Introduction, Significant Operations Principles, and Corporate Strategy
Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company is an American international tire manufacturing organization that was initiated around 1900. Seiberling Frank founded it, and it first located in Ohio State (Goodyear Corporate). Goodyear obtained its name from Charles Goodyear, an American who invented vulcanized rubber. The company’s initial auto wheels gained popularity because they required little maintenance, apart from being easily detachable. Currently, Goodyear Tire Company produces auto wheels for heavy commercial trucks, automobiles, light tricks, racing cars, motorcycles, airplanes, heavy earth-moving machines, farm equipment, and many more (Goodyear Corporate; Skoropad, 2017)).
It also manufactures bicycle tires, after halting its production for some time. In the international market, Goodyear stands among the big four tire manufactures, including Michelin based in France, Bridgestone, which is Japan-based, and Continental located in Germany. Today, the company is among the popular advertising icons in the United States.
Goodyear’s business goal is to deliver sustainable revenue and grow profit while increasing their product value. Through innovation and excellence, the company strives to develop unique products and services that anticipate and meet customer needs. Moreover, Goodyear uses sales and marketing excellence to build brand value and help consumers to win in their product search by accessing this preferred commodity (Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report, 2018, p. 1). Operational success is based on the relentless improvement of product quality and efficiency in delivering the right tires to the right locations, at the time they required, and at the appropriate cost.
Furthermore, Goodyear focuses on five core principles of success. First, acting with integrity enables to work with respect and honesty, earning trust and confidence to protect the company’s name. By energizing its team, Goodyear creates a workplace that inspires associates through duty performance, wellness, and community service commodity (Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report, 2018, p. 1).
Moreover, the company promotes collaboration by linking associates globally and encouraging open conversations to meet organizational goals. Goodyear works with agility by encouraging adaptability to change and acting hastily with purpose. Another principle concerns result delivery, where the company makes firm decisions, expects challenges, and seizes every profitable opportunity. The company wins intersections, apart from engaging and helping employees to realize their full potential.
Moreover, focusing on consumer experience enables Goodyear to sell large volumes, and encourage customers to recommend the products. Its customer service drive makes it a great supplier collaborating with buyers. Focusing on high-value segments helps Goodyear to outcompete rivals where they seize the optimum brand value commodity (Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report, 2018, p. 2). The company has mastered business complexity, enabling them to manage fruitful operations and eliminate the unnecessary ones.
Goodyear’s corporate strategies are commitment to integrity, as well as diversity and inclusion. The first strategy is established in the company’s department of compliance and ethics (C&E) each year. The agent’s board of directors reviews every activity and process tailored to foster commitment to ethical conduct. The organization also defines the behaviors designed to support high standards and encourage associate adherence to applicable business laws and practices. Goodyear expects all employees to know and comprehend compliance and ethics policies and observe them. Therefore, current and new associates undergo online training to familiarize themselves with the policies.
More than 90% of them responded to the training rule in 2019, focusing on competition law, anti-bribery and anti-corruption (Goodyear Corprate). Goodyear offers physical training programs tailored to develop to develop workforce in all critical business units. The aim of this development is to emphasize compliance and promote workplace culture of respect, autonomy, expression ethics, and privacy of personal and organization information.
Goodyear’s morals awareness campaign occurs in the company-owned retail and wholesale locations. It also takes place in the commercial product service locations in Africa, Canada, Australia, France, the United Kingdom, the United States, and their airship service locations (Goodyear Corporate). Further, the company provides an integrity hotline, expecting associates to report any intended, actual, or anticipated misconduct, apart from communicating them to the management. The C&E group reviews the matters and take appropriate disciplinary measure following alleged misconducts. The company strictly illegalizes retaliation against anyone for reporting issues in good faith (Goodyear Corporate). It conducts awareness and education campaigns to remind employees of the integrity hotline and informs them to report concerns.
Regarding information privacy and protection, Goodyear’s corporate strategy is to develop regulations and best practices to mitigate the challenges. It passed a comprehensive privacy law in California, apart from updating global online privacy rules and implementing additional programs for employees who interact with personal data (Goodyear Corporate). Overall, the corporate strategy focuses on protecting personal information for associates, customer, and suppliers.
