Minimum Wage law is legal body that protects employee’s rights from being exploited by employer. The laws protect workers by making sure that they are paid hourly, daily or monthly wages according to the required laws. The issue of globalization has put a critical view on the existing minimum wage system on developed and developing countries. In the essay we will identify all the weak points in the Hong Kong economic systems and finalize the research by proposing what will benefit Hong Kong’s economy, with the aim of improving the functionality of the minimum wage systems.
Minimum wage laws were enforced to protect workers from employer’s exploitation; the laws were formulated to regulate minimum wages. In early years, in order to ensure that globalization was not based on cheap labor, minimum wage mechanisms were established. Fighting poverty; boosting of social justice will empower economic development. Social justice will be maintaining sound wage systems. For effective functionality of minimum wage in the elimination of poverty, the minimum wage has to be framed in accordance to consumer demands. In order to bring equity in income distribution, minimum wage must be set accordance to moderate earnings. To prevent cheap labor export, minimum wage should be regulated in correlation to wages in different countries. Some positive consequences for minimum wage systems are; Poverty reductions, purpose for developing the economy and reducing injustice (Bronson 2002, p.1).
International labour Conventions wage fixing machineries in Hong Kong will include the involvement of statutes, wages board, competent authorities, labor courts and collective agreements from workers and employers. It is suggested that Hong Kong should adopt Singapore’s National Wage council System for the welfare of its employers, employees and the government. The set up council to undertake minimum wage reforms should formulate, modify and amend minimum wage policies. Merits of launching minimum wage system in Hong Kong consists of short term and long term effects are
Long term effects
Poverty alleviation
Hong Kong has really set a very low minimum wage compared to other developed countries. Setting a high minimum wage for Hong Kong would incredibly reduce poverty levels. However, researchers argue that any increases in minimum wage do not reduce poverty since many of the power people are not permanently employed. But actually this should not hold a reason why a country should permit low pay. If at all minimum wage is directed at reducing poverty, then tax system in any given country should be effectively regulated and also there should be surplus benefits from social security. Hong Kong citizens are crying out for a decent minimum wage (Bronson 2002, p.1).
The system will help it produce products of good quality that can be sold in Hong Kong markets and as well as internationally. Hong Kong will be in a better position to safeguard its human resources. During periods of economic recessions, the system will help the country maintain social stability. The gap between the rich and the poor will greatly narrow down. Semi-skilled workers, aged people and female employees will be given protection by ensuring a minimum wage for them (Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, p.8).
Reduces injustice
Low paid employees are normally causalities of social and economic structures that barred them from condensing on equal terms as others. Some employers discriminate against employees; this prevents them from applying for better positions. And what the employers prefer in job placements are paid better than the less preferred hence unequal job opportunities. An example of the social disadvantaged groups in the job markets are women, immigrants, partially educated people, immigrants, racial backgrounds and people from certain religious backgrounds. Actually improving terms or increasing the minimum wages would greatly help achieve equal pay for workers of all walks of life. The most benefactors will be women as they will be able to bargain for position in companies. Low pay is actually some form of injustice it is also injustice for employers to from cheap labor markets and pay their workers low wages (Bronson 2002, p.1).
Develops the economy
A sober minimum wage rate changes the terms of trade in different productive systems that making it difficult for infant companies to rely on disabled labor supply. To actively enforce efficient minimum wage rates, Hong Kong will invest in better machines and equipments, better methods of running the company and training its workers. For any stable company to successful penetrate country’s labor markets, labor laws need to be enforced. Countries that have higher minimum wages are able to compete on international levels and therefore more efficient firms. Higher minimum wages also raise the level of spending and this reflects to more employments opportunities. Lets look at it this way, workers with minimum wage spent all their earnings on locally produced goods whereas better paid workers spent more on purchasing local products therefore add more to the local demand than an additional pay at other points in income distribution (Bronson 2002, p. 2).
Minimum wage laws are not as effective because of liberalized prices, for instance in East Europe, the value of wages fell that resulted to inefficiency of minimum wage laws. If foreign countries relocated their manufacturing companies to developing countries, the labor markets would be affected in developed countries. Manufacturing companies have highly contributed to labor employment any reduction on this companies will change the nature of employment; weaken trade unions and a reduction of pay for many workers. With the increased Globalization labor markets have advanced non-union competition that has accessorized to the elaboration of strategies of low wage employment rates. With the move of Manes to developing countries, a lot of pressure was put on trade unions and workers to agree to wage levels and conditions (Bronson 2002, p.4).
