Executive Summary
The stability of workforce is considered essential for a company’s success. Effective control over attrition rates is crucial for employees’ retention. This reportprovides a critical review of three studies concerning the attrition rates within companies. The methodology used in theanalysed research papers includes primary methods of data collection, such as questionnaires and interviews.The analysis demonstrates that the reasons for high attrition rates may include the lack of organisational support and disregard for such major attrition factors, as compensation, company culture and senior management performance. Also, the differences in cognition and behavioural patterns between the Generation Y employees and Generation X human resources managers must be taken into account, and the intrinsic approach is to be employed.
In order to address the attrition issue effectively, some recommendations are made. Firstly, the focus on employees’ recognition on the part of supervisors and managers will allow the company to increase the level of organisational support. Fair compensation and benefits scheme and development of culture that supports professional growth and creates positive working environment will address the most significant attrition factors and contribute to workforce stability. Finally, special attention to the intrinsic factors of employees’ motivation, such as task significance, job enrichment and strong interpersonal work relationships will close the gap between Generation Y and Generation X.
Introduction
Effective HR management is essential for the efficiency and productivity of a company. Attrition is an HR area of high importance, as staff stability is critical for the company and stakeholders’ well-being. The term ‘attrition’ relates to the gradual reducing of the number of a company’s employees because of resignation, retirement or death. However, voluntary attrition requires special attention and will be researched in the paper.
The issue of attrition has been selected for the current report since this problem presents one of the most essential areas of human resource management. The importance of the attrition rate analysis cannot be understated for a number of reasons. First of all, keeping track of the attrition rate allows HR managers to recruit employees more effectively, with a focus on critical positions. Secondly, understanding the reasons why employees are leaving the company is crucial for preventing a high turnover rate affecting the company’s productivity. Dunn (2015) underlines that employees’ motivation is directly related to job commitment, which is necessary for effective staff retention. In order to increase employees’ motivation, it is important to comprehend the reasons leading to voluntary attrition.
What is more, authors claim that a high attrition rate raises the company’s costs allocated to the recruitment of new employees and their job training. The company may incur not only significant financial losses but also the loss of knowledge and skills (Beynon, Jones, Pickernell&Packham 2015). Conversely, maintaining a low attrition rate through a number of tactics can increase a company’s efficiency and reduce costs. Thus, careful consideration of attrition factors is vital for the company’s success. This report will address the issue of attrition and present a review of three literature sources dedicated to the topic. Also, the data provided in the sources will be compared, the factors of high employee turnover will be identified and some measures for increasing staff retention and benefiting the stakeholders will be proposed.
Methodology
The Stages of the Research Process and Primary Methods
Research process encompasses ten stages, beginning with the selection of a research problem which should be quite significant. The next step is the literature review, including a thorough survey of the literature, relevant to the topic. It is followed by the development of hypothesis narrowing down the field of the research. Preparing the research design is the next important stage in the research process, followed by sampling and data collection through a variety of primary or secondary methods. After the data is collected, it must be analysed using data processing and measurement. The next stage includes hypothesis testing, which is verification whether the hypothesis relates to the found facts. If the hypothesis proved acceptable, the research proceeds to the generalisation and interpretation stage of making theory or presenting its interpretation. The final stage consists of preparing a report, containing objectives, hypothesis and methodology of the research.
This paper will compare the main features, advantages and disadvantages of two primary methods of data collection used in the analysed research papers: questionnaires and interviews. Questionnaire represents a series of questions with the aim of gathering data from the respondents. The types of questionnaires may include face-to-face, paper-and-pencil and computerised. The questions must be given in a logical order, with the most sensitive ones at the end. The advantages of questionnaires are an easy and fast process of data collection and quantification, relatively low cost and the possibility to be carried out not only by the researcher personally. The disadvantages include the possibility of misunderstanding by respondents, as well as the respondents’ subjectivity.
An interview consists of posing questions and receiving answers from the participants of the research. The types of interviews are structured, with a pre-prepared series of the same questions, semi-structured, following a question guide with some variation, and unstructured, with little guidance of the interview. The advantages of interviewing include the detailed responses and the possibility to check understanding of the question and clarify it in case of misunderstanding. The disadvantages may be the complications in planning and organising the interviews, the process of coding which can be time-consuming and higher costs, compared to questionnaires. All in all, both methods have their pros and cons: questionnaires present an easier and less costly method of data collection while interviews provide more in-depth information.
Discussion
The First Research
The study, conducted by Joy and M. J. Chiramelin 2016, analyses the importance of the organisation’s support in controlling the employees’ withdrawal behaviours, with respect to the attrition rates. The research included a sample of 350 employees from 25 IT companies. The data was collected with the help of structured questionnaires. The employees’ withdrawal behaviours were measured according to the scale of 18 items, and the data were analysed with multiple regression analysis. The research demonstrated a significant negative impact of the perceived organisational support on job dimension and employee attrition rates.