Through diversity and inclusion strategy, Goodyear strives to ensure that the workforce reflects customers and societies they serve. The corporate leadership team in the company reviews information regarding diversity across the workforce and informs the board of directors commodity (Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report, 2018, p. 4). As a result, Goodyear has seen an increase in the number of minority and female associates in the US and internationally. It has seven associate resource groups to attract, connect, motivate, and retain talent. They include the Goodyear Pride Network, Hispanic/Latin, Goodyear Women’s Network, the Asia India Middle East Network, Next Generation Leaders, Goodyear Veterans, and the Goodyear Black Network (Goodyear Corporate).
The agents provide opportunities for employees to serve as organizational ambassadors, playing a fundamental role in talent recruitment and development. Lastly, diversity and inclusion in Goodyear is a crucial corporate strategy. The company continues to build relationships with various professional associations using social media platforms such as Glassdoor and LinkedIn to reach potential associates (Goodyear Corporate). Today, the company works with more than six percent of military workforce in the US (Goodyear Corporate). The world remembers Goodyear with several employer awards to its multicultural recruitment efforts.
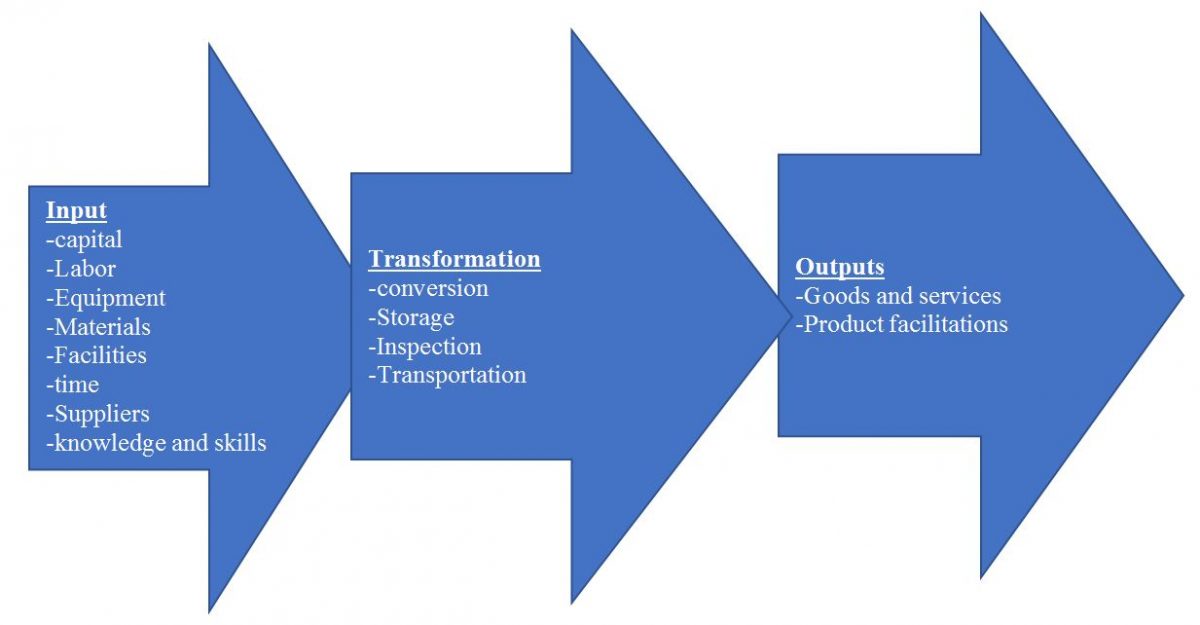
Control and monitoring actions, as well as the external environment, which comprises suppliers, economy, technology, regulations, consumers, and competitors, influence the above system. The ultimate goal of Goodyear’s transformation and operations management is to deliver satisfactory outputs and protect organizational competitive advantage (Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report, 2018, p. 4). Goodyear faces many challenges in its operations and they have led to product cuts. Economic depression is the leading factor posing considerable impacts on industry volume and consumer demand. When quarterly volumes fall below the expected levels, the company faces production challenges across all its business units.
It faces challenges forcing them lower inventory levels and cope with the lower demand environment. Goodyear faces increasing pressure from government regulations, and the need to provide faster deliveries (Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report, 2018, p. 4). Consumer needs are also evolving following technological transformations. As a result, there are many opportunities for haulers and manufacturing companies to deliver more orders, which reduce negative impacts on the environment.
