Executive Summary
This dissertation aims to examine the effects of the global financial crisis on the Saudi market and to find out the solution to save the economy from this credit crunch. Firstly, this report concentrates on the significance of the study, research objectives, background of the problems, scopes of this research and so on. The literature review of this paper also concentrates on the roots and origins of the global financial crisis, macroeconomic impact, and micro-economic influences of economic downturn.
The researcher discusses the impact of the economic downturn on the Saudi economies by relying on primary and secondary data sources. To discuss the effects of the financial crisis on the Saudi market, this paper highlights the current position of the banking sector, labour market, stock exchange, foreign exchange, consumer market, export market and so on. Finally, this dissertation suggests some solutions to the governments, foreign investors, and foreign development partners or policymakers act effectively to rescue the country from the economic downturn or aftermath of the crisis.
Introduction
Background of Study
According to the report of Jadwa Investment, the world is passing through an exceptional economic disaster because enormous financial institutions have already collapsed or taken financial help from the governments (1).
Historically the economic growth and performance of Saudi Arabia before the year 2009 was tremendous and outstanding (forty-fifth annual report of SAMA, Jadwa Investment, IMF and World Bank reports). However, the global financial crisis has a large impact on the Saudi market because this crisis reduced oil price and foreign direct investment, economic growth and revenues.
Bourland reported that food prices have increased speedily in current years due to higher prices of the international agricultural products, for example, food prices amplified more than 16.8% within the last three years (1). He further added that the purchasing power of Saudi customers had also changed dramatically because this factor was interrelated with living costs. In addition, the shift in global food consumption patterns, vulnerability to weather conditions, mounting transportation costs, dollar weakness, and reduction of subsidies were the major factors to create this position and all that matters were interrelated with a global financial crisis.
Research questions and Objectives of the study
This dissertation has aimed to rejoinder to the subsequent research questions, what factors global financial crisis most influenced to establish economic growth and competitiveness Saudi Arabia, acceptable, and to comprehend the potential barriers to implementing the effects of GFC (Global Financial Crisis)? The answer to this question would enable the present researcher and Saudi government to organise the policy and towards a greater motivation to increase productive output of the nations. To reach the research objectives following research questions has risen –
- What are the roots and origins of the Global Financial Crisis?
- What are the Microeconomic and Macroeconomic impacts and measures of the Financial Crisis?
- How US Credit crush turned into Global Financial Crisis and seriously affect other countries like Saudi Arabia?
- How Saudi market has responded to the effects of the global financial crisis and gain desired economic growth?
Significance of the Study
Karam (2008) Saudi’s finance minister and central bank governor believed that the impact of global economic downturn on the oil industry is the temporary problem and this situation will not sustain for a long-time because government and international associations will work together for the development of this position. However, the prediction of finance minister was apparently correct for that moment as Saudi financial system recorded remarkable growth in 2008 by taking benefit of the constructive developments oil market (all-time high of $147 a barrel), but this position has changed due to long-term financial crisis. In this circumstance, the market researchers and government executives try to assess the actual impact of global financial crisis on Saudi market because financial conditions have worsened the country. On the other hand, the researcher considers this topic “effects of the global financial crisis on the Saudi market” to save the country from the adverse effect of economic turmoil.
Limitations of the project
The researcher of this dissertation faced following problems in order to finish this project–
- From the primary data, it is difficult to find out the exact figure of the effects of global financial crisis on the Saudi market;
- There are too many sources, which deal with the global financial crisis of KSA, but few of these sources are reliable;
- Limitation of budget to cover the research project;
- The main is available of inaccurate or inconsistent data as the data are not matched with one another;
- A limited number of words was also a big problem of this project because the Saudi market is a vast area of research;
- Furthermore, the given deadline is also another notable limitation for this study and this problem deliberates the researcher to rely more on secondary resources.
Scopes of the study
- One of the main objectives of this research is to evaluate the impact current financial crisis on the Saudi market;
- It has an opportunity to suggest possible fruitful and realistic solutions to overcome the adverse effect of the global financial crisis;
- The researcher has scope to focus on the consequences of the financial crisis in Saudi Arabia;
- The aim of the researcher is to fill in the gap or loophole of the outcomes of other research documents;
- This study has huge scope to shape the paper with full of information;
- The topic of this dissertation allows dealing with the effect of the global financial crisis on the labour market, employment rate, oil and non-oil sector, capital and financial market;
- In addition, the researcher also takes into account the stock market, banking sector, food market, mortgage and housing industry;
- Moreover, the study also seeks to establish the consequence of other goods costs, fixed Saudi riyal, and the result of reduced international inflation on Saudi Arabia’s inflation.
Literature Review
Overview of the Topic
This literature review has elaborately organised with the writings, research, and scholarly opinion concerning the description, dimension, and evaluation of global financial crisis and root to its resolution. The roots and origins of GFC are associated with the theoretical background of Keynesian ‘Debt Deflation Theory of Great Depressions’, and ‘General Theory’, which has contributed the global economy to overcome the Great Depressions (Keen, 21). It provides the background evaluation of what financial crisis is, and which factors are most significantly persuading the concerned financial crisis though the Keynesian prescription has totally failed to recovery the global financial crisis of 2008. The scrutiny and illumination of contemporary researchers concerning global financial crisis of 2008 and their motivation, programme strategies, acceptance and effectiveness discussed simultaneously with the chronological theories as well as modern approaches form an unyielding foundation from which it is deliver a research study rather than Keynesian views.
Roots and Origins of the Global Financial Crisis
There are much more controversy to identifying the actual reason of global financial crisis. Allen (2) added that the financial crises have been enveloping observable fact all the way through economic history, but in the modern era, the frequency of financial crisis has increased tremendously than Bretton Woods Era (1945-1971) as well as The Gold Standard Era (1880-1993). Bretton Wood’s conference that has given birth of IMF and World Bank to negotiate and regulate inter country currency relations among the independent states, turned more concerned with strength and preference of US currency than rest of the world. The financial crisis that fired up from the US housing sub-prime mortgage market in 2008, how it swiftly accelerated and switch on the rest of the world’s financial markets and distorted the financial landscape is really a grand surprise and raised question mark to the role of IMF and World Bank.
Crotty (22) identified that the eventual reason of the global financial crisis of 2008 is the extremely defective institutional practices those are frequently point toward to the New Financial Architecture, the internationally incorporated structure of enormous banks and multinationals including investment banks, mortgage companies, hedge funds and other exceptional investment instruments (5). Moreover, NFA (New Financial Architecture) has given the opportunity to the carelessly and poorly regulated institutional operation and in some events without any regulation at all, which is a pact protected by the foremost concept of financial economics presumption labelled as the ‘theory of efficient capital markets’. Consequently, NFA has engendered the chain of stronger financial crises those have been resolute by means of huge governmental bailouts (Crotty 1).
Cox (3) pointed that a few causes have stated about the economic downturn, but it has not yet clearly pointed whether the global economy has stayed at the beginning of global complex economic recession or how this phenomenon would be overcome rapidly. In simple form, a detailed account of the recession origins would be evidently exposure in near future. Amongst the appraisal of the global financial crisis, two have most common. Firstly, ‘profligate loans’ those have motivated people purchasing expensive properties, but in practice, it has impossible to afford for a long time. Secondly, land law of this country gave excessive land use opportunity and offered flexible provisions in terms of mortgage issues, which was one of the main causes to change the environment of financial market. These two major issues have toxic affiliation in producing complex financial crisis (Cox 1).
Before August 2007, a small number of people have heard about the economic downturn though it has started earlier than the French Bank BNP Paribas has reported. The global dictionary has defined this term by “the harsh scarcity of money”. The French bank BNP Paribas has pointed to high-interest rates as the core reason of the financial crisis. A snapshot of the global financial crisis has been analysed below (BBC 1) –
- Sub-prime dilemmas: from 2004 – 06, the US interest rates grew up from 1% to 5.35 % through which their real estate market has slowdown, consequently, a record number of mortgage defaulters have generated because of high-risk credits and they have no alternative scope devoid of selling their properties to the banks and investors. The Sub-prime dilemmas have slowdown the global investments, as well as bond selling as a result billions of dollars, have worth.