The most persuasive point of the study was the statistical evidence that organisational support in the form of career enhancement strategies and upward mobility opportunities allows reducing attrition rates (Joy & Chiramel 2016). The authors’ suggestions, concerning employees’ withdrawal behaviours and attrition rates respectively, include increasing the employees’ commit men to the company through firm culture promotion, work setting improvement and employees’ recognition (Joy & Chiramel 2016). All in all, this research is authentic, valid and reliable, despite some limitations. It seems that the main limitation in this study relates to the fact that the information provided in the questionnaires filled by the participants of the study was self-reported. In this case, the possibility of information misrepresentation exists, which requires additional data verification to enhance the accuracy of the results.
The Second Research
The following research was conducted by V. Pereira, A. Malik and K. Sharma in 2016 and analysed the employer-employee perspectives of employee turnover. The methods used in the study include a qualitative case research design and semi-structured interviews in the sample of 66 participants, both employees and HR managers. Specifically, the research analysed ten exit interviews with former employees, followed by the interviews with HR managers of the organisations-participants. The study showed that employees’ decision occurs via a complex interaction of these factors: the place, the people and the organisation’s people management course (Pereira, Malik &Sharma 2016). The research suggested adopting a longer-term and intrinsic approach to employment, rather than an extrinsically rewarding and short-term approach to people management, in order to reduce the attrition rates.
It is important to note that one of the most significant points of the study relates to the generation variable of the analysis. The average age of the participating employees was 22-24 years, whereas that of the HR managers was approximately 36 years, differentiating the groups of workers as Generation Y and Generation X, respectively. The high employee turnover across the analysed IT companies was attribute do the differences in cognition and action between the Generation Y workers and Generation X HR managers (Pereira, Malik &Sharma 2016). It appears that Generation X HR managers could not comprehend the employees’ motivation, concentrating on the extrinsic approach, rather than the intrinsic one. As a result, these HR managers were not able to address the attrition issue effectively.
To conclude, the validity and reliability of this research are strengthened by a diverse set of respondents that include not only employees but HR managers, as well as by the semi-structured interview schedule. What is more, the objectivity of the study is ensured due to the lack of the employees’ liabilities with their former organisations (Pereira, Malik &Sharma 2016). Nevertheless, it seems that there is a certain limitation in the study, as the responses in the interviews might have been affected by the former employees’ potential bias towards their organisation. Therefore, this limitation might have an influence on the effectiveness of the participants’ survey.
The Third Research
The third study regarded in this report was carried out by N. El-rayes, M. Smith and S.M. Taylor, in 2019. The authors developed tree-based models to conduct explicative and predictive research of the employee attrition issue. The probability of a worker leaving a company during a job transition was estimated with the sample of approximately five thousand anonymously submitted resumes in Glassdoor portal. The statistics were examined through four exploratory studies and used to engineer subsequent attrition-related predictive models. The research demonstrated that the major attrition factors affecting an employee’s decision to leave a company are compensation, company culture and senior management performance.
The most persuasive part of the research is the possibility to predict the attrition rates through a tree-based model. It was achieved through identifying and analysing the variables which had the most remarkable changes in the distribution for employees who left or continued working with their current employers (El-rayes, Smith &Taylor 2019). The model proved effective in predicting the employees’ decision-making concerning their current and potential employment. In addition, the authors suggested obtaining companies’ attrition data before and after the implementation of special attrition prevention programmes with the aim to evaluate the effectiveness of these programmes (El-rayes, Smith &Taylor 2019). Also, it would allow the researchers to identify the common features in the attrition prevention programmes that yielded the best results. To sum up, the research by El-rayes, Smith and Taylor is authentic, valid and reliable due to the usage of tree-based models developed by the authors. It is crucial to underline the importance of an attrition prediction tool for efficient HR management.
Comparison of the Sources
The analysis of the three studies demonstrates some commonalities in their results. To begin with, all authors are in agreement that a stable and productive workforce with low attrition levels is critical to the overall prosperity of the company. Also, it is generally agreed that researching the issue of attrition may present a difficulty for a number of reasons. Firstly, it can be problematic for HR to discern an employee’s real motivation for leaving the company. Leaving the company, employees may feel reluctant to expose their true thoughts about their former employer for fear that it may affect their future career plans (El-rayes, Smith &Taylor 2019). Secondly, attrition data generally present confidential information which is accessible to key stakeholders in a company. Thus, these factors can create some impediments to the objective research on the topic.
Another point in common in all the studies concerns the preventative measures that may reduce the attrition rates within a company. In general, the authors agree that the first priority is to increase the employees’ motivation and commitment to the company. Competitive salary, challenging work, improved quality of work setting, employees’ recognition, as well as rising educational levels in accordance with career aspirations of the workforce are named as key factors of employees’ motivation. It is beyond any doubt that all the mentioned factors contribute to employee retention. The authors agree that these necessary conditions preventing a high turnover can be provided through organisational support.
