaders should understand the factors that motivate these young employees in the workplace environment. They need to know how they can be driven to achieve greater success despite the existence of numerous challenges in the workplace environment. Connell believes that generation Z employees have the most desirable traits for startups in the modern business environment. Female managers only need to understand how to maximize these traits to ensure that their startups achieve the desired level of success.
What Generation Z Want from a Leader
In the past, Ngunjiri and Madsen explain that managers majorly focused on what their companies needed of their employees. In this period, the unemployment rate was high and workers would contend with the strict working environment. The silent generation would work diligently, spend long hours at the workplace, and sometimes sacrifice family time just to ensure that they retained their jobs. Managers during this period did not have to worry about what employees needed because it did not matter. However, that has been changing consistently as unemployment rates continue to drop. Connell notes that generation Y can easily resign from a company when they feel their needs are ignored. The same is the case with generation Z employees. As such, a time has come when leaders have to understand what the younger generations want to ensure that they can be retained in the workplace.
Generation Z wants a leader who is understanding and compassionate. Women who hire these young workers need to appreciate their unique attributes and remain committed to providing an enabling environment. Tulgan rejects the claim that generation Z gets into the job market less prepared to deal with the realities of the workplace environment. It is true that the education system has been transforming at a relatively lower rate compared with the changing workforce environment. However, these employees also have unique capabilities that the older generation lacked when getting into the workplace environment. One of them is the ability to embrace diversity. According to Ngunjiri and Madsen, most of these people have grown up in diversified neighborhoods and attended schools where they interact with people from different racial and socio-economic backgrounds. As such, they can work well in a diversified workplace environment, which was a major challenge to the older generation. They prefer leaders who focus on these strengths instead of weaknesses.
Generation Z employees want leaders who would assist them in their career growth. Instead of having managers, they prefer having managers. Instead of issuing instructions, a leader should focus on guiding these young employees towards achieving specific goals. Given that they are futuristic, they often want to focus on improving their competency and the ability to achieve career growth. These young employees want leaders who can support them when they feel demoralized. Various challenges may emerge that may inhibit their capacity to work effectively. Espinoza and Ukleja observe that some of these issues may not be related to their work. However, a good leader must understand that when an employee’s private life is unsettled, they cannot perform optimally in the workplace. The restlessness and troubled mind would impair their judgment, and sometimes it may result in them making mistakes with devastating impact. As such, it is critical to ensure that these personal issues are addressed. Female leaders should create units within the human resource department where employees can be supported when they are going through challenging times in their lives.
How Companies Can Learn from This Young and Modern Generation
Companies of different sizes in varying industries can learn from the young and modern generation how to redefine their operations to meet emerging needs. Large corporations can learn about the changing tastes and preferences in the market and ways in which they can redefine their products to remain relevant in the market. According to Lamont, for the past two decades generation Z have remained influencers of purchasing decisions without the capacity to make critical decisions. They were children who could only make requests about specific products they desired. However, that is no longer the case as they reach the age of the majority and start supporting their expenditure. It means that they are no longer mere influencers. They can now make decisions about products they want to purchase, when to purchase them, quantity and quality they consider desirable, and any other factors that define buyer decision. As such, large corporations cannot afford to ignore this generation any longer. Learning about the needs and fears of these employees can help a firm to understand how to meet the emerging needs of customers in the same class.
Small and medium enterprises also have a lot to learn from these young employees. They have unique skills that can enable startups to achieve growth in the market. They are dynamic, a trait that is crucial for a small business enterprise. Their uncanny ability to identify and embrace emerging technologies is also of great importance to such firms. Rhode argues that in the modern business environment, technology plays an important role in defining the manner in which firms produce and deliver goods to the market. Communication is also currently entrenched deeply in emerging technologies. The modern approach of the employer-employee relationship and the desire for gender equality among these employees give women the chance to lead. These young workers appreciate women’s traits and their talents when it comes to leadership. Unlike the silent generation, these young employees find it comfortable working with female leaders in various organizational settings.
Women seeking corporate leadership can take advantage of that young mindset of changing the world as opposed to the old-fashioned hierarchical male-dominated leadership. Schiefelbein explains that women who have attained the highest leadership positions in their corporations went through numerous challenges to achieve such goals. However, forces are changing as the new open-minded group of employees get into the job market. Their positive attitude towards female leadership offers women a unique opportunity to climb the career ladder without having to face challenges that generation X leaders had to go through to achieve success. Schiefelbein warns that women should be reminded that such leadership positions would not be offered to them on a silver platter. They have to fight for these positions by showing competence and unique skills. Women have the advantage of working in an environment where they will not be judged based on their gender. Instead, their ability to become top leaders would always be defined by their skills and unique attributes. According to Ngunjiri and Madsen, affirmative action is losing its meaning among this young generation of employees.
In the past, some women gained leadership positions because of affirmative action. However, that strategy may not work for the current female leaders, especially when working with generation Z employees. These young workers believe that gender does not define the capacity of an individual in the workplace. As such, they do not believe it is necessary for them to get favors primarily because of their gender. Showing competence and the ability to subdue emotions is a unique trait that women have to learn. Although these young employees value female leadership, there is still a general belief that leaders should be strong and capable of controlling their emotions even when faced with various challenges in their workplace. Espinoza and Ukleja observe that sometimes a leader may be overwhelmed with emotions because of the challenges they go through. Women are more likely to break down when faced with such strong emotions than men are. The problem is that when one breaks down before the followers who look upon her as a role model, the respect and admiration may be lost. In such cases, it may not be possible to guide the followers when respect and admiration is gone. Trust will be lost soon after that, and it would be almost impossible for such a leader to manage her unit.
Comparison of Male and Female Leadership
The hypothesis of this research project was that women make better leaders for generation Z employees. Responding to this hypothesis would require a comparison of male and female leadership. Comparing the advantages and disadvantages of both helps in defining which form of leadership is appropriate to help determine which is more desirable for generation Z employees. Table 2 below compares the trait of female and male employees on four parameters. They include communication style, the reward system, self-branding, and feedback. The traits in each of the parameters have advantages and disadvantages for people who are in leadership positions.
In terms of communication style, it is evident that female leaders can sustain conversations more than men who do not like lengthy discussions with junior officers. This trait is advantageous to women when managing generation Z employees. These workers prefer an environment where they do not feel ignored and despised. When a leader creates time to have a conversation with junior employees, it emphasizes the value that the firm attaches to its junior workers. Women prefer a democratic way of communicating with their junior workers, especially when trying to find a new approach to undertaking a given task. On the other hand, men prefer a commanding and controlling approach to leadership. The democratic approach of managing workers is effective when handling generation Z employees. Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell explain that these employees prefer working in an environment where they can be consulted when making decisions that affect them. The only disadvantage of this strategy is that sometimes it may be time-consuming. However, the benefit of having a team of highly motivated workers who are committed to their work makes it a worthy leadership strategy. Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell also note that men tend to be more task-oriented than men are when communicating with junior employees.
In terms of the reward system, Bungay explains that female leaders tend to motivate employees to find self-worth and self-satisfaction. They embrace transformational leadership while men tend to prefer transactional leadership. According to Burton and Leberman, transactional leadership works well when a manager is focusing on short-term goals. However, transformational leadership is more effective when focusing on long-term objectives. In this context, women once again emerge as better leaders than men do when it comes to managing the younger generation of employees. Kumar contends that these workers value leadership that can help them identify their inner abilities without making them feel incompetent. They want a leader that can take their time to discuss their strengths and weaknesses in a constructive manner.