- CDOs: the CDOs (Collateralised Debt Obligations) have bundled high-risk credits, bonds, and assets into the portfolios where the US banks have provided lands to the clients of poor credit history as well as invested globally. Failure of the CDOs has frozen the credit markets and due to bad loans of the rival’s account inter-bank lending has also stopped, increasing interest rates, decrease house price, increase mortgage defaulters and ultimately investors have suffered from great losses.
- Interest Rate: In order to motivate lending and strengthen money market through available funds in more favourable terms the Central Bank of the UK and US have cut interest rates;
- Liquidity crisis: Short-term initiatives have no impact on liquidity crisis. Consequently, recession threats have increased the number of job loser, bankruptcy, cost of living, and repossessions;
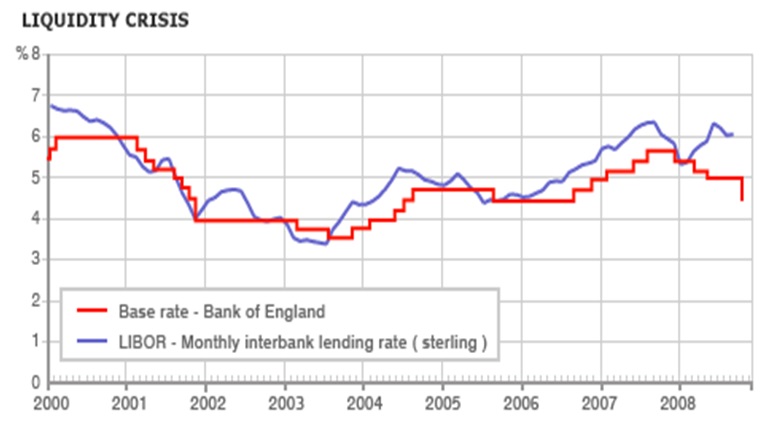
- Lehman Brothers Collapse: The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers was the prevalent collapse of an investment bank in the course of fraud or regulatory failure that has demonstrated lacking of US economic order. The Northern Rock bank of the UK has turmoil and afterward nationalized because of £2bn withdrawal by their clients and the collapse of the Bear Stearns in US has forced to terminate the policy “investments only in banks”;
- US bailout program: to stabilize housing sector US government has agreed US$ 700 billion bailout program by borrowing money from the world financial markets;
- The UK bailout program: For marginal investment availability, UK bailout program has agreed £400 billion to their eight largest financial institutes as well as housing sectors in terms of preference share.
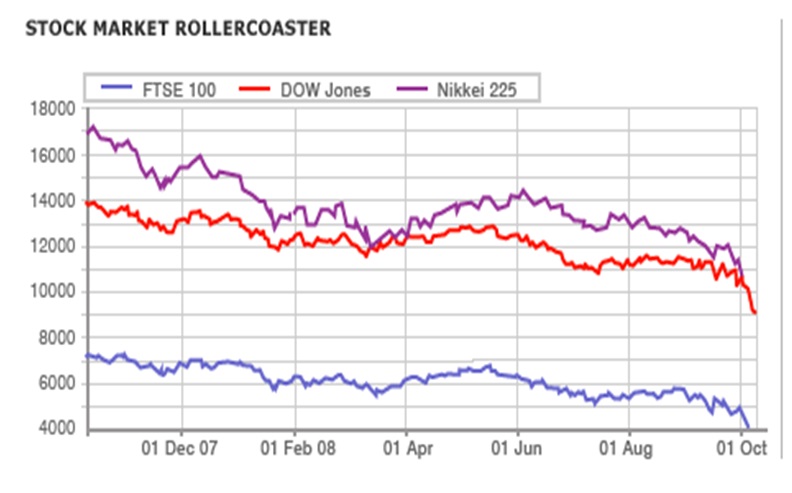
- Global action: Due to a global credit crunch, most of the American and European banks have nationalised. Additionally, they have cut down 0.5% interest rates to flexible the crisis. News of the bailout program has hammered stock market and reflected all stages of the financial sector as well as in consumer’s confidence by decreasing house prices, job loose threat.
Microeconomic Influences of Global Financial Crisis
The theory of micro-economic has studied individual decision-making components as well as the circular flow of economic activities or the production factors of a business firm like consumer demand, supply of raw materials, price of the products and goods, and wages of labours. In following discussion global oil supply, demand level and price fluctuation have present in view point of current economic downturn.
Demand Elasticity under GFC
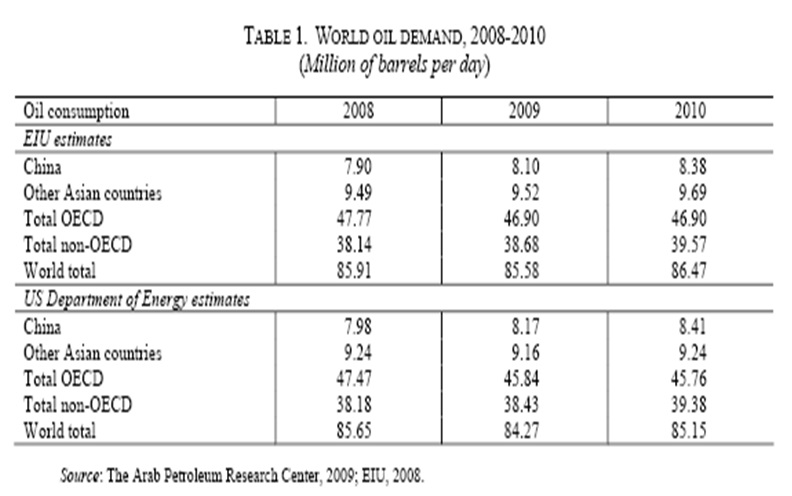
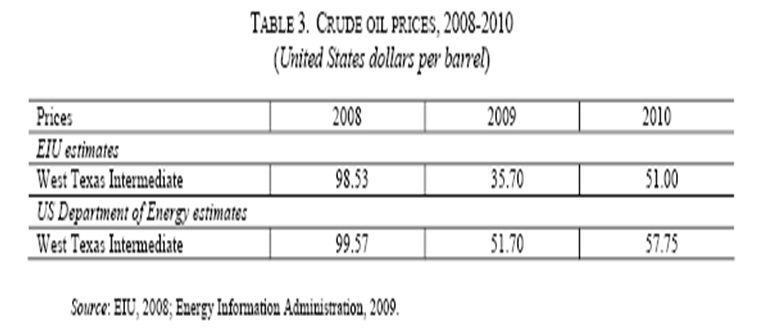
Generally, demand elasticity of any product and service has fluctuated proportionally with the fluctuation of consumption ratios. As said by EIU (Economist Intelligence Unit), from starting of the economic disaster, worldwide oil demand has fallen since 2008. The EIU has estimated that in 2008 and 2009 global oil demand has reduced 0.2% and 0.4% respectively. In the developed nations, consumption ratio has fallen promptly, which has descended oil demand globally. More specifically, in the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) affiliates oil demand have declined of 2.9% in 2008 and consequently 1.8% in 2009. Moreover, in 2009 Europe and North America cut off their oil requirements by 2% and 1.7% correspondingly. However, in the non-OECD region, oil demand has grown significantly for instance, in 2009 1.4% and in 2010 2.3%. Continuation of the global economic turmoil it has difficult to predict oil demand fluctuations, but dramatically in the developing nation like India, China oil demand has grown rather than Arab oil exporting nations. For example, Chine oil demand increased 1% compared to last year. More elaborate oil demand account has plotted in following table (ESCWA 7) –
Supply Elasticity under GFC
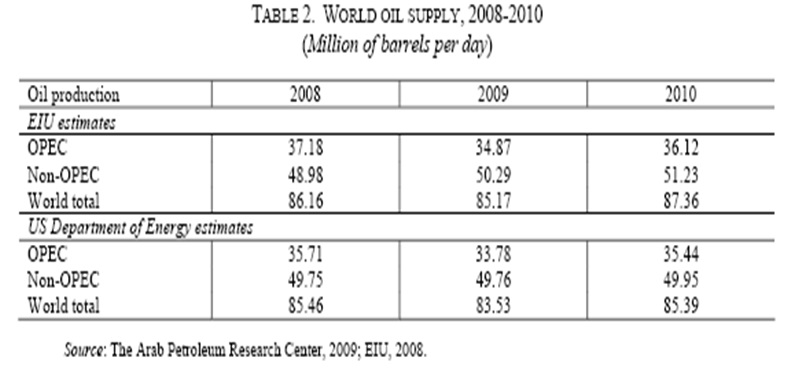
Supply elasticity of product has affiliated with the change of price and production volume. Due to change in oil price, OPEC members have grudgingly needed to reduce oil supply scale in their major oil exporting realms. From November 2008, OPEC has gradually condensed their production volume due to lower oil price. The EIU has reported that compare to 2008; in 2009, globally crude oil production has reduced by 1.15%. Then again, terrific production has fallen in OPEC by 6.2% while non-OPEC has produced 2.7% than previous year. Since gloomy economic downturn it has tough to forecast future fluctuation figure, but the EIU estimators have wished that near future crisis will be overcoming gradually (ESCWA 5).