On the other hand, there are some distinctive points in the studies. For instance, Pereira, Malik and Sharma (2016) claim that the success of attrition prevention programmes is impossible without taking into account the intergenerational differences, which are not considered in the other studies. Besides, El-rayes, Smith and Taylor (2019) put under doubt the validity of the research based on exit-interviews as potentially biased while Pereira, Malik and Sharma consider this method valid. Finally, the most current study reveals a new factor that may influence the attrition rate, which is the year of the company’s foundation. It is stated that earlier founded firms tend to demonstrate lower attrition rates (El-rayes, Smith &Taylor 2019). Generally, it can be noted that the presented studies complement one another.
Data Analysis
Based on the literature review researching the issue of attrition, it can be stated that high turnover rates are attributed to a number of factors, presented in figure 1.
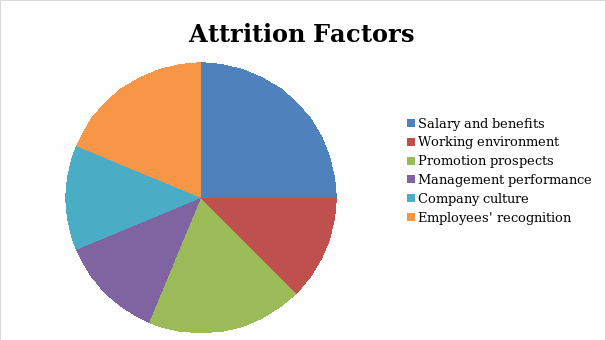
The diagram demonstrates the main factors which influence the attrition rates, according to the analysed sources. The presented data encompass extrinsic factors, such as salary and benefits and promotion perspectives, as well as intrinsic ones, for instance, employees’ recognition. It is clear that the main reasons causing high attrition rates are inadequate salary and benefits system, lack of promotion prospects and insufficient employees’ recognition. Additionally, inefficient senior management performance, poor company culture and unsafe or stressful working environment affect staff retention and workforce stability significantly.
Conclusions
To sum up, the identified factors which may increase attrition rates in the company include:
- Poorly developed system of benefits and remuneration with the lack of financial incentives.
- Absence of career advancement prospects and associated professional growth.
- Insufficient recognition of staff’ contribution, which makes the employees feel unvalued.
- Uncomfortable working environment that causes health-related problems, stress, distractions or general discomfort.
- Poor company culture lacking strong interpersonal relationships within a company.
- Ineffective performance of senior management, which affects staff motivation considerably.
All in all, the presented factors decrease employees’ motivation and job commitment.
Recommendations
In order to provide effective recommendations, one should perform a stakeholders’ analysis. In this case, the primary stakeholders, benefiting from the recommendations proposed below, are the employees, since these measures will significantly improve their working conditions and motivation. The secondary stakeholders are the HR managers, as reduced attrition will result in decreasing the recruitment frequency and the subsequent workload. Finally, the owners of the company will benefit as well due to the increased staff stability that will enhance the performance and reduce costs on recruitment and job training.
To solve the identified problems, one is recommended to implement a retention programme that will allow the company to reduce the attrition rates and maintain a stable workforce. A number of important measures within the retention programme include:
- Introducing an enhanced system of remuneration and improved benefits package. These extrinsic factors will contribute greatly to workforce stability. The implementing of a new remuneration system will increase the compensation costs by approximately 10 % and will take about 6 months to be devised and implemented, but the company will benefit from the reduced costs of the decreased attrition rate.
- Developing promotion strategies based on employees’ performance. These strategies will provide necessary opportunities for professional growth and will roughly take 6 to 8 months to be put in action.
- Making a special focus on employees’ contribution as a part of perceived organisational support. It will be possible through organising workshops for supervisors. This solution will be fast to implement and at a relatively low cost.
- Revising working environment to make sure it is safe and comfortable. Special attention should be paid to eliminating health risks and distracting factors.
- Building team spirit and promoting strong interpersonal relationship within the company. It will improve the company culture and can be done through a series of team-building workshops, which could be organised regularly at a relatively low cost.
- Promoting transparency of senior management performance levels will allow the employees to feel trusted and motivated by the high results.
All in all, the recommendations above will be beneficent for all the stakeholders, including the employees, HR managers and the senior management of the company. The proposed measures influence employees’ motivation and job commitment, increasing the retention rates, which, in turn, decreases the workload for the HR department and reduces costs for the company in general.
Reference List
Beynon, MJ, Jones, P, Pickernell, D &Packham, G 2015, ‘Investigating the impact of training influence on employee retention in small and medium enterprises: a regression‐type classification and ranking believe simplex analysis on sparse data’, Expert Systems, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 141-154.
Dunn, D 2015, ‘Motivation: what makes you tick’, OR Nurse, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 38-47.
El-rayes, N, Smith, M &Taylor, SM 2019, ‘An explicative and predictive study of employee attrition using tree-based models’, Web.
Joy, MM &Chiramel, MJ 2016, ‘Importance of perceived organizational support in controlling employee withdrawal behaviours’, International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 37-42.
Pereira, V, Malik, A &Sharma, K 2016, ‘Colliding employer‐employee perspectives of employee turnover: evidence from a born‐global industry’, Thunderbird International Business Review, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 601-615.