Intensive competition from other manufacturers poses considerable challenges as well. Goodyear faces a stiff competition from Yokohama, Michelin, Continental, Pirelli, and Bridgestone (Skoropad, 2017). The challenge is worsened by Cooper, which is an American brand as Goodyear is. Rivals reduce its consumer base, forcing the company to remain inventive to maintain a competitive edge. Further, there are various political challenges facing tire manufacturing at Goodyear. Political stability is the factor because it affects its consumption market. A compromised system might lead to losses through military invasion and local unrest in the manufacturing state. Corruption affects the business through regulations in the consumer goods sector because politicians may lay tight rules to particular companies to enable others to grow in the market.
Additionally, there is bureaucracy and interference from federal governments in the plastics and rubber businesses (Skoropad, 2017). Legal frameworks for contract procurement change, affecting organizational operations. Moreover, Goodyear faces trade regulations and tariffs targeting consumer goods. Affiliations with other companies compromise its intellectual property protection. Lastly, pricing regulations, taxation, labor laws, industrial safety rules, product-labeling requirements, and mandatory workforce rules affect company operations.
A Review of Operations Strategy
Goodyear operations strategy emphasizes health and safety, operational impacts, product quality, long-lasting tires, and business sustainability. The roadmap calls for the company’s commitment to operational excellence; it includes supportive practices in business growth. The company strives to deliver products of a high quality inefficient manner. Its health and safety (H&S) slogan reminds the company’s fraternity to prevent serious injuries in each operational unit. Thus, Goodyear is known for having the safest operations worldwide, focusing on occupational and environmental health and safety. The company identifies critical damage vulnerabilities through its serious injury indicators following a review of incident history.
They then develop maturity strategies for each indicator to warrant mitigation measures. Furthermore, Goodyear’s H&S strategy focuses on industrial hygiene to prevent occupational illnesses. It teaches workforce to understand potential impacts of noise and other materials used in manufacturing processes. Goodyear’s industrial cleanliness process seizes the best practice and regulatory, as well as consensus standards work beyond adherence to company rules (Goodyear Corporate). The company assesses workplace exposures through monitoring to ensure that control measure is effective and transparent all associates.
Further, the company has Ergonomic Core Teams (ECT), which implement troubleshooting and problem-solving processes to minimize or eliminate injuries. According to Goodyear Corporate, the team has ensured maximization of workplace performance by reducing overall incident rate reduction. Goodyear’s other focus in safety and health is measuring performance. As such, it measures its safety progress by leading and logging demonstrative factors such as ESH management system maturity, workforce engagement, preventive or corrective action from audits, check-ups, and frequent incidents reporting. It also uses total incident rate, and critical injury potential to evaluate its safety progress. The former refers to the incidents requiring medical remedies beyond restricted and first aid solutions.
The second strategy is a continuous reduction of operational impacts. The main focus is on energy consumption, waste reduction, water cleanliness, and carbon dioxide emissions. By 2023, Goodyear anticipates a reduction 25% in carbon dioxide release, and 25% in energy consumption. The company aimed to achieve zero waste to landfill expectations in 2006, and it anticipated to reduce water consumption by 33% by 2020 (Goodyear Corporate). With continuous efforts to offset operational implications, Goodyear will not only meet and exceed ecological regulations but also sustain the environment.
Further, on operational impacts, the company’s executive in global operations and technology manages the teams implementing the robust framework to environmental impacts. They include Goodyear’s network of global, local and facility leaders in sustainability, environmental health and safety, as well as procurement and engineering (Goodyear Corporate). The primary policy guiding its sustainable operations is the Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) framework. It controls all levels associates, management, and contractors, ensuring a continuous improvement in the wellness of workforce, and protects the environment.
Goodyear monitors carefully oversees greenhouse gas emissions and water consumption. It has established goals in particular facilities to control such impacts, apart from complying with other applicable rules and regulations. Through the company’s procurement, engineering and sustainability teams, it has incorporated its energy management into the PO operating system, which is active 30 plants (Goodyear Corporate). It involves the alignment of daily equipment protection, activity improvement, reliability excellence and on-time equipment management.