Price Level under GFC
Usually, low supply and high demand have increased product price level. Currently, economic meltdown has significantly affected oil price instability. There have two key channels behind these circumstances. Firstly, stretched economic crisis have turned scores of oil producers to liquidate them in the commodity market in order to recover losses as well as margins.
Dwindle of the oil demand has the outcome of global economic stagnation. As a result, worldwide 64% oil price have decrease in 2009 where as annually anticipated average oil price per barrel has US$ 35. Considering all of these factors the EIU has wished to improve oil prices from this year and their anticipated modes are- recent oil production reducing forces, influence of the dawdling growing dynamics in non-OPEC production regions and minute degree of the global demand recovery (ESCWA 3–7).
Macroeconomic impact and measure of GFC
In explaining current economic crisis, most of the economists have focused on housing as well as credit market collapse in US. In this case, besides housing market collapse existing macroeconomic components, structures and practice have also responsible. Moreover, global economic growth has needed the housing bubble to continue its journey. Significance of macroeconomic dynamics has struggled in this economic slowdown due to their indirect operation. Consequently, significant components of the macroeconomic have motivated to operate openly in the financial market (Palley 5).
Monetary Policy Responds
Growth factor of a country has greatly affected by the monetary policy. Objective of a sound monetary policy has included safer gold reserves, stable price level, balance of payments, full employment scope and for the under-developed and developing counties faster economic growth. Monetary policy has generated growth model emphasising effects on the workers of a country. In the following figure four-faced economic policy named “neo-liberal policy box” has plotted where globalization, employee, government style, labour-market elasticity and employment ratio has described. These forces have played a significant role to regulate economic policies as well as financial disasters. According to this model, employees have faced a tight pressure from four sides as drawn in the following figure. Globalization encouraged a free-market economic system as well as resource mobility to capture low wage foreign labour markets.
Government style has shaped the government legitimacies, scope of privatization, scope of deregulation, establishment of light-touch policies. For instance, small government regulation has protected independency of economy from harmful interference of the government, but reshaped flexible economic rights. The labour-market elasticity has included lower wages, employee rights and benefits, job loose advantages and composition of labour unions. These attributes of the labour market has promoted unequal income ratios. Considering all of the four issues free-market economic policies, uneven income distribution, and high inflation rate has greatly stimulated current economic downturn worldwide (Palley 10–13).
Influence on GDP
Theoretically, GDP (Gross Domestic Product) has measured aggregate market value of the production during a year. Key economic growth has solely driven by the investment and savings, but in long-time investment-quantity could not resolved economic growth due to capital-intensive economies of scale. Moreover, long-time economic growth persistence has stimulated through technological development. Recent financial crisis has shaken the GDP in both developed and developing countries therefore balance between investments, saving has collapsed, and market value of the production has downturn dramatically in the US, UK, France, Germany, China, India and Ireland (Pfeffenzeller 1).
Influence on Employment
Global financial recession has terrifically increased unemployment ratios. Generally, interim fluctuation of the economic growth has made the scope of unemployment, but long-lasting unemployment carried reproduction of the resources. As a result, economic growth has become slower as the global economy has currently faced (Pfeffenzeller 1).
Influence on Savings
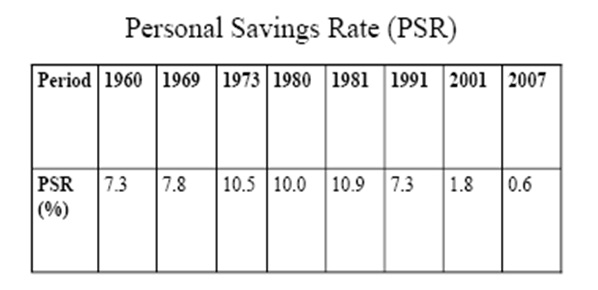
The high living costs, as well as the increasing credit ratios, have slimed the scope of household’s savings. On the other side, a decrease of savings has provided marginal demand scope. In this way, corporate profit, as well as the rich households, has boosted their profit volume, but the poor and middle class households has loose their savings scopes. Additionally, expensive asset purchase and maintaining have also promoted rising credit liability. Limitation of this circular flow has continuously weakened personal or households savings ratios as plotted in the following table (Palley 13).
Trade and Investment under GFC
The trade and investment cycle has greatly promoted the economic growth of a country. Frank international trade cycle could be specialized labour markets as well as productivity or GDP. Moreover, economies of scale has also promoted through this mode. For instance, Germany has exported largest volume of products globally since their industrial sector has developed through a dynamic foreign trade cycle. Alternatively, FDI an efficient mode to promoting countries economic growth, but in many developing countries has now faced FDI crisis due to global recession as well as the imbalance trade cycle.
Housing Bubble & GFC
In case of owing housing property, the US economy has faced trouble of “Two-America nature”. Among the 50 states, half of them have followed excessive land utilization policies and the rest half has made restriction in land utilization. Thus, housing bubble has busted not only in the US market, but also globally and collapsed global economic growth (Cox 3).
Inflation under GFC
With increase of housing interest rates as well as mortgage defaulter, inflation ratio has become magnified therefore value of money has decreased and price level of products and services has increased. This circular flow has hampered stable economic growth as well as generic fiscal decision-making merits. During 1970, the inflation rate was double digits for the first time and in 2008, the inflation rate has figured at 11.1%. The inflation rate has been driven through two key dynamics- firstly, global food price increase and secondly, house rents. Since 1970, commodity price collapse, as well as high transportation cost, has wiped away imported food price increase. Alternatively, price decline in the import of goods through board has strengthened the US dollar at the early phase of the economic meltdown.
US Credit Crush turn to Global Financial Crisis
Berkmen et al (1) identified that the financial factors of the emerging markets come into view with the major formative shape of growth modification while the BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India and China) and GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) countries hold near about fifty percent of the Foreign Exchange Reserve comparing a seven percent worth by G& countries. Through practice many countries have gained well understanding that with strapping credit crush were more defenceless to the decelerate while leverage has been deliberated as a credit to deposit ratio involving increasing credit growth and illuminating variables with a variety of stipulation.
From the previous financial crisis, it has proven that the countries along with pegged foreign exchange rates have practised stronger descending growth adjustments in relation to countries that practice extremely flexible exchange rates, but not any of the least-affected states were in exercise of pegged exchange rate. The stock of global foreign exchange reserves has not any standard measures which quantity would be preserved and there is no statistically noteworthy effect on the growth by this reserve.
The strong foreign currency reserve may be a sign of the reality that the benefits of global reserves possibly will reduce roughly while it grew up at the exceeding a level measured adequate to safeguard alongside risks and quite a few countries that had biggest growth revisions, mostly EU countries. As IMF and World Bank are seriously proactive for Americanisation rather than the other member’s interest, they very notoriously influence the less developed countries to keep US dollar as their foreign currency reserve. As a result, when the US dollar goes down, all the currencies will fall those countries who kept US dollar as their reserve.
Since fiscal year 2007, global recession has severely hammered individual superpower status of the US though in between 2001–03 in both Afghanistan and Iraq, they have already stretched out militarily. Philosophically the US have followed a free-market economic system. Currently, whenever US own markets have split up, their economic policy has lost public support globally. Worldwide, blooming housing markets, as well as other industrial developments, have delicate while sub-prime mortgage market has malformed. As a result, a rapid financial crash has scrutinized in the Latin America, Europe, Asian region, and African countries.