Self-branding was another issue that was taken into consideration in this analysis. According to Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell, women tend to be silent about their accomplishments while men like to talk about their achievements. Although the approach taken by women helps to demonstrate their humility, it may be disadvantageous when is seeking career success in a competitive business environment. Women should learn to show the community that they could also achieve success. Being silent may only demonstrate their weakness and their inability or unwillingness to compete against their male counterparts. As shown in table below, women tend to be comfortable with periodic feedback, while men often want constant feedback from their juniors.
Table 2: Comparing traits of male and female leaders
The Chance of Women Leadership in Startups
Startups offers women a unique capacity to be in leadership positions. Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell argue that women should be aware of the chance that startups and generation Z brings, in order to lead them successfully and make the next generation of leaders and future of companies successful and bias-free. However, that can only be possible if they identify the existing opportunities and make an effort to take advantage of them. They must demonstrate their capacity to lead by being diligent when undertaking responsibilities assigned to them. Ngunjiri and Madsen argue that due to the glass ceiling and old-fashioned male-dominated cultures in bigger companies, it is difficult to change such an environment. That is why young leaders should focus on startups because they share traits that generation Z employees have as shown in the discussion above. They work better together in combination and can easily achieve success. Starting with these small companies and later ascending to successful bigger companies is one of the ways through which these women can achieve career growth.
Starting and sustaining a company is a challenging endeavor. According to Tulgan, most start-up companies often fail soon after being unveiled, especially within their first year of operation. Another significant number often fail after operating in the market for two or three years. However, some manage to remain agile and achieve rapid growth despite the numerous challenges. One of the challenges that often make these firms fail soon after being launched is leadership. In most cases, the entrepreneur is expected to be the manager of the company. Some of them lack management and leadership skills. They struggle to coordinate the few employees they have and spread the resources available. They make ambitious plans and end up making costly mistakes that the firm cannot recover from, especially those which are operating on a tight budget. Such start-ups have leaders who lack the capacity to coordinate activities.
Women form a significant portion of those who are venturing into business. Schiefelbein believes that most of them often face unique challenges that men do not have to encounter. One such challenge is the perception that women cannot run a business without the direct support of men. As such, many feel that they have achieved their current positions because of favors they get from men. Such perceptions eliminate the respect that should exist between a business owner and customers, employees, suppliers, or business partners. An entrepreneur must master the art of making deals. One must negotiate mutually beneficial deals with different parties in a business arena. The problem that many women face is the demand for sexual favors from male colleagues. Some men feel that they can only negotiate for good deals if they can have their way with the woman. Such cases are frustrating, especially when the leader has to make several deals with different entities.
Managing generation Z is another issue that women have to face when running small and agile start-ups. These young employees need to be guided for them to understand how to behave under different contexts. Tulgan argues that they can only be mentored if they demonstrate respect and willingness to learn. Women in leadership have to earn that respect for them to have the capacity to guide these young employees. They have to demonstrate the ability to guide junior workers without fear or feeling intimidated. They have to learn when to be strict when it is necessary, and when they need to show concern and commitment to help. Schiefelbein notes that being strict and principled does not involve being harsh and using force to achieve specific goals. Instead, one needs to show love and concern at all times while making employees understand that her principles and values cannot be compromised in any way. A female leader must be tough but in a way, that demonstrates care and love.
In small companies, teamwork is critical in ensuring that the intended success is achieved. It is common to find cases where such firms lack clearly defined departments such as finance, procurement, marketing, warehousing, and production because of the small number of employees and financial constraints. However, that does not mean these activities will be ignored. The management must integrate these tasks and find ways of undertaking them successfully. Through teamwork, it becomes possible to delegate important tasks and to coordinate different activities that would enhance the ability to realize specific goals.
Women Leadership in Large Corporations
The study by Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell shows that women are flourishing in the corporate world. In the section above, it is evident that women have achieved success in small and medium enterprises. The majority of them started these firms as small entities, and through hard work, commitment, and determination, they have transformed these entities into successful business ventures. Another group of women is pursuing success in the corporate world. These women have high academic qualifications, and they have gained relevant experience in a lower and mid-level managerial positions. Bungay observes that leading a large corporation requires a different set of skills than managing a small or medium enterprise. Some of these corporations, such as General Motors, Anthem, IBM, Oracle, and PepsiCo operate in the global market. Understanding the local culture and customer needs within the country would not be enough. The top leader must understand how such a firm can achieve success in different countries despite socio-economic, political, and cultural differences. The manner in which PepsiCo operates in the United Kingdom or Germany would be different from the approach it takes in China or India because of these environmental differences.
Women have demonstrated that they have the capacity to take control of such multinational corporations despite the unique challenges that they have to overcome. According to Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell, for a long time, women were denied the opportunity to lead such large corporations. The cultural beliefs and practices at that time, especially during the silent and the lost generations, did not allow women to get into such powerful managerial positions. However, women’s empowerment in those days through girl-child education helped in introducing significant changes to the workplace environment that denied women the opportunity to achieve career success. Katharine Graham was the first female chief executive officer when, in 1972, she ascended to the top managerial position at Washington Post. Katherine stayed at the helm of the company for over a decade, initiating major projects that helped in transforming the company to its status. She introduced numerous revolutionary policies at the company, which helped it to achieve massive growth.
In 1979, Margret Thatcher took over the leadership of the United Kingdom as the Prime Minister. At that time, the country was experiencing economic challenges and there was a need to introduce economic policies that would revolutionize the economy. Thatcher was able to bring the changes needed in the country. Bungay observes that during her reign, the country started experiencing economic growth and other social reforms that transformed the country. She demonstrated to the world that women could not only be trusted with corporate leadership but also with the highest political offices. Since then, many women have climbed the career leader to become chief executive officers of different Fortune 500 companies around the world. In 2016, 32 Fortune 500 companies were headed by women, which marked a significant improvement. Leading large multinational corporations is significantly different from heading small start-ups. It takes time for one to acquire the necessary skills and be able to convince the board of directors about their capacity to lead. Figure 1 below shows the number of women who are currently engaged in leadership positions.