Hong Kong Special Administration Region Government should start implementing minimum wage system that would in turn benefit its citizens. The government should call upon all suppliers and contractors to have a signed agreement to undertake the adoption of minimum wages system for their workers (Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, p.8).
Coverage
In setting minimum wage brackets, most countries rely on bargaining power in conjunction with collective agreement from workers. Few countries have a set up minimum wage levels that apply to every worker, in most cases, the rates are determined by bargaining power or even determined by the government. Market forced determines that, the higher the level of minimum wage set up, the greater the size of labor force that’s affected. Different countries have different groups of categorizing minimum wage rates for workers, for instance Portugal pay their domestic workers lower rates whereas Kenya and Morocco have lower rates workers employed in the agricultural sector and other countries pay low rates for part-time and young workers. Workers may be subjected to low wage levels because most of them are employed in informal sectors that have no legal framework therefore hard for the police to monitor their operations. Minimum wage levels must meet the cost of living for any given country. In 1977, Council of Europe proposed to set its minimum wage level at 68% but it did not come to light. The researcher’s show that 77 percent of women were among the minimum wage levels (Bronson 2002, p.5).
Short term effects
Inflation
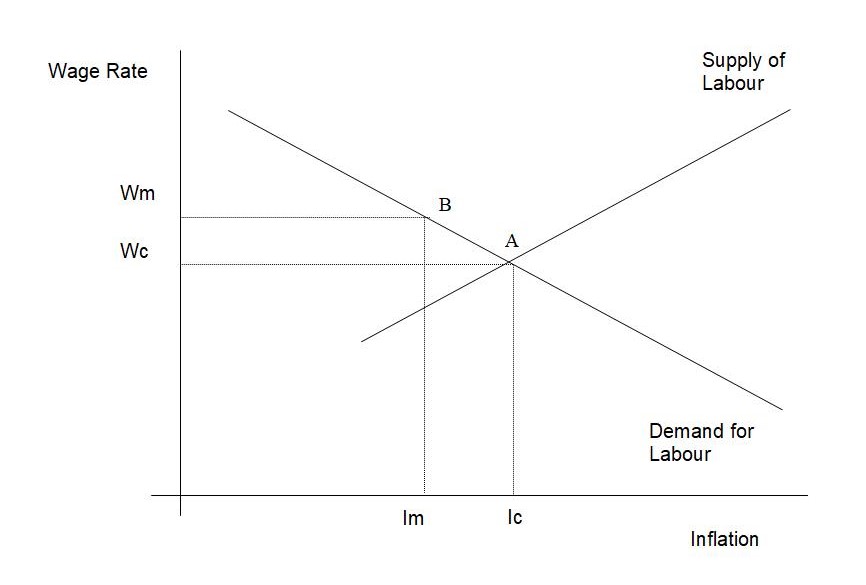
Policy makers anticipate that increased wage rates would cause increase in prices. This concern was raised by trade partners/rivals that have constant prices. In equilibrium, inflation caused by increase in minimum wage is not high as the rate of inflation will be caused by inflation will be compensated by increased productivity or even reduced profits. The emergency of globalization has helped labor markets greatly by weakening the capability of trade unions responding to the ever changing trends of labor markets. Figure 1 shows the competitive of these two markets forces at equilibrium point A, wage rate being Wc and Ic for inflation rates. If Hong Kong sets high minimum wage, it will experience increase in prices therefore inflation. If the labor markets move to equilibrium point B where inflation is at Im and higher wages offered at Wm, it will also reduce inflation rates. Ic- Wc depends entirely on how much wage rate was increased depending on demand of labor (Bronson 2002, p.7).
Disadvantages of fixing minimum wage system in Hong Kong are because of the recent increase rates of unemployment over the past few years. Government perception of increased minimum wage rates is that a lot of jobs will be scrapped. Econometric coefficients do not support this theory as the predicted relationships between the two do not exist. In a situation where the two factors co-relate, other factors are reported to be responsible. The Increased in export prices does not hold water because, when the country is exporting goods, it receives higher wages
- If actually export depends on efficient production, then wages and profits will be higher
- Most low paid workers are not employed in exportation sectors. Low wages is not the main factor in determining the preferred places for tourist; nevertheless, tourist would chose to go to higher minimum wage countries as compared to low waged ones.