Externally, limitations of the global economic organism have motivated the major monetary products and appliances to form into complex as well as twisted. Consequently, principal financial organisations of the world have severely collapsed. To prevent this situation some of them have continued their competitive journey by offering low price commodities. On the other hand, wealthy countries’ government like the UK and US has agreed bailout program individually for survival of their bank as well as financial organisations. Additionally, they have nationalized a few of their private banks in support of the same goal. Now, after four years frequency of the recession has teetered worldwide the same as it has earlier due to a few major dynamics for instance, economics of scale, high commodity prices, burst out of the US housing bubbles, in few nations practice of restrictive monetary guiding principles, and unsteadiness of the stock markets (Shah 2-15).
At earlier stage of recession, key financial organisations of the Europe have greatly affected and amongst few of them have needed to liberate. Moreover, Europe has failed to seek several effective as well as efficient responses to come up from these circumstances. For instance, few European countries have taken step to nationalizing their major organisations in order to protect people’s savings; provide support stockbroker deals with largest banks. Furthermore, to stretchy people’s increasing living costs Europe has worth approximately € 200 billion for the last two years by reducing tax payment. Besides tax reducing, Europe has also tried to expand employment opportunity, green technology promotion, encourage the banks to start giving credit again.
ODI has coordinated and reported about the effects of the global economic downturn along with the monetary policy implications by scrutinizing ten both developed and developing nations. This research has pointed that in these ten countries major communication attacks like trade-off, FDI (Foreign Direct Investment), private capital inflows and outflows, remittances and aids have affected diversely (ODI 2-12).
All of the above-mentioned data has presented a wide range of global economic meltdown and this distress has become a result of economic policy. Though tasks of the economic polices have responsible to utilize proactive approaches so that business activities would be went through a smoother path. A few nations have considered and implemented speedy economic growth policies such as Cambodia. However, in Kenya and Uganda, they have followed narrow degree of monetary policy and in Indonesia; they have preferred intensive fiscal policy implementation. ODI 2009 has examined that Bangladesh, Ghana, Kenya, and Nigeria have created emergency task force to protect and prevent the current monetary slowdown (ODI 2).
Besides monetary policy, there have a large number of social policies, which have equally responsible to creating financial crisis, but in different countries, social policy factors have influenced diversely. On the other hand, some counties evidenced sponsor support, condition of the social protection have vastly established in the lower level of the society while the others has focused on how to response during crisis and Indonesia have spread out intense approaches to response whilst need has boosted. Three major dynamics have determined the degree of the social policies how they would be responding in crisis. They have expansion ability of the revenue retrenchment, efficiency of the government to invest marginal resources to meet up monetary scarcity and social protection system through a proactive approach.
Effects of the global financial crisis on the Saudi market
GFC on Saudi Financial Market
Saudi financial market has been patronized by both public and private investment. Following are the key areas of the Saudi financial market (Trivedi 18–33).
- Government investments: usually, the Saudi government has invested in lengthy pipeline projects through utilizing their budget surplus. As a consequence of this, in the current recessionary period the Saudi financial market has forecasted a neutral impact.
- Capital Flows: the recession has shaken the availability of fund pool as a result private capital flow or the FDI has slowdown significantly. Bedsides this atmosphere, the Saudi government has expected a handsome amount of FDI due to their flexible buying power as well as friendly business atmosphere. On behalf of the World Bank, during the recession period, Saudi has continued their neutral business flow by ranking in the position of 16 globally and at top of the Middle East countries.
- Private investment sectors: In the housing segment, Saudi has been unfavourably affected, but this adverse circumstance has put several positive results in the real estate division. Other private investments areas, which have worked for inhabitants’ necessities fulfilment has not yet influenced negatively the actual purchasing power of the Saudi clients.
- Jobs: due to structural difficulty, the Saudi job sector has not demand driven and hence there have not any scope of adverse impact because of the demand decline. If the Saudi Government has started to execute surplus projects as well as additional restructuring dealings, they have abundant scope of new job fields. In this way, Saudi has protected humidity of their neutral financial depression
- Tourism sector: for the Saudi resident financial crisis might be made a positive scope to travel in a foreign country since stronger dollar has strengthen Saudi Riyal.
- Inflation: in case of inflation, with the decrease of inflation rate globally, Saudi might get positive supports by exchanging foreign currencies because of stronger US dollar.
GFC on Saudi Banking & Stock Exchange
As any other countries in the world, Saudi banks have also suffered from potential liquidity crisis due to banks have experienced loss in their foreign investments. On the other hand, at the last quarter of 2008, Saudi governmental has neutralized this incident by adequate liquidity supply as well as bank deposits safety assurance (Trivedi 18–33).
Saudi’s official stock exchange the Tadawul has also the largest stock exchange in the Gulf region. In 2008 GDP, 70% GDP or the current market capitalization in terms of $325 billion has provided by the Tadawul. It has quoted that Saudi stock share prices have principally driven by the oil prices and in the tremendous recessionary period the Tadawul has efficiently interconnected with the global stock markets and now at present this correlation has enough stronger.
During most of the 2009, in the area of bank and petrochemical balance sheets have reflected anxiety since a few emerging market has lagged by scores of margin. On the other hand, in 2005–06 fiscal years, structural inflexibility of the market has supplied considerable price accumulation modes. Consequently, a few painful regulatory transformations have occurred rapidly in order to focus on the transparency of the corporate governance. Hence, scope of FDI has opened partially. Interim figure of the Saudi stock market has responded comparatively better for the external demand as well as stronger government spending in order to boosts corporate profit and at the end of 2010, global economic growth would be turned flexible (SAMBA 1–13).
GFC on Saudi Foreign Exchange
At the end of 2009, world foreign currency reserve has enlarged up to $8.1 trillion where as Saudi Arabia has absorbed approximately $400 billion. Like any other major countries of the world Saudi has also kept continuing foreign reveres, but to daily credit repayment. Alternatively, they have reserved in terms of the self-insurance to protect and prevent sudden loss in the overseas countries as well as flow of FDI. Moreover, Saudi has fastened exchange rates to handling recessionary pressure on their currencies like Riyal. Whilst the global currency reserved has down at $7.2 trillion or 5.8%, Saudi has taken fund stimulus programs to terminate depreciation of the currencies. After February 2009, like another reserve holding economies Saudi has accumulated foreign currencies to create effective exchange rates (Saudi Gazette 1).
GFC on Saudi Consumer Market
In spite of the strong recession period has continued Saudi consumption expenditures has not yet affected adversely. Emigrant customer expenditure has declined in few of the private business sector like housing projects, but those would be exploited, it might be delayed. Considering all of these, it has to be said that Saudi government has efficiently balanced a positive consumer demand.
GFC Effect on Saudi Export Market
As well as other Gulf countries Saudi industrial and construction sector has affected adversely which have monitored key export market of Saudi. Saudi typically has exported in Africa and Middle East and HFZ (Hamriyah Free Zone) has the most efficient strategic manufacturing region has absorbed big contracts featuring full production factories for the next six years. Conversely, costly shipping infrastructure of the Saudi has constrained their entrance into the Asian and full coverage of the Middle East. On the other hand, Chinese raised floor industry has dominated through their competitive price aid.
However, situation has been changing from last year and few of Chinese companies have taken strategic location advantages by trade-off with the Gulf regions as well as with Saudi. In near future Saudi have abundant trade scope in the South East Asia in the construction and industrial sector. Moreover, in India, manufacturing competencies have enlightened their industrial forecasts. Consequence of all Saudi has efficiently executed their export market during this recession (Rizvi 1–3).
GFC Effect on Saudi Oil Market
In between 2008–09, oil prices of Saudi have fluctuated unpredictably. According to the report of WTI, the oil price was $98-$147 per barrel in first two quarters of 2008, but at the end of 2008 oil price declined dramatically by $44 per barrel, so Saudi economy has faced challenged in order to survive in export-oriented market and consumer market (Rizvi 3). Surprising news was that any of the predictor could not accurately forecasted oil price fluctuations. Most of the economists have agreed that oil price has shaken since principal transformation has occurred in the market equilibrium. In between 19980–90, oil price was $20 per barrel due to oversupply of oil in market. After 2003, oil price has become increased $50–$80 per barrel which has an indicator of sharp growth in the promising market demands for instance in China. During 2009, stretched financial circumstances have created a new dimension in oil price determining. According to the economists, oil price could be decrease than $20 per barrel what would be the new equilibrium pricing strategy.