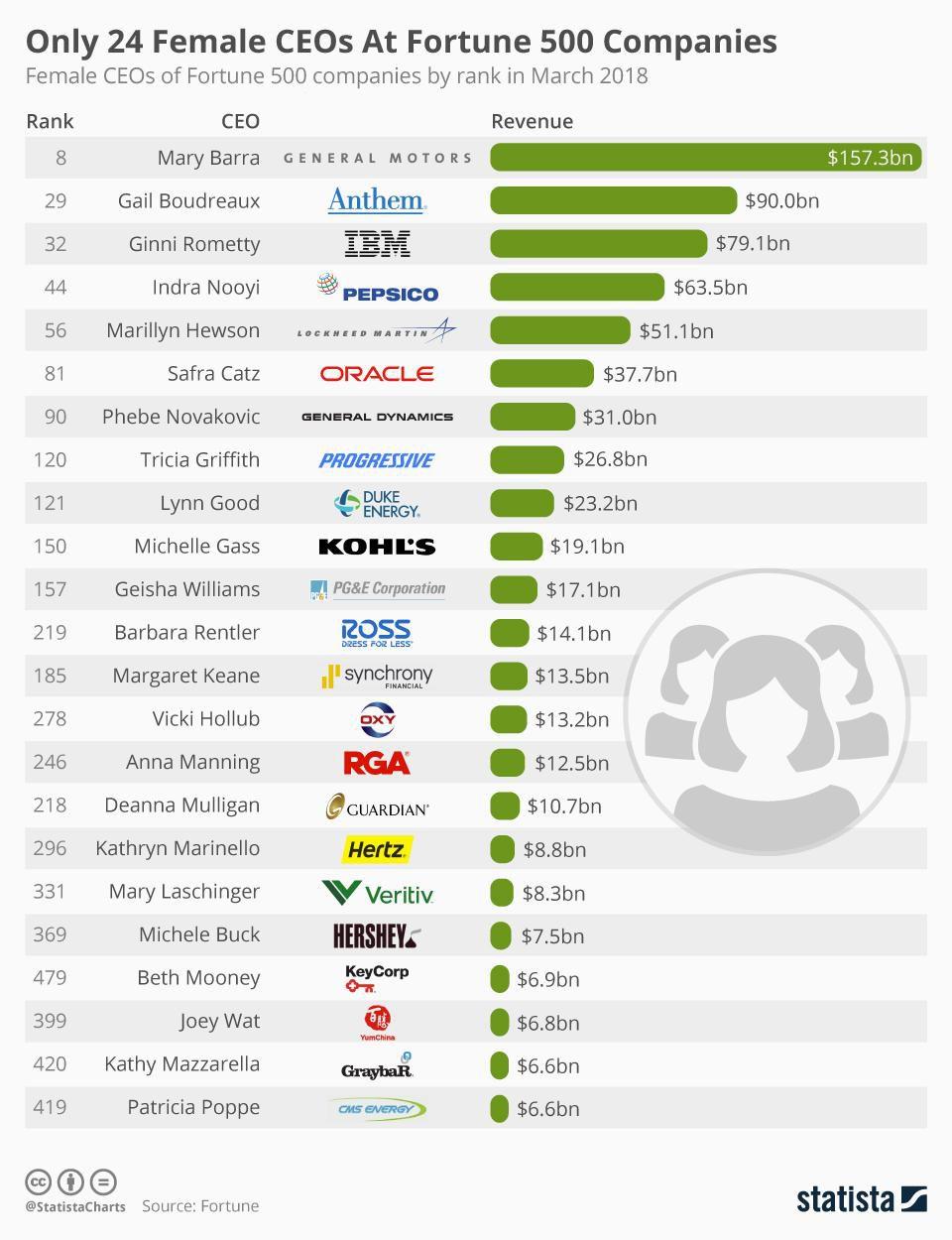
As shown in figure 1 above, the number of female chief executive officers at Fortune 500 companies dropped from 32 in 2016 to only 24 in 2018. It is worrying when the gains made in an effort to increase the number of women in these large corporations are lost significantly within such a short period. It means that women still have to make a lot of effort to compete favorably against their male counterparts. Mary Barra currently heads one of the largest companies in the world, General Motors. She is the only female leader of a firm that is ranked in the top ten of the largest firms in terms of annual revenue generation. Gail Boudreaux of Anthem, Ginni Rometty of IBM, Indra Nooyi of PepsiCo, Marillyn Hewson of Lockheed Martin, Safra Catz of Oracle, and Phebe Novakovic of General Dynamics are the other female chief executive officers of 100 companies in the Fortune 500 list. The current trend shows that women are overcoming many traditional stereotypical beliefs that questioned their capacity to lead.
Leadership Methods
The concept of leadership has evolved over the years because of the changing socio-economic and political environment. Different theories have emerged on how people should lead and why specific management approaches are more effective than others are. In the past, the dictatorial approach of leadership was considered effective in the workplace environment. However, the changing environmental forces have made it necessary for leaders to embrace mentorship as a way of managing employees. In this section, the researcher focused on discussing leadership theories, which have gained relevance over the past decade.
Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Leadership
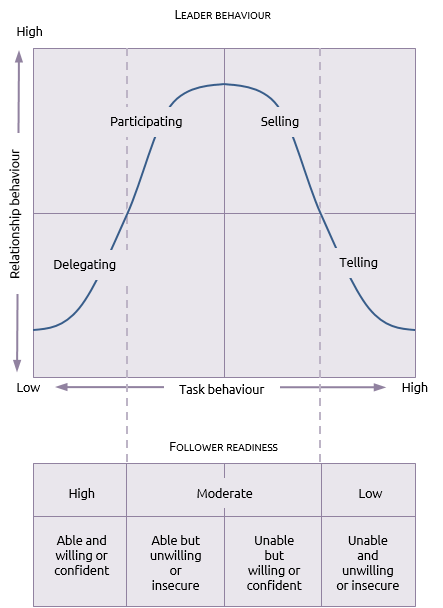
The situational model proposed by Hersey Blanchard holds that no specific style of leadership is superior to the rest. Different situations would emerge within an organization and an effective leader would understand when and how to adjust leadership style. A leader should also take into consideration the ability of followers when selecting the right approach to guide them towards success. This theory suggests that a leader should embrace any of the four leadership styles below depending on the task, relationship with employees, and their capacity. Delegating is one of the styles that the management can embrace. The low-relationship, low-task style involves a leader assigning different employees responsibilities depending on their capacity and department where they work. After delegating tasks, a leader is expected to allow employees to work without close supervision. It works in cases where a leader is dealing with highly-skilled, experienced, and disciplined employees who understand what is expected of them and are loyal to the firm.
The participating style is a high-relationship low-task style of leadership where the one in the management is expected to share ideas and decisions with junior employees without dictating how specific tasks should be accomplished. The model is popular when dealing with skilled and experienced employees but lack confidence and would like to make regular consultations. This model is effective when working with a team of highly disciplined employees who are able to develop creative ideas for undertaking their responsibilities. However, these employees often prefer getting approval from those in power before putting into practice their new ideas. The leader is expected to discuss their ideas and help them arrive at a specific decision instead of dictating what they need to do.
Selling style refers to a high-relationship, high-task approach to leadership where the manager is expected to influence followers by selling the ideas persuasively to make them behave in a given manner. The unique characteristic of these followers is that they have the ability to undertake a given duty but they are unwilling to do so. The persuasive approach that the leader takes is to convince them to use their skills and experience to achieve specific organizational goals. The carrot and stick model of persuasion, where those who register impressive results are rewarded and those who perform dismally are punished, is one of the common strategies that leaders often use.
The last style is the telling approach, which is a low-relationship, high-task style. The model has become common in cases where a firm is dealing with employees who have limited skills and are often unwilling or insecure when handling tasks assigned to them. In this case, leaders are expected to give specific directions to the followers on how to undertake a given task. The leader is expected to maintain close supervision to ensure that these employees follow the instructions given to them. It is the most undesirable leadership approach because a leader has to maintain close observation of what employees are doing. As Tulgan observes, a significant portion of Generation Z employees may require such a management approach where they are subjected to close supervision. The aim of the leader should be to empower them so that they can move from this segment to the others discussed above. Figure two below shows the three styles that a firm can embrace depending on the situation that it faces.