- Some countries import agricultural products which are actually sold at “World prices” regardless of the production costs, this products are produced in places that workers are low-paid or the informal sectors that do not comply with the required regulations, so how would higher wage rate affect the profits? (Bronson 2002, p. 8) (Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, p.13).
Data base on particular Policy Issue (1998) argues that with increase minimum wage system in Hong Kong will amount to high wage costs, reduce business competitiveness and subject small industries unfavorable working conditions resulting to job cuts.
Minimum Wage and the Level of Employment
In inference to the International Labor Organization laws of Minimum Wage fixing, what determines the standard of minimum wage system in Hong is; the level of social security benefits, employment rates, family and workers needs and wage levels for various occupations. Competitive labor markets and supply models are the determining factors that affect the minimum wage levels in employment sector. A competitive labor market consist of large number of qualified workers voluntarily offering their skills to a large number of firms and none of the firm has power to leverage the wage rates. With this technique, workers and firms have perfect information and mobility is cheaper or even costless. In real sense, the wage rate and the level of employment are determined by that nature of labor demand and supply (Liu & WU 1999, p.16).
Employment effects of minimum wage
Hong Kong Government is making efforts to reduce poverty by amending labor system. In a competitive equilibrium point where minimum wage rate is set higher than employment level, labor markets move equilibrium where employment opportunities are at a lower level than the employment rates an offering a higher wage rate. This trend reduces employment levels effects known as “Employment effect of minimum wage”. On the other hand, any reductions in employment rates will entirely depend on increased levels wage rates and flexibility of demand and supply. If the labor markets will depend on fixed wage rates, then the set minimum wage will reduce the number of people being employed. Employment is mostly affected by failure of the employment firms to abide by minimum wage law, reductions of fringe benefits i.e. training employees and retirement benefits. But these instances will not affect minimum wage rate (Liu & WU 1999, p.17) (Paul & Nordhaus, 2005, Part III Chapter 12).
Minimum wage rates are enforced to all companies operating from China but also other autonomous region such as municipalities and provinces are given authority to determine Minimum Wage Regulations in their county and townships. The local Department of Labor Administration in china is given the responsibility of fixing local minimum wages together with local Chamber of industry and commerce (Liu & WU 1999, p.40)
Establishment of minimum wage system in Hong Kong
The minimum wage reforms were put in place with the help of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) Government, Hong King Social Security Society (HKSSS), employer association and labor unions. The objective of these formed bodies was to implement machinery that would fix the underlying problem of minimum wages, put some fixed working hours and adequate compensation for overtime workers. As we have seen earlier, Chinese government had the power to fix rates of minimum wages and all the parties were involved in the legislation reform that was called “Minimum Wage Ordinance” of 1932, since that time, this legislation has never been put to use. Until now, China does not have a provision for the economy statutory minimum wage rates (Liu & WU 1999, p.85).
Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government (HKSAR) argues that setting minimum wage rates for Hong Kong will disfigure the wage structure of its labor markets and also increase stiffness in future wage adjustments in the times of economic decline. As a result of this business sectors and the economy would be crippled as it would be struggling to adjust to the recessions. Its argument was also that minimum wage would subvert incentive offered at the workforce. They argue that the incentives will only subject the unskilled and low paid workers to advance their quality but Hong Kong’s economy will not benefit from it.
Set up statutory minimum wage rates predetermined from market equilibrium levels would not benefit works, since most employers would not be able to pay the high set up wages there low number of people being employed and companies may also be shut down due to high labor costs, on the other hand lower minimum wages set up below the determined market price would mean that employers would be able to meet the required manpower. This could results to employers abusing labor laws by paying lower the market price because the labor market is flooded. This set up minimum wage would become the maximum wage after sometime and therefore the statutory minimum wage will never increase (Liu & WU 1999, p.86).
It’s almost impossible to set up minimum wage for all trades and industries. Hong Kong’s labor markets are free and dynamic for business at any given point, so setting up a minimum wages would seem impractical. 1998, HKSSS proposed a monthly minimum wage rate of HK$5,850. The advantages of launching minimum wage rate in China would;
- Serves as safety net for protecting workers interest to ensuring families attain average living standards.
- The system will also protect low income earners and semi-skilled workers, an approach that would benefit women workers and aged individuals
- The gap between the rich and the poor will significantly reduce
- The proposal will protect low skilled workers from living on very low poverty lines and an expenditure reduction on Comprehensive Social Security Assistance (CSSA).