It was mentioned earlier that Goodyear faces challenges from the high cost of raw materials, price and dollar fluctuations, competition and other factors lowering its products demand. As a result, it can build and maintain a capacity for excellent value products, set strategic prices, establish a larger market share at home and in foreign sates, as well as ensure that its goods and services are stable in quality and other aspects that consumers consider.
Regarding expensive raw materials, strategic pricing is fundamental in earning profits. The company can set relatively high prices, but they should deliver high value tires to win buyers. Currently, Goodyear makes close to $9-$26 profits from selling large-diameter and high-value tires (Shingler, 2019). A slight increase and a little change in its brand will warrant price increment to earn more profits. Moreover, it was noted earlier that Goodyear experiences challenges with the US dollar fluctuations in the global market.
Although the company can do little with it, it can focus on more sales volumes to increase exports, which eventually more income when foreign currencies are converted to dollars. Furthermore, Goodyear has formed a joint venture with Bridgestone Americans Inc. to wholesale their tires through TireHub (Shingler, 2019). It has also formed the Roll service, which enables buyers to order products from the company’s dealers and receive installation services at home. This strategy attracts customers, increasing sales volumes.
Challenges with strict rules and regulations require the company to strengthen its goals to maintain sustainable operations. Moreover, many businesses have been affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, especially due to lockdown and other safety rules. Goodyear, in this situation, can maximize cross-border trade only within its locations to avoid extra prices arising from safety measures.
Additionally, the pandemic has limited mobility among many people and most of them work from home. As a result, the tire market has fallen, demanding strategic marketing efforts. Goodyear can seize this opportunity by strengthen delivery services, to deliver products to customers at their convenience while observing safety rules. This step will ensure continuity in business operations and sustainable income, reflecting the company’s principle of agility.
Supply Chain Management
As Goodyear commit their efforts to responsible sourcing, supply chain management remains its top priority. The company’s executive officer in procurement leads the logistics team to manage materials and service sourcing. Goodyear’s procurement and logistics team controls the supply chain and implements policies and programs that promote ethical sourcing.
For instance, it emphasizes corruption-free procurement systems, anti-human trafficking, and conducts audits and assessments of suppliers to ensure they observe the company’s code of ethics (Goodyear Corporate). New procurement associates undergo more than a day’s training on procurement-specific themes, apart from annual training for all. Training covers the topics, which help the procurement team to identify potential issues and respond accordingly. Suppliers should comply with the company’s supplier code of conduct apart from their moral code to ensure fruitful procurement services.
Various supply chain strategies have been identified to contribute to a smooth and profitable enterprise. The first one is strategic partnerships with suppliers and it requires better organization and coordination skills. Bridgestone Corporation exemplifies similar companies which uphold strategic partnership through capacity building with suppliers (Bridgestone, no date). Goodyear should primarily establish long-term relationships with suppliers to actualize significant ongoing benefits.
A strategic supplier partnership requires the company to acquire and services from suppliers and influence their system and operational abilities by value addition and better procurement performance. Establishing excellent relationships with customers also benefits the company because all procurement activities will focus on consumer satisfaction. Long-term relationships with buyers enable an organization to respond hastily to their changing needs. Aligning suppliers with the company’s agenda can bring a difference to the company’s energy efficient strategies and other operations. Hewlett Packard’s procurement policy exemplifies this strategy (Hewlett Packard Enterprise, no date).
The company is ready to terminate contracts with suppliers who fail to comply with its corporate policies and energy efficiency rules. Since its establishment, the organization involved its major suppliers in energy improvement plans. It will be an impressive achievement to Goodyear as it focuses on EHS and profitable operations.
Supply chain integration is another trending strategy in SCM that Goodyear should incorporate or strengthen in its operations. It includes the affiliation of suppliers, customers, and organizational activities. It ensures effective communication among them (Hewlett Packard Enterprise, no date). Consumer responsiveness directly reflects information availability in a company, improving organizational performance. Goodyear needs flexibility and it should originate from buyers asking for quality, variety, quick delivery, and affordable prices (Gryaznov et al., 2021, p. 290). Therefore, supply chain integration will ensure that the company make design changes and respond speedily customers to maintain its competitive advantage.