For Saudi Government as well as the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) members, handsome oil price has provided comfortable level of funding for producing oil. Though economic atmosphere has enough rough globally, still 2009, Saudi government expenditures, and the oil production have presented a small amount of budget scarcity. It has to be noted that moderate high oil price has simplified to adjust oil value to be steady US dollar declining. Since 2003, oil price have has increased by 140% where as US dollar has declined its value by 25% in terms of trade weight approach. Most of the economists has also pointed that emerging market demand has also affected bulk of the oil prices globally. The OECD members has needed to be concern on environmental issues as well as increasing oil prices which have a great impact on global financial meltdown.
GFC Effect on Saudi Non-oil Market
Following are the major non-oil sector of Saudi market (Trivedi 18–33).
- Raw Materials: entrance of the intermediaries along with the global recession has reduced commodity prices and hence, construction materials costs have dropped. For instance, steel, copper, iron price has reduced worldwide, but raw material segment of the Saudi Arabia has still stronger than any other countries.
- Unskilled labour: due to stretched economy, job loss ratio has increased as well as wages payment has also decreased. Consequently, the OECD member’s unskilled worker number has magnified along with a downward wage pressure. On the other hand, Saudi has driven through migrant workforce their profit curve has moved upward and a positive impact of recession has observed here.
- Skilled labour: similar figure has examined in the Saudi skilled labour segment. Ratio of job loss increased with a downward wages pressure. This circumstance has positively affected Saudi labour market.
Research Methodology
Introduction
According to the view of Marshall & Rossman, the research methodology usually devises the specific processes and techniques for specific research purpose (19). Zikmund (32) and Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis (120) expressed that the research methodology usually works as a compass to guide the research activities throughout every phase of the study. However, the researcher of this dissertation would formulate the paper in accordance with the research approach of Malhotra as case study approach only applicable for single case. To organise the paper, the author would prepare a questionnaire taking into account the topic and research questions, gather primary data from the target groups, eliminate all mistakes from survey, and illustrates the results with recommendation and conclusion. Moreover, the author would rely on both quantitative and qualitative research approach as the effects of global financial crisis on Saudi market is a sensitive approach.
Significance of descriptive research
Global financial crisis has affected most of the business sectors and destroyed economic balance of the world. Few important sectors of Saudi market also faced various challenges to sustain the market in economic downturns, for example, production of oil reduced. In this context, descriptive research method helped the researcher to assess the Saudi market in terms of international economy.
Primary research
The primary data collection process would be different from other research paper because global financial crisis affects the entire market of Saudi economy. As a result, the researcher has to consider financial market, labour market, banking sector, oil and non-oil segment, foodstuff, housing industry and so on. However, Malhotra pointed out that primary data should generate for the specific reason or resolve the research problem (103). Therefore, the researcher of this paper would consider this type of data in order to find out the actual scenario and to recommend possible solution to overcome from global economic downturns.
For data collection, the researcher would consider three possible affected sectors like oil and non-oil segment, banking area, consumer, and labour market. However, the following table shows more details about the respondents –
Selection of Interview process
Malhotra (134) and Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis (78) expressed that face-to-face interview is the most effective approach to collect primary data. However, the researcher of this dissertation had not mange enough time to collect primary data by conducting face-to-face interview, as the deadline and budget was too short to adopt this process and number of respondent was more than 100 individuals. In addition, it was not possible for the researcher to conduct direct interview as most of the respondents lived in different areas like Riyadh, Jubil and other industrial regions. In this context, the researcher applied more instantaneous methods to serve the purpose, such as, traditional telephone, e-mail, face book, twitter, and so on
Data Analysis process
The author of this paper would recheck all the information to eliminate the inconsistent and fabricated information about the recessionary impact on the Saudi economy. Here, it is significant to mention that the researcher would refine primary data by considering secondary data related with the effects of global financial crisis in Saudi market. However, the researcher would compare and contrast the primary and secondary data regarding the impact of global economic downturn in Saudi market by presenting graphical charts and applying other descriptive approaches.
Secondary data
The author of this dissertation would formulate the literature review by using secondary data sources, as there is huge information available in this topic. According to the view of Malhotra (153) and Zikmund (69), using of secondary data has many advantages because these are more authentic as it means processed data for serving the current purpose. In addition, global economic meltdown is one of the most sensitive issues for recent financial market, so it would be easy for the researcher to gather this type of information with short time and no costs.
However, the author of this thesis paper would use the information from published euro-journal articles, related research papers on the impact of global financial crisis, forty-fifth annual reports of Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA), SAMBA report and other published data from monthly bulletin. In addition, the author of this report would take into consideration the recommendation of International Monetary Fund, Would bank and other financial institution, as they provide authentic data with proper discussion about the positive and negative side of the economic meltdown in Saudi market.
Questionnaire Design
The author of this research paper provided highest effort on the questionnaire as it is one of the most significant parts of the dissertation. Malthotra argued that broad conversation with target respondents might bring unjust results with different view while particular questions assist the participants to ignore major dilemmas (281). However, the researcher emphasized more on this issue because recommendation, conclusion, and the results of the research derived from the answer of the respondents. To formulate the questionnaire, the researcher would consider simple questions with easy contents in three parts. However, the following table shows the questionnaire design procedure for this dissertation –
Limitation of Data Collection Process
Due to tight deadline and budget problem, the researcher had to contact with target respondents by using e-mail though face-to face interview is the best way to collect primary data from respondents.
Findings & Discussion
Section A: (design to assess Labour market)
Question 1: About respondents
The researcher of this dissertation has designed the first question of the questionnaire to introduce with the target respondents.
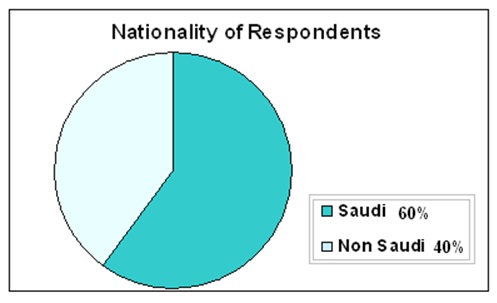
Question 2: Separating respondents by nationality
This question has significance to measure the affects of global financial crisis on the Saudi labour market. In order to formulate this paper, the researcher contacted with thirty ordinary labours because they have practical experience in this field. According to the survey report, 60% of total respondents (20 employees) were national workers and rest of the respondents were overseas workers.
Question 3: Employment status of the respondents
It was a straightforward question to know more about the respondents. From the response of this question, the researcher of this paper find outs that 70% of the total respondents were employed person, and 20% of the respondents were job seeker. Here, it is necessary to mention that most of the job seekers had worked to complete projects of the multinational companies.
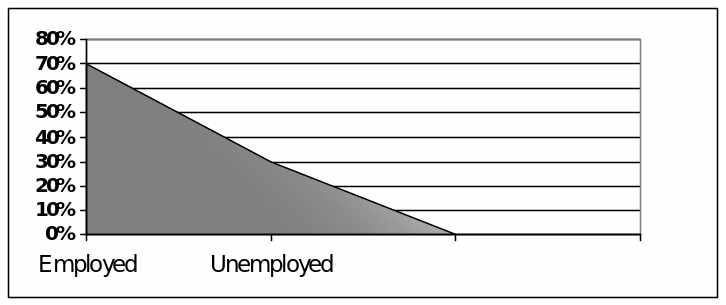
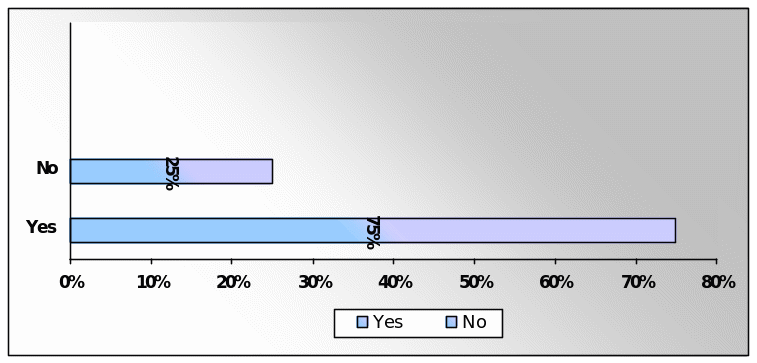
Question 4: Saudi labour market has adversely affected by Global financial crisis
About 75% of total respondents (25 respondents) believed that Saudi Labour market has affected by the global economic downturn while only five respondents disagreed with the statement.