- Human resources will be protected as it will monitor proper use of the sources
- During economic recessions, Hong Kong will be able to maintain social stability (Liu & WU 1999, p.87).
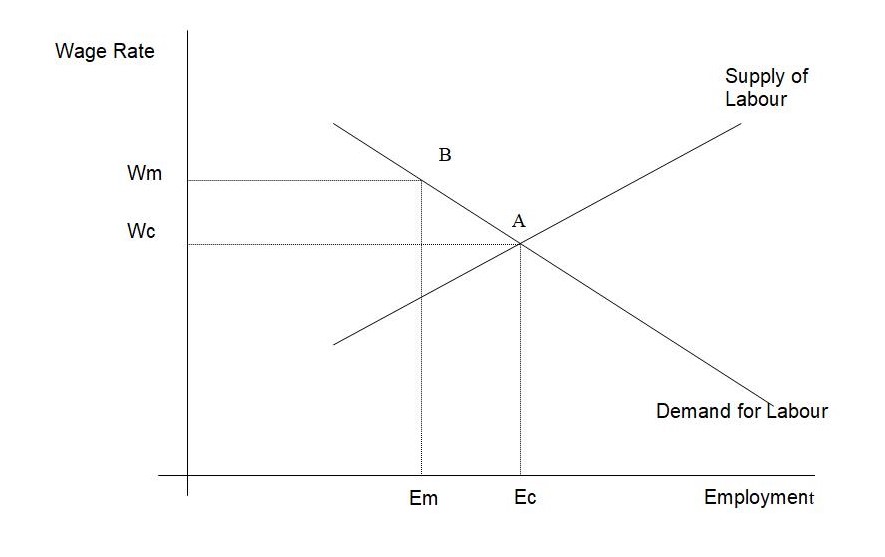
In fixing minimum wage system in Hong Kong, the concerned bodies should consider number of hours and related it to the real wage rates. Wage rate and level of employment are usually determined demand and supply. Figure 2 shows the competitive of these two markets forces at equilibrium point A, wage rate being Wc and Ec for employment level. If Hong Kong sets high minimum wage, it will experience reduced employment rates. If the labor markets move to equilibrium point B where is lower at Em and higher wages offered at WM, it will also reduce employment levels. Ec- Em employment reductions depended entirely on how much wage rate was increased depending on demand of labor. If employments rates are determined by increase in wage rates, then minimum wage will reduce employment rates significantly (Liu & WU 1999, p.15).
Increasing minimum wage would
- Weaken the country’s regional competitiveness
- Production costs will increase in firms that employ a lot of manpower, therefore foreign countries will be discouraged in investing in the country that would results to unemployment
- The government in collaboration with HKSAR will need a lot of monetary resources in initiating the system
- Labour markets should be in a position to determine their own wages basing on demand and supply, qualifications and abilities that the policy will not effectively determine.
- The country’s politics will interfere with minimum wage systems.
Since Hong Kong’s economy is still awakening, minimum wage system would force businesses to close down. Normally minimum wages are determined by market forces and the implementation of the system would affect Hong Kong’s competitiveness. Other manufacturing companies would also move their firms to mainland China to reduce wage costs therefore unemployment. Employers will also reduce the number of permanent employed people to gain advantage of the hourly-rated employees to reduce operational costs. Full times workers will also be affected as more people will be attracted to the minimum wage system. During economic downturns, employers may take advantage of this by hiring people for low pays. Inexperienced workers will also be discriminated against because there will be more people willing to take up the jobs (Liu & WU 1999, p.89) (Mankiw 2007, Part III Chapter 12).
Consequences of minimum wage system
Launching minimum wage system in Hong Kong would force some employers recruit employees who do not posses minimum qualification in the required job positions therefore weakening Hong Kong’s competitive market. Minimum wage system will not better the lives of the poor; better living standards should be determined by HKSAR government not the labor markets. Small enterprises will be faced of the competitive markets since they make small profit margins as compared to larger firms (Liu & WU 1999, p.91).
Minimum wage will protect employee’s interest. It proposes that the legislation set should be above poverty line. Workers will be protected from employers turning minimum wade rates to maximum rates that would oppress workers. Minimum wage system will give the employees authority to bargain for the rates they are comfortable with. Since Hong Kong as the majority of self employed people, the system leaves them out because there is no employee-employer connection. Minimum wage will not be able to protect its workers because many firms in Hong Kong do not sign any legal documents that bind them to the employers therefore workers are not bound to any benefits such as retirement benefits, hospital pensions and accident cover (Liu & WU 1999, p.93) (2008-09 Policy Address 2008, online).