Systemic Leadership
Systemic leadership is another theory that has become relevant in the modern business environment. According to Jean and Twenge, this theory focuses on larger systems and understanding how strengthening the relationship among people is critical in solving challenges that are complex. Some of the problems that firms face cannot be addressed at an individual level because it affects different departments and many employees. It is common to find cases where an entire organization is affected by an issue. Focusing on an individual or a department when addressing such a problem may not yield the desired result. This model of leadership emphasizes the need to start by understanding how that problem cuts across the organization.
The leader would be expected to identify departments and leaders who are affected by the issue. The next step is to involve the head of the relevant departments or all individuals affected in finding the solution to the issue. A leader is encouraged to find a way of making the departments and all the affected individuals work as a unit. They have to understand that they are a system, and the success of the organization depends on the effectiveness of the relationship. The manner in which tasks should be shared needs to be clarified at every stage of the implementation. The model encourages teamwork over an individualistic approach of undertaking tasks.
Cooperative Leadership
Cooperative leadership style is another emerging concept that managers use to achieve specific goals within an organization. In this context, a leader is expected to downplay their leadership positions and focus on similarities that they have with the rest of the population. Instead of being a boss, the manager would be expected to become a mentor. Working closely with junior employees without imposing one’s leadership privileges makes it easy to understand challenges that exist in the workplace environment. The manager will understand factors that slow the performance of the individual employees and understand the complications that exist from the perspective of the leader.
Junior employees would be able to express themselves without the fear of intimidation. Believing that they are working with a mentor instead of a manager, these workers will express their strengths and weaknesses. It becomes easy for the leader to define how to help them overcome the weaknesses using their strength. Cooperative leadership has become popular when managing new recruits. It creates a platform where a leader can work closely with everyone and come up with ways of coordinating activities of different departments. The goal of this leadership model is to create a close working relationship between a leader and junior employees. It eliminates the possible barriers and fear that workers may have when they are newly hired.
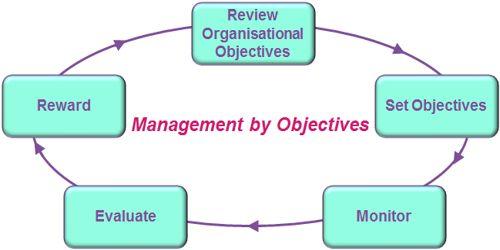
Management by Objectives
Management by objective is a popular leadership model that is also gaining popularity in modern society. This strategic management model focuses on the continuous improvement of organizational performance by setting objectives that both the management and employees find acceptable. As shown in figure 2 below, the process has five stages that have to be taken to achieve the desired goals. As shown in the figure below, the first stage is to review organizational objectives. The management should define what the firm should achieve and determine if the current policies have the capacity to ensure that the vision can be achieved.
The second step is to set objectives based on the initial review. These goals should be capable of addressing the organizational weaknesses while taking advantage of the existing opportunities. The third stage is to offer mentorship. Tulgan explains that instead of issuing instructions, leaders should focus on helping junior employees on how to achieve specific goals. The next step is to evaluate the capacity and performance of the employees. The management should always ensure that employees practice new skills and concepts they learn through the mentorship. The evaluation stage gives the manager an opportunity to determine the capacity of the employees to undertake specific responsibilities without close supervision. The next stage in this model is the reward. The goal is to ensure that employees are motivated at work. Rewarding performing employees is a reminder that those who remain committed to their work will always benefit. Figure 3 below summarizes the five steps that one should observe when using this model.
Transformational Leadership
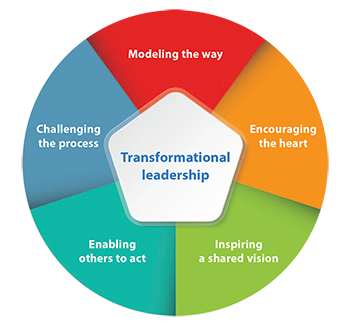
Transformational leadership is one of the contemporary leadership theories, which have gained massive popularity over the recent past. According to Tulgan, transformational leaders are expected to inspire their followers in a way that enables them to achieve extraordinary outcomes in every action they undertake. Such processes should enable these followers to gain leadership skills, making it possible for them to make critical decisions even in absence of their supervisors. The model emphasizes the need for those in management to foster confidence and creativity among junior workers. Consistently challenging their capacities makes them understand that they can stretch their limits regularly, each time increasing their performance and capacity in the workplace. As its name suggests, a transformational leader should change the capacity, perception, and attitude of the employees within an organization. It encourages continuous improvement through close coordination between a leader and followers without using any form of coercion. This theory identifies five areas of leadership that one should embrace.
Modeling the way is one of the important factors that this theory places emphasis on. According to Schiefelbein, leaders are expected to set examples that junior employees are expected to follow. The leader should demonstrate what followers should do through commitment and exemplary skills. A leader should come to work on time, remain loyal and committed to the firm, and demonstrate excellence at all times. These attributes will have a positive reflection on the employees. They will understand what is expected of them by observing their leader instead of getting constant instructions, some of which they may not understand. When dealing with generation Z employees, modeling the way makes a lot of sense, especially among female leaders. When a woman demonstrates her unique skills in undertaking a given task, it earns her respect as a leader. It eliminates some of the common stereotypes often leveled against female leadership, such as the view that women are emotionally weak, sentimental, and poor when it comes to decision-making. Schiefelbein argues that male chauvinists to deny qualified women the opportunity to lead in the different organizational settings have used such perceptions. They claim that trusting women with important positions that involve making critical decisions may have a negative impact on the progress of a firm. Eliminating such perceptions would pave way for women to achieve career growth in different industries.
Encouraging the heart is another factor that a firm should consider when using this model of leadership. It requires a leader to involve junior employees when making critical decisions, especially those that affect their area of work. It creates the impression that the management considers junior employees a critical part of the organization and that their views will always be respected. A leader should constantly appreciate good performance and celebrate accomplishments. Tulgan explains that such measures emphasize good performance among employees. They get to learn that their individual performance has a profound impact on the general performance of the firm. Female leaders should find ways of motivating generation Z employees by making them understand they are of great value. It is not necessary to use monetary strategies every time a leader intends to motivate an employee. Saying a word of encouragement and appreciating an individual’s effort may be enough to achieve the intended goal.
Inspiring a shared vision is one of the most important aspects of transformational leadership. As explained above, a transformational leader does not intend to use threats and punishment to make employees behave in a given manner. Instead, they convince and influence followers to embrace a given set of practices. Junior employees must understand and get to to appreciate the vision before they can act in a given way. As such, the leader has a major responsibility of sharing the vision with every stakeholder within the firm. The leader needs to state the vision in an articulate manner, always explaining any issue that may remain unclear to any of the junior employees. Having a shared vision means that employees will understand and appreciate why they need to follow a given path and act in a given way to achieve the intended goals. It creates harmony in an organization and eliminates cases where a leader has to use force to achieve specific goals.