According to the response of the interviewees, it can assume that the labour market was not in perfect condition. However, the secondary data sources provide different information in aspect of the Saudi labour market. In this context, the researcher of this dissertation would find out the reason behind the contradictory result among the survey result and secondary sources.
Question 5: Please select real affected group
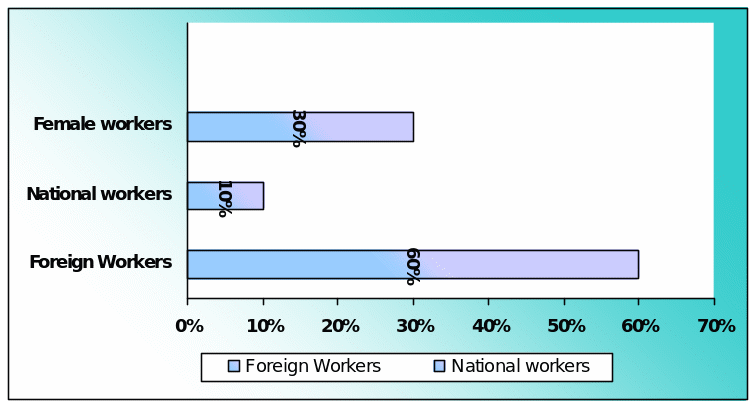
The researcher of this dissertation has designed this simple question in order to identify the most affected labour group. According to the primary data, the majority of the respondent selected first option and few of them chosen option B & C. However, following figure shows that 60% of the total respondents said foreign workers has seriously affected by the global financial crisis –
Question 6: Additional Comments
In this phase, the respondents expressed their opinion about the recent crisis. Most of the respondents said that theoretically Saudi labour market is in stable condition as the total employment rate has increased after this economic disaster, but the practical situation is different. They argued that the bargaining power of the general workers has weakened, such as, workers have limited control on salary, pension funds, duration of work, and other issues related with facilities. As a result, increase of employment rate does not indicate the actual scenario of this market especially for foreign labour market.
Saudi Labour Market Position – Secondary Data
Indexmundi reported that unemployment rate has been decreasing gradually, for instance, in 2010 unemployment rate was about 11.6% while this rate was 25% in 2003 (1).
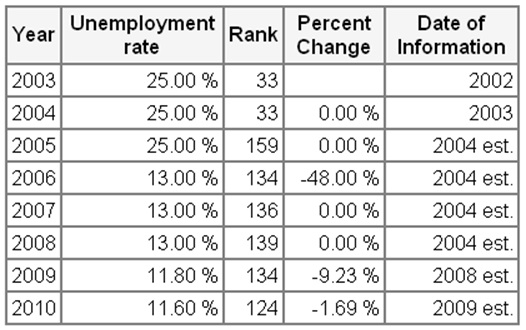
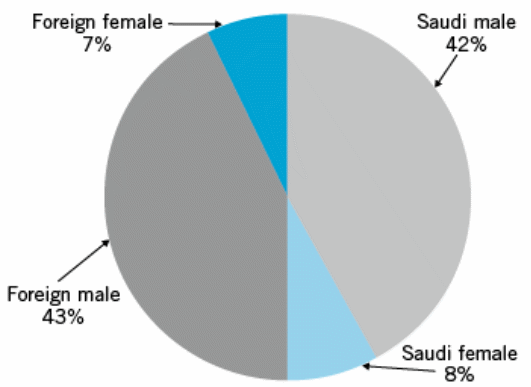
At the same time, foreign
According to the report of ILO, the overall Saudi labour market associates with more than 4.32 million overseas work force and 4.29 million Saudi workers. However, Saudi labour market is in stable condition as the government has taken realistic decisions in budget to avoid the current economic crisis. SAMA stated that the government of KSA agreed to boost the investment for infrastructure development including other mega projects by 16% in order to decrease the unemployment rate both for national and foreign workers (47). From the discussion of secondary data, it can be said that the effects of the global economic meltdown on the Saudi labour market have been comparatively mild because the Labour Ministry has not identified any noticeable distress.
Section B: (design to assess banking sector)
Question 1: Name of respondents
The author of this paper considered this question in order to introduce with the interviewees.
Question 2: Please specify your bank name
The aim of this question is to divide the respondents in accordance with different banking sector and the researcher considered respondents from one Islamic bank and two commercial banks. However, the researcher interviewed 30 employees (10 employees from each bank) to gather primary data to discuss the effects of global economic downturn of Saudi banking sector.
Question 3: Please select your job position
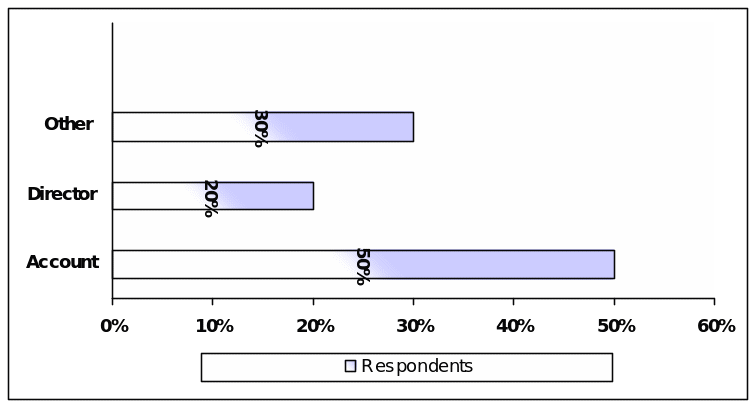
As banking sector is an important segment of Saudi financial market, it is essential for the researcher to have a clear idea about the opinion of employees of the bank. The author had selected Accounts, directors or high officials from different three banks to interview, as the researcher try to identify the actual scenario from reliable sources in order to assess the effects of credit crunch on Saudi economy. However, the survey report demonstrates that 30% of total respondents were high officials, 20% respondents were directors, and about 50% participants were accounts.
Question 4: Saudi banking sector has affected by Global financial crisis
According to the figure no 15, about 40% respondent said that credit crunch affected the baking sector, 20% respondents selected option B, and 30% respondents had not replied this question.
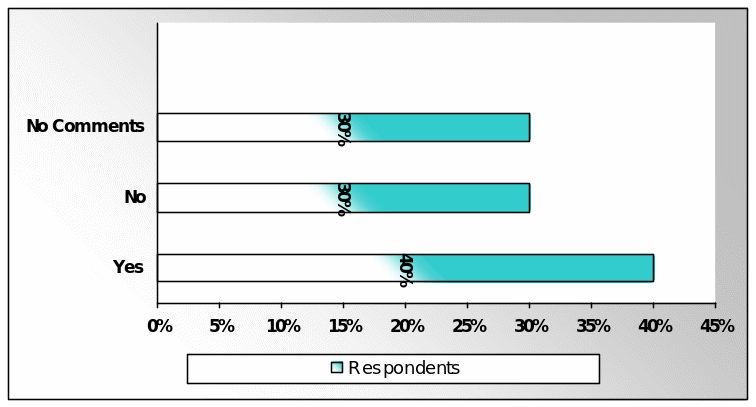
From the survey report, it is clear that the effect of financial crisis was very little on Saudi banks, so the answer of the respondents varied from one another.
Question 5: Financial downturn has impact on the profit margin
It is interesting that 15 respondents (50% the total respondents) agreed with this statement. On the other hand, 25% respondents totally disagreed with the statement, 20% employees believed that global financial crisis has mild the banking sector and 5% respondents have no opinion in this aspect.