Criteria for determining the level of minimum wages are
- Cost of living
- General standards of wages in the country
- Needs of employees and that of their families
- Social security benefits
- Relative living standards of other employees in comparison to the poor
- Economic factors such as levels of productivity and forces of demand and supply.
Fixing minimum wage system would require the involvement of statutes, decision by wages boards or councils, industrial/labor courts and force of law be given the provisions of collection agreements. Adjustments of minimum wage should be done time to time to account for the cost of living. In order to assist in setting up the minimum wages, the set up bodies should periodically survey national economic conditions such as income required per person, productivity of the country and levels of employment/unemployment cases. The surveys conducted should be able to determine in light of national conditions (Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, p.12).
Enforcement of minimum wage system
Setting minimum wage system would require i). Adequate penalties awarded for individuals who infringe minimum wage provision laws ii). Inspectors who are trained and equipped with powers to adequately carry out their duties iii). Publicizing minimum wage system to all workers in different dialects IV). Protection of workers against employers’ abuse through workers organizations and other labor organizations. Countries that have ratified the international labor conferences on Minimum Wage fixing and Establishments as a system are Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America and North America (Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, p.12).
Examples of countries with minimum wage system
Australia
Inspectors are appointed by Commonwealth Government in the Employment Advocate sector to implement the Workplace Relations (WR) Act. These inspectors randomly visit work places unexpected to check on accounting books, documents and welfare of employees. Under this organization, a penalty of A$1,000 (HK$4,888) and A$5,000 (HK$24,400) is awarded to any employee who fails to pay an employ his or her minimum. With the penalties in place, industrial disputes in Australia have decreased 17% in 1997 (Liu & WU 1999, P. 58).
United States
Department of Labor (DOL) ensures that workers are paid the minimum. It makes efforts to enforce Fair labor standards and educational campaigns of the same. DOL also provides minimum wage information in its Internet website. The set up investigators are called upon to do random checks in companies to make sure that wages, hours, working conditions are in accordance with minimum wage law. Any violation of the laws by an employer such as firing or discriminating against employees should pay up to US$ 10,000 (HK$77,450). Repeated violation of minimum wage law by employers would result to imprisonment or made to pay up a civil money penalty of US$ 1,000 (HK$7,745) for each single violation (Liu & WU 1999, p.56).
It is difficult to determine the rate at which minimum wage should be fixed because Hong Kong has been experiencing unemployed problems in the past months. Unemployed rates have risen to 4.2% exposing the county to an economical crisis. Economic aspect of setting minimum wage rates is that the system will increase wage costs and reduce enterprise competitiveness thereby forcing small enterprises to close down that would result to job cuts (Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, p.13).
In conclusion, Hong Kong’s government should work in collaboration with HKSAR to emending the proposed minimum wage rate to protect workers exploitation from employers and also prevent loss of low paid jobs. It should also follow an example from the two countries mentioned Australia and the United States, in awarding appropriate penalties to employers who violate minimum wage laws. HKSAR Government should work together with employers to set a favorable minimum wage rate that will improve workers living standards. Actually an increase of the current minimum wage rate in Hong Kong would increase spending therefore create many job opportunities and thereafter boost the economy. A stable economy attracts investors that will in turn create more job opportunities and reduce poverty levels. Let there be minimum wage rate and constant amendments to the minimum wage rate to avoid employers from fixing the minimum rates as maximum wage rates.
List of references
- Bronson, P. 2002. Globalization and Minimum Wage Systems. pp.1-10.
- Data base on particular Policy Issue 1998, ‘ A proposal on minimum wage in China’: A Research Paper on the Proposal on the Proposal For a Minimum Wage in Hong Kong from the Hong Kong Social Security Society’. LC No. CB (2) 87/98-99(01).
- Liu, E., & WU, J. 1999, Minimum Wage Systems. 1999, p.1-115.
- 2008-09 Policy Address 2008, ‘Embracing New Challenges’. Web.
- Mankiw, G. N. Ed. 4. 2007, Principles of Economics. Thomson Learning.
- Paul, S., & Nordhaus, W., Ed. 18. 2005, Economics. McGraw-Hill.