Cost retaliation is another crucial SCM for Goodyear and any other enterprise. PriceWaterHouseCoopers (PwC) conducted supply chain management research in China firms and found that it is crucial to balance a firm’s cost considerations against supply chain attributes including flexibility, asset performance, and responsiveness. The primary costs to consider according to PwC include supply chain costs, taxation, as well as labor and materials. Taxation affects localized incentives for locating and operating firms in various regions. Therefore, SCM should consider their value, and how it fits into a particular setting to earn tremendous tax benefits.
Furthermore, the company should consider choosing the right location for the supply chain. Goodyear is a large company and it is likely to employ its staff to work in the procurement department, but small companies tend to outsource such services. SCM should factor in infrastructural issues and localized regulations in its procurement plans (PwC). Locating logistics in the coastal hubs serves export and import needs while inland placement will serve growth in domestic businesses.
Goodyear should also optimize quality and supply chain assurance to sustain a competitive advantage. The company’s SCM should ensure that data from suppliers are reliable and they can have positive impacts on product quality. Excellent supplies ensure reliable workflows, credible services, and observation of environmental, labor and health standards, as well as earning trust from business partners. Multinational organizations use high degree of vigilance and regular audits to avoid compromising the quality of information that suppliers provide (PwC). The company should also have many backup suppliers to help in case it needs to mitigate quality problems under tight deadlines.
Quality Management Approaches
Most manufacturing firms focus on entrepreneurship, business, and operations strategy. Issues such as quality management should also be of top priority to them. Peters and Simaens (2020, p. 1) assert that most business managers have failed to recognize that quality and innovation go hand in hand in a company’s sustainability factors. Thus, Goodyear’s management approaches should be customer-oriented. Consumers determine the destiny of a product’s quality and meeting their needs wins their loyalty. To tailor its management approaches to customer needs, Goodyear must go beyond its knowledge for customers and understand today’s needs and expectations.
With this information, it will strategically align customer needs with company expectations, communicate with them, measure their satisfaction, and eventually improve its processes. The same approach should manage customer relationships and balance their satisfaction with those of other interested parties. In the end, it will achieve a larger market share, receive referrals, sell more items, and earn higher income.
Moreover, quality management means fostering adherence to company. The frameworks ensure that proper procedures are followed in a consistent and quick production system. To implement this approach, the company encourage executives to utilize management tools to define roles and responsibilities for each staff member. Creating visual action plans are also helpful in viewing specific activities that need completion to achieve particular objectives. A manager should analyze and measure conventional procedures to determine points of improvement to eliminate any bottlenecks. Further, this approach requires management team to evaluate the effects of various activities and processes on suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders.
In the end, the company benefits from faster production and development cycles, lower expenses, and more revenue. Using integrated systems and process control is valuable in quality management as well (Galea-pace, no date). All activities are processes in an organization, and problem-solving steps continuously opens an individual’s mind various possible solutions. Process control is key in total quality management and it will promote sustainability at Goodyear.
Furthermore, Goodyear should continuously implement fact-based decision-making. states that this quality management approach is suitable to manufacturing companies and it can be achieved through benchmarking, and conducting scientific research, apart from using experience to make decisions, on critical operations. Analysis of data gathered from research and other industries can lead to better decision-making. Goodyear will actualize the approach by ensuring that data is accurate and reliable, availing relevant information to stakeholders, using valid research methods, and applying experience and credible data to make decisions.
Training and continuous development is crucial in quality management due to the changing business demands. It also comprises employee empowerment and involvement in decision-making. It will enable the company to create knowledge stocks at personal levels, which is top key in a sustainable human capital (Peters and Simaens, 2020). The UK’s companies and other tire companies worldwide have sustained a competitive advantage through this approach (Kumar et al., 2017, p. 813). Goodyear trains its new and current employees, especially on sustainable codes of conduct. Incorporating other development themes ensures that the company not only share knowledge but also ensure they operate efficiently in the changing environment.
How a Big Data Driven Platform can Further Enhance Overall Business Operations
Today’s companies require valuable information and relevant insights to remain competitive updated in a changing business environment. Big data driven platforms ensure that an organization finds what their clients want, forecast their needs, and respond to current technological demands. Thus, big data is among the leading decision-making tools when information is processed and analyzed correctly (Galea-pace, no date). Goodyear’s production systems should meet the ever-increasing requirements. Its dynamic factors such as trends in batch size and the growing variety require efficient and flexible operation.