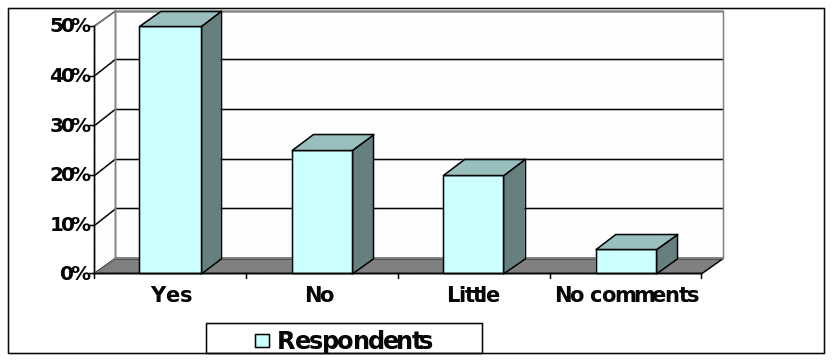
According to the feedback of the accounts, the profit margin of large banks had weakened because of financial crisis.
Question 6: Additional Comments
The researcher of this dissertation has modified the additional comments of the accounts and other officials. After conducting research on additional comments, the researcher included their opinion on recommendation segment of this dissertation.
Impact on Banking Sector – Secondary sources
According to the forty-fifth Annual report of SAMA, Saudi banking sector untouched from the financial crisis and this segment performed better than previous years. In addition, SAMA provided enough evidence, which shows positive economic growth of banking sector in such global financial crisis, for instance –
- The government deposits amplified more than 104.7% in 2008 whereas it was only 50.3% in 2007;
- Notes issued increased from 14.2% to 48.7%;
- One of the most important sign of developments is that international investments grew by 46.1%;
- At the same time, the deposits of commercial banks’ with SAMA raised by 23.2%;
- Its deposits abroad improved by 53.8% and the amount was SR 132.7bn;
- Net cash value amplified by 13.5% compared to a rise of 86.6% in the previous year;
- The growth rate for the last two years was 35.31% and 42.89% accordingly.
- On the other hand, many sources stated that global financial crisis is the old issue and the Saudi banking sector is out of the influence of this economic meltdown.
Section C: (design to assess Consumer Market)
Question 1: Name of respondents
It is essential question to communicate with the interviewees.
Question 2: Global financial crisis changed the purchasing power of consumer
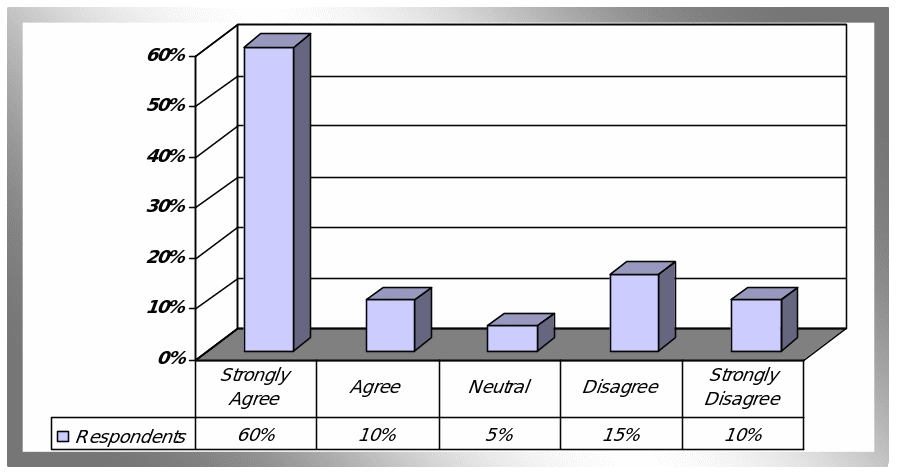
The researcher has designed this question to get a clear idea about the consumer market from the position of ordinary people. However, it is interesting that labour market was not seriously affected from credit crunch, and banking sector was in stable position, but 60% of respondents selected strongly agreed with the statement, 10% chosen agree, 15% simply disagreed, and 10% strongly disagreed, and only 5% respondents were neutral.
Question 3: Financial downturn has impact on consumer market
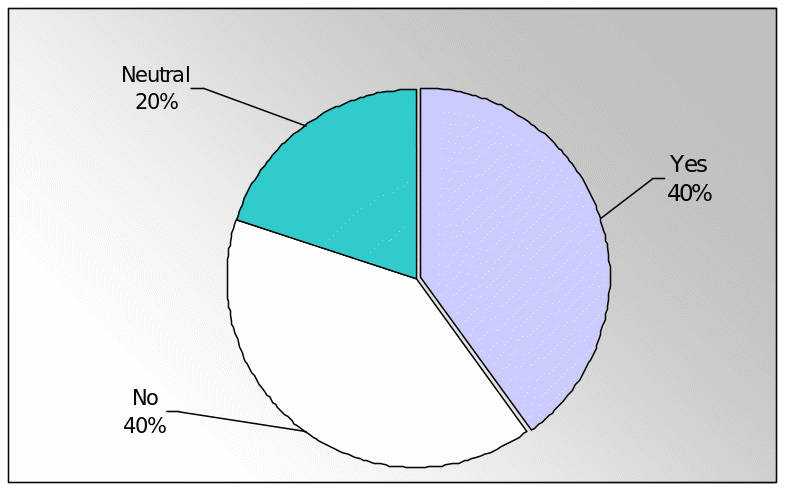
The rationale of this question was to examine the impact of the global economic crisis on the Saudi consumer market. However, among 30 customers, 12 customers argued that Saudi Consumer market affected by the credit crunch, 12 respondents said no, and six customers mentioned had no opinion in this aspect.
Question 4: Additional Comments
The respondents said that government should put more focus on agricultural sector in order to decrease food products. On the other hand, many respondents said that global financial crisis is one of the major issues to create disturbance on consumer market, but it is not the sole cause of the problems. In addition, the customers mentioned that credit crunch effect the consumption and the purchaser switched from buying luxury to essential products, as the rate of products has increased dramatically. However, secondary data sources also agreed that the Saudi consumer market had adversely affected by the financial crisis.
The impact of GFC and recovery modes of Saudi
Expand FDI scopes and reduce expenditures
During harsh period of the recession the Gulf region banks as well as the Saudi banks have efficiently supervised their credit losses in the housing segments. Consequently, Saudi has taken initiative to transparent their FDI sector more than ever. On the other hand, to reduce spending Saudi stock market has adopted modern technological infrastructures. Moreover, they have also wished to introduce new products and services along with several strategic agreements of FDI entrance in their economy at lower interests and flexible trade policies. Consequently, Saudi stock exchange would have gotten larger FDI and ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) by attracting foreign investors (Platt 1–4).
Speed up development agendas
For both short term and durable financial downturn, continuous development of the reforming agendas would be efficiently upgraded regulatory atmosphere of the Saudi Government. Alternatively, Saudi oil market has also started work in the post oil market. Adequate budget surpluses $70.6 billion and $47.6 billion respectively in 2006 and 2007 has made easier way of investment reforms therefore Saudi would effortlessly absorb positive impact in their economy after recessionary period.
Investment via mutual funds
According to the CMA (The Capital Market Authority) of Saudi Government, their regulatory authorities have enough experts to create scope for the global investors via mutual funds. The CMA has also pointed that new investment segment has profoundly attracted by the retail investors as well as the housing interest have magically attracted investors. Since 2003, capital market culture has introduced in the developing nations attaching with regulatory committee. As a result, internal audit as well as corporate report have been greater stringent. In 2008, the CMA has declared that foreign investors have to invest in Saudi through swap agreements along with the local firm’s authorization. Considering all of the issues it can say that besides mutual funds Saudi has enough flexible to build opportunity in their country therefore they would positively recover from recessionary affects (Platt 1–4).
Expand technological investments
To protect environmental pollution, reduce petrochemical uses Saudi has needed to focus more on technological development along with the green technologies. Consequent of this Saudi government would have confidently recovered their financial damages. Another merit of technological development would be reduced complexities of the banking activities like- handling multiple assets trading, currency management including the entire cash appliance, derivatives, Islamic financial appliances, structured products, and services and so on. With the aim of these initiatives, BFX (Bahrain Financial Exchange) has owed FTGI (Financial Technologies Group of India) for a flexible liquidity ratio and for the next 25 years, MENA (Middle East and North Africa) has wished to work for emerging markets to achieve annual growth from 6–10%. Alternatively, with attachment of Gulf regions Saudi has needed to invest more on SICO (Securities & Investment Company) to promote large scale of security markets more willingly than the retail markets. On behalf of SICO, within next five years budget surplus and currency reserves would be enlarged per capita GDP of Saudi as well as other GCC regions.