Enabling to act is another requirement that a transformational leader should observe. When using this model, a leader should focus on empowering employees so that they can make independent decisions that are of benefit to the firm. Schiefelbein explains that it should start by engaging them when making decisions. Having a collaborative approach to management means that for every action that a leader takes, they must engage junior workers. The model also encourages leaders to create a sense of trust among employees. Assigning them sensitive roles within the firm and allowing them to make guided decisions creates the trust. Maintaining an open communication system where issues can easily be discussed and addressed without any repercussions may be critical. Professional governance, accountability, shared decision-making, and inter-professional collaborations are some of the important concepts that a leader should not ignore. These concepts and principles are critical when managing generation Z employees, because they lower cases of dissatisfaction within an organization.
Challenging the process is the final element when using this model, as shown in figure 4 below. A transformational leader should constantly challenge the status quo. Rhode explains that even in cases where the organization is on course towards achieving specific goals, a transformational leader is expected to find better ways of improving the overall performance. Taking risks, trying new ideas, and learning from mistakes in ways that identify opportunities and support a positive change are essential when using this model. However, care should be taken when trying to stretch the capacity of employees to new heights. Tulgan (2016) explains that employees should be allowed to enjoy their new capacities and managers should celebrate them whenever they register impressive performance. However, they should be reminded that a lot more still needs to be done and that they should remain committed to their work.
It is important to compare leadership styles and models, and figure out how women can make use of the ones that fit best to typical female characteristics. Each of these theories of leadership is important and can be applied by women in leadership under various contexts. In some cases, it may be appropriate to integrate some of these theoretical concepts to achieve the expected outcome in an organizational context. Women can make better leaders if they are offered the opportunity and given the necessary support, and some great female leaders such as Margret Thatcher and Angela Markel have proven the claim. It is necessary to understand that women do not need special skills to become good leaders. They need to understand the needs and capacity of their employees and provide a path through which they can achieve specific goals, as discussed in various theories discussed above.
Methodology
The previous chapter provided a review of the literature, which provided background information about the topic under investigation. This chapter discusses methods that were used to collect, analyze, and interpret primary data from various sources. According to Hewson, Vogel, and Laurent, once a review of literature has been conducted, the next important step is to gather primary data to address knowledge gaps identified during the review. This chapter provides critical steps that were taken to obtain the desired information and challenges that the researcher faced in the process.
Data Sources
When conducting academic research, Lamont explains that one of the factors that should be explained in clear terms is the source of information. The credibility and trustworthiness of the information collected from different participants can only be confirmed through the sources of information used to make specific conclusions in a study. Data used in this study were collected from two main sources. The first source of data was from secondary materials. Books, journals, articles, and reliable online publications were useful in providing crucial information. Some of the books and journal articles were obtained from the school library. Online databases such as Jstor and Google Scholar were also crucial. Using keywords such as women leadership and generation Z, the researcher was able to gather facts needed in the study.
Primary Data Collection
After collecting secondary data from the sources discussed above, the researcher considered it appropriate to collect primary data from a sample of respondents. According to Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault, primary data helps to understand current issues in a given field of study. It helps to address the possible knowledge gaps based on information obtained from specific individuals. It was necessary to interview women who are currently in positions of leadership to understand their experience, challenges, and aspirations in life. They would help to explain how women achieve career success and issues that they consider affect them in a unique way. It was equally important to collect data from generation Z employees in the country. The researcher was interested in understanding their perception towards women’s leadership, the expectations they have of their leaders, issues they face in the workplace, and any other relevant factor that affects their life in relation to their work.
Sampling and Sample Size
One of the most important steps that a researcher should take when planning to collect primary data from respondents is to have a sample of participants from who data would be collected. The criteria explained above meant that many people could qualify to take part in the primary data collection. Grubb explains that the number of women in different managerial positions across the country has been growing rapidly. As such, it was necessary to have a manageable sample from which data could be collected within the limited time. The researcher collected data from two groups of people. The first group was female chief executive officers in various companies around the country. It was important to understand some of the challenges that they go through when managing their agile startups or large corporations in the country. They would also help explain their encounter with generation Z employees and their unique characteristics. Hewson, Vogel, and Laurent explain that although it is common for some people to be less truthful when asked about their competency, it is often advisable to ask them. As such, it was necessary to ask the female chief executive officers if they believe that they are better leaders for the generation Z employees.
The second group was generation Z workers who represented members of the group. Studies have suggested that these workers have unique characteristics. They are more flexible than the older generation of employees. They are techno-savvy and are often willing to take on new challenges in the workplace environment. However, they are not as resilient as the older generation of workers. The majority of these employees prefer freedom and a flexible work environment to job security. It means that they are comfortable moving from one job to another as long as they are assured of their freedom in the new workplace environment. It was necessary to interview them to understand these unique characteristics. The researcher also wanted them to explain leadership styles that they consider most desirable for them. It was also necessary for these participants to explain if they believe those female leaders are more desirable for them than men are in a workplace environment.
It was necessary to select an appropriate sampling technique after defining the two groups of people who needed to be interviewed. The researcher used a stratified sampling technique to identify individuals who participated in the data collection process. This sampling technique was chosen because it was necessary to interview women in leadership and generation Z employees. The two strata would provide crucial information about women leadership and generation Z workers, as explained in the background of the study and the section above. The researcher used a simple random sampling technique to select specific participants in each of the two strata. A sample of 20 individuals was selected for the study. The goal of using this technique was to ensure that views of female chief executive officers and generation Z employees were integrated when summing up the report and providing relevant recommendations.
Collecting Primary Data
Once the sample was identified, the next step was to collect information from each individual participating in the study. The first step that was taken was to contact the management of two local companies to allow their employees to take part in the investigation. The goal of the study was explained to the management and approval was obtained. The management identified individuals who meet the specified criteria to be part of the investigation. It also helped in contacting the participants and giving them permission to be part of the investigation. All the respondents identified to be part of the data collection process were contacted through their supervisors at the selected companies. The researcher informed them of the intention to conduct the study and the role they were expected to play. Each of them was allowed to select the day and time that they felt would be most appropriate for data collection.
Data was collected from the respondents through face-to-face interviews. The interview was conducted within the firm, mostly during the lunch hours and in the evening after the break. As Lamont explains, a face-to-face interview is one of the best ways of collecting primary data. Respondents always appreciate the significance of the study when there is that physical interaction. Chances that the respondents would provide misleading information are also low because of such engagements. Kara Gergen and Gergen argue that a researcher can gather further details over an issue by reading the body language and facial expressions of the participants. As such, it is possible to know when a participant is providing misleading information deliberately. The researcher developed a simple questionnaire that was used in the data collection process.
Data Analysis
When the primary data has been collected, Bryman and Bell believe that the next important step is to conduct an analysis. Analyzing data can take different approaches depending on the research topic and questions that have to be answered. In this study, the researcher considered it appropriate to use mixed-method research. Quantitative data analysis was considered important in enabling the researcher to the magnitude of an issue under investigation or the number of people who support a given idea. It was necessary to understand the number of participants who agree with that statement. The outcome of data analyzed quantitatively was presented using graphs and charts to make it easy for the readers to understand the information presented. The qualitative method was also used because it helps in explaining a given phenomenon. If participants feel that women make better leaders, they needed to explain specific attributes that these women have, which makes them better leaders in society. The mixed method of data analysis was considered effective in providing a detailed understanding of the issue being investigated.