Digitalization such as artificial intelligence means the company will have more information available from production to be used in monitoring and optimizing operations. For example, Goodyear requires geometric models for layout planning and other tire requirements. A wide range of information has been generated in the previous engineering phases and it is crucial apart from the current data obtained from ongoing operations. PriceWaterHouseCoopers states that commissioning stages require kinematic models, which are available in big data driven platforms, simulating motion sequences.
Artificial intelligence (AI) also helps the company’s researchers to acquire information about parts of tires, component numbers, and other manufacturers’ information to guide decision-making. However, such simulation models are not appropriate for making the final judgments concerning real operation phases because various stakeholder information must be included.
Big data driven platforms helps companies to avail information to suppliers and consumers efficiently. They provide product information and tire prices through the platforms to ease purchases. In return, customers can place orders based on the available data and arrange for pickups without traveling to the company. Furthermore, manufacturers acquire equipment information concerning usage behavior and operational information of installed equipment. The data is useful in research and development as well as optimizing customer operations.
Further, different companies have diverse revenue generation strategies. A big data driven platform can be instrumental in helping the company to earn income by selling their models, apart from goods and services, online. In this case, they set a fee for each access and in suitable options for buyers (Stecken et al., 2019, p. 204). Upcoming companies can purchase them to be used in guiding their operations having learned that the seller is reputable in a particular field. For example, many companies sell their ideas through Amazon, EBSCO, Udemy and others (Rangaswamy et al., 2020, p. 72).
In essence, AI enables enterprises to operate in a value chain, where they purchase inputs and transform to value-added products through assembly, production, and branding. Then, they utilize marketing channels to reach consumers, while transmitting some of their values to other members in the channel. AI can help Goodyear to generate income by selling its production models, although rivals can use such information to imitate them and create best practice procedures to outcompete Goodyear.
The leading risk associated with big data driven platforms is unauthorized access to personal information. Companies collect, analyze and store consumer and supplier data online. The information is vulnerable to cybersecurity issues where third parties can steal client data and use them in other activities. Bandara et al. (2017, p. 543) assert that consumers are worried about submitting information to sellers online. They face critical challenges including identity theft, privacy infringement, and cyberbullying (Bandara et al., 2017, p. 543). However, Goodyear should continue providing gratifying benefits in form of highly personalized services, such as customized consumer recommendations, real-time customer services, convenience, and competitive pricing while protecting its client information.
Reference List
Bridgestone. (no date) Procurement. Web.
Galea-pace, S. (no date) PwC: supply chain strategies. Web.
Goodyear Corporate. (no date). Workforce safety and health. Web.
Goodyear Corporate Responsibility Report (2018). Web.
Gryaznov, M., Kurganov, V., Vasiliev, V. and Dorofeev, A. (2021). ‘Road transport outsourcing for a metallurgical company and its alternatives’, Transportation Research Procedia, 54, pp.290-299.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (no date). Web.
Kumar, V., Chibuzo, E.N., Garza-Reyes, J.A., Kumari, A., Rocha-Lona, L. and Lopez-Torres, G.C., (2017). ‘The impact of supply chain integration on performance: evidence from the UK food sector’, Procedia Manufacturing, 11, pp.814-821.
Peters, J. and Simaens, A., (2020). ‘Integrating sustainability into corporate strategy: A case study of the textile and clothing industry’, Sustainability, 12(15), p.6125.
PriceWaterHouseCoopers. (no date). Sourcing and logistics in China: costs, processes, and strategies of German companies procuring in the Chinese market. Web.
Rangaswamy, A., Moch, N., Felten, C., van Bruggen, G., Wieringa, J.E. and Wirtz, J., (2020). ‘The role of marketing in digital business platforms’, Journal of Interactive Marketing, 51, pp.72-90.
Shingler, D. (2019). Goodyear facing bumpy roads as market conditions take toll for toll on tire industry. Web.
Skoropad, M. (2017). Tires made in USA: American and foreign brands. Web.
Stecken, J., Ebel, M., Bartelt, M., Poeppelbuss, J. and Kuhlenkötter, B., (2019). ‘Digital shadow platform as an innovative business model’, Procedia CIRP, 83, pp. 204-209.