Conclusion
Recommendations
- The government should more concentrate on oil exports and prices, hydrocarbons exports as these sectors expected to slump by around 52% within this year;
- Strict monitoring and enforcement systems need to develop in order to reduce internal conflict because this conflict is one of the major factors of the global financial crisis, for instance, executive directors influenced non-executive directors to increase their remuneration. At this point, this report suggests the government to control the remuneration of the directors of the oil and non-oil industry as the economy of Saudi Arabia largely depend on industrial sectors;
- In addition, other multinational companies should take into account the aftermath the global financial crisis and maintain a strict inspection or monitoring process where it will exercise the recommendation of corporate governance theories, listing rule of CMA, and other audit reports.
- Moreover, the government of KSA should more careful on the corporate fraud issues because they can disintegrate money market, for instance, the collapsed of Lehman Brothers greatly intensified financial crisis by withdrawing $56 billion from money market funds;
- According to the view of IMF, the urgent challenge for this nation is to complete the cleaning up of banks’ balance sheets and assist the restructuring of the non-banking segment;
- However, the vice-president of SAMA stated that there was no need to grant emergency funds to banks in the world’s prime oil exporter as the financial segment faced no shortage in liquidity;
- Here, it is important to mention that Kuwait issued a Financial Stability Law and the UAE plans to amend the banking law, so Saudi Arabia should keep a close look upon the national rules and regulations;
- The government of Saudi Arabia should subsidies weak companies at the initial stage of financial crisis in order to protect capital outflow, encourage trade, strengthen the economic segment, and enlarge lending for transportation, and help to overcome horrible economic crisis;
- Since Saudi banks remain well capitalized in comparison with their Gulf peers, now it is banking sector’s job to assess the vulnerability of the economic downturn to devise specific instrument a financial policy to rescue the economies;
- ILO reported that the effects of the global crisis on the Saudi economy have been relatively mild, so the policy makers should try to maintain this position;
- Before attempt to take any major step, the government and other financial institutions should try to discover the actual basis of economic recession, as this crisis has not created automatically or arbitrary, but it occurred because of over-investment by international bankers and other ventures’. Therefore, this dissertation recommends that the management should differentiate between long-term secular improvements and the medium-term financial conjuncture;
- Though Saudi Arabia has enough resources and capabilities for further development in such economic condition, but it should measure their existing resources and review the Debt Sustainability Framework;
- In addition, the policy makers can review the fiscal and monetary policy;
- Rizvi pointed out that oil demand dynamics between the emerging markets as well as in the OECD members would be seek alternative source of oil supply therefore the current market price would be balanced (3);
- The export oriented sectors (e.g. Oil, petroleum, and so on) and high value sectors (e.g. tourism) have assumed as the conjugal growth drivers for KSA. For this reason, the policy makers should develop macroeconomic policies to facilitate the growth driver;
- As the investment has reduced, the government should more concentrate on infrastructure development issues to facilitate private investors;
- At the same time, macroeconomic policies should be flexible enough in order to ensure sufficient resources to improve infrastructures. The policy makers should allow private-public partnership in infrastructure development projects
Conclusion
The global financial system of modem era has sequenced different countries in such a chain that no one can keep apart from the impact of recent global financial crisis rose from the credit crush of US hosing mortgage market. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the world’s largest oil producing country cannot keep its economy isolated from the impact of global financial crisis of 2008, but the influence was comparatively lesser than other country and the policy respond and path to recovery relatively easy than other countries. The worsened provision of GFC (Global Financial Crisis) did not allow KSA financial system without enormous wealth devastation, while the Saudi banks were forced and strained to write-off billions of dollars due to close coordination with gigantic foreign financial institutions those have turned bankrupt.
GFC also has thrown the challenge to KSA with drastically lower oil price, resulted with reduced oil production, and generated intensive impact on oil revenues. Consequently, employment opportunities rate has decreased, consumer goods turned more expensive, and pressure on national budget, project implementation, and infrastructural development become stringent that affected the labour market. It has demonstrated the challenge for KSA to concentrate on macroeconomic policy maters towards bring-back the confidence of investors in the financial sector rather than controlling inflation while the dynamism of Saudi domestic economy has capabilities to boost the national economy forward within short span of time and gain healthy growth momentum from both oil and non-oil sectors as well
Works Cited
Allen, Franklin et al. Financial Crises: Theory and Evidence. 2009. Web.
BBC. Timeline: Credit crunch to downturn. 2009. Web.
Berkmen, Pelin et al. The Global Financial Crisis: Why Were Some Countries Hit Harder?. 2010. Web.
Bourland, Brad. Saudi Arabia and the Global Financial Crisis. 2009. Web.
Cox, Wendell. Root Causes of the Financial Crisis: A Primer. 2008. Web.
Crotty, James. Structural Causes of the Global Financial Crisis: A Critical Assessment of the New Financial Architecture. 2008. Web.
Econbrowser. Analysis of current economic conditions and policy. 2010. Web.
ESCWA. The Impact Of The Global Financial Crisis On The World Oil Market And Its Implications For The GCC Countries. 2009. Web.
ILO. Saudi Arabia’s Response to the Crisis. 2009. Web.
Indexmundi. Saudi Arabia Unemployment rate. 2010. Web.
Keen, Steve. The Minsky Thesis: Keynesian or Marxian? 2008. Web.
Malhotra, Naresh. Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall, 2009. Print.
Marshall, Catherine. & Rossman, Gretchen. Designing qualitative research. Thousand Oaks – CA: Sage, 1999. Print.
ODI. The Global Financial Crisis and Developing Countries. 2009. Web.
Palley, Thomas. America’s Exhausted Paradigm: Macroeconomic Causes of the Financial Crisis and Great Recession. 2009. Web.
Pfeffenzeller, Stephan. Economic Growth: What Macroeconomic Factors Lead to Economic Growth. 2009. Web.
Platt, Gordon. Gulf Report: Exchanges Enrich Technology Exchanges Upgrade Technology And Add New Products. 2010. Web.
Rizvi, Muzaffar. UAE to Lead Raised-floor Industry. 2010. Web.
SAMA. Forty- Fifth Annual Report of Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency. 2009. Web.
SAMBA. The Saudi Stock Market: Structural Issues, Recent Performance and Outlook. 2009. Web.
Saudi Gazette. World foreign currency reserves surge. 2010. Web.
Saunders, Mark. Thornhill, Adrian. & Lewis. Philip. Research Methods for Business Students. London: FT Prentice Hall, 2006. Print.
Sekaran, Uma. Research Method for Business. London: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. Print.
Shah, Anup. Global Financial Crisis 2008. 2008. Web.
Trivedi, Prajapati. Global Financial Crisis: Causes and Consequences. 2009. Web.
Zikmund, William. Business Research Methods. Orlando: Harcourt Publishers, 2006. Print.
Appendix 1
Questionnaire
Section A: (design to assess Labour market)
- Your name: ______________________________
- Please select your nationality:
- Non Saudi
- Saudi
- Your employment status:
- Employed
- Unemployed
- Saudi labour market has adversely affected by Global financial crisis
- Yes
- No
- Please select which group was mostly affected?
- Foreign workers
- National workers
- Female workers
- Additional Comments:___________________________
Section B: (design to assess banking sector)
- Your name: ______________________________
- Please specify your bank name:
- The Arab National Bank
- The National Commercial Bank
- Al Rajhi bank
- Please select your job position:
- Account
- Director
- Other
- Saudi banking sector has affected by Global financial crisis
- Yes
- No
- No comments
- Financial downturn has impact on the profit margin
- Yes
- No
- No comments
- Additional Comments:____________________
Section C: (design to assess Consumer Market)
- Your name: ______________________________
- Global financial crisis changed the purchasing power of consumer
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
- Neutral
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
- Financial downturn has impact on consumer market
- Yes
- No
- No comments
- Additional Comments:_____________________