Research Constraints and Ethical Considerations
It is common to face different challenges when conducting academic research. Lamont advises that it is important to discuss these challenges and the manner in which they were managed to enhance the credibility of the study. One of the main challenges that the researcher faced was the withdrawal of some of the participants on the day of the interview without prior notice. In such cases, the researcher had to find their replacements immediately, which took a lot of time. The study had to be completed within the specified duration, which meant that the researcher had to convince new participants to be part of the investigation within the shortest time possible. Some of the participants were reluctant to be part of the investigation for personal reasons.
The researcher had to observe ethical considerations in this study. According to Bryman and Bell, one of the primary ethical concerns that a researcher has to observe is the protection of the participants. It is important to ensure that the identity of the respondents remains anonymous. This ethical requirement was met by assigning participants codes instead of using their real names. The codes helped in hiding their identity. As such, they would not be subjected to any criticism or unfair treatment because of their opinion, which may be different from that of the majority of those in leadership positions. Given the fact that this was academic research, it was important to avoid any form of plagiarism in the paper. The researcher wrote the paper from scratch. Information that was gathered from different books, journal articles, and other sources was cited accordingly using the American Psychological Association (APA) referencing format. A list of all the sources used in the study was provided on the reference page. The project had to be completed in time and handed in as per the specification stated by the school.
Findings and Discussion
The previous chapter explained in detail the method that was used to collect and analyze data from various sources. This chapter will provide findings from the primary data analysis and discussion of the issue under investigation. Data obtained from secondary sources were presented in chapter 2 of this paper. In the discussion section of this chapter, information obtained from primary sources will be integrated with that from secondary sources to understand the concept of women leadership and managing generation Z employees. According to Grubb, data analyzed from primary sources should be presented in a way that makes it easy for readers to understand the facts presented.
Research Question
The researcher was interested in analyzing responses that each of the participants provided during the interview. The following four questions were fundamental in this study because they formed the research objectives that had to be realized by the end of the investigation. As explained above, the researcher used both qualitative and quantitative methods of analysis depending on the nature of the question. It is necessary to present the findings made through the investigation.
Do women make a better leaders for the next generation of employees?
The first question focused on determining if the respondents felt that women make better leaders. Some scholars have argued that women if offered the opportunity and provided with the right platform, can make better leaders. It was necessary to determine if participants shared the same view based on personal experiences. As shown in figure 5 below, the opinion of the respondents varied on this issue. It is evident that 45% of the participants agree with the idea that women make better leaders. Another 25% of the respondents believe that women do not make better leaders. A significant population, 30% of the respondents, stated that they are not sure whether women make better leaders than men.
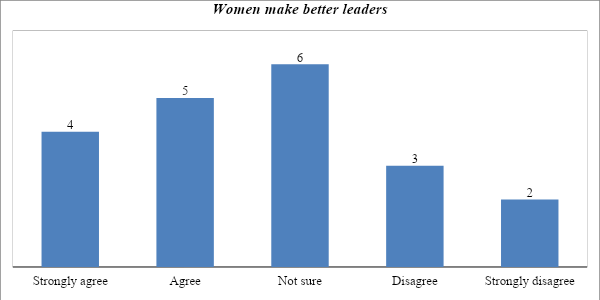
Those who stated that women make better leaders explained that they are more compassionate than men are. They tend to be more understanding when addressing challenges that employees face. They can take time to listen to issues that workers face. These traits are crucial when leading generation Z employees. These young workers need someone who would take time to understand their issues and find effective ways of addressing them. Those who were opposed to the argument stated that based on their personal experiences, women tend to be judgmental and easily swayed. It means that when addressing some issues in the organization, they base their decisions on what others think and sometimes, stereotypical arguments instead of facts. It clouds their judgment and sometimes leads to poor decision-making. Some of the respondents also noted that emotional instability is another major issue of concern that cannot be ignored among female leaders. Some of them take issues personally and are quick to make conclusions that they are not respected because of their gender. They end up making erratic punitive decisions just to prove a point at a time when a better approach existed for addressing the concern. Most of the participants felt that women have the capacity to lead, and should be offered the opportunity in small, mid-sized, and large companies.
What are some of the challenges that women have to address when managing generation Z employees?
Studies have suggested that women in leadership often face unique challenges that male leaders do not have to go through in the corporate arena. It was necessary to determine if indeed women face such unique challenges. Participants in this study were asked to share their views on this issue. As shown in figure 6 below, an overwhelming majority of the respondents (80%) strongly agrees with the argument that women face unique challenges when they are in a leadership position. Another 15% also agreed with the statement. Out of the 20 participants interviewed in this study, 19 felt that female leaders often have to go through more challenges than men would have to primarily because of their gender. Only 1 of the respondent had a contrary opinion. This participant explained that society is in transition, and people have come to appreciate the capacity of women in leadership.
The respondents were asked to identify some of the challenges that women face. One of the issues noted was sexist comments from some of their colleagues. Sometimes their capacity to make critical decisions would be questioned primarily because they are women. Another issue that was also noted was struggling with the glass ceiling. Bungay explains that some male leaders often make unreasonable demands even when it is evident that a woman has the right qualifications to hold a given position. Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell argue that there seems to be a higher bar for women than men in the career growth. It is evident that women have to demonstrate higher capabilities for them to be considered for promotions in specific positions. The burden of single parenting was also identified as a major issue that mainly affects women in leadership. A study conducted by Kumar shows that single parenting is on the rise in both North America and Europe. In most of these cases, women have to raise their children without the support of the male parents. Such issues often affect their ability to concentrate on their work. It slows their career growth.
The respondents noted that women still struggle with social bias in the workplace environment. It is difficult for them to assert their position when they find themselves in the workplace environment. On the one hand, when they embrace tough policies, Hewson, Vogel, and Laurent observe that they are perceived as being bossy and trying to act as men, a trait that many still frown upon in modern society. If their male counterparts act in the same way, they are perceived to be principled and keen on achieving organizational goals. On the other hand, when they become understanding and soft when dealing with their employees, they are considered weak and unable to provide the needed leadership within an organization. It becomes difficult for them to embrace a given stand without getting unfair criticism from different stakeholders. One of the female leaders interviewed in the study noted that for a woman to achieve success, as a leader in the modern business setting, one must learn to ignore negative criticism at all costs. Positive criticism tends to be constructive as it helps a leader to identify personal weaknesses that need to be addressed to achieve specific goals. However, when an individual or a group of people attacks one’s strength and positive values based on a leader’s gender, they should be ignored. It may not be easy to ignore such individuals, but Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell warn that paying attention to them may destruct one from achieving the set goals. In fact, one should try to prove the naysayers wrong by delivering results beyond their expectations.
What is the perception of generation Z towards women’s leadership?
The perception that an individual has towards a person defines their behavior towards them and the level of respect that they would demonstrate. It took a long for women to gain corporate and political leadership because of the societal perception that they tend to be indecisive, emotional, and incapable of providing guidance. However, various leaders who have demonstrated excellence in both the political and corporate arena have disapproved such stereotypical arguments. In this study, it was necessary to understand the perception of those who were interviewed towards women leadership. They were asked whether they would prefer having a woman as their leader. A significant majority of the respondents, 65%, stated that they would prefer having female leaders. Another 25% stated that they would not prefer having a woman as their leader. Another 10% of the participants stated that they are not sure about their preferences of a leader of choice in terms of their gender. Figure 7 below shows the outcome of the analysis
It is evident that generation Z employees have fully embraced female leadership. Most of those who were interviewed stated that based on their experiences, they prefer women to lead them in their respective departments. They feel that they are more understanding than men are, especially when it comes to handling complex tasks. They also feel that female leaders are easy to please when they remain committed to their duties and are respectful.
What are skills that women need to achieve success as leaders in the current corporate environment?
The last question focused on determining skills that women need to achieve success in the current corporate environment. As Tulgan explains, leadership is earned in the corporate environment. The stiff competition that companies face in the market forces them to select some of the finest people to lead different departments or to head the entire organization based on their actual capacity to deliver the best outcome. As such, the researcher wanted to understand the views of the participants on the issue of the skills that women would require.
Respondent 1 explained, “Women need to be decisive when faced with issues that require their approval. They can seek for more information from junior employees, but they should not demonstrate fear or inability to make decisions.”
The opinion of this respondent was shared among most of the participants. Women have to master the art of making decisions. It demonstrates their ability to provide leadership when the organization is facing numerous challenges. They can provide a platform where people can share their views on an issue, but they should have the final say. Being emphatic is a trait that would earn them respect. According to Bungay, when making such critical decisions, a leader should not forget the relevance of consulting. When a leader makes several wrong mistakes, especially without consulting the relevant stakeholders, their capacity to lead an organization would be put to question. They may end up losing their respect and authority within their department or in the entire organization.
Respondent 4 said, “Women should learn to be tough while at the same time not being over-reactive or emotional when faced with different challenges.”
One of the challenges that women in leadership often face is sexual advances from their male colleagues. They need to be tough when wading off such advances but not in an emotional manner. They should demonstrate their stance by showing that they competency cannot be defined by their sexuality. The trait will ensure that they are not weighed down by these advances or some of the sexist sentiments that they may come across in their work. The respondents also explained that women should learn how to use their feminism to win important debates that can reaffirm their position as a leader in their organization. They should always be articulate and at all times avoid situations where others may feel they can take advantage of them. Being compassionate is an important trait that can help when managing the generation Z employees. These young workers need to be given attention, especially when they are facing challenges in the workplace. These leaders should also demonstrate commitment.
How Women Can Retain and Leverage Their Talents
Women in leadership need to find ways of leveraging their talents to achieve success in their endeavors. Bungay argues that they need to take advantage of their unique skills when working in those modern-thinking and flexible environments to support and mentor the next generation of female leaders. They should have a balanced score as female CEOs when compared with their male counterparts. Since women are said to have certain characteristics such as care and compassion, and young generations are striving for those traits -leading styles and models as an example, women ought to demonstrate that they can make leaders for the modern-day young employees. Gender should not be the basis upon which women are denied opportunity to be in the position of leadership. Transferring theory to practice in companies is necessary when addressing some of the challenges that women may face in their respective places of work. For instance, situational leadership theory holds that a leader should be dynamic when managing followers. Every situation would require a different management approach based on different factors.
The young generation is diving into the job market, and will soon climb the corporate ladder to the c-suite. Rhode argues that it is critical to understand how they tick, what their motivations are, and what their value for companies is to define how they should be managed. The generation Z employees reason differently from the older generations. Most of them still get the financial support from their parents hence they do not have to work to earn a living. They can easily quit their job whenever they feel that the environment is not sustainable. For a company, it is costly to train an employee only to lose them soon after. As women find themselves in leadership positions, they have to use their unique characteristics to manage the younger generations in the current workplace environment. The desire to hire and retain some of the top talents does not mean the manager should ignore mistakes and undesirable behavior among employees. They need to be strict but in a way, that shows concern and care.
Leading Approaches Women Should Use To Prove the Hypothesis
The hypothesis that women make better leaders for generation Z employees has been confirmed through the analysis of both primary and secondary data. However, Antoniou, Cooper, and Gatrell argue that as women continue to get into higher managerial positions, they need to embrace specific approaches to leadership that would make them more effective in their endeavors. In the literature review, specific traits of generation Z employees were identified. It was evident that they are significantly different from the older generations in different ways. As such, female leaders should understand approaches that would be critical in managing such individuals. Hewson, Vogel, and Dianna believe that one such approach is to embrace an open-communication system in the workplace. These young employees prefer working in environments where their voices can be heard. As such, a leader should embrace an open-door policy where these workers can engage senior managers when they feel they have an issue of major concern. In such an environment, these employees can afford to be innovative in their areas of assignment.
Female leaders should remain flexible when managing generation Z employees. Hewson, Vogel, and Dianna state that these employees are tech savvy and find it easy changing from one system to another when it is necessary. Flexibility would allow such a leader to keep pace with the changing forces in the market. Transformational leadership approach would be a critical tool for women to prove this hypothesis. This method of leadership would allow these female managers to challenge the current capacities of employees in a positive way and without exerting excess pressure on them with the goal of improving their capabilities. It would enable the young employees to understand their competencies and identify ways of improving it. Ngunjiri and Madsen argue that cooperative leadership is another approach that would be effective when managing these young workers. This model allows a manager to create a workplace environment where employees can work as a unit when undertaking different tasks. In the modern society where technology has improved communication and integration, it is easy to inculcate a culture of teamwork among employees. Female leaders should also not forget about the fact that these employees value work-life balance. As such, it is important to appreciate the need for the employees to have personal time where they can be with their family and friends. Such personal times should be respected and protected through company policies.
Conclusion
Summary
Former President Barack Obama once stated that women are better leaders. The study demonstrates that this statement is true in many ways, especially when it comes to managing generation Z employees who are currently getting into the job market. The hypothesis set in the study has been confirmed through primary and secondary data analysis. Women are becoming increasingly involved in leadership in the current corporate environment. As shown in the paper, women were traditionally considered unable to become leaders in the corporate and political arena. However, the trend has changed over the past decade, especially in North America and Europe. The number of women in top managerial positions in Fortune 500 companies has been increasing consistently over the past decades. Societal systems and structures made it difficult for them to climb the corporate ladder. However, girl-child empowerment through education has played a critical role in enabling them to achieve success in their careers. Their excellent performance in these corporate entities has proven that women can be trusted with top leadership positions.
The study shows that although women are increasingly getting involved in corporate leadership, they still face numerous challenges that affect their capacity to achieve success. The study shows that the perception that many people have towards women is a major hindrance. Some men feel that many women earn their leadership positions because of sexual favors or their relationship with company owners other than their actual capabilities. As such, they fail to accord them the respect they deserve. It is not easy for an individual to lead a group of people who fail to show respect. Some of these female leaders in the corporate world are also burdened by single parenthood. They have to find ways of balancing their time for work and family. The study has shown that despite these challenges, these women are making progress and demonstrating their managerial capacities in both large corporations and small companies.
Generation Z is joining the job market and the current leaders have to understand how to manage them. The research shows that these young employees have unique needs compared to the older generation. They can easily resign from a company when they feel that their needs are ignored. It takes time and resources for a company to train workers. A trend where employees quit after a short while should be eliminated for a firm to have consistency and success in its operations. As women find themselves in positions of leadership, they need to understand how to manage these young employees. The study shows that women tend to be more compassionate than men are a trait that makes them better leaders for generation Z employees than men.
Recommendations
The study shows that there are challenges that women in leadership have to be ready to overcome. However, the objective of the study was to show the strength of women’s leadership. The study has shown that Generation Z has fully embraced women’s leadership. In fact, some of the traits of female leaders are suitable when managing female employees. The focus of future scholars should be to identify emerging challenges that these women have to face and the manner in which they can overcome them. They need to understand the unique traits of generation Z employees and how their skills and capabilities can be maximized to achieve specific organizational goals. Women in leadership should consider the following recommendations to enhance their capacity to achieve success when managing generation Z employees:
- Women managing start-ups should embrace cooperative leadership where they work as mentors to the junior workers to improve their performance.
- Women managing large corporations should embrace situational and transformational leadership models to guide their generation Z employees.
- Leaders should involve employees when making decisions that affect them. It makes them feel respected, which improves their morale.
- Women in leadership should ignore negative stereotypes in the corporate arena and instead focus on demonstrating their capabilities through the excellent execution of their duties.
- Training is critical for women who are keen on achieving leadership positions. Regular training would equip them with the skills needed to manage employees of different generations.
Bibliography
Antoniou, Alexander-Stamatios, Cooper Cary, and Gatrell, Caroline. Women, Business and Leadership: Gender And Organisations. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2019.
Bryman, Allan, and Bell Emma. Business Research Methods. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2015.
Bungay, Michael. The coaching habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead Forever. Toronto: Box of Crayons Press, 2016.
Burton, Laura, and Leberman Sarah. Women in Sport Leadership: Research and Practice for Change. New York: Routledge, 2017.
Caraher, Lee. The Boomerang Principle: Inspire Lifetime Loyalty from Your Employees. New York: Bibliomotion Inc. Connell, Joanie. Flying Without a Helicopter: How to Prepare Young People for Work and Life. New York: iUniverse.
Dunn, Gaby. Bad with Money: The Imperfect Art of Getting Your Financial Shit Together. London: Simon & Schuster.
Espinoza, Chip, and Mick Ukleja. Managing the Millennials: Discover the Core Competencies for Managing Today’s Workforce. Hoboken: Wiley, 2016.
Grubb, Valarie. Clash of the Generations: Managing the New Workplace Reality. New York: Wiley, 2017.
Hewson, Claire, Vogel Carl, and Laurent Dianna. Internet Research Methods. Los Angeles: SAGE, 2016.
Jean Twenge. IGen: Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids are Growing up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy, and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood. New York: Simon & Schuster Inc, 2017.
Kadakia, Crystal. The Millennial Myth: Transforming Misunderstanding into Workplace Breakthroughs. London: Berrett-Koehler Publishers, 2017.
Kara, Helen, Kenneth Gergen, and Mary Gergen. Creative Research Methods in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide. Bristol: Policy Press, 2015.
Kumar, Payal. Unveiling Women’s Leadership: Identity and Meaning of Leadership in India. London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015.
Lamont, Christopher. Research Methods in International Relations. Los Angeles: SAGE, 2015.
Madden, Claire. Hello Gen Z: Engaging the Generation of Post-Millennials. Sydney: McPherson’s Printing Group, 2017.
Montes, Javier. Millennial Workforce: Cracking the Code to Generation Y in Your Company. New York: Lulu Publishing Services, 2017.
Ngunjiri, Faith, and Madsen Susan. Women as Global Leaders. Charlotte: Information Age Publishing Inc, 2015.
Rhode, Debora. Women and Leadership. New York: Oxford University Press, 2017.
Schiefelbein, Jill. Dynamic Communication. Irvine: Entrepreneur Press, 2017.
Taylor, Steven, Bogdan Robert, and DeVault, Marjorie. Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods: A Guidebook and Resource. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2016.
Tulgan, Bruce. Bridging the Soft Skills Gap: How to Teach the Missing Basics to Today’s Young Talent. Hoboken: Jossey-Bass, 2015.
Tulgan, Bruce. Not Everyone Gets a Trophy: How to Manage the Millennials. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 2016.
Tulgan, Bruce. The 27 Challenges Managers Face: Step-by-step Solutions to (nearly) All of Your Management Problems. Hoboken: Jossey-Bass, 2014.
Appendix
Appendix 1: Research Questionnaire
[The primary goal of this research is to determine whether women can make better leaders for generation Z employees. The aim is to identify unique characteristics of female leaders and their appropriateness in meeting the needs of the young generation getting into the job market. Your participation in this study is needed to help in collecting relevant information in the project. You are kindly requested to answer each of the following questions to the best of your knowledge. Your participation in the study is on a voluntary basis. You are at liberty to withdraw from the study at any stage for personal reasons]
Part 1: Respondents’ Demographic Information
Kindly tick your age group based on the classes below
- 18-25
- 26-33
- 34-40
- 41-55
- Over 55 Years
What is the highest academic qualification you have attained?
- A high school graduate
- A college certificate
- A bachelor’s degree
- A master’s degree
- A doctorate degree
How long have you been working in your current organization?
- Less than 2 Years
- 2-4 Years
- 5-9 Years
- 10-15 Years
- Over 15 Years
Part B: Women Leadership and Generation Z Employees: Women Leaders
Do you believe that you, as a female leader, make better leader in the current workplace environment? Tick as appropriate
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not Sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe that women leaders are subjected to unfair workplace environment compared with their male counterparts? Tick as appropriate:
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not Sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
If you believe that women face unfair challenges in the current corporate world, kindly explain some of the challenges that you encounter as a female leader _______________________________________________________________________________________
What are some of the unique characteristics of generation Z employees and how can they be managed to maximize their performance in a workplace environment?_______________________________________________________________________________
Do you agree with the statement that the current beliefs and practices in the corporate world have contributed to the low number of female chief executive officers in Fortune 500 companies?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not Sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
If you believe so, kindly identify some of these beliefs and practices and factors that have made them persist despite changes that have been witnessed._________________________________________________________________________________________
As a female leader, kindly state what you believe is your role in transforming the workplace environment to make it sustainable for female leaders.___________________________________________________________________________________________
Do you believe that women have unique characteristics that make them leaders that are more effective for generation Z employees?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe that the current local community socio-economic, political, and cultural forces support women leadership based on your personal experience?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe that the female leaders are more suitable to lead small start-ups than male leaders?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe the number of female chief executive officers in Fortune 500 companies is set to increase in the coming years?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe in your capacity as a female leader to provide guidance to generation Z employees in the current dynamic corporate environment?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
What are some of the areas of weakness that you have as a female leader and how can you overcome them in your current workplace environment?______________________________________________________________________________________
Kindly explain what you believe to be the future of female leadership in the corporate world based on your personal knowledge and experiences.________________________________________________________________________________________
Part C: Women Leadership and Generation Z Employees: Generation Z Representatives
Do you believe in women leadership as a generation Z employee?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe that women leaders are more compassionate, understanding, and more appropriate leaders than their male counterparts are?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
As a generation Z employee, do you believe that the current workplace environment is sustainable?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
What are some of the characteristics of female leaders that you consider unique, and do you believe these traits make you prefer having them as your seniors?_____________________________________________________________________________________
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Do you believe that women leaders face unique challenges that make it difficult to achieve success in the corporate ladder?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Not sure
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
What do you believe are unique traits of generation Z employees and how does it affect their ability to thrive in the current business environment._______________________________________________________________________________________
Thank you for participating in this study. Information obtained from the interview will be used strictly for academic purposes. The identity of all the participants will be protected from third parties as was initially promised.
